Lecture 11 Monochromatic Aberrations in the human eye part 1
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
How does diffraction affect the retinal image?
For the eye, only a section passes through the pupil; the iris is an obstruction that diffracts the light. This diffraction blurs the image. For a system limited obly by diffraction, the image radius for a point object = 1.22λ f/d meters.
Diffraction affects image quality for
small pupils
Aberrations affect image quality for
large pupils
Pupil size controls impact of
ocular aberrations and diffraction on retinal image quality (emmetrope)
What pupil size provide the best retinal image quality?
~3mm
Due to optical aberrations, a plane wavefront becomes aberrated spherical wavefront after passing through
a spherical lens optics
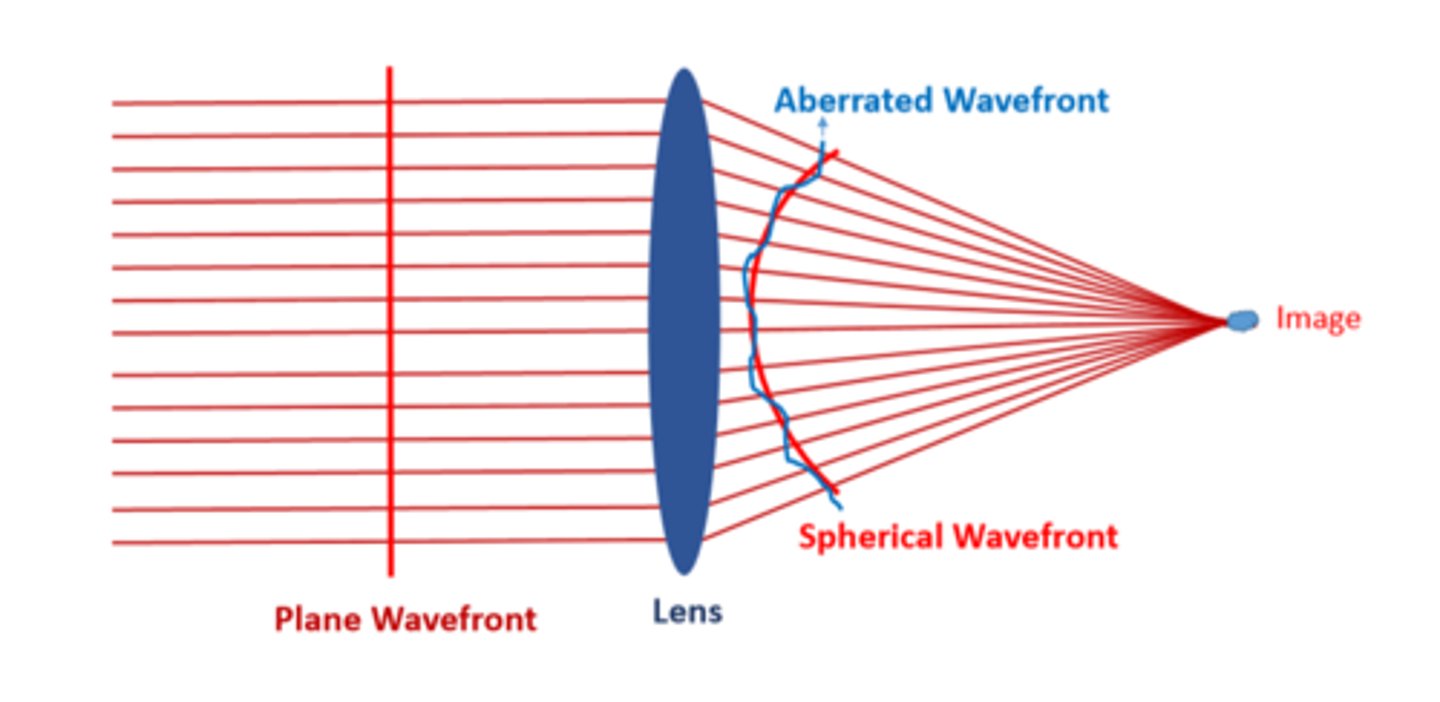
Optical aberrations can be measured as
-an 'aberrated wavefront' on the pupil plane
or
-a 'point spread image' at the image plane
Significant optical aberrations in the human eye are
-Defocus
-Astigmatism
-Spherical Aberration
-Coma
-Distortion
-Field Curvature
Aberrations degrade the
quality of image
Aberrations are important in
-the design of spectacles, contact lens, IOLs and Refractive surgeries
-Correction of refractive errors
Positive Longitudinal Spherical Aberrations (LSA)
light rays striking the periphery of the lens (non-paraxial rays) are focused closer to the lens than those striking near its center (paraxial rays)
Positive LSA is present in both
plus and minus lenses
Negative LSA
light rays striking the periphery of the lens (non-paraxial rays) are focused farther away to the lens than those striking near its center (paraxial rays)
What is the amount of LSA dependent on?
the radii of curvatures of the front and back surfaces of a lens
What lenses minimize LSA?
lenses with approximately plano-convex shapes that are oriented so that the front surface is more convex
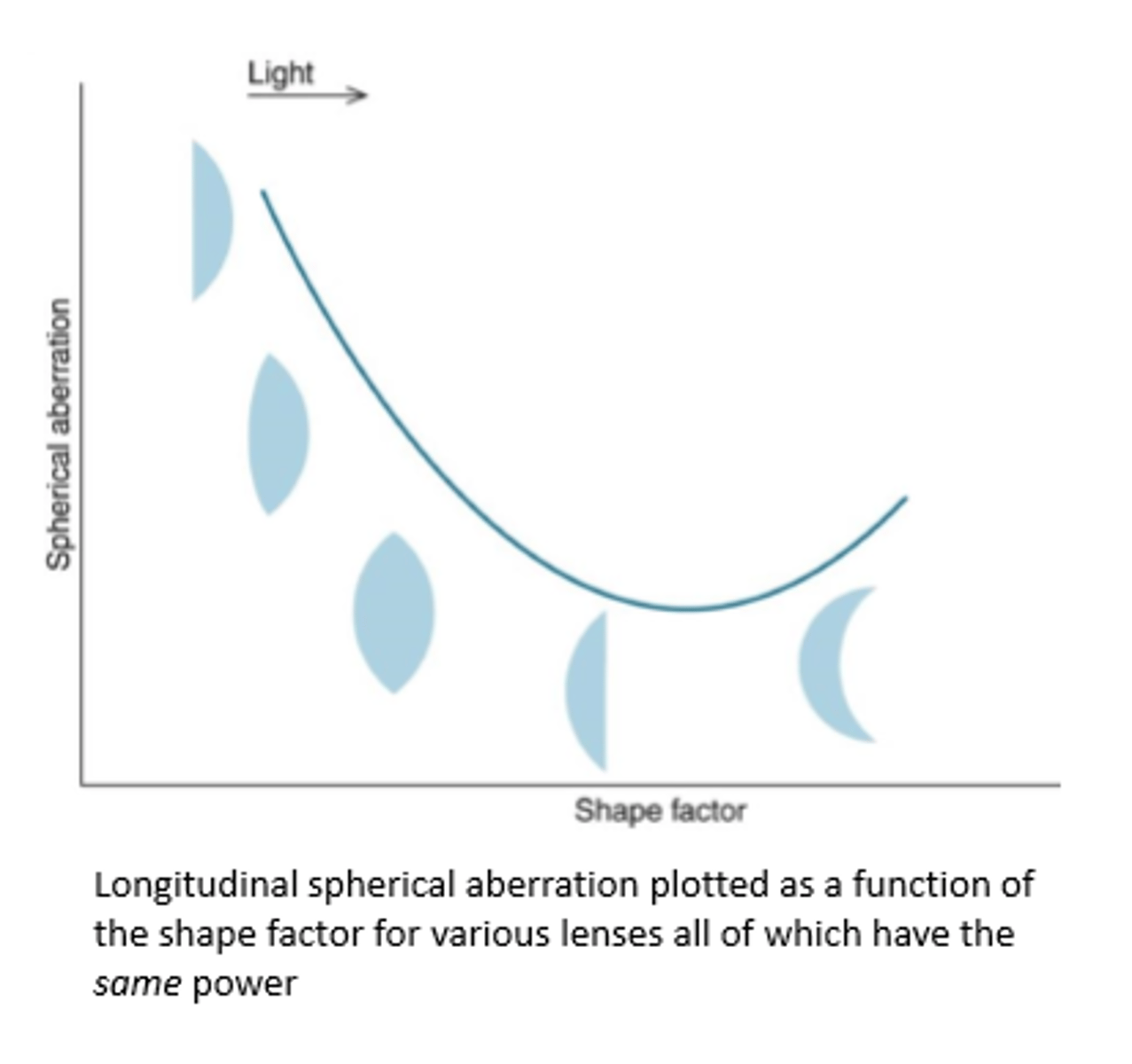
The unaccommodated eye manifests positive spherical aberration, which tends to increase with
age
As the eye accommodates, the amount of positive spherical aberration
decreases
Night myopia
under dim lighting conditions the pupil dilates, exposing the retina to non-paraxial (or marginal) light rays. These light rays may be focused in front of the retina, making the eye myopic
-The eye's spherical aberration may have clinical implications for nighttime vision
-Clinically, prescribe lenses with slightly more minus power for those patients who do considerable nighttime driving.
Both spherical aberration and coma occur because
the refractive power of a spherical surface is not uniform
Off-axis Coma
-results when the light rays are oblique with respect to the optical axis (Spherical aberration result when light rays are parallel to the optical axis)
-Because of coma, an off-axis point source results in an image with a comet-like shape
How do you tell if the coma is positive or negative?
When the tip of the comet is pointed toward the optical axis, the coma is said to be positive, and when it is pointed away, the coma is negative.
Light distribution in Coma image
The light distribution is not uniform across the comatic patch, but is highest at the pointed end.
On-axis decentered coma (induced)
occurs when the optical components are non-centered and tilted with respect to each other
-A decentered eye, where coma may be major foveal aberration.
If the pupil is decentered by 0.25 mm, the magnitude of induced coma will be
same as spherical aberration
If the pupil is decentered by 0.50 mm, the magnitude of induced coma will be
twice as spherical aberration
How to reduce coma?
If an aperture is placed close to a lens and the diameter of the aperture is decreased, the amounts of coma decrease.
Coma is dependent on the
lens shape factor
-It can be minimized by making the curvatures of the lens surfaces similar to those that also reduce spherical aberration
Oblique astigmatism
occurs when light rays emerging from an off-axis object pass through the center of a lens
-It is of clinical significance in the design of spectacle lenses
-Correct selection of the front surface power can minimize this aberration
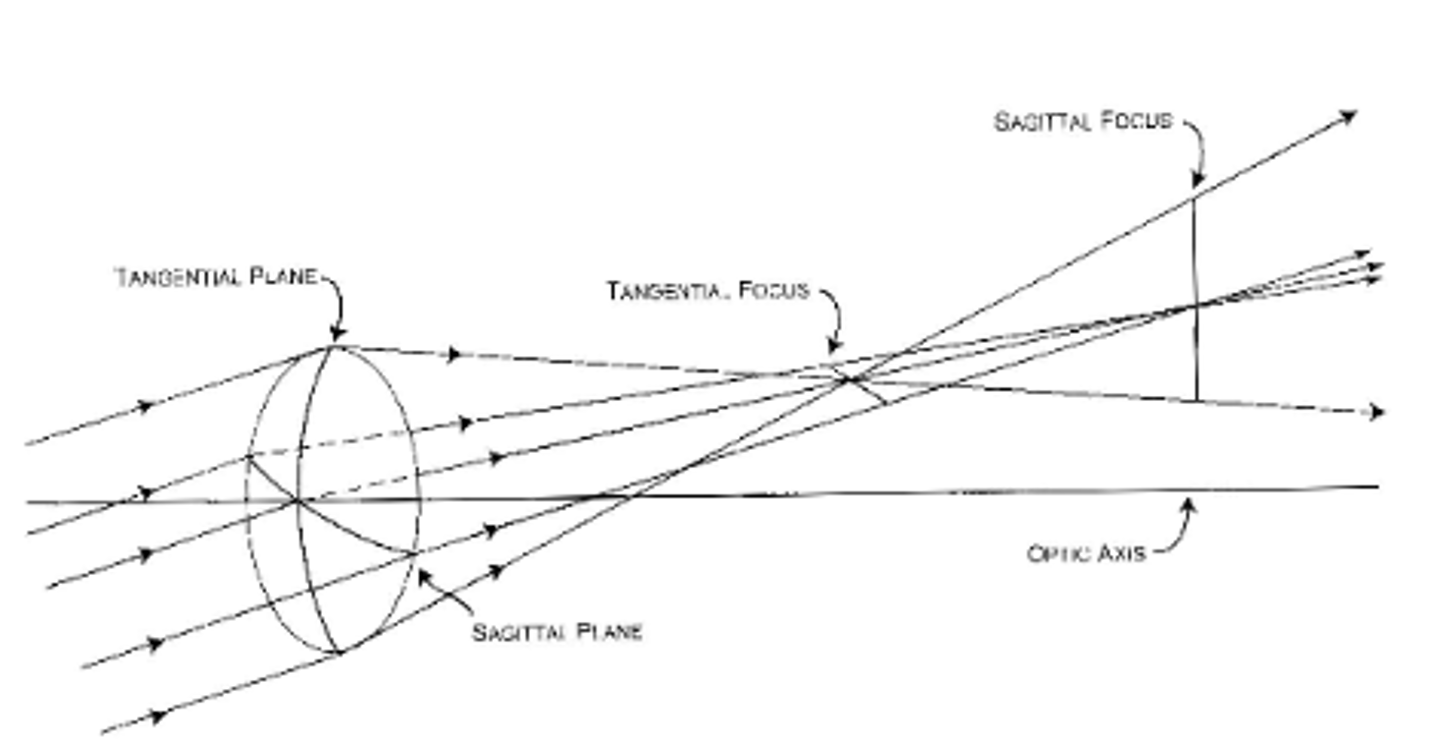
Curvature of Field
Not all points on the extended object are the same distance from the spherical converging lens. An image plane that is not flat but curved.
-Off-axis rays that pass through the center of a lens can cause curvature to field
-This aberration is clinically important in the design of spectacle lenses.
-It can be minimized by the proper selection of the lens front surface power.
Distortion
the central and peripheral regions of a spherical lens do not produce the same amount of lateral magnification
-a consideration in the design of spectacle lenses
barrel distortion
distortion found with minus lenses
-occurs because minification in the periphery of a minus lens is greater than in its center

pincushion distortion
distortion found with plus lenses
-results from greater magnification in the periphery of a plus lens compared to its center
