Neurons and Synapses
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What is the term for the nerve cells that make up the nervous system?
neurons
Messages that nerve cells carry are in the form of…
electrical impulses
What is the small gap called of myelinated nerve fibers?
node of Ranvier
What is saltatory conduction?
signal jumps from node to node of Ranvier
Does saltatory conduction speed up or slow down electrical transmissions?
Speeds up
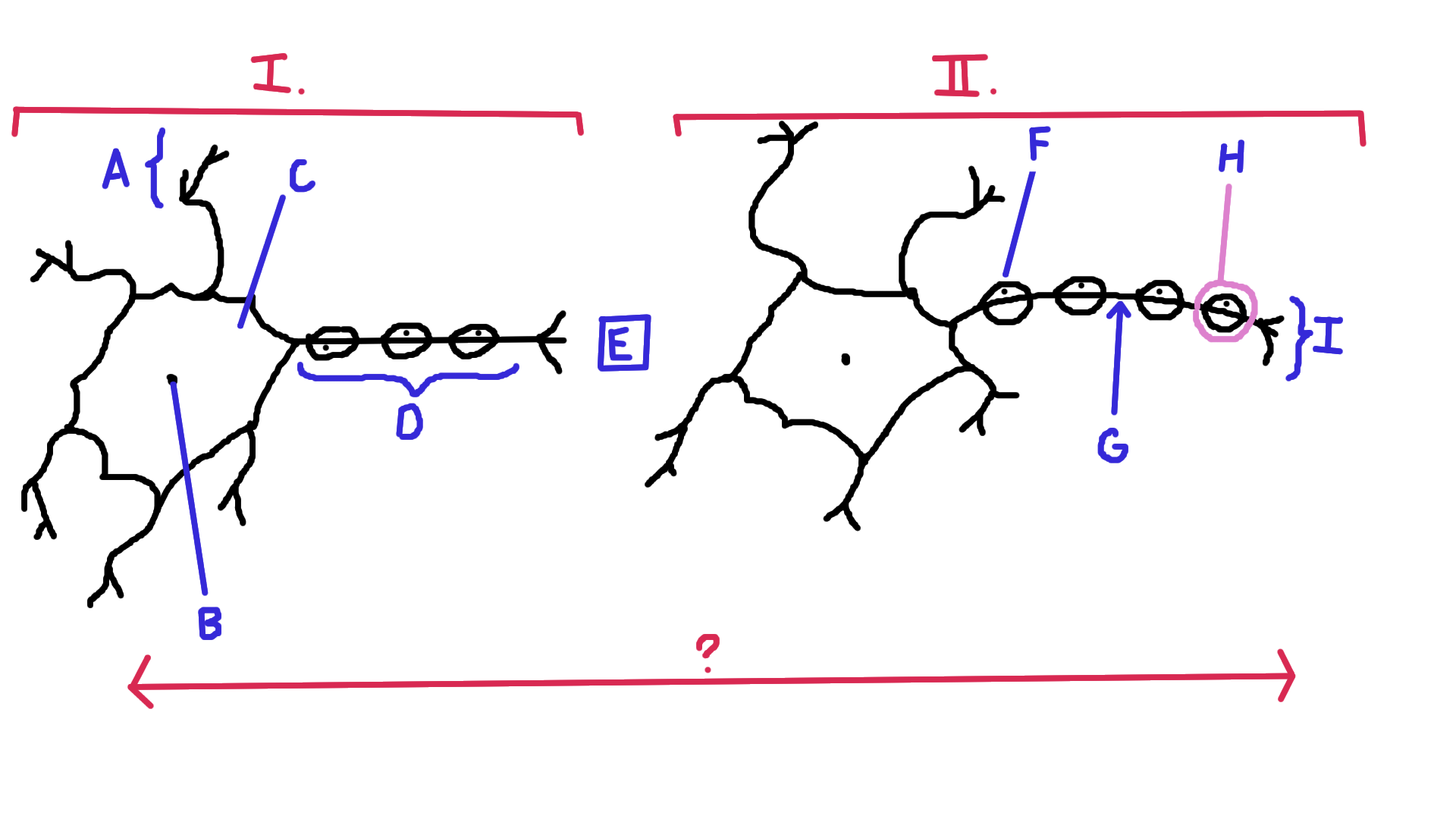
Identify A
Dendrite
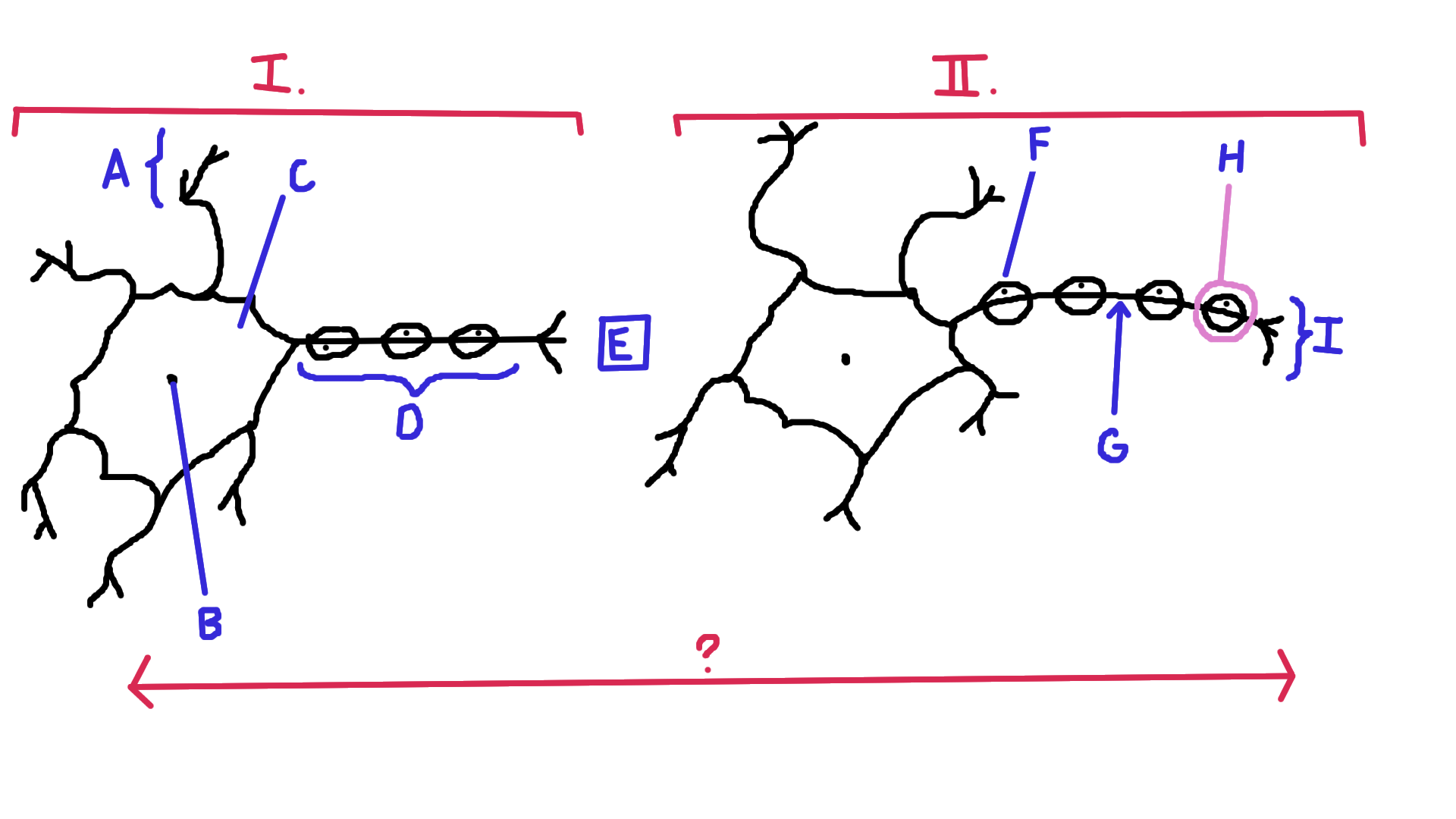
Identify B
Nucelus
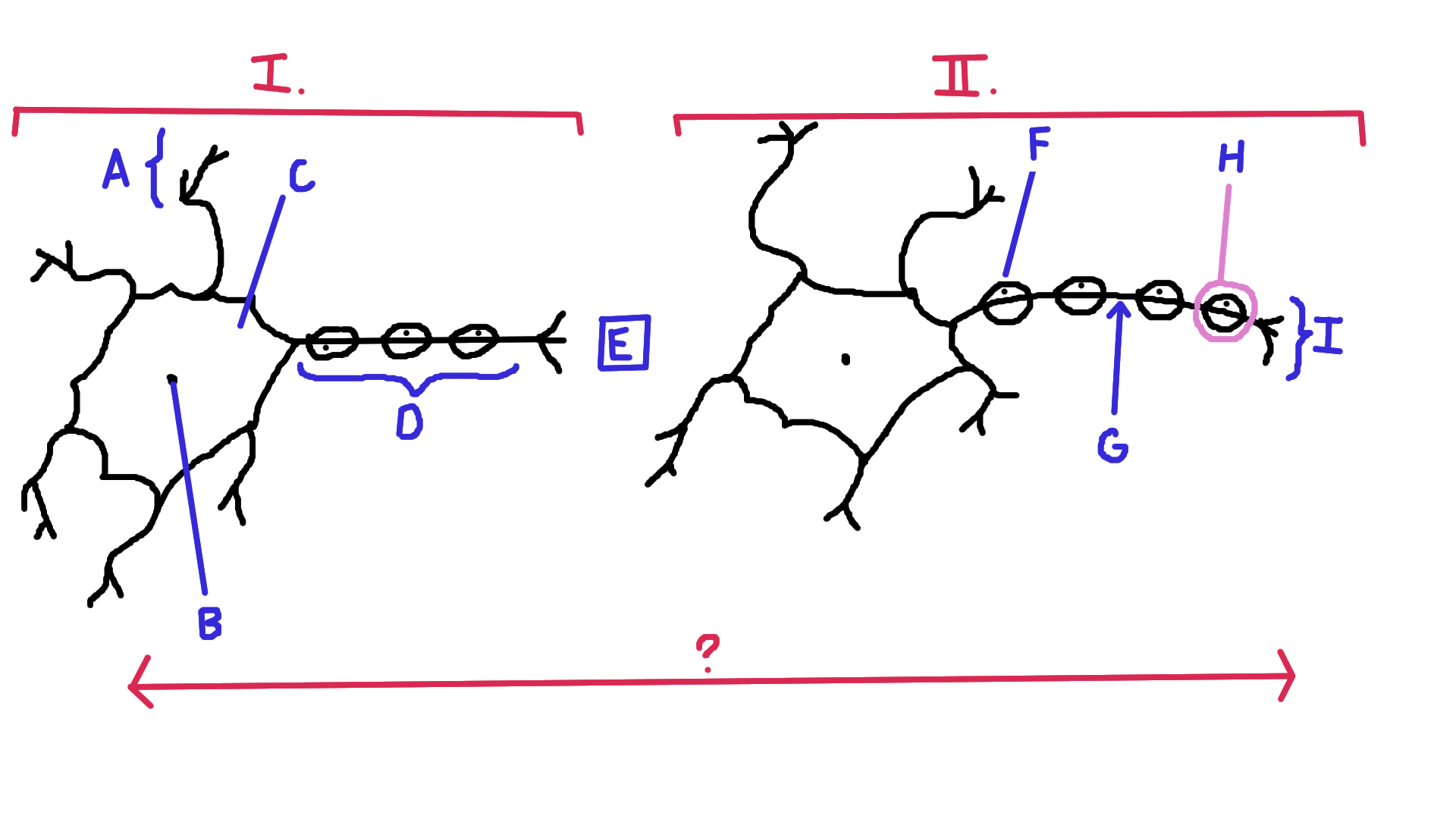
Identify C
Cell body
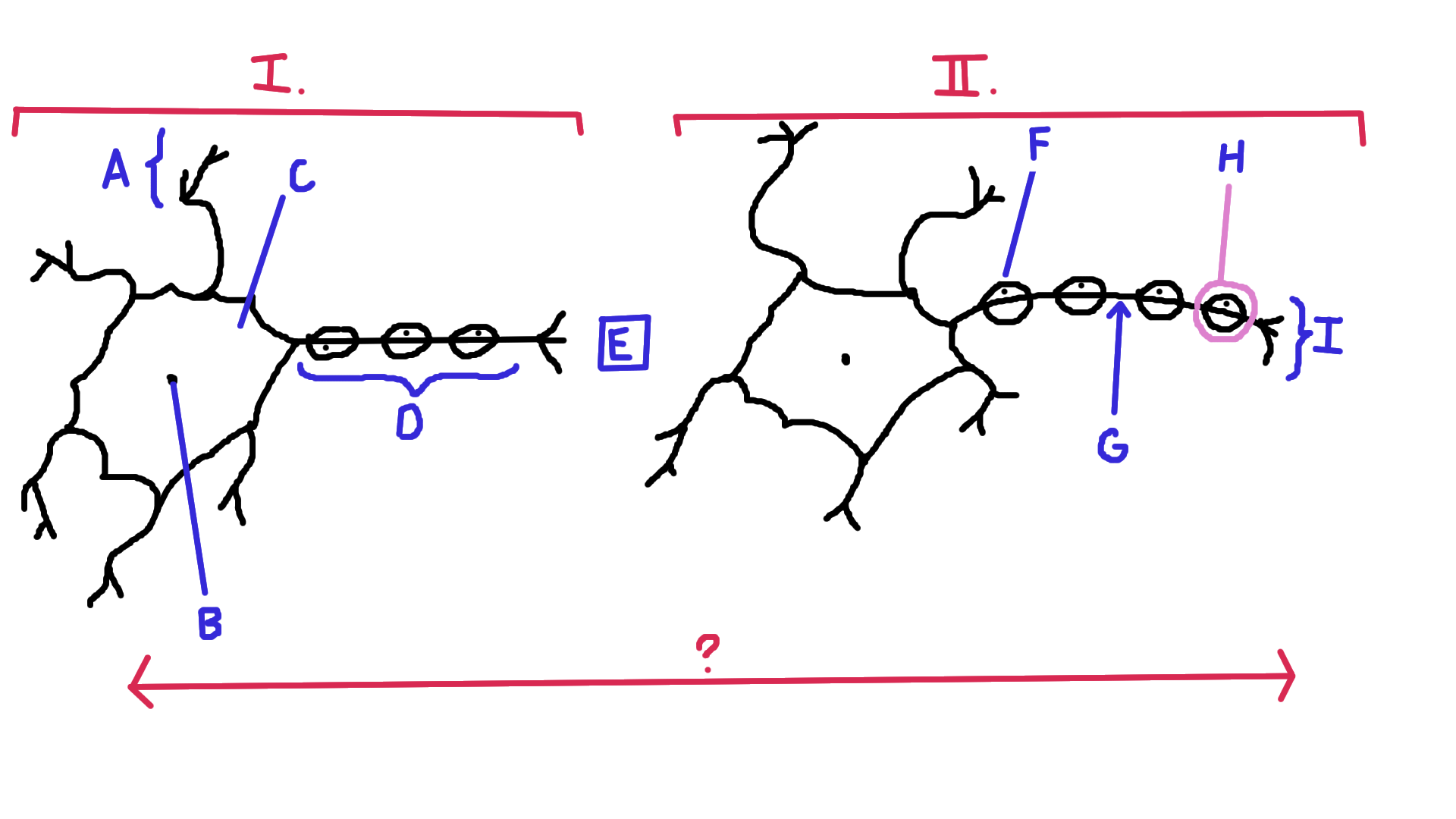
Identify D
Axon
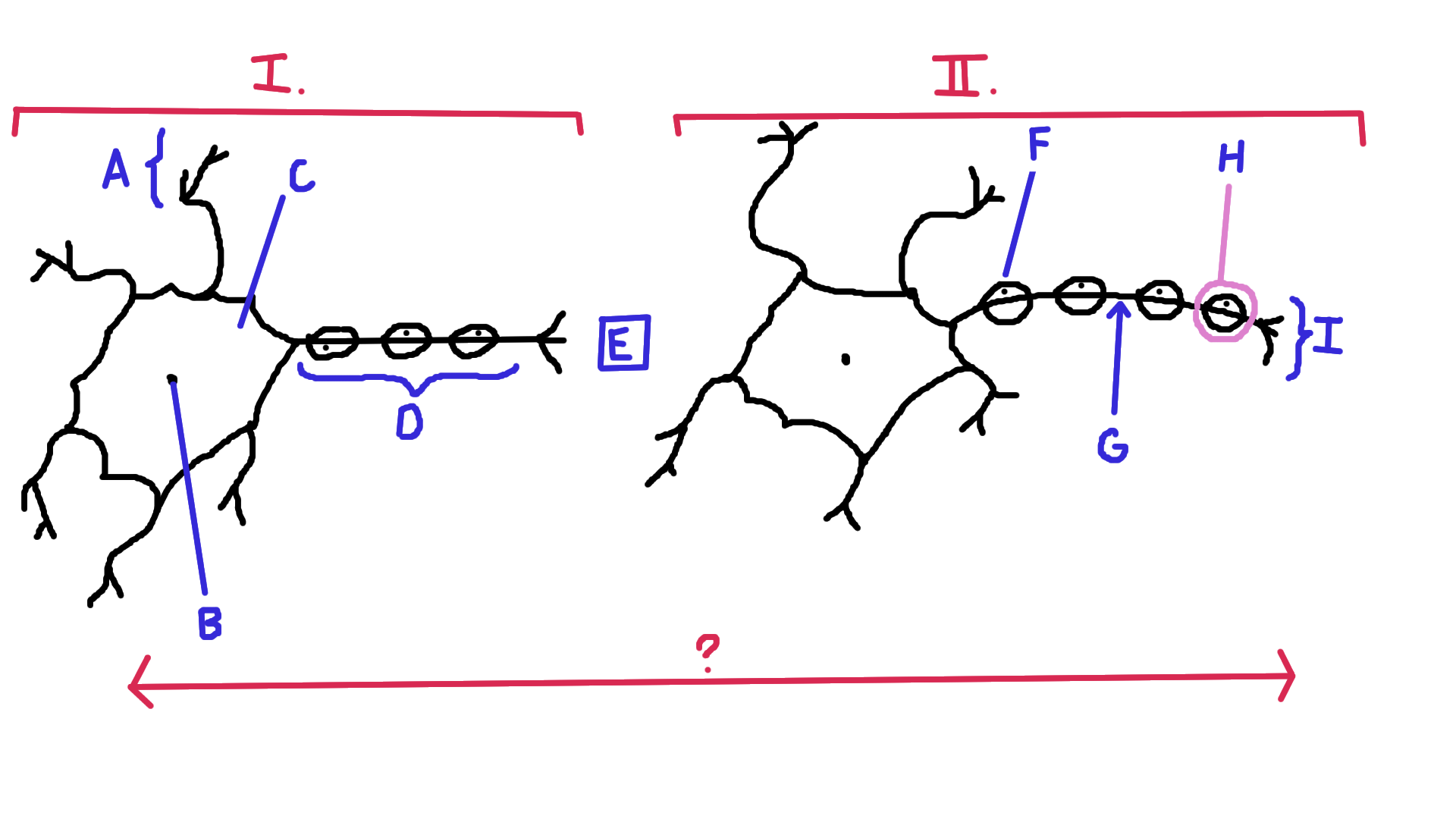
Identify E
Synapse
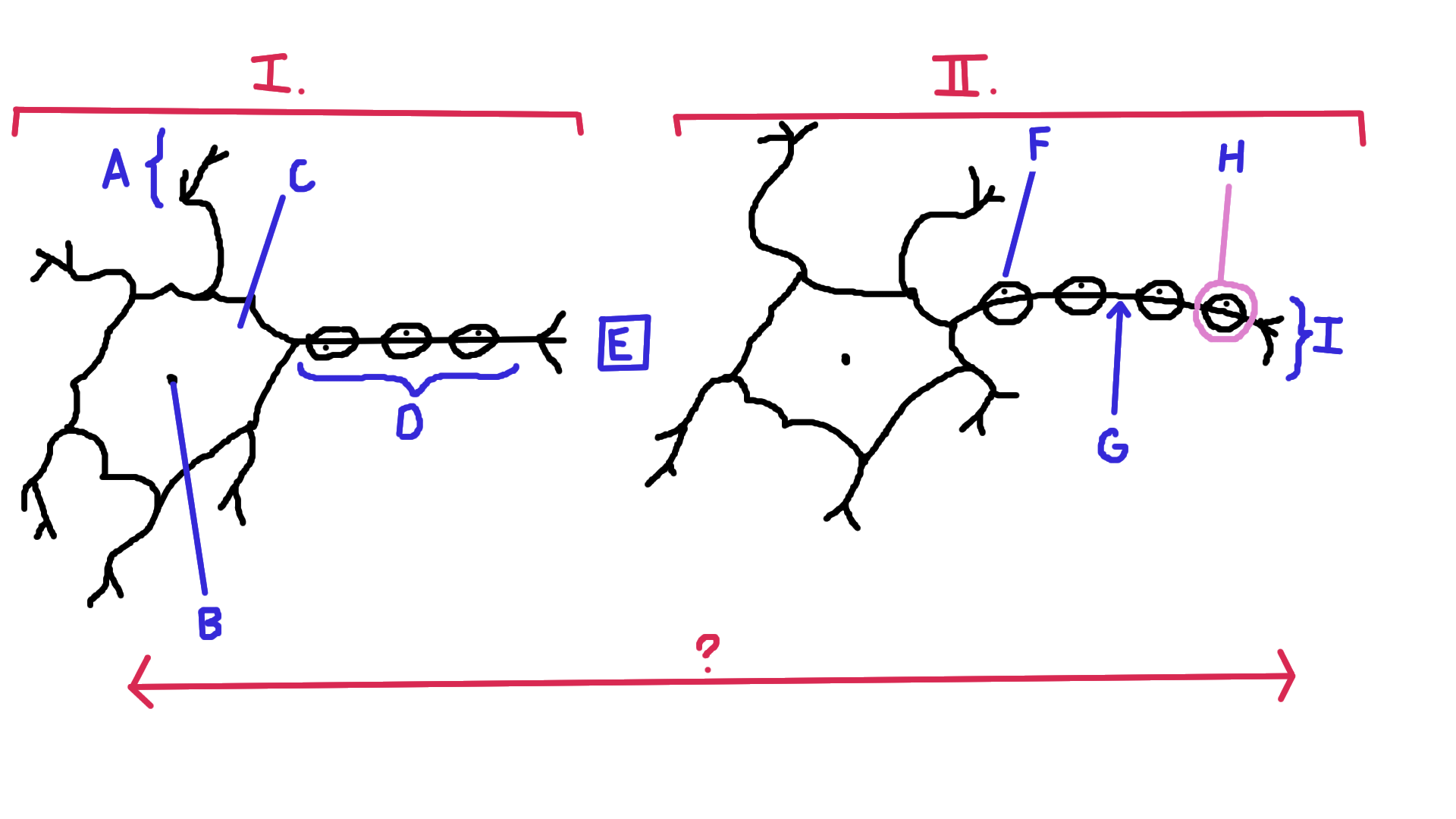
Identify F
Schwann cell
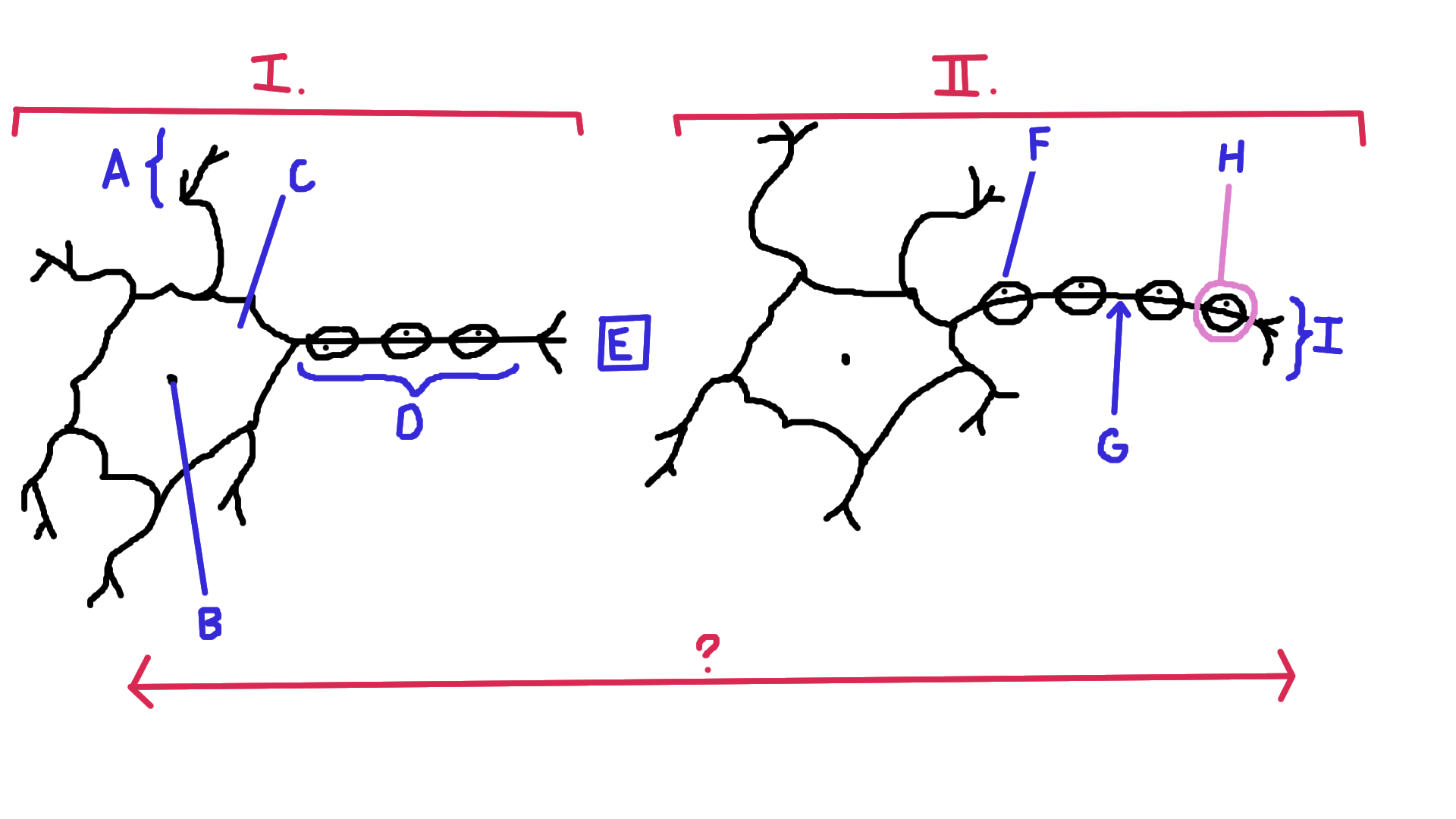
Identify G
Node of Ranvier
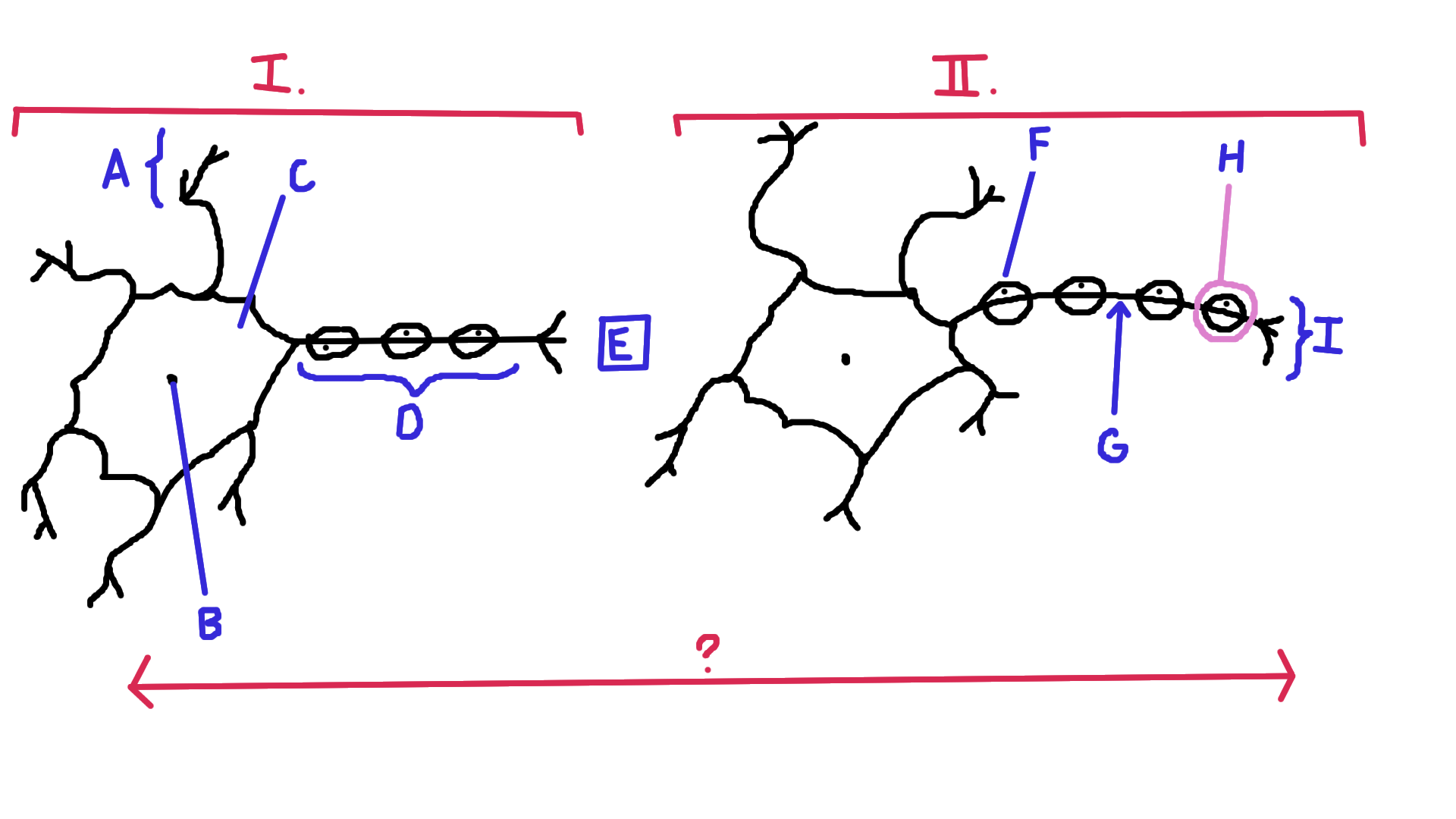
Identify H
Myelin
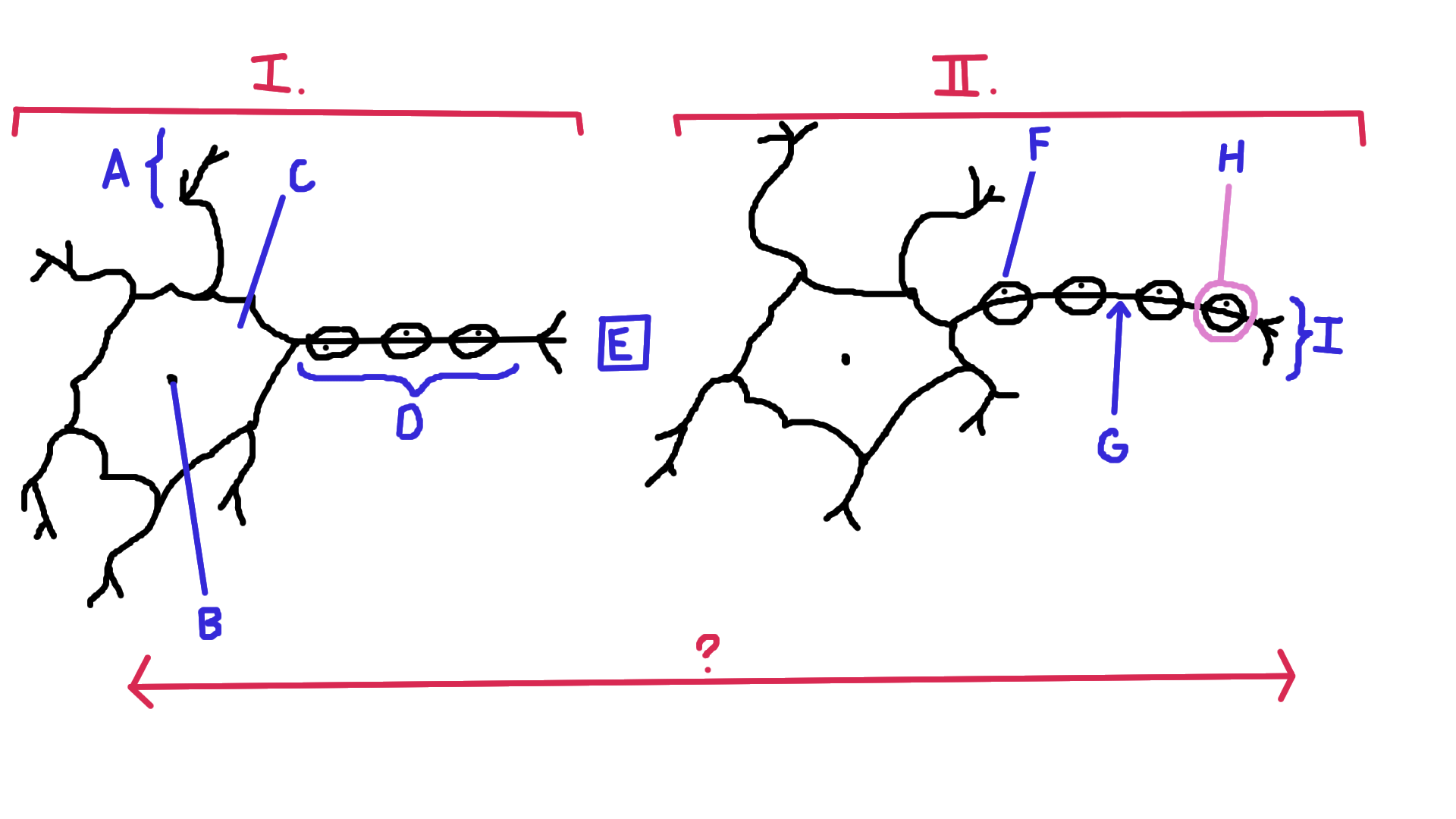
Identify I
Axon terminal end
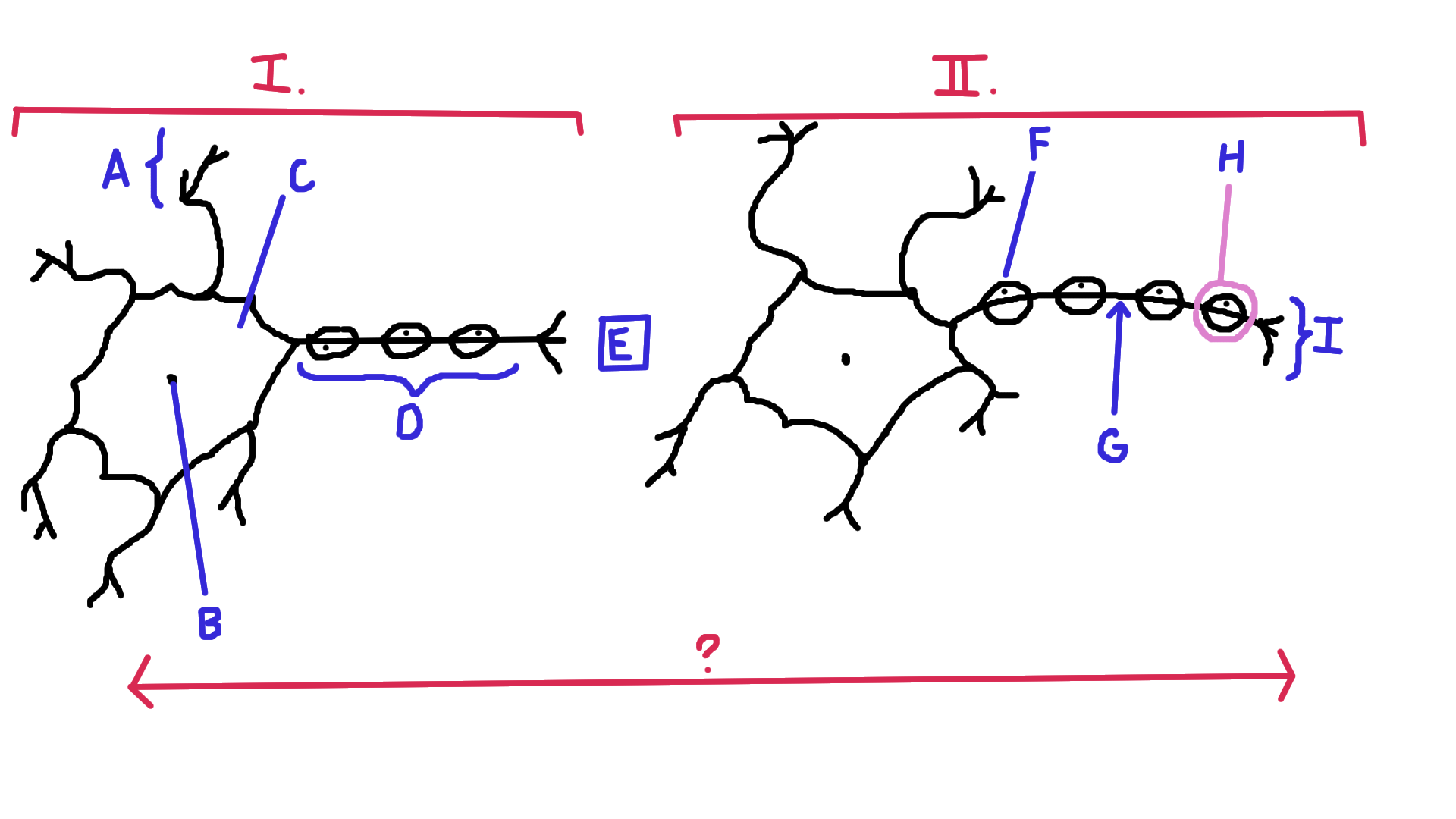
Identify the direction of electrical impulse (under ?)
From dendrite to axon (left to right in this example)
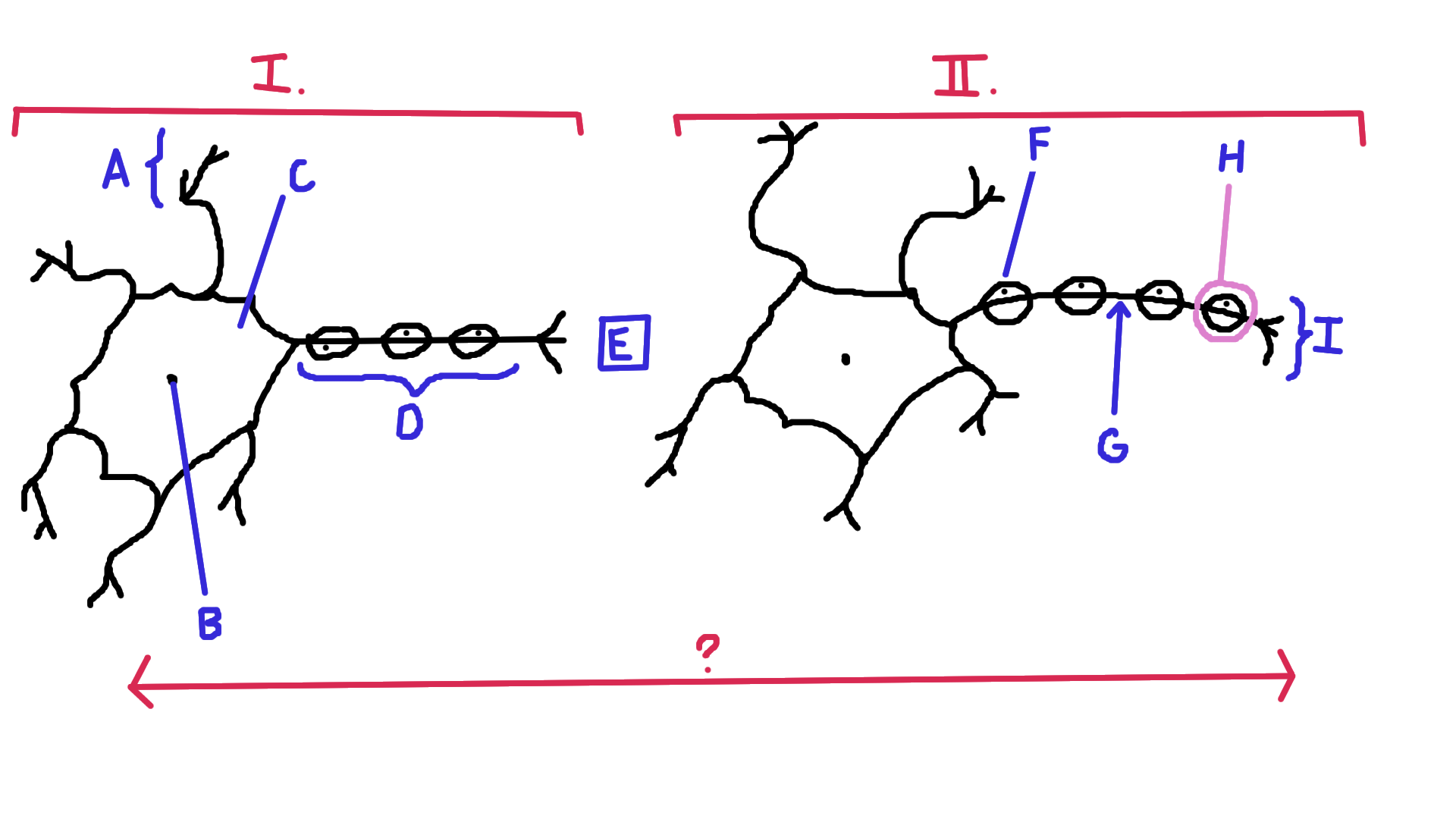
Identify I.
Presynaptic impulse
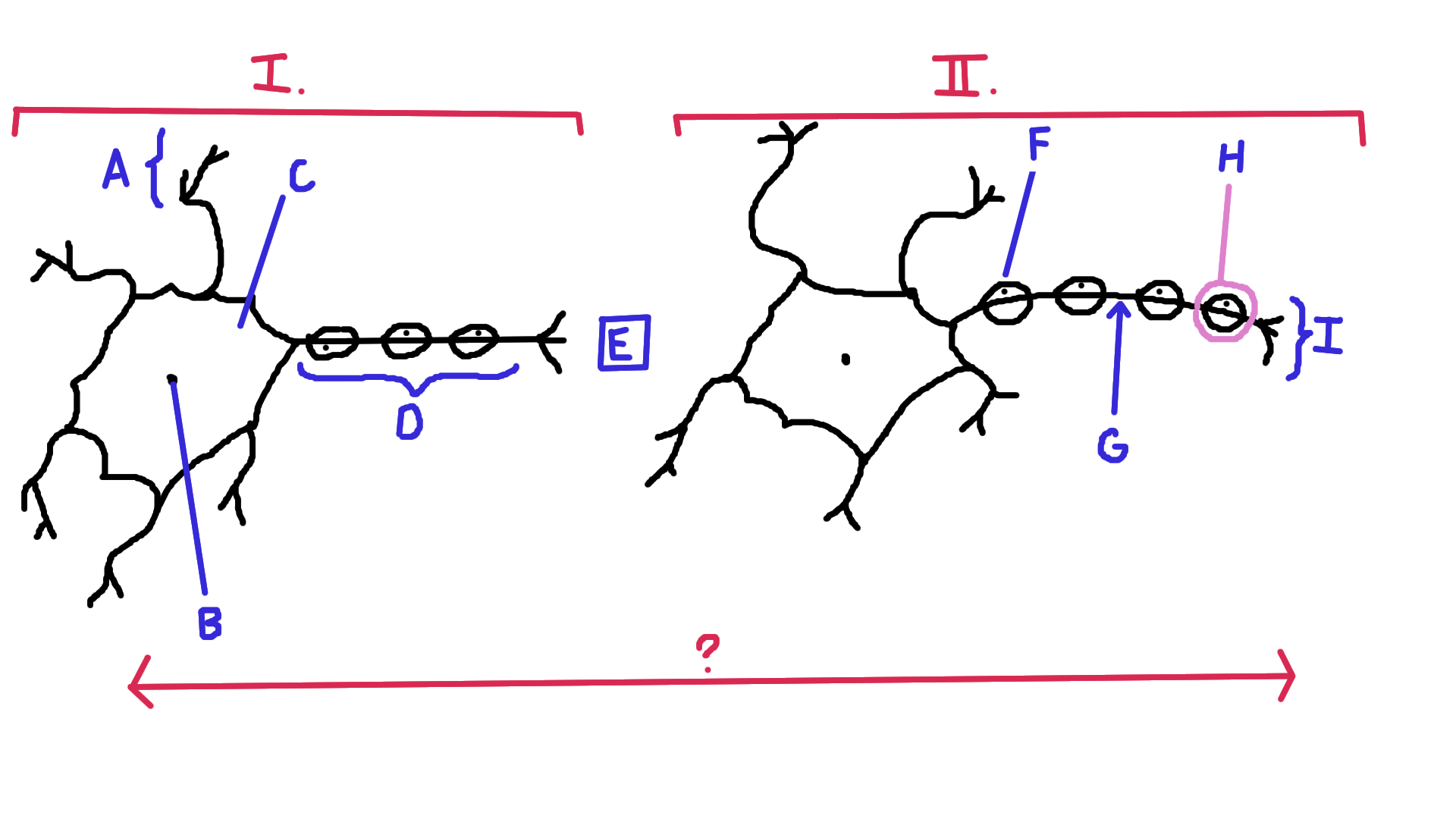
Identify II.
Postsynaptic impulse
What is the name for the small junction or space between two neurons?
synapse
What is the term for a chemical released into the synapse?
Neurotransmitter
How are neurotransmitters released?
By exocytosis
Why is the nerve message referred to as electrochemical? State the reason for electric and chemical
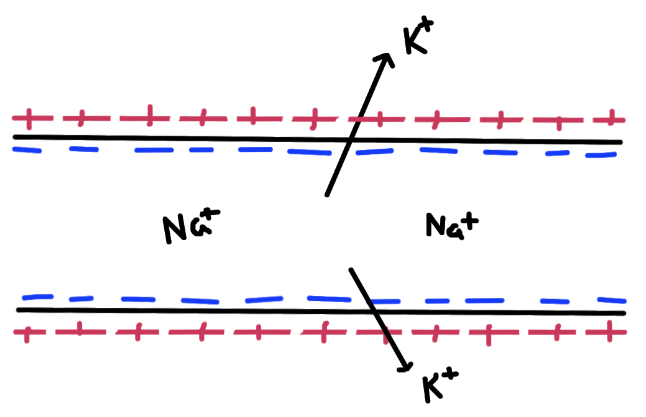
Electric: ions (Na+, K+)
Chemical: neurotransmitter across the synapse
What is the name for the neuron that releases the neurotransmitter?
Presynaptic neuron
What is the name for the neuron that receives and is affected by the neurotransmitter?
Postsynaptic neuron
Describe the release of a neurotransmitter in terms of Calcium ions and neurotransmitter molecules
Calcium ions diffuse into the pre-synaptic neuron and cause the release of the neurotransmitter molecules into the synapse
What is the effect of the presence of the neurotransmitter in the post-synaptic neuron?
It causes sodium ions to move into the post synaptic neuron, depolarizing the membrane
What is the term for the small membrane sacks that neurotransmitter are released out of?
vesicles
What type of transport is always required to move ions across a membrane?
facilitated or active transport
What is the name of the transport protein that moves ions across membranes?
gated ion channel or pump
What stops continuous synaptic transmission?
Enzymes
What is the name of synapses that use acetylcholine?
Cholinergic synapses
What enzyme breaks down acetylcholine?
Cholinesterase
Where does the choline go after it is formed?
Presynaptic neuron
Describe how neonicotinoid pesticides work on the nervous system of insects
Blocks the binding of acetylcholine which stops nerve signal and paralyzes insects
Resting potential
electrical potential of a cell that’s not conducting an electrical impulse
Action potential
reversal and restoration of electrical potential of a cell that is conducting an electrical charge
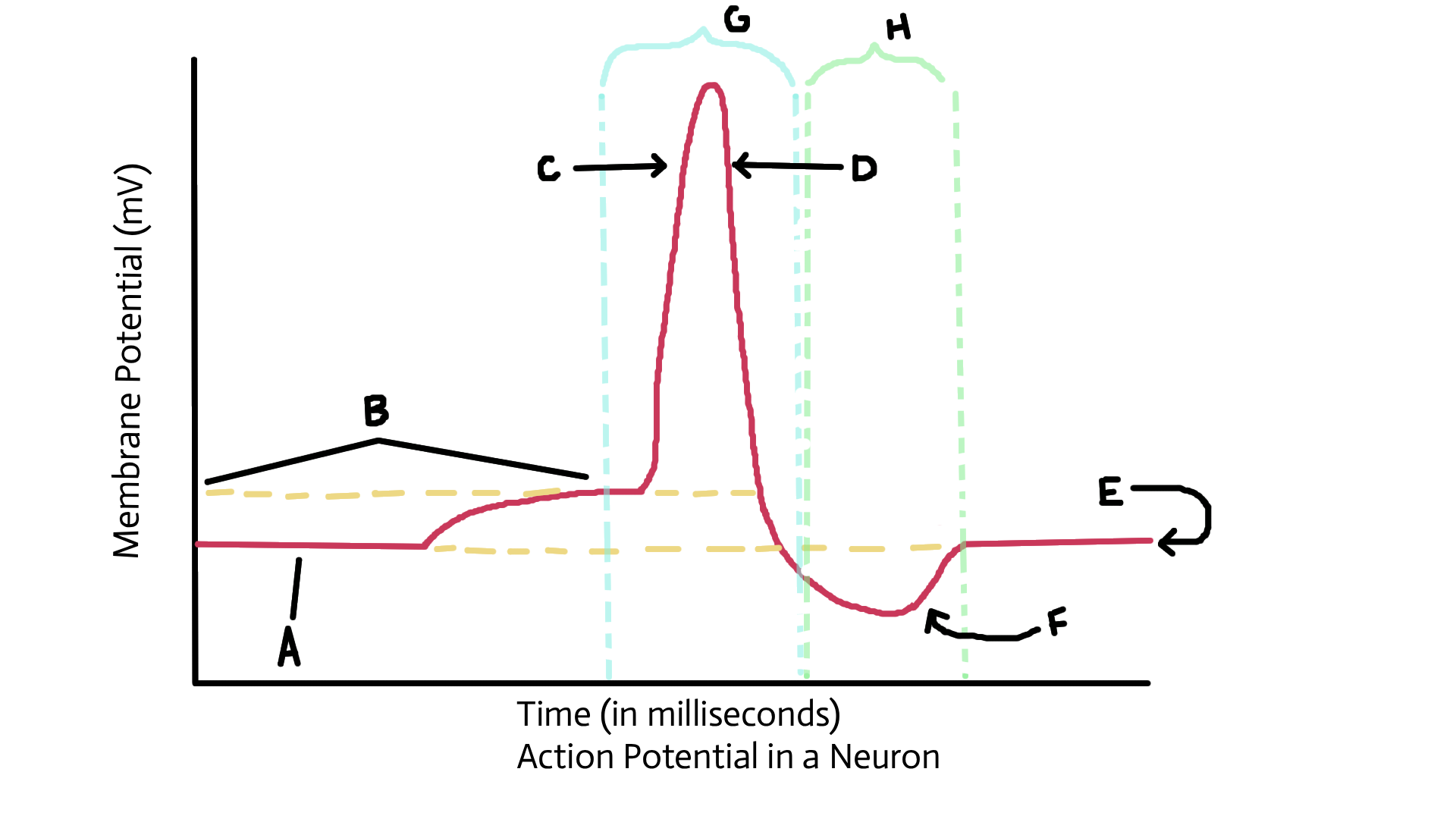
Identify A
Resting potential
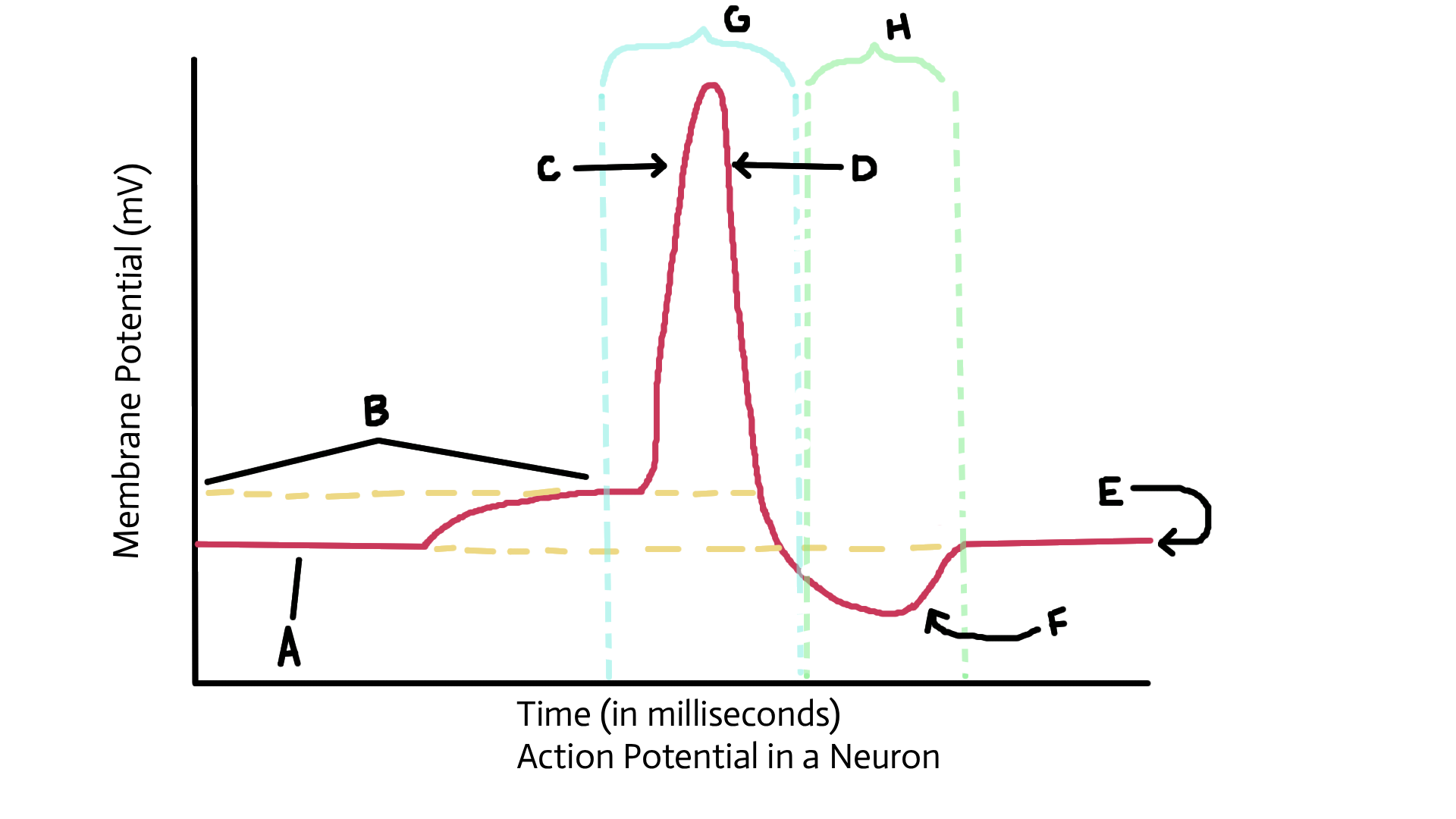
Identify B
Threshold potential
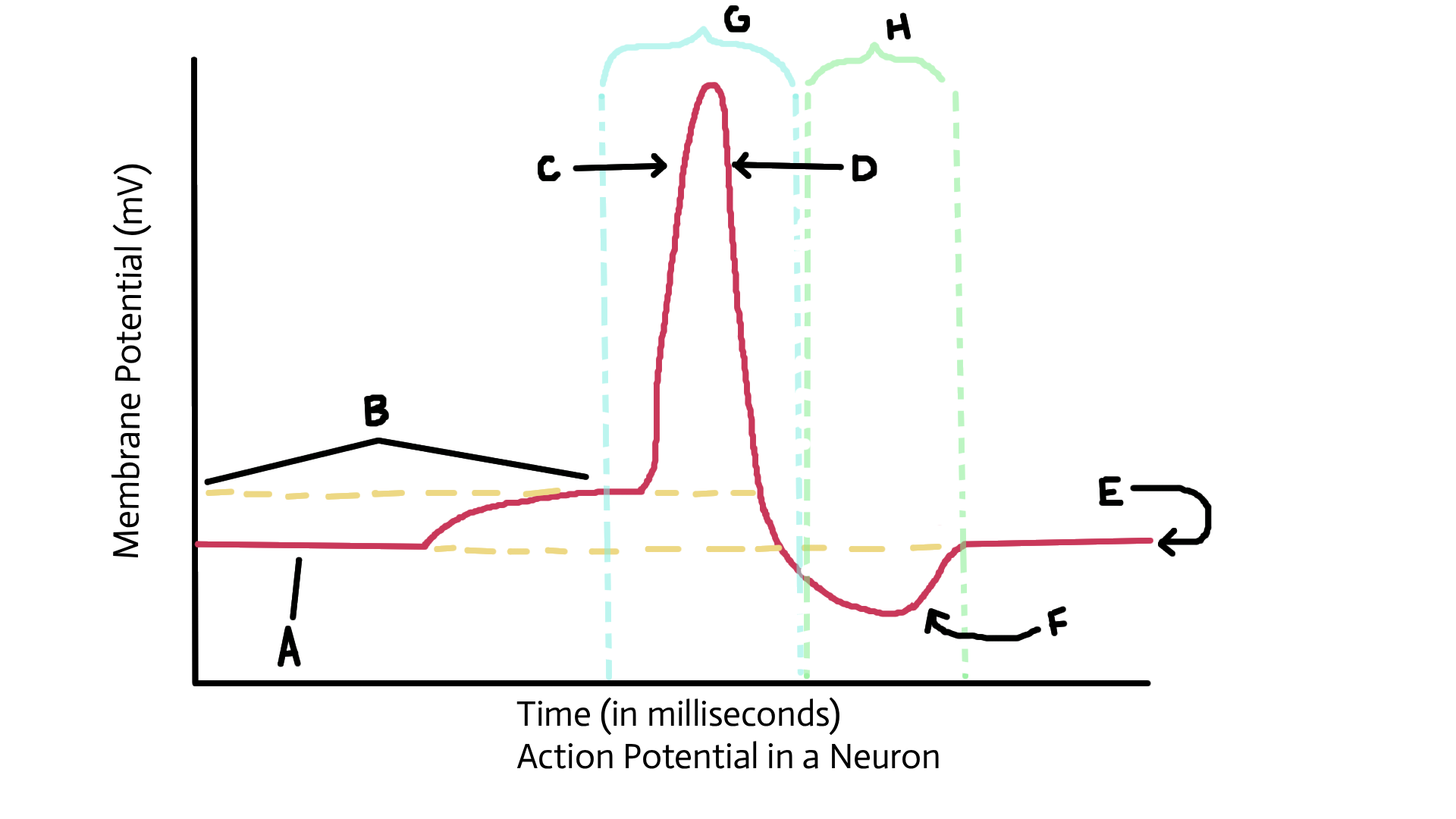
identify C
Depolarized (sodium ions in)
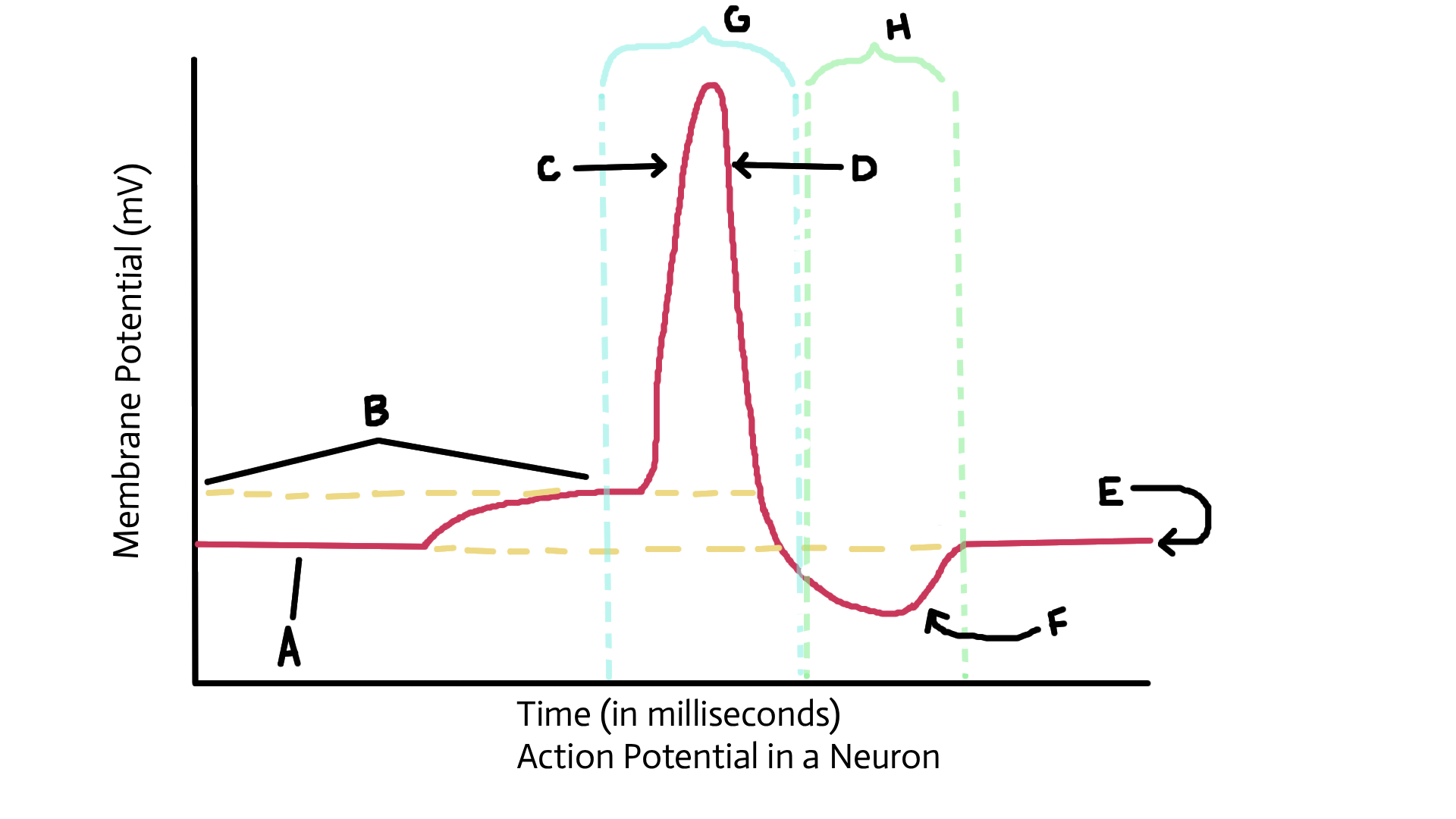
Identify D
Repolarization (potassium ions out)
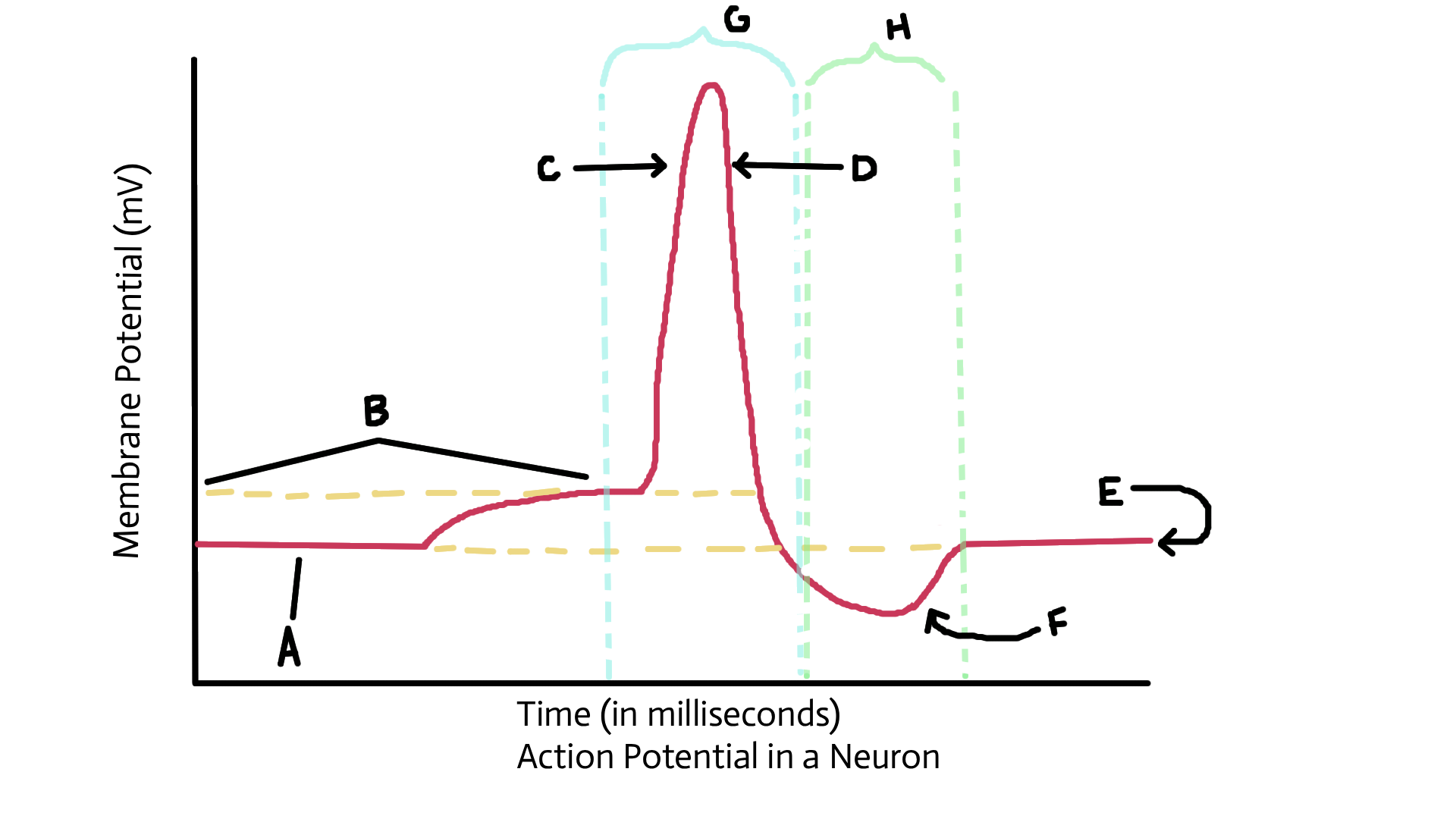
Identify E
Resting potential
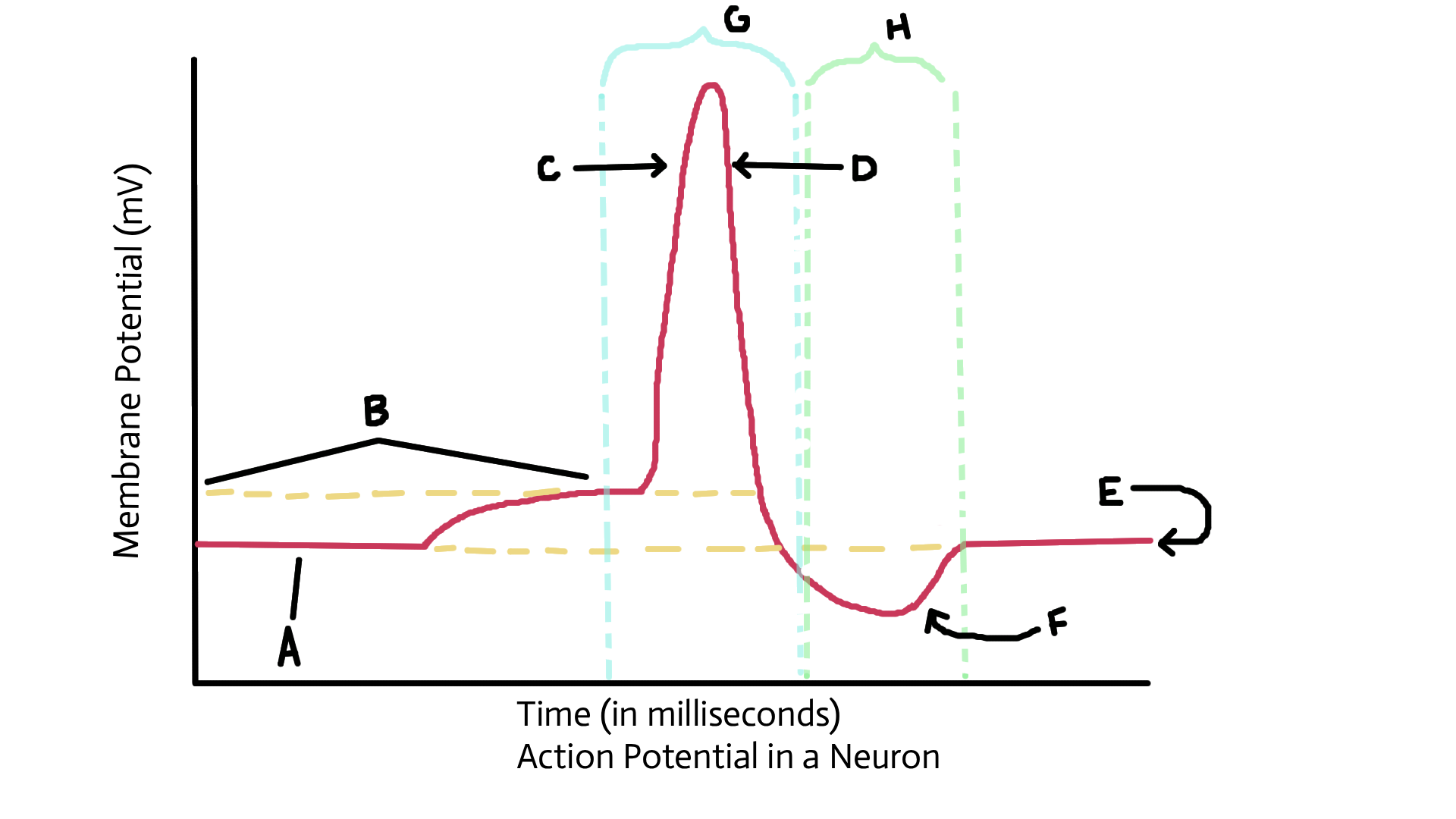
Identify F
Recovery or restoration (sodium/potassium pump; active transport pump)
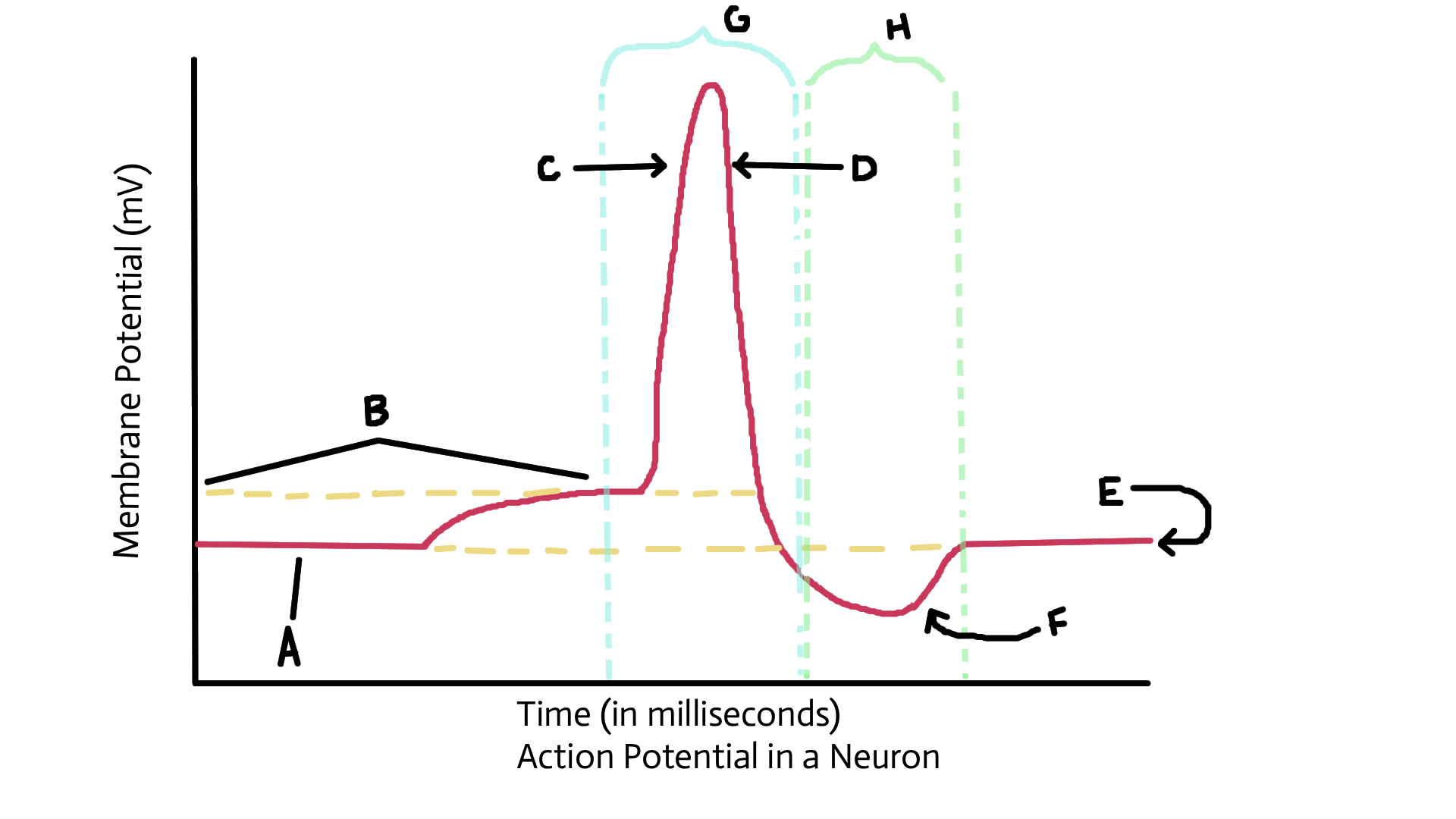
Identify G
Action potential
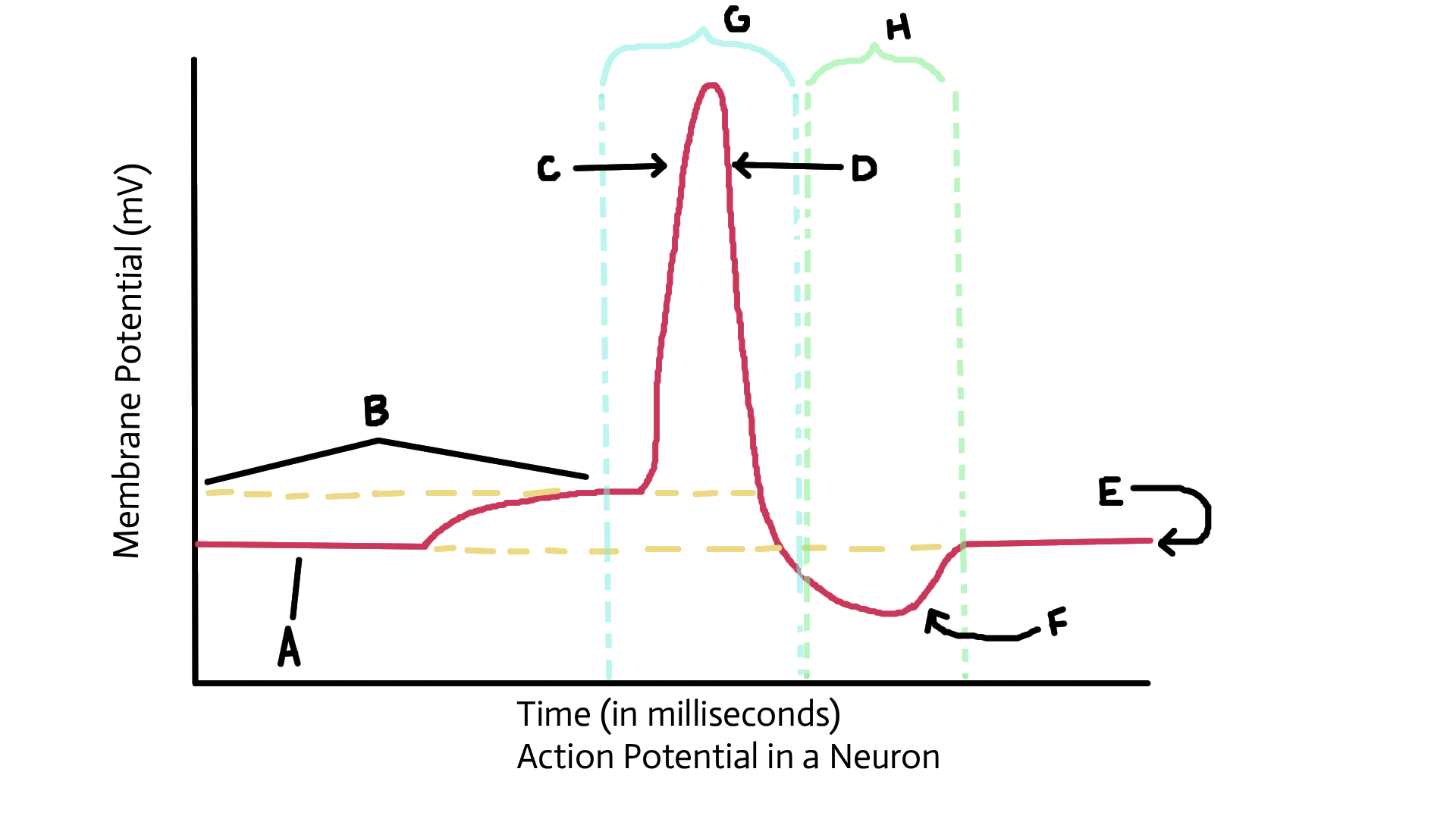
Identify H
Refractory period
What happens to sodium and potassium ions after the action potnetial?
3 sodium ions and 2 potassium ions are pumped back into original location
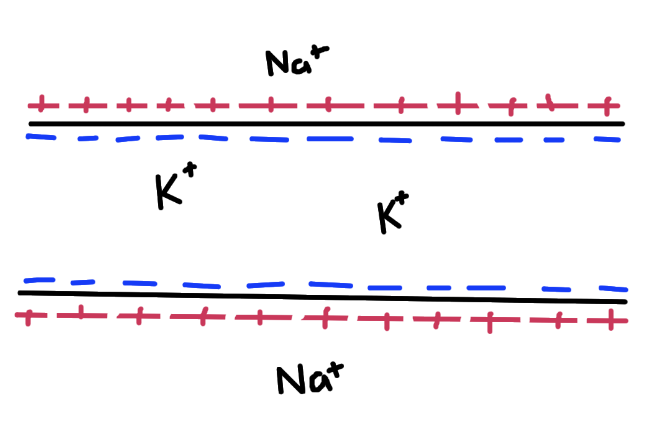
Describe the charges of the inside and outside a resting neuron
negative inside and positive outside
Draw and annotate the axon (represented as a tube) during resting/polarization
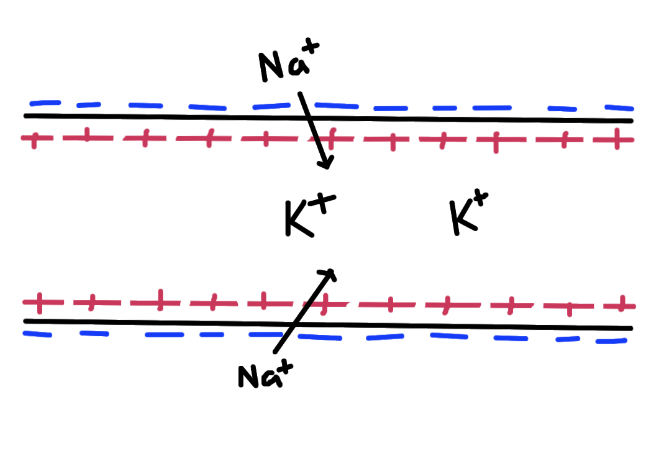
Draw and annotate the axon (represented as a tube) during depolarization
Draw and annotate the axon (represented as a tube) during repolarization