Anatomy Exam 1 Shobnom Auburn University
1/169
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
170 Terms
Flow of organism
atoms-->molecules-->organelle-->cellular level-->tissue level-->organ level-->organ system-->organism
Anatomy
"to cut apart", study of structure of body parts and relationships to each other
Physiology
study of function of the body parts, how they work together
Hippocrates
separated disease from superstition
Gross Anatomy (macroscopic)
study of large visible structures
Microscopic Anatomy
tissues and cell anatomy, need help to see them ex: microscopes
Histology
study of tissues
Cytology
study of cells
Developmental Anatomy (Branches of Anatomy)
study of structural changes that occur between conception and adulthood
Embryology (Branches of Anatomy)
study of developments before birth
Gross/Macroscopic Anatomy (Branches of Anatomy)
studies of large body structures such as stomach, lungs, or heart
CT Scan (Computed Tomography)
uses x-rays passed through body in this cross sections (3D)
Ultra Sound
uses waves that are then reflected/scattered when they hit something and are then analyzed by a computer to generate 2D/3D images, very safe but not good for looking at structures surrounded by bone
Anatomic Position
Standing erect, facing forward, upper limbs hanging to the sides, palms facing up upwards
Supine
on back face up
Prone
on belly face down
Superior (Cranial) (Directional Term)
cranial, toward the head end or upper part of a structure or the body, above
Inferior (Caudal-tail) (Directional Term)
away from the head end or toward the lower part of a structure or the body, below
Ventral (Anterior) (Directional Term)
toward or at the front of the body, in front of
Dorsal (Posterior) (Directional Term)
toward or at the back of the body, behind
Medial (Directional Term)
toward or at the midline of the body, on the inner side of
Lateral (Directional Term)
away from the midline of they body, on the outer side of
Intermediate (Directional Term)
between a more medial and a more lateral structure
Proximal (Directional Term)
closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
Distal (Directional Term)
farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
Superficial (External) (Directional Term)
toward or at the body surface
Deep (Internal) (Directional Term)
away from the body surface, more internal
Bilateral (Directional Term)
2 sided, affecting both sides equally (humans), symmetrical about our midline
Ipsilateral (Directional Term)
located on same side of the body, right and left leg
Contralateral (Directional Term)
on opposite side, right arm and left leg (right and left arm)
Axial (Body Regions and Planes)
head, neck, trunk (think axis)
Appendicular (Body Regions and Planes)
appendages/limbs
Sagittal Plane
vertical plane that divides the body in right and left halves, midsagittal-equal, parasagittal-unequal
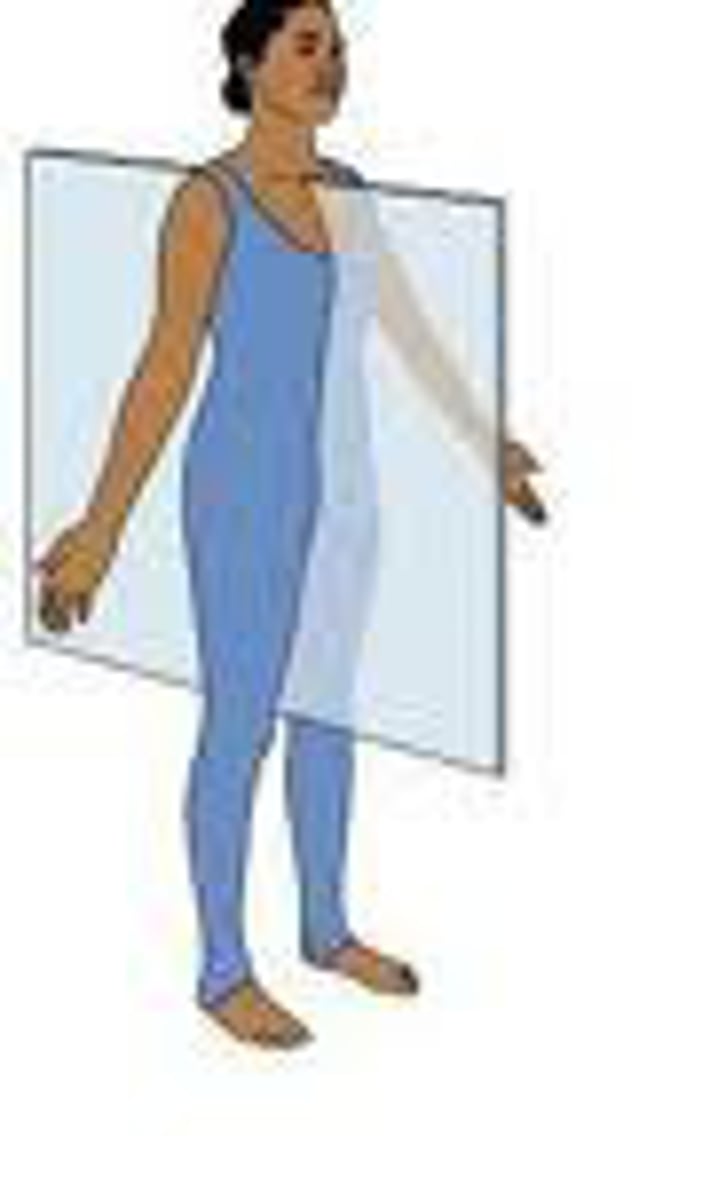
Frontal Plane
vertical plane that divides the body into anterior and posterior halves
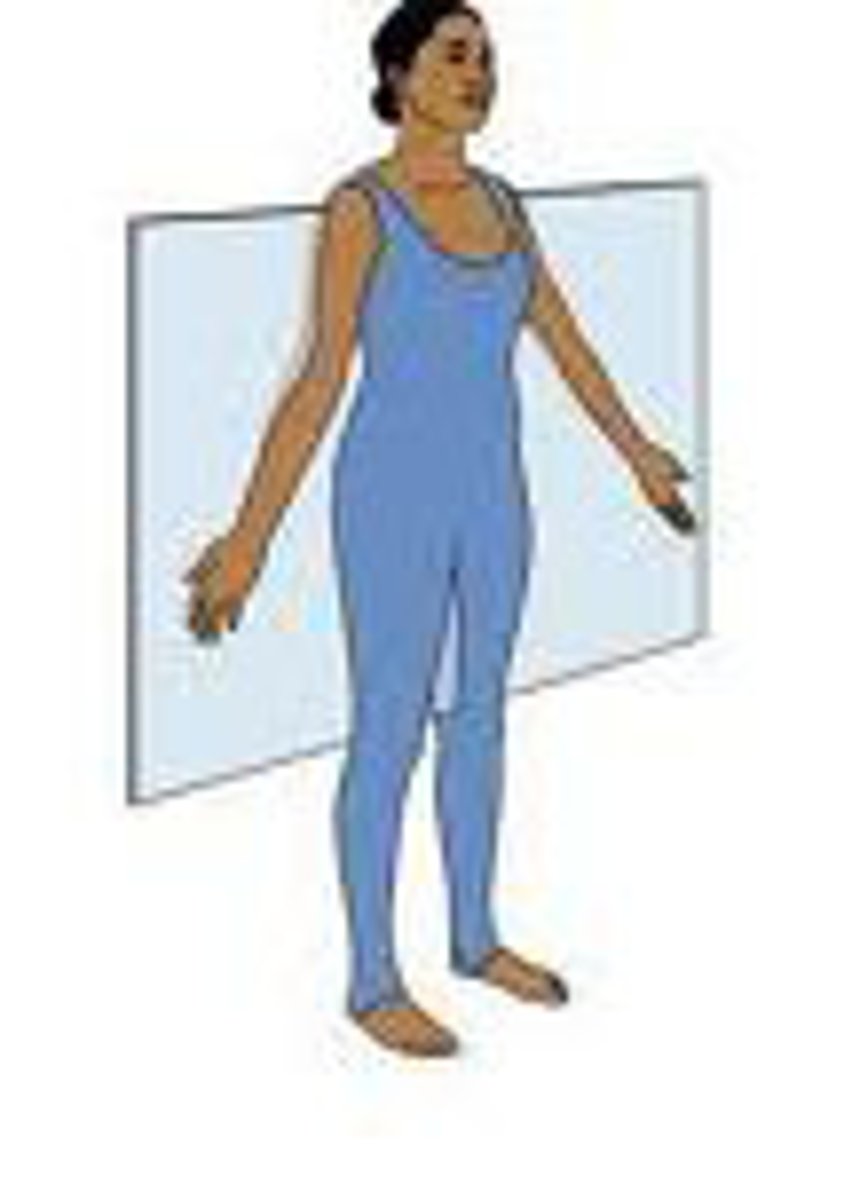

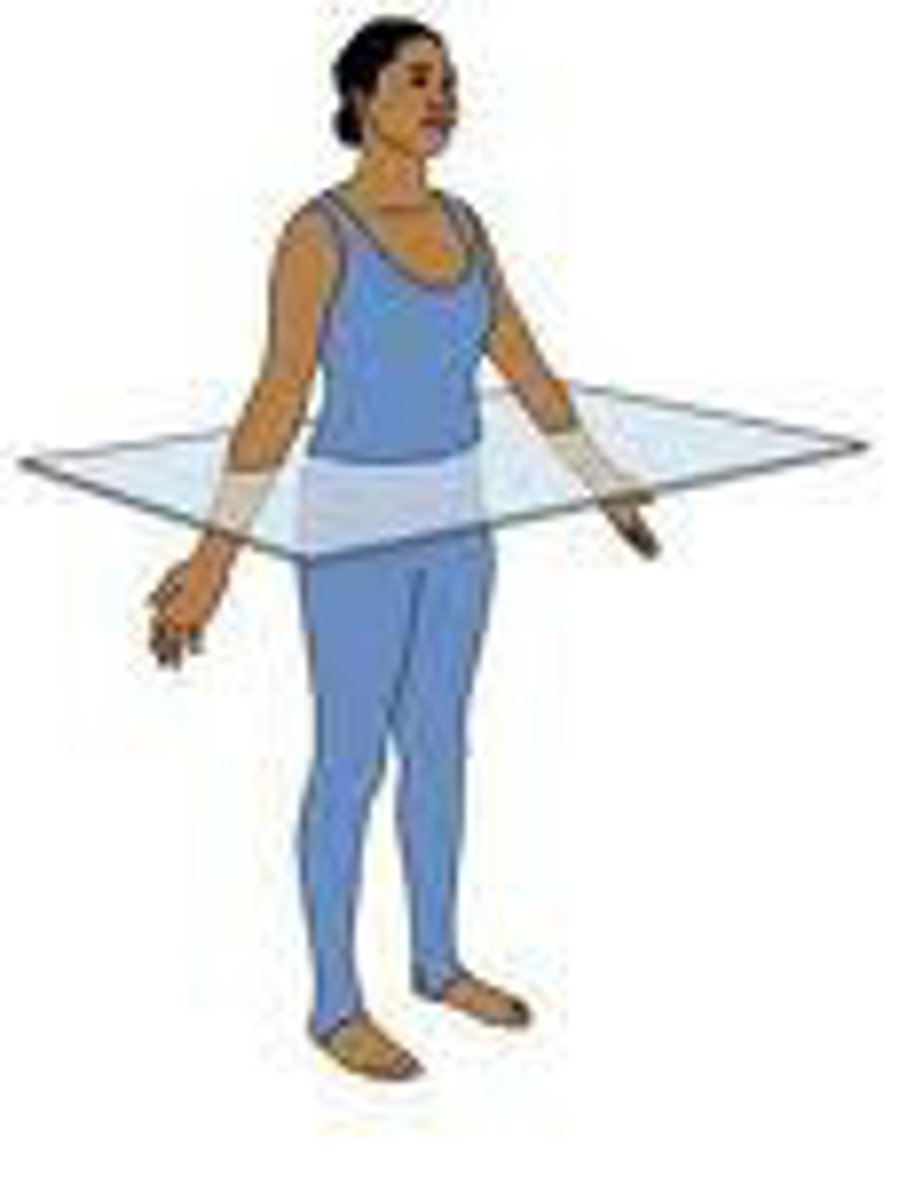
Transverse Plane
horizontal plane that divides the body into superior and inferior parts
Dorsal Body Cavity
contains cranial cavity (in the skull and contains the brain) and vertebral cavity (contains spinal cord)
Ventral Body Cavity
divided into two main cavities separate by the diaphragm
Thoracic Cavity (included in ventral body cavity)
superior to diaphragm, contains heart and lungs
A). pleural cavities (2)- contains lungs
B). mediastinum- contains pericardial cavity which encloses the heart
Abdominopelvic Cavity (included in ventral body cavity)
inferior to diaphragm, 2 parts separated by muscle or membrane
A). abdominal cavity (superior portion)- houses stomach, intestine, spleen, liver, other organs
B). pelvic cavity (inferior portion)- lies in pelvis, houses urinary bladder, some reproductive organs, rectum
Serosa (serous membrane)
thin, double-layered membrane, lines walls of ventral body cavity and outer surfaces of organs
Visceral Serosa (serous membrane)
covers organs
Parietal Serosa (serous membrane)
lines cavity walls
Pleurisy/Peritonitis (serous membrane)
causes roughening of pleurae or peritoneum, causes organs to stick together and drag across one another, very painful
Pleurisy
inflammation of pleura(e)
Peritonitis
inflammation of periotneum
Red Blood Cells (specialized cell)
small, no nucleus, biconcave disc
Skeletal Muscle Cell (specialized cell)
cylindrical, multi-nucleated, long
Neuron (specialized cell)
cell body wth axon and dendrites, neuron may not be detectable to human eye but can have an axonal process one meter long
Sperm Cell (specialized cell)
flagellated
Plasma Membrane (function)
acts as an active barrier separating intracellular fluid (ICF) from extracellular fluid (ECF)
Plasma Membrane (structure)
consists of membrane lipids that form a flexible lipid bilayer, specialized membrane proteins float through this fluid membrane, resulting in constantly changing patters a.k.a fluid mosaic
Glycocalyx
formed by surface sugars (carbs), sticks out of cell surface, some cancer cells can change so rapidly our immune system cannot detect them as being damaged cells, this allows them to replicate
Tight Junctions (integral protein)
between adjacent cells, keeps substances from passing between cells, ex: found between epithelial cells of digestive tract
Desmosomes (integral protein)
"velcro" protein filaments, extend from adjacent cells and link them together
Gap Junctions (integral protein)
allow communication between cells, used to spread ions, simple sugars or other small molecules between cells, found in electrically excitable tissues, ex: smooth muscle, heart
Cytoplasm/Cytoskeleton
material between plasma membrane and nucleus, contains cytosol and organelles
Lysosomes
organelle in cells, "cleaning crew", breaks down waste
Smooth ER
most cells contain relatively little if any, enzymes involved in many functions, storage site of calcium in skeletal and cardiac muscle cells
Tay Sachs Disease
specific enzyme found in lysosomes breaks down lipids in brain and nerve cells, lipids build up and damage cells, first listlessness, then blindness, then seizures, children rarely live beyond 4-5 years, no cure/treatment
Plasma Membrane (type)
selectively (differentially) permeable, some molecules pass through easily and osme do not
Electrochemical Gradient
concentration gradient + electrical gradient
Diffusion
movement of molecules down their concentration gradients (from high to low), energy is not required
Passive Transport
no ATP needed, substances move down their concentration gradient from (high to low), proteins work by changing shape
Active Transport
ATP needed, substances go against their concentration gradient from (low to high), proteins work by changing shape, requires carrier proteins (solute pumps), bind specifically and reversibly with substance being moved, some carriers transport more than one substance
Simple Diffusion (passive transport)
substances pass through lipid bilayer, small molecules like O2, CO2, and lipid soluble vitamins, and lipid soluble molecules
Facilitated Diffusion (passive transport)
substances move across membrane by protein channels or carrier proteins, glucose, amino acis, ions, carrier proteins are specific for one substance, ions mostly pass through channels, ex: Na channel only transports Na
Clinical Homeostatic Imbalance
if plasma membrane is severely damaged, substances diffuse freely into and out of cell, compromising concentration gradients, ex: burn patients lose fluids
Osmosis (passive transport)
water moving through semi-permeable membran
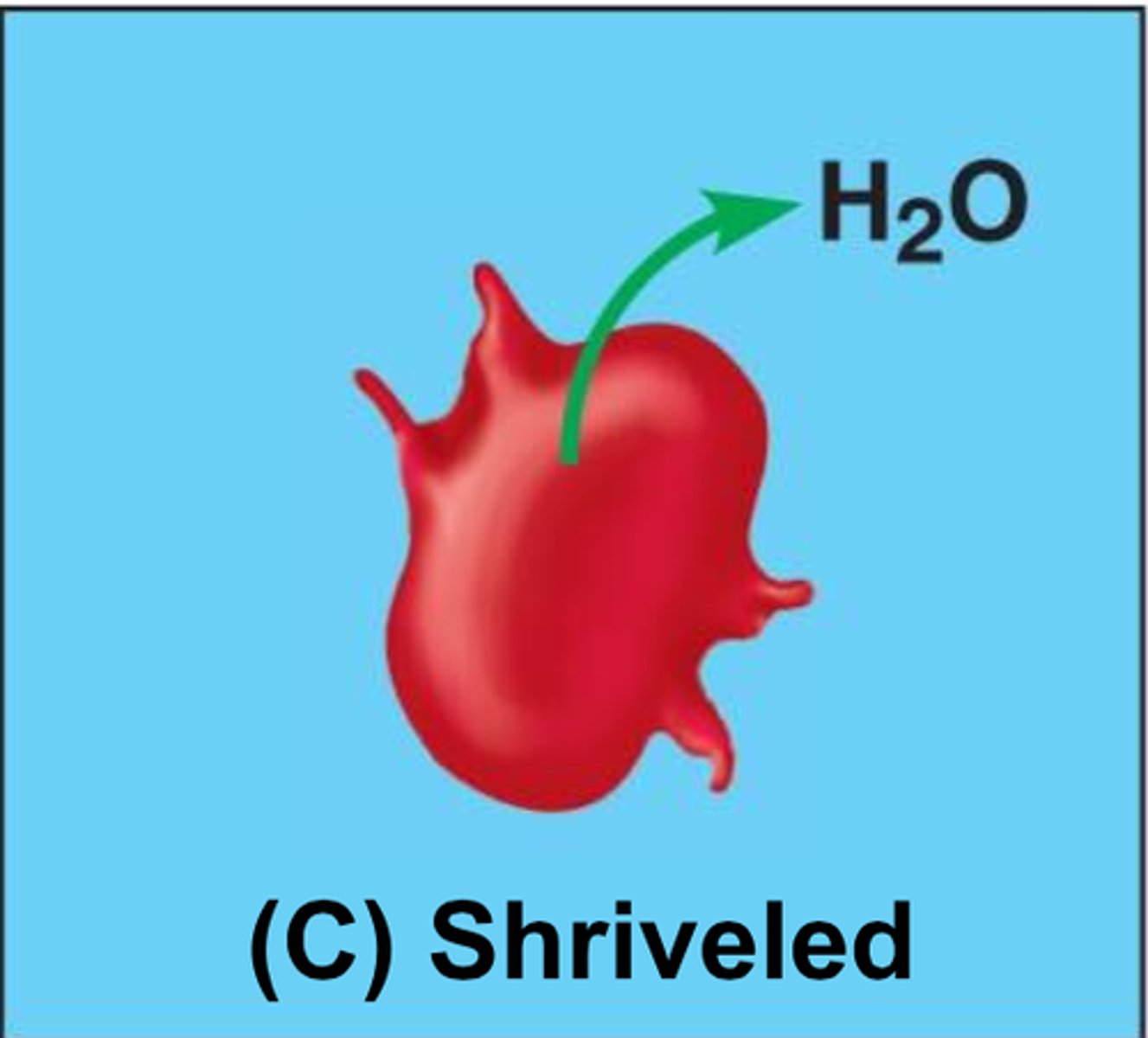
Hypertonic
cells lose water and shrink
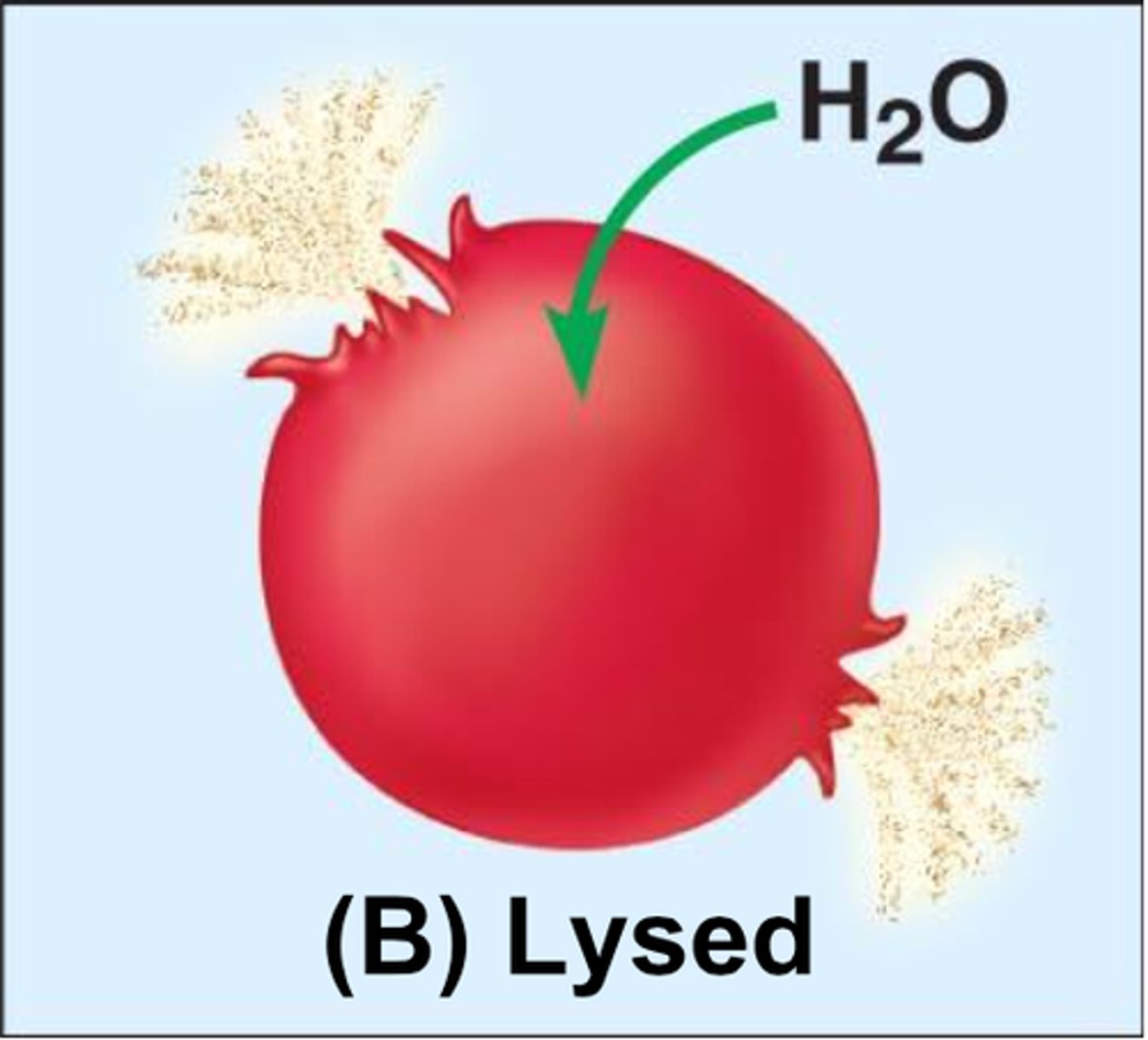
Hypotonic
cells swell and take in water until they burst (lyse)
Isotonic
cells stay the same size
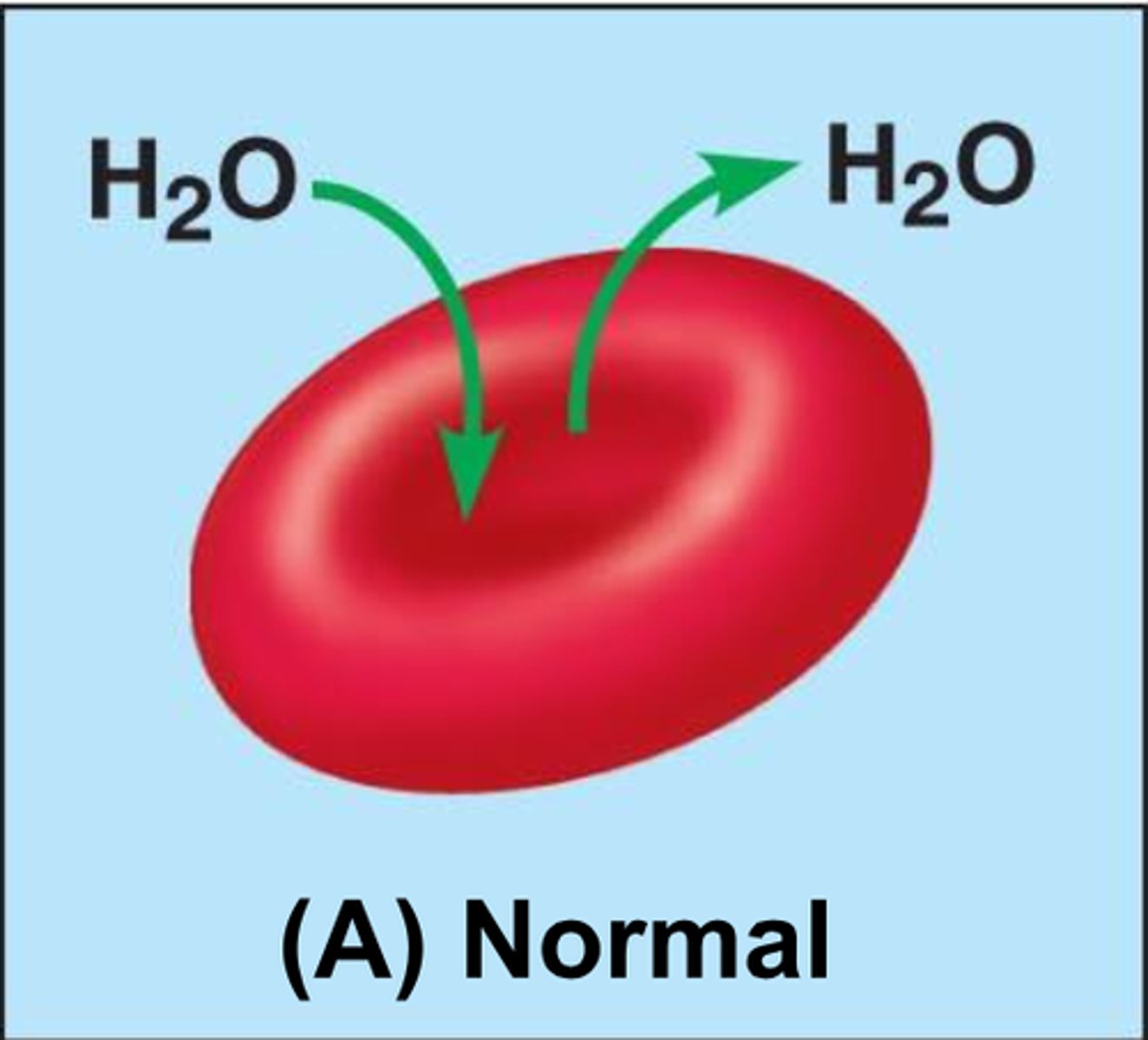
Bulk (filtration) Flow (passive transport)
movement of solutes and water from high pressure to low pressure, faster rate than diffusion and osmosis, ex: bulk flow in kidney
Antiporters (active transport)
transport one substance into cell while transporting a different out
Symporters (active transport)
transport 2 different substances in same directon
Bulk (vesicular) Transport (active transport)
large substances transported in vesicles
A). endocytosis- bringing substance into the cell
1. phagocytosis- engulfing molecules/bacteria "cell-eating"
2. pinocytosis- engulfing water "cell drinking"
B). exocytosis- removing substance from the cell
Exocytosis
secretory vesicle contains substance to be removed, moves to and fuses with plasma membrane, ruptures which expulses the contents
Phagocytosis
particle binds to receptors on cell surface, pseudopods (cytoplasmic extensions) develop and reach out to envelope particle forming a vesicle around the particle
Pinocytosis
invagination of plasma membrane which surrounds extracellular fluid
Primary Active Transport
solutes bind to the transport protein, ATP is split into ADP and P, provides energy for protein to change shape which "pumps" solute across the membrane against its electrochemical gradient, ex: Na+/K+, ATPase Pump, (3Na+ out for every 2K+ in)
Secondary Active Transport
low Na+ concentration that is maintained inside cell by Na+/K+ pump strengthens Na+ drive to want to enter cell, Na+ can pick up other molecules as it enters cell through carrier proteins, simultaneous movement of 2 substances through transport protein
Membrane Potential
difference in electrical charge across plasma membrane
Resting Membrane Potential
membrane potential when cels in resting state about (70mV), inside cell has overall negative charge relative to outside
How is resting membrane potential established?
K+ diffuses out of cell by leakage channels down concentration gradient, negative charged proteins can't leave so cytoplasmic side of cell becomes more negative, K+ is pulled back by more negative interior, when drive for K+ is balanced by drive to stay, RMP is established (RMP is usually about -90mV), electrochemical gradient K+ sets up RMP, Na+ also affect RMP, attracted into cell by negative charge when Na+enters, RMP goes up to about (-70mV), membrane is more permeable to K+ than Na+ so, K+ is primary drive of RMP, Cl- does not influence RMP because concentration and electrical gradients are equally balanced
Tissues-
group of cells similar in structure and serve a similar, specialized function
Polarity
have top (apical surface) and bottom (basal surface)
Basement Membrane
point of attachment for epithelial and connective tissue
Basal Lamina
what makes up the basement membrane, glycoproteins from epithelial tissue and collagen fibers
Reticular Lamina
glycoproteins from connective tissue and collage fibers
Cilia
hair like projections, help propel substances, ex: nasal cavity, trachea
Microvilli
extensions of plasma membrane, help increase surface area, small intestines
Endocrine
produce hormones and secrete them into bloodstream via exocytosis
Exocrine
secrete product onto body surfaces (skin) or into body cavities
Unicellular (exocrine glands)
mucous and goblet cells, produce mucin which is a glycoprotein that dissolves in water when secreted forming mucus, secret product by exocytosis
Multicellular (exocrine glands)
consist of a duct and secretory
Simple Duct (exocrine glands)
unbranched duct (simple tubular, simple branched tubular, simple alveolar, simple branched alveolar)
Compound Duct (exocrine glands)
branched duct (compound tubular, compound alveolar, compound tubuloalveolar)
Alveolar (acinar) (exocrine glands)
secretory cells form small sacs (simple alveolar, simple branched alveolar, compound alveolar, compound tubuloalveolar)
Tubular (exocrine glands)
secretory cells from tubes (simple tubular, simple branched tubular, compound tubular)
Tubuloalveolar (exocrine glands)
alveolar + tubular (compound (tubuloalveolar)
Holocrine (exocrine glands)
"whole membrane rupturing", ex: sebaceous glands, pimple