Botanical Structures, Nomenclature, and Plant Taxonomy: Key Concepts and Definitions
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
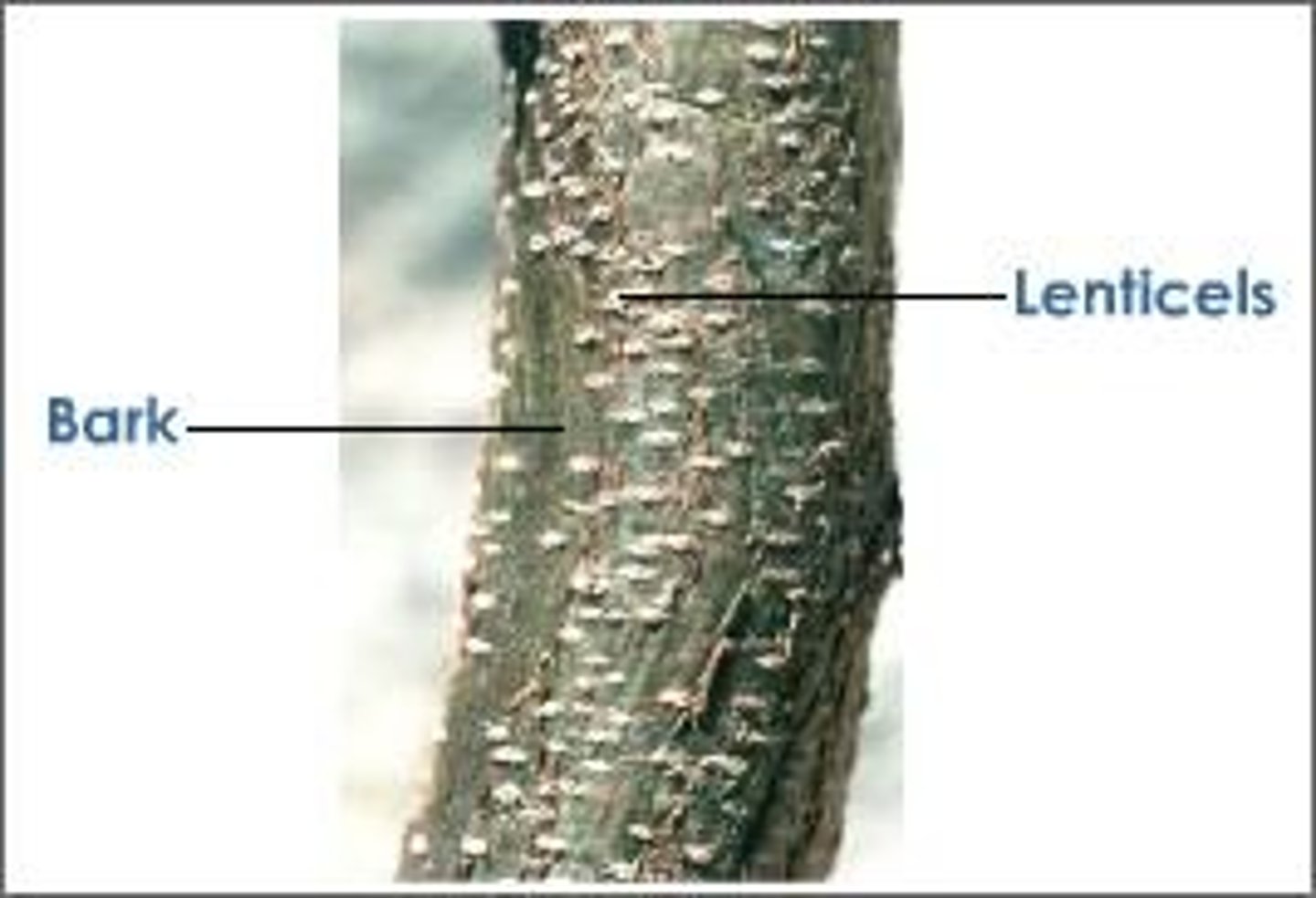
What are lenticels?
Raised pores in the stem of a woody plant allowing for gas exchange.

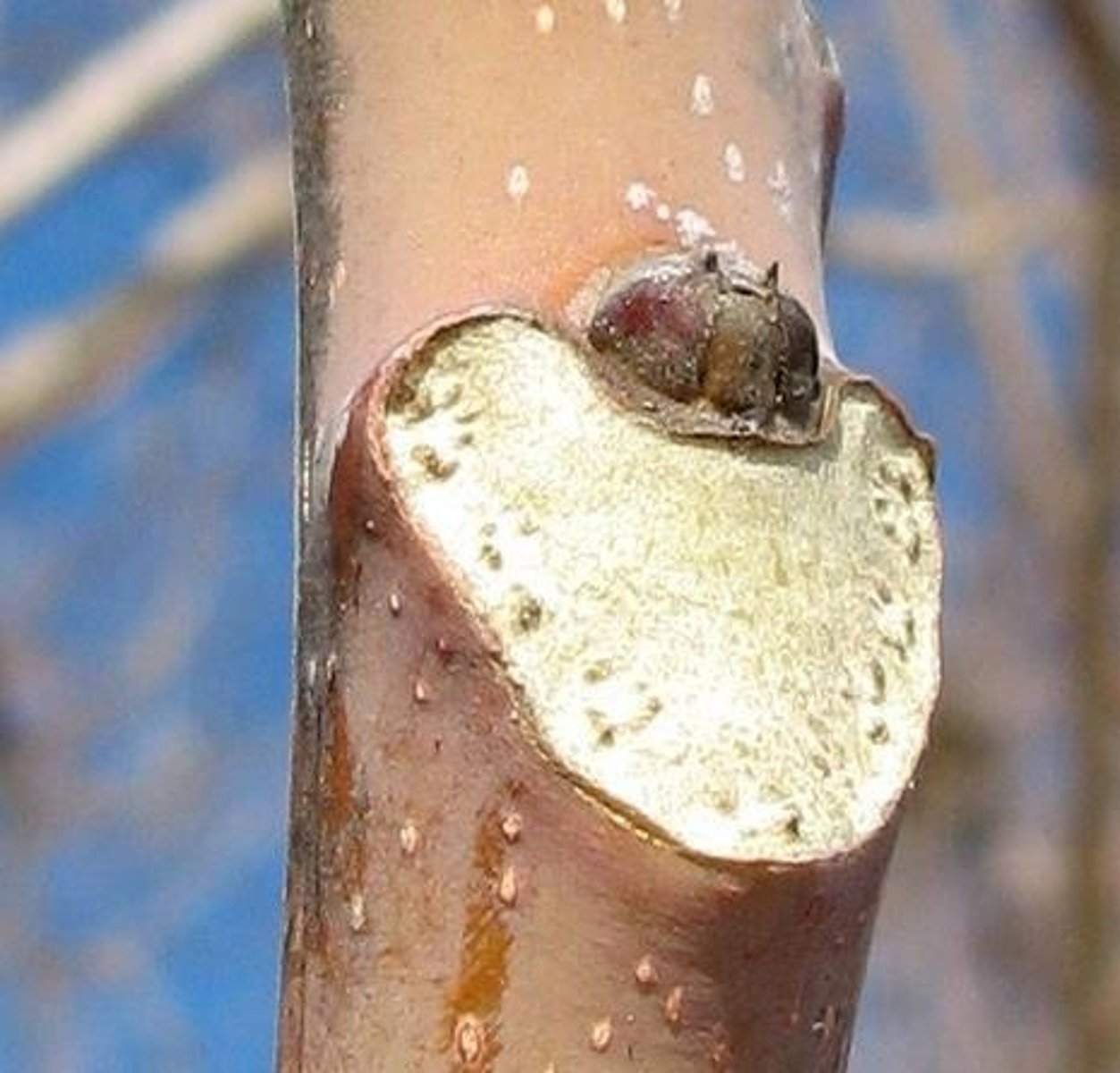
What is a leaf scar?
The mark left on a stem after a leaf falls.

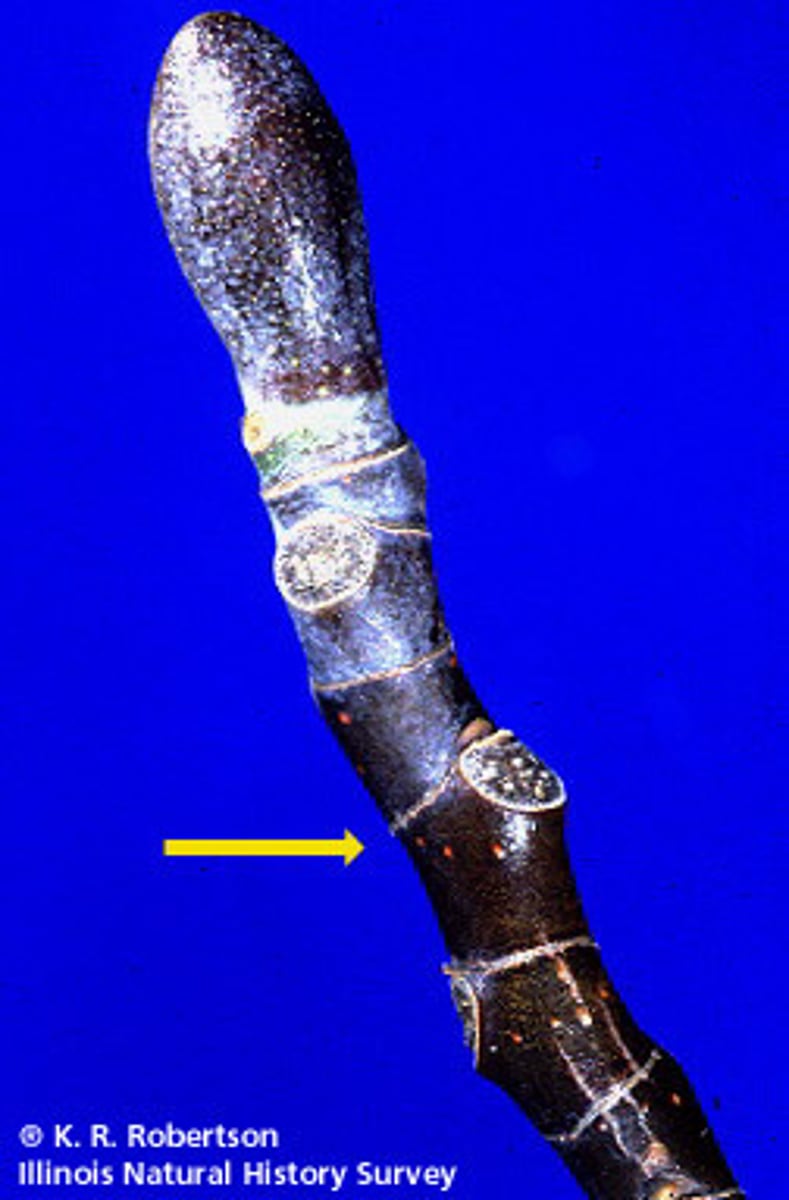
What is a stipule scar?
Remnants of leafy appendages that were attached to the petiole.

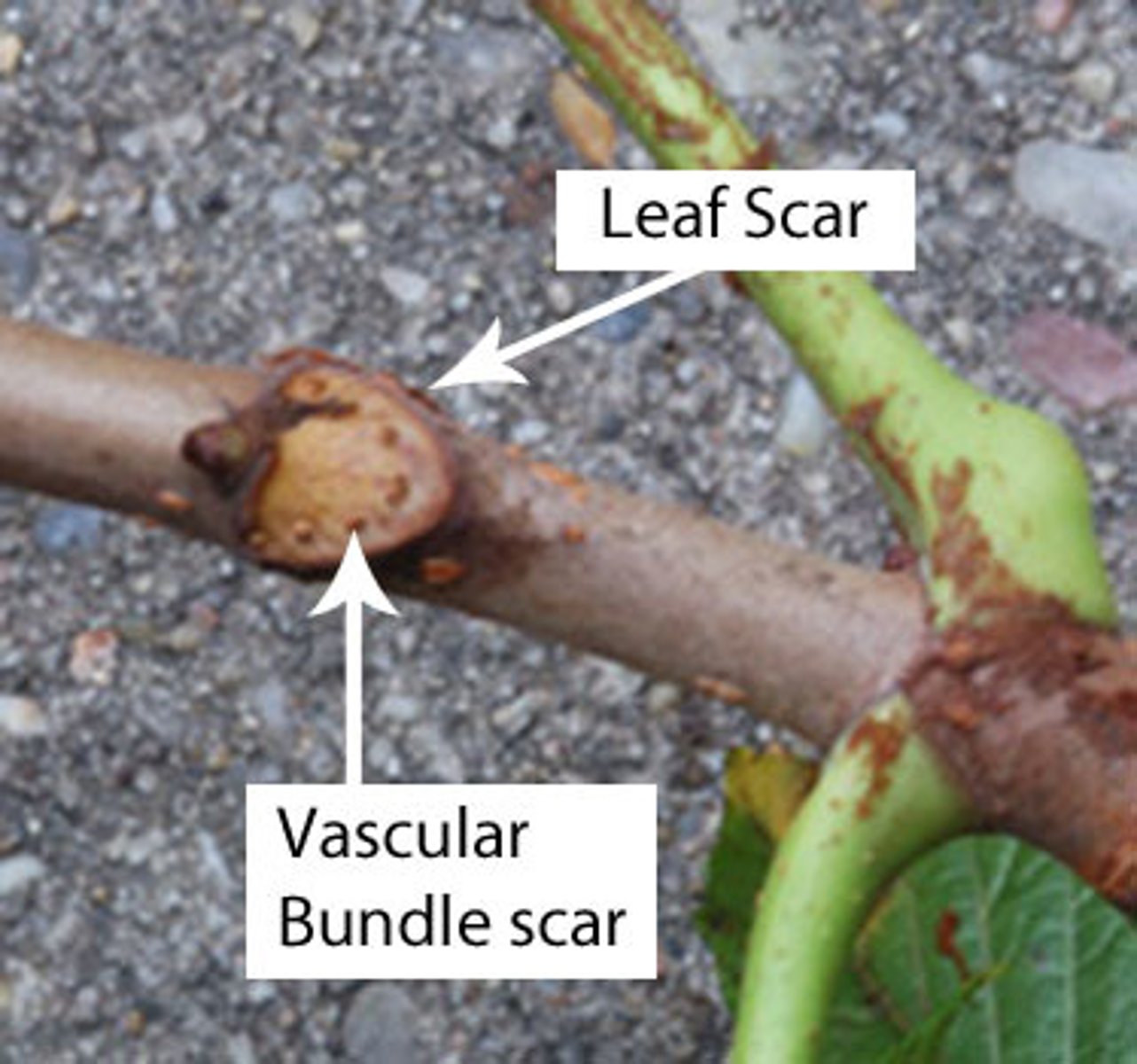
What is a vascular bundle scar?
Marks within leaf scars.

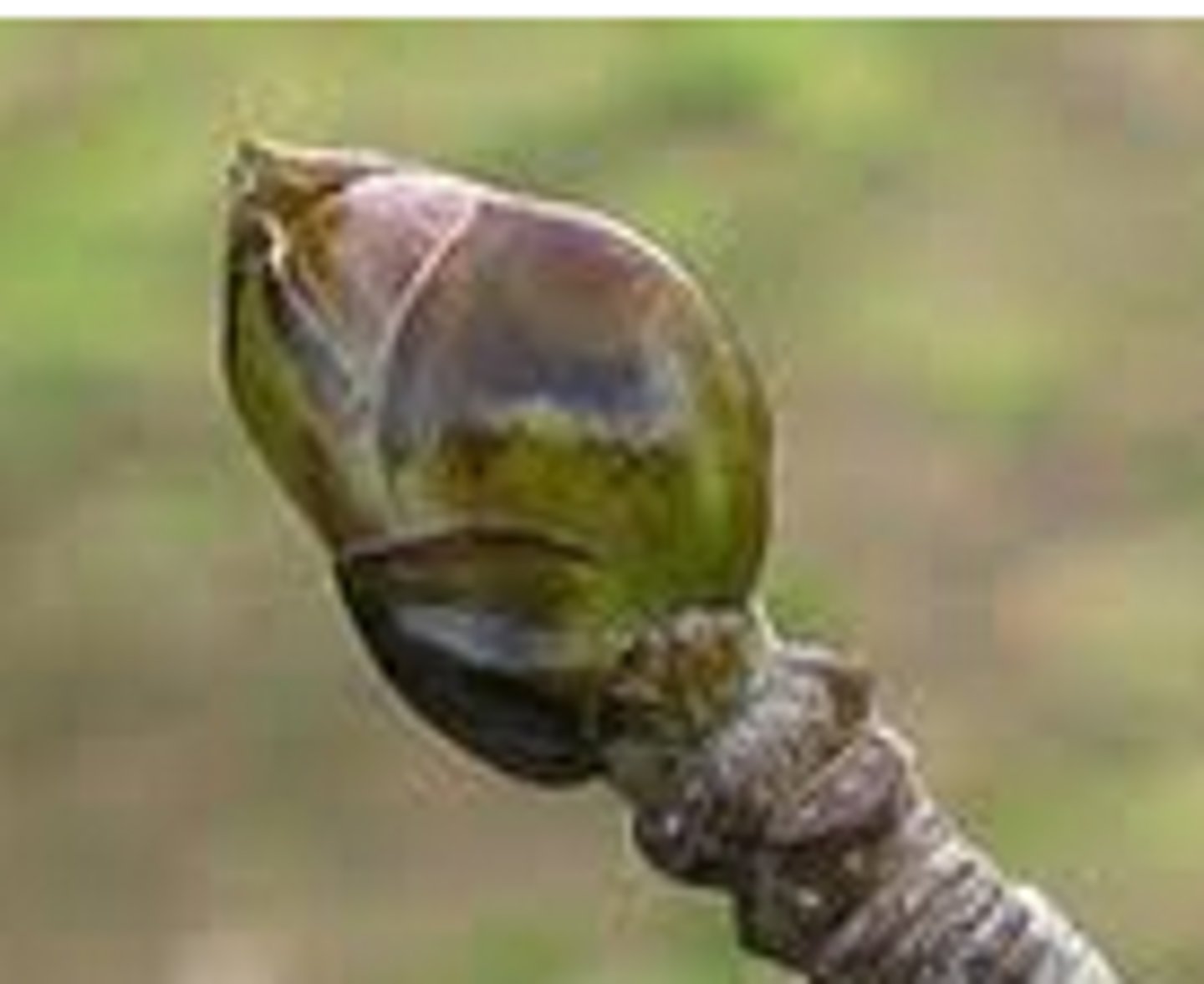
What is a bud?
Undeveloped shoot with the potential to grow into a new part of the plant.
What is a bud scale?
Scale-like modified leaves protecting lateral and terminal buds.
What are valvate scales?
Two or three scales that do not overlap.
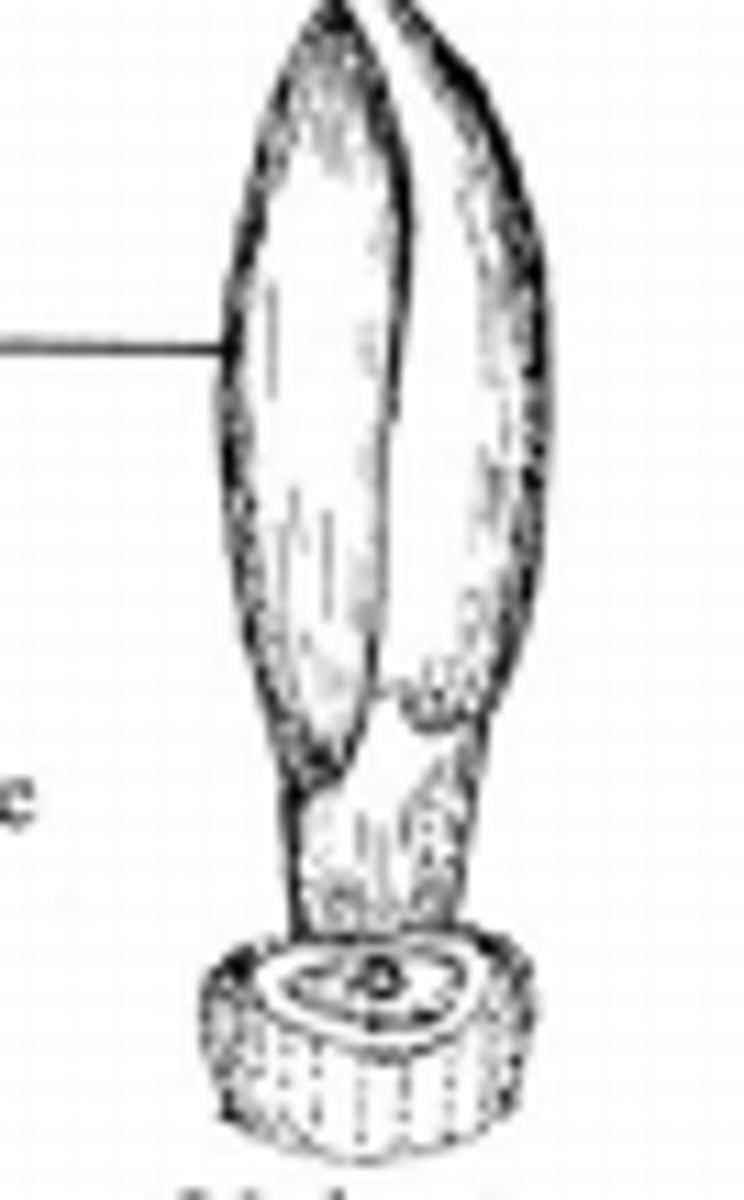
What are imbricate scales?
Numerous scales overlapping one another in shingle-like fashion.

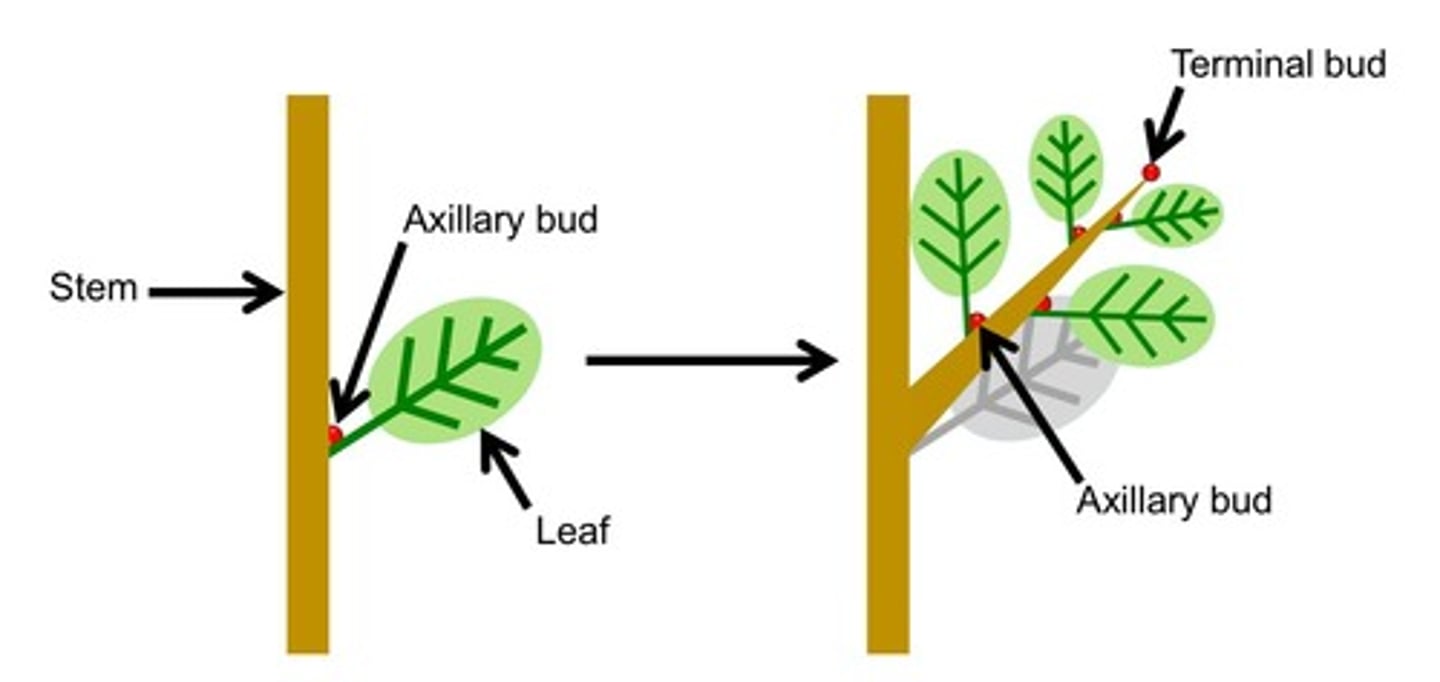
What is an axillary bud?
Bud located in axil of leaf that can develop into new branches or flowers.
What is a lateral bud?
Another term for axillary bud.
What is a terminal bud?
Bud(s) on apical end of twig.
What is a pseudoterminal bud?
Lateral bud that is on apical end of twig due to dieback.
What is a node?
Point where leaf grows from stem.
What is an internode?
Segment of plant stem between two nodes.
What does opposite mean in botany?
Two leaves, one on each side of twig.
What does alternate mean in botany?
Only single leaf attached at each node.
What is a seta?
Unbranched stalk that extends from the base of the sporangium to connect with the stem tip of the gametophyte.
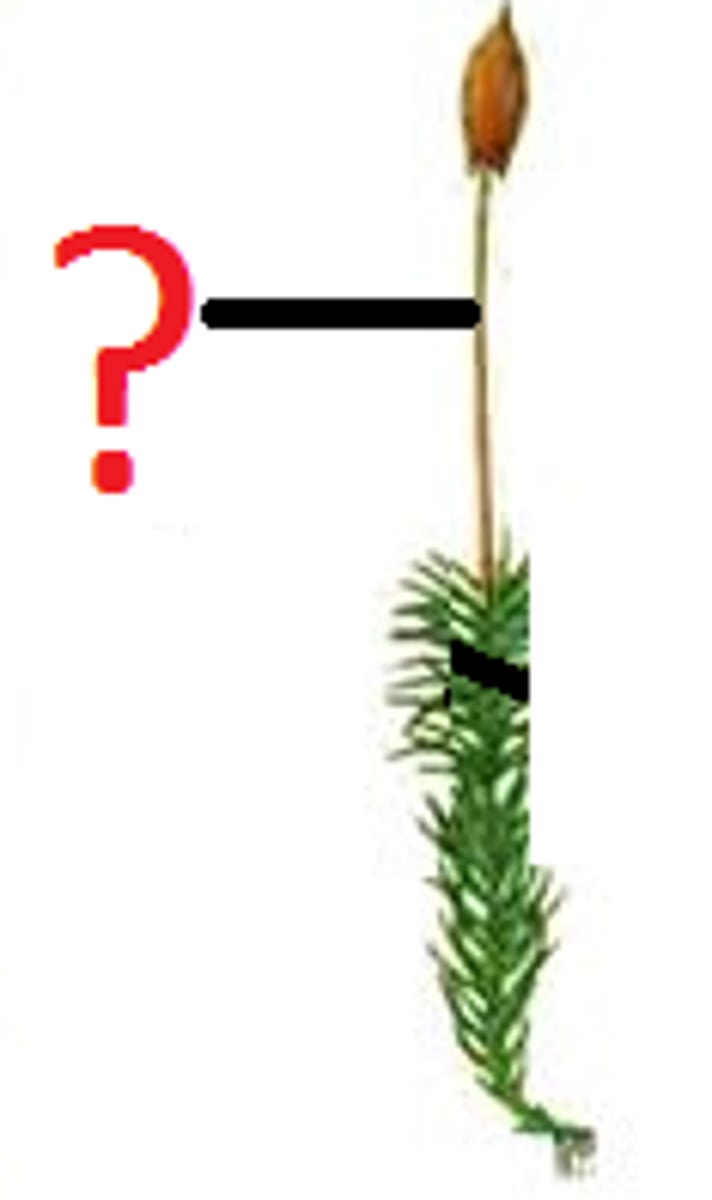

What is a sporangium?
Develops after seta elongates.
What is a sporophyte?
Diploid, spore-producing structure consisting of seta and sporangium.
What are the parts of a moss sporangium?
Calyptra, operculum, peristome.
What is calyptra?
Gametophytic structure temporarily attached to sporangium, modified remains of the archegonium.
What is operculum?
Lid that covers the opening of the sporangium.
What type of bryophyte sporangia splits into 4 valves?
Liverworts.
What type of bryophyte has leaves spirally arranged on the stem?
Moss gametophyte.
What type of bryophyte has leaves in 2 rows & a 3rd row of smaller leaves on the underside?
Liverwort gametophyte.
What is the perianth in liverworts?
A gametophytic structure that surrounds a small cluster of archegonia and the single sporophyte that forms after fertilization.
What is the most common liverwort species in all of eastern NA?
Frullania.
What species has leaves that overlap like roof shingles?
Frullania.
What does thalloid mean?
Having a flattened form and without stems and leaves.
What is an urn in botany?
Holds the spores.
What are peristome teeth?
Around mouth of sporangium, aiding in spore release.
What is a feature of the female gametophyte in liverworts?
Perianth.
What are some disadvantages of common names?
They can differ between locations, are not specific, may be misleading, and some can have the same one.
What does ICN stand for?
International Code of Nomenclature.
What are nomenclatural synonyms?
Names based on the same type specimen.
What are taxonomic synonyms?
Names based on different type specimens.
What is a polynomial?
Longer descriptions for naming a species.
What is a binomial?
Two part naming system.
What is a nomenclatural type?
A specific specimen serving as permanent anchor for scientific name in biological nomenclature.
What is a holotype?
Single specimen the author designates to represent the name published.
What is an isotype?
Duplicate of holotype.
What is a lectotype?
Chosen from author's citations.
What is a neotype?
When all original specimens are lost.
What are tautonyms?
Genus and species names are identical (in zoology).
What are homonyms in taxonomy?
The same name applied to two different species.
What is another accepted family name for Apiaceae?
Umbelliferae.
What is another accepted family name for Brassicaceae?
Cruciferae.
What is another accepted family name for Asteraceae?
Compositae.
What is the common name for Apiaceae?
Carrot family.
What is the common name for Brassicaceae?
Mustard family.
What is the common name for Asteraceae?
Sunflower family.
What is the story behind Franklinia alatamaha?
Discovered by William & John Bartram; it is a descendant of past plants saved from extinction.
Who was Theophrastos?
The father of botany.
Who was Carolus Linnaeus?
Developed the sexual system of classification; namely arrangement of stamens and pistils.
Who was de Jussieu?
Improved Linnaeus's artificial system to create a natural classification.
What is the Doctrine of Signatures?
An ancient belief that plants are marked with a divine sign indicating their purpose.
What is the difference between phenetic and phylogenetic classification systems?
Phenetics classify by physical similarity while phylogenetic classifies based on shared ancestry.
What did Linnaeus publish in 1753?
Species Plantarum.
When did modern botanical nomenclature begin?
In 1753 with the publication of Species Plantarum.
Who was the author of Genera Plantarum published in 1789?
de Jussieu.
What are the primary ranks in the hierarchy of classification?
DKPCOFGS.
What are herbals and their significance?
Botanical/medical books with accurate illustrations based on original observations.
What were the primary features used in Linnaeus's sexual system of classification?
Based on the number and arrangement of stamens and pistils.
What is an eponym?
A name formed after a person (e.g., Quercus michauxii).
Fagus grandifolia (American beech) twig
terminal bud
leaf scars alternate
leaf scar with 3 or more bundle scars
buds long and pointed, cigar-shaped
bud scales imbricate
stipular scars present, nearly encircling the twig
Platanus occidentalis (sycamore) twig
pseudoterminal bud
leaf scars alternate
leaf scar very narrow and encircling the bud
leaf scar with numerous bundle scars
bud with single cap-like scale
stipular scars encircle twig
Acer negundo (boxelder maple) twig
terminal bud
leaf scars opposite
stipular scars absent
leaf scar with 3 bundle scars
adjacent leaf scars meeting at a point higher than the lateral bud
twig bright green
Morus (mulberry) twig
pseudoterminal bud
leaf scars alternate
leaf scar with numerous bundle scars
stipular scars present, small
bud scales imbricate
Diospyros virginiana (persimmon) twig
pseudoterminal bud
leaf scars alternate
leaf scar with single banana-shaped (lunate) bundle scar
bud scales imbricate
stipular scars absent
Ostrya virginiana (hop hornbeam) twig
pseudoterminal bud
leaf scars alternate
leaf scar with 3 bundle scars
bud scales imbricate
bud scales with striations (fine stripes)
stipular scars present, small
Staphylea trifolia (bladdernut) twig
pseudoterminal bud
leaf scars opposite with three bundle scars
stipular scars (usually) very noticeable
Ulmus (elm) twig
pseudoterminal bud
leaf scars alternate
leaf scar with three sunken bundle scars
bud scales imbricate
bud often positioned off center, above leaf scar
stipular scars present, small