
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
What is the point of fertilisation?
i) ensures the transfer of genetic information from one generation to another to ensure continuity of species.
ii) results in production of genetically dissimilar offspring
What is sexual reproduction/fertilisation?
Sexual reproduction / Fertilisation is the process involving the fusion of nuclei of a male and female gamete (reproductive cell) to form a zygote.
What are gametes?
Gametes are special reproductive cells which fuse to form a zygote in sexual reproduction.
How are gametes formed?
through meiosis where haploid cells containing half the usual number of chromosomes are produced
What is the use of asexual reproduction?
i) ensure the transfer of genetic information from one generation to another to ensure continuity of species.
ii) results in production of genetically identical offspring
What is asexual reproduction?
Asexual reproduction is the process resulting in the production of genetically identical offspring from one parent, without the fusion of gametes.
What does asexual reproduction rely on to produce genetically identical cells?
mitosis
a
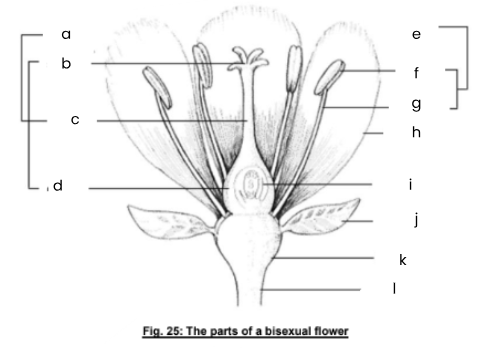
carpel
b

stigma
c

style

d
ovary

e
stamen

f
anther

g
filament

h
petal

i
ovule
j

sepal

k
receptacle

l
flower stalk (peduncle)
What is the structure of the sepal?
Modified leaves which form the outermost layer of floral leaves
What is the function of the sepal?
Encloses and protects the developing (flower) bud
What is the structure of the petal?
Modified leaves forming the most obvious (conspicuous) part of the flower
What is the function of the petal?
Attract insects that help pollinate the flower
What does the carpel (or pistil) consist of?
stigma, style, ovary and ovule
Carpel (or pistil) is the … part
female
What is the stigma?
a swollen structure where pollen lands
What is the function of the stigma?
Mature stigma secretes a sugary fluid that stimulates the pollen grains to germinate
What is the function of the style?
Elevates the stigma to receive pollen
What does the ovary contain?
one or more ovules
What does the ovule contain?
female gamete called egg/ovum
What is the function of the ovary?
Becomes the fruit upon successful fertilisation
What is the function of the ovule?
Becomes the seed upon successful fertilisation
Stamen is the … part
male
What does the stamen consist of?
anther and filament
What is the anther?
where pollen grains are produced
Where are pollen grains produced?
anther
What is the function of the anther?
Mature anther splits open to release pollen grains
What is the function of the filament?
Holds anther in a suitable position to disperse the pollen
What is the function of the pollen grain?
contains male gamete
What is the function of the flower stalk (peduncle)?
attaches flower to stem
What is the function of the receptacle?
Supports the weight of the flower or fruit as it develops
What is the receptacle?
Swollen part of the flower stalk
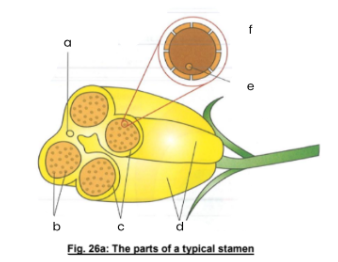
a
vascular bundle

b
pollen grains

c
pollen sacs

d
anther lobes

e
male gamete

f
mature pollen grain
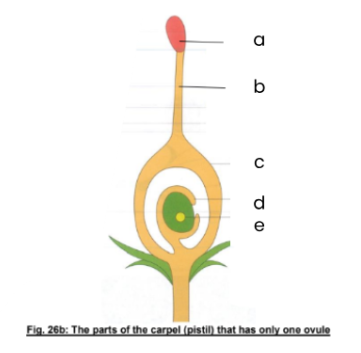
a
stigma

b
style

c
ovary

d
ovule

e
ovum
To reproduce sexually, … must be transferred from … to the … so that male and female gametes can meet.
To reproduce sexually, pollen grains must be transferred from the anthers to the stigmas so that the male and female gametes can meet for reproduction.
What is pollination?
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma.
What are two types of pollination?
self
cross
What is self-pollination?
Transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of the same flower (type 1) or another flower on the same plant (type 2)
What is cross-pollination?
Transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower on a different plant of the same species
What are the features of self-pollination flowers? [3]
Flowers are bisexual with anthers and stigmas that mature at the same time
Stigma being located below the anthers or in close proximity
In some species, some flowers never open. Only self-pollination occurs in such flowers.
What are the features of cross-pollination flowers? [2]
In plants with bisexual flowers, the anthers and stigma mature at different times
Stigmas may be situated some distance away from the anthers e.g. stigma located above the anther
What are dioecious plants?
Dioecious plants bear either male or female flowers
e.g. papaya
Advantages of self-pollination [5]
Only 1 plant is required.
Offspring inherits its gene from parent plant after fertilisation → beneficial qualities are more likely to be passed down to offspring
Doesn’t need to depend on external factors for pollination (insects, wind)
Higher success rate of pollination due to close proximity of anthers and stigma
Less pollen and energy is wasted
Advantages of cross-pollination [3]
Offspring can inherit beneficial qualities from both parents.
Greater genetic variation in offspring → increase survival chances during environmental change
More viable seeds are produced → seeds survive longer before germination
Disadvantages of self-pollination [2]
Less genetic variation in offspring → species is less well-adapted to changes in the environment
Continued selfing may lead to offspring becoming weaker, smaller and less disease resistant
Disadvantages of cross-pollination [4]
2 plants are required.
Depends on external factors like insects or wind for pollination
Lower rate of successful pollination
More energy and pollen are wasted