Electrical Energy
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Electrical Energy
the energy of electric charges, can be kinetic or potential; lightning (kinetic), batteries (potential/stored)

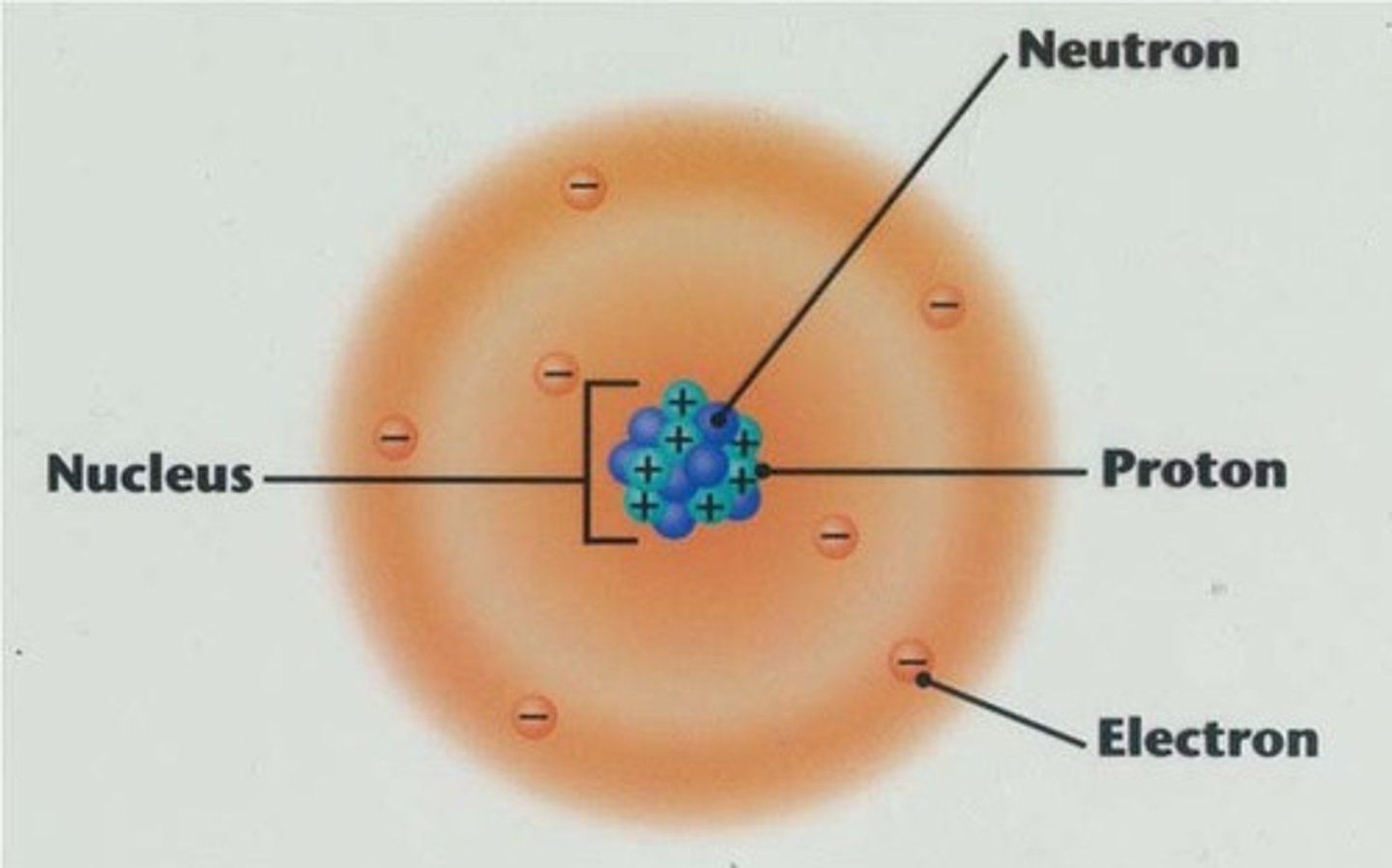
Nucleus
center of an atom, contains protons and neutrons
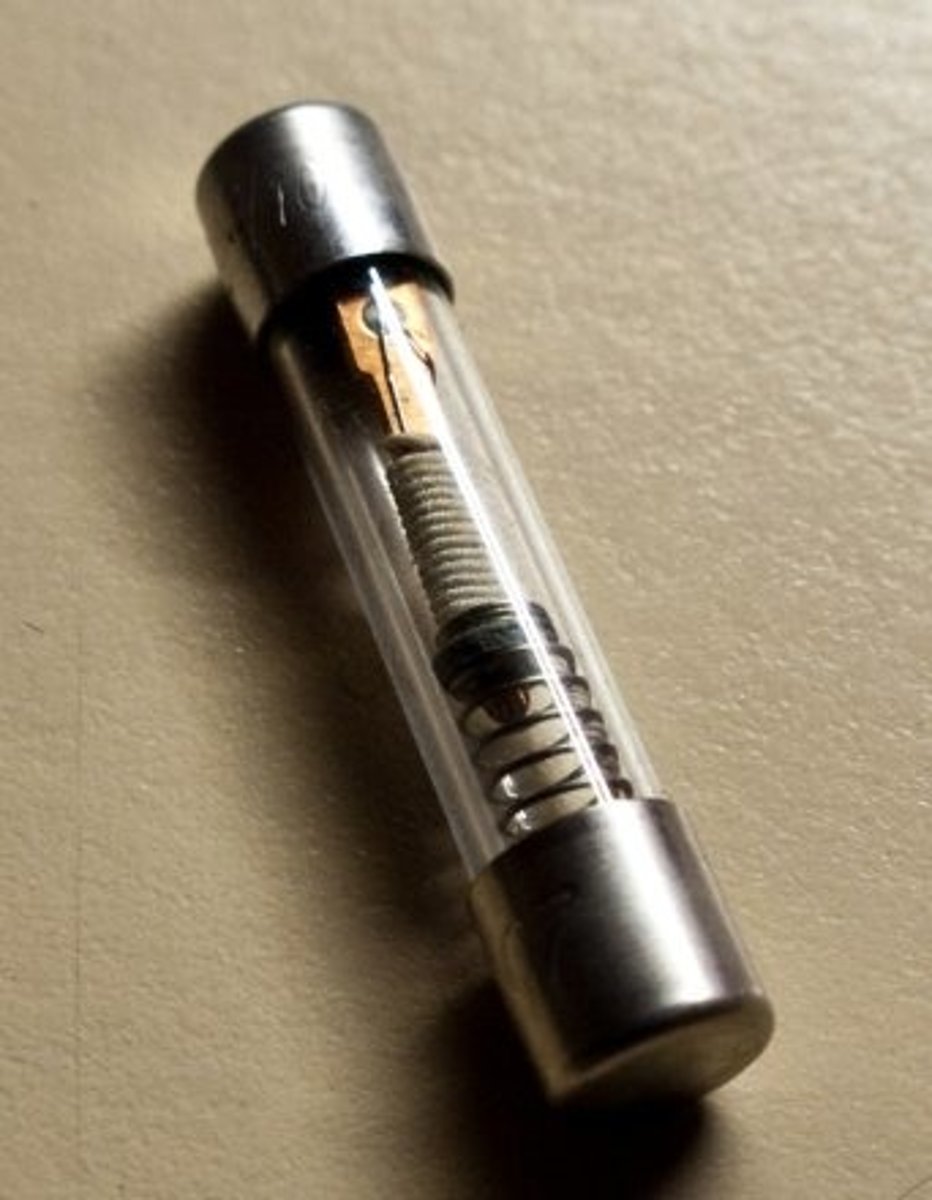
fuse
A safety device with a thin metal strip that will melt if too much resistance passes through a circuit decreasing the current

circuit breaker
A reusable safety switch that breaks the circuit when the resistance gets too high and current decreases by bending away from the contact
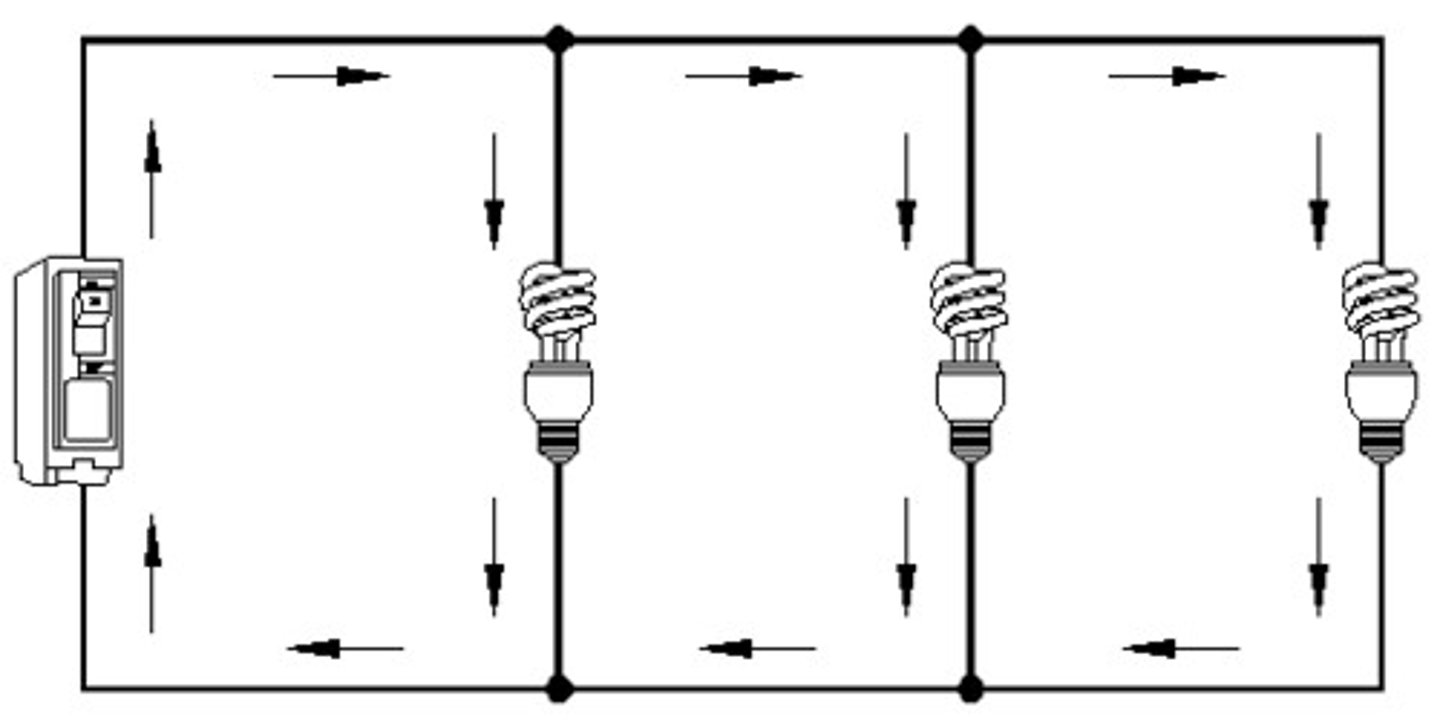
parallel circuit
A circuit that contains more than one path for current flow. This type of circuit allows for some electrical devices to be one while others are off
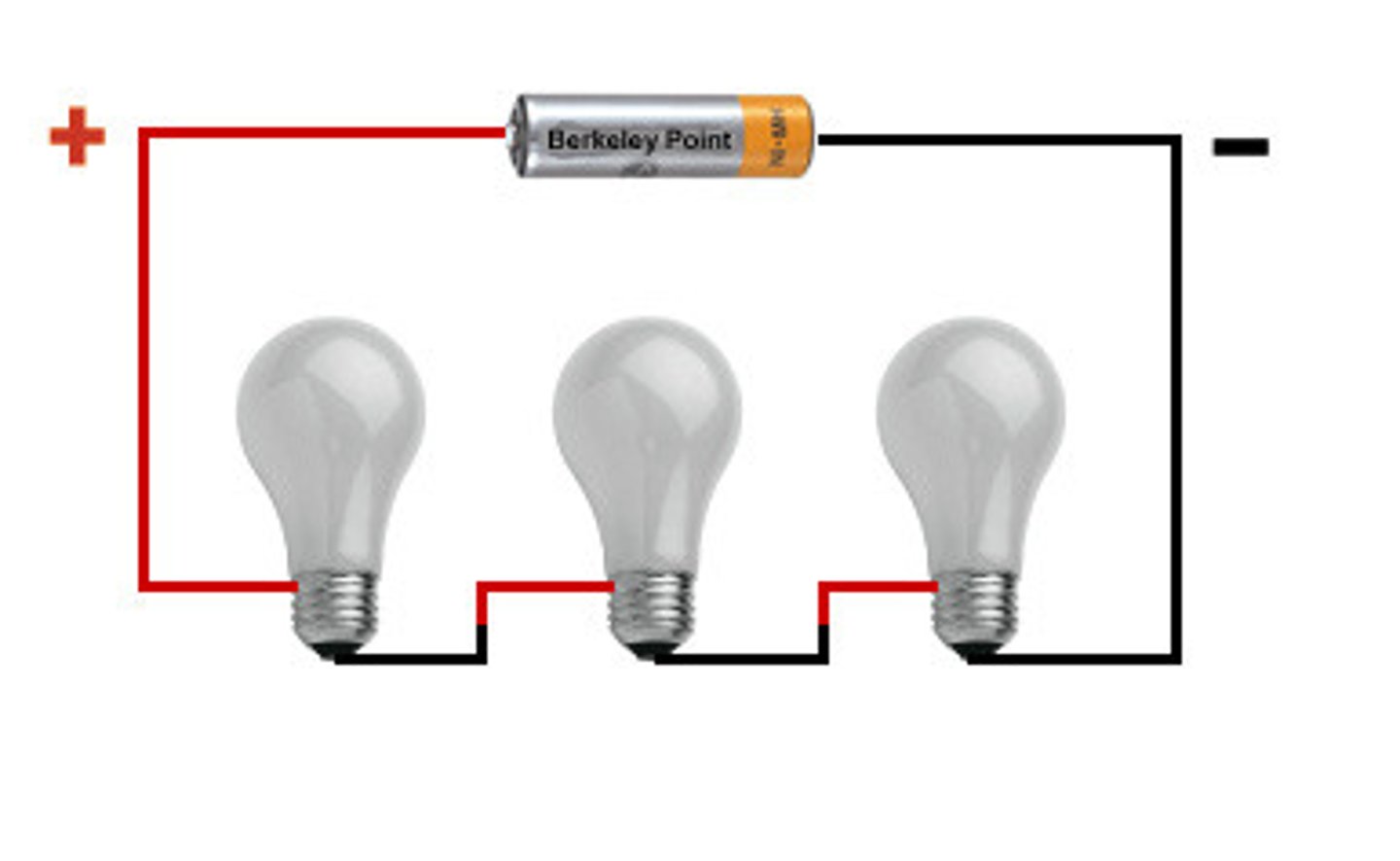
series circuit
An electric circuit with only one path through which charge can flow, when one electrical device is off, all others will be off in that circuit
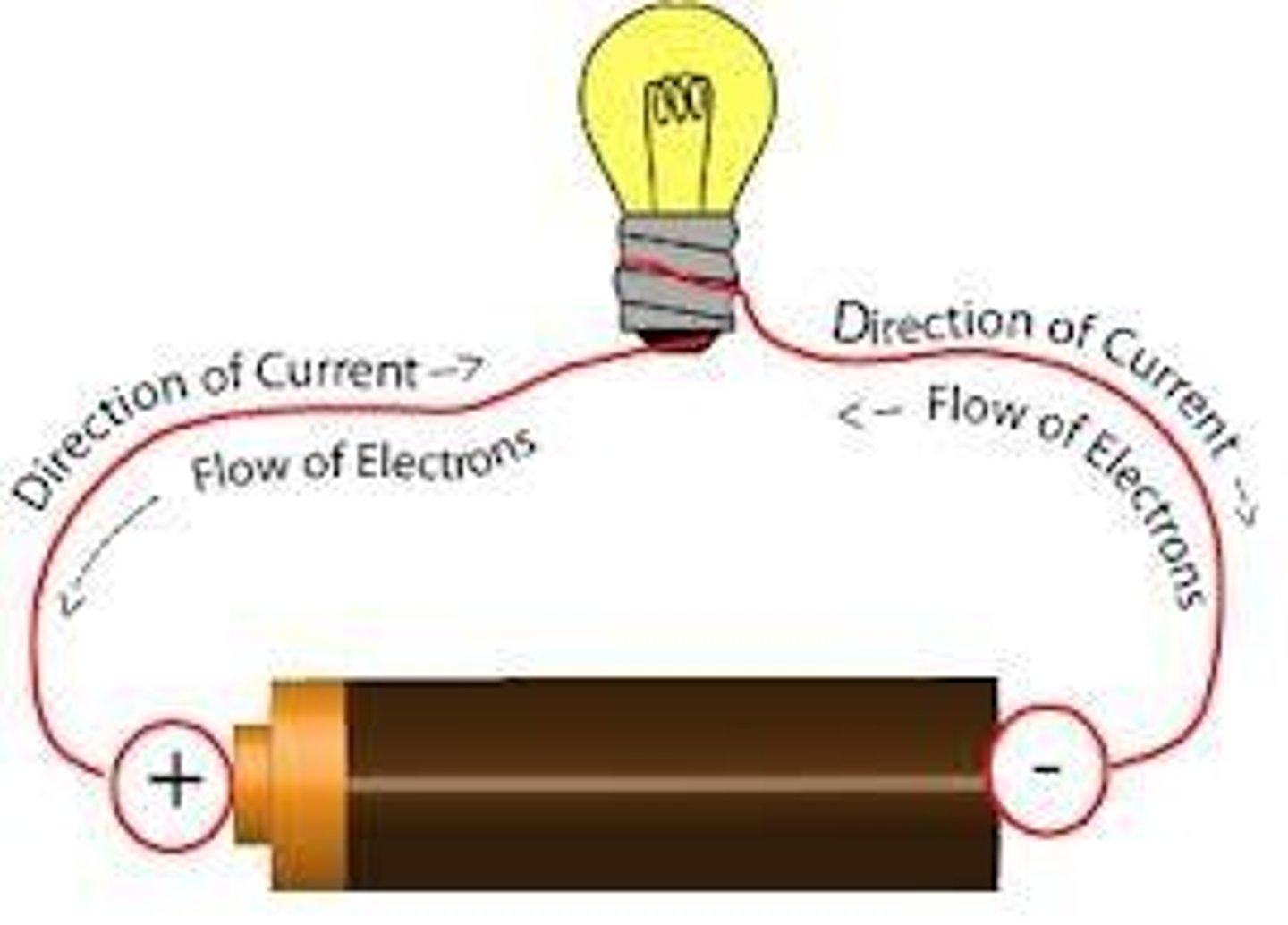
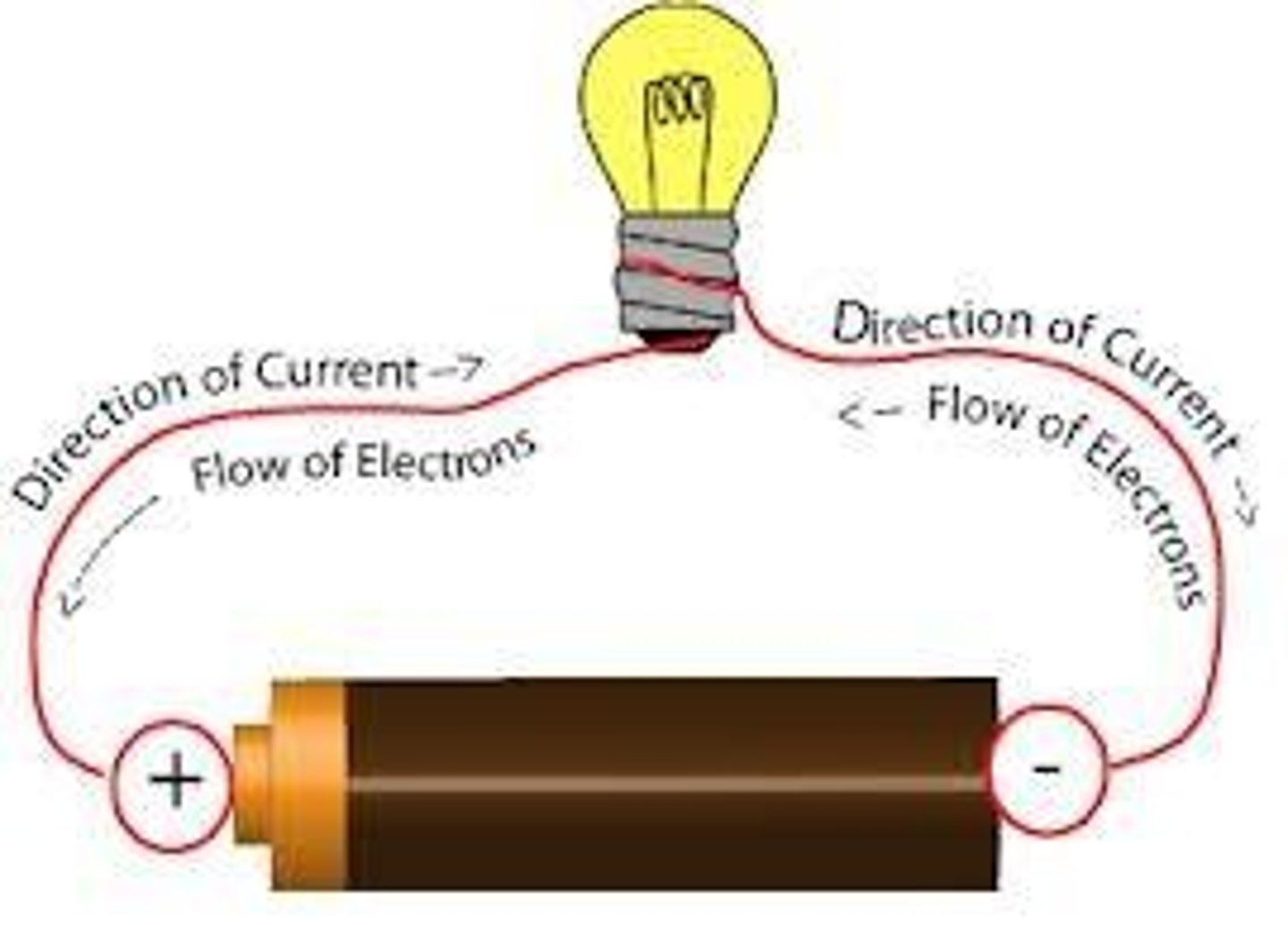
current
A flow of electric charge (electrons)
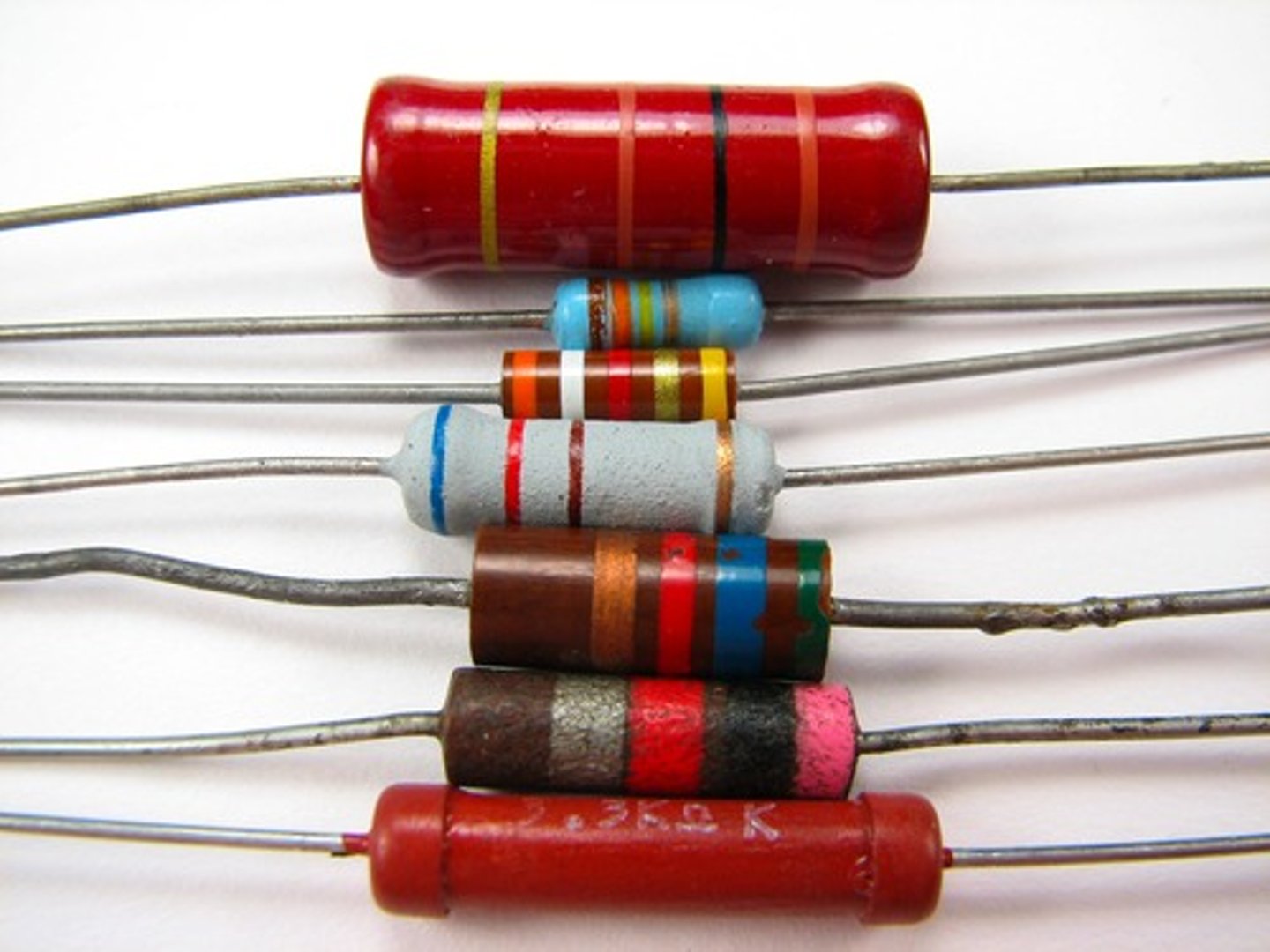
electrical resistance
a measure of how difficult it is for the current to flow through an electrical device (caused by friction)
Voltage
The difference in electrical potential energy between two places in a circuit, the push behind a current

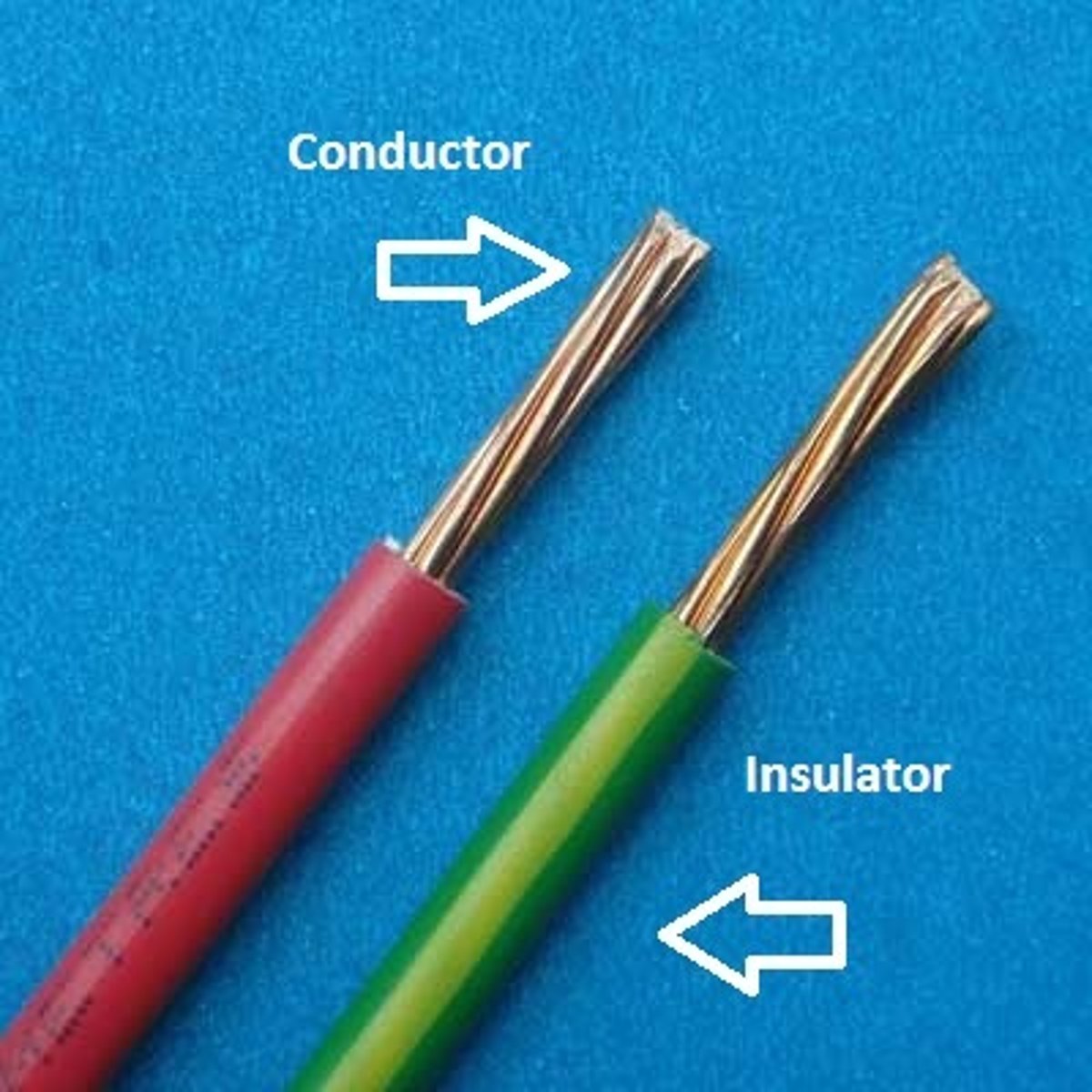
conductor
A material that allows the flow of electrons through it, allows electricity and heat to pass through it. Metals like copper and silver are conductors.
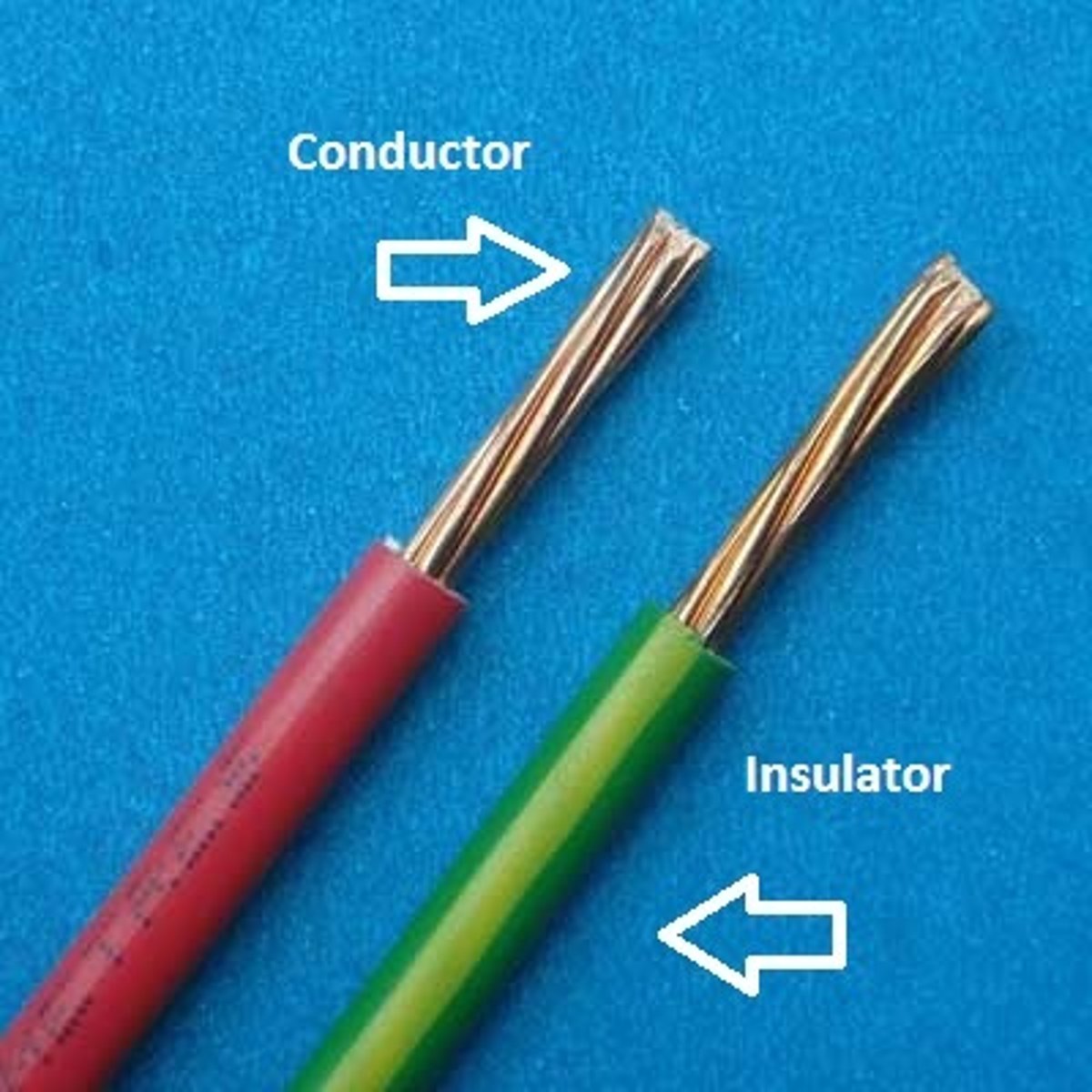
insulator
A material in which electrons are not able to move easily, does not conduct electricity or heat. Materials like rubber, plastic and wood are insulators
Ways to change electrical resistance
Change the temperature, the diameter, the length, and the material of an object such as a conducting wire

electron
The negatively charged particle in an atom that is loosely held by some materials, attracted to protons, repelled by other electrons
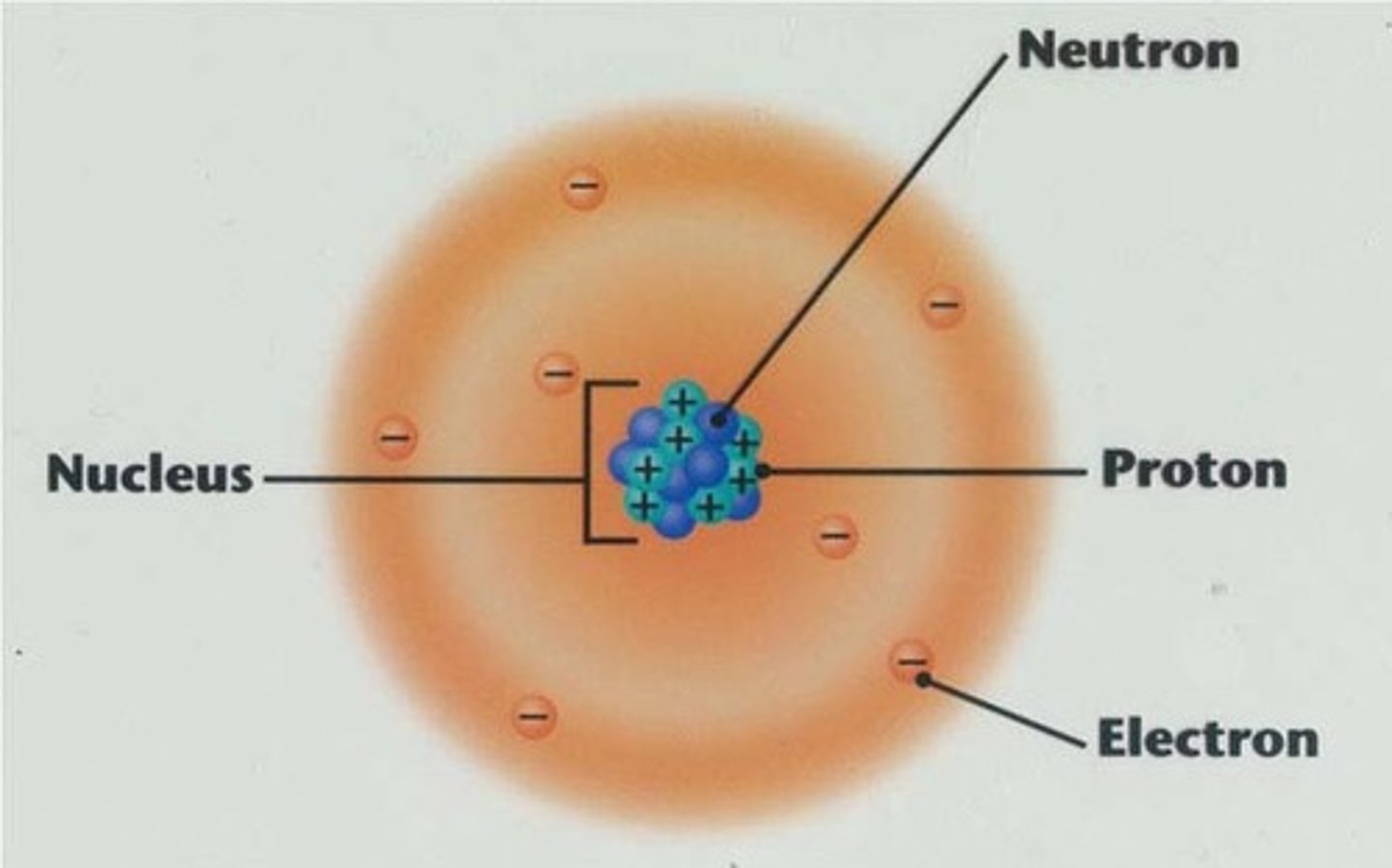
proton
The positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom, attracted to electrons, repelled by other protons

load (electrical component)
anything in a circuit that uses electricity

increased temperature
increased electrical resistance due to friction as energy of molecules increases

Ohm
unit of electrical resistance

Ampere (A)
unit of electrical current (I)
Volts
unit for voltage (V)

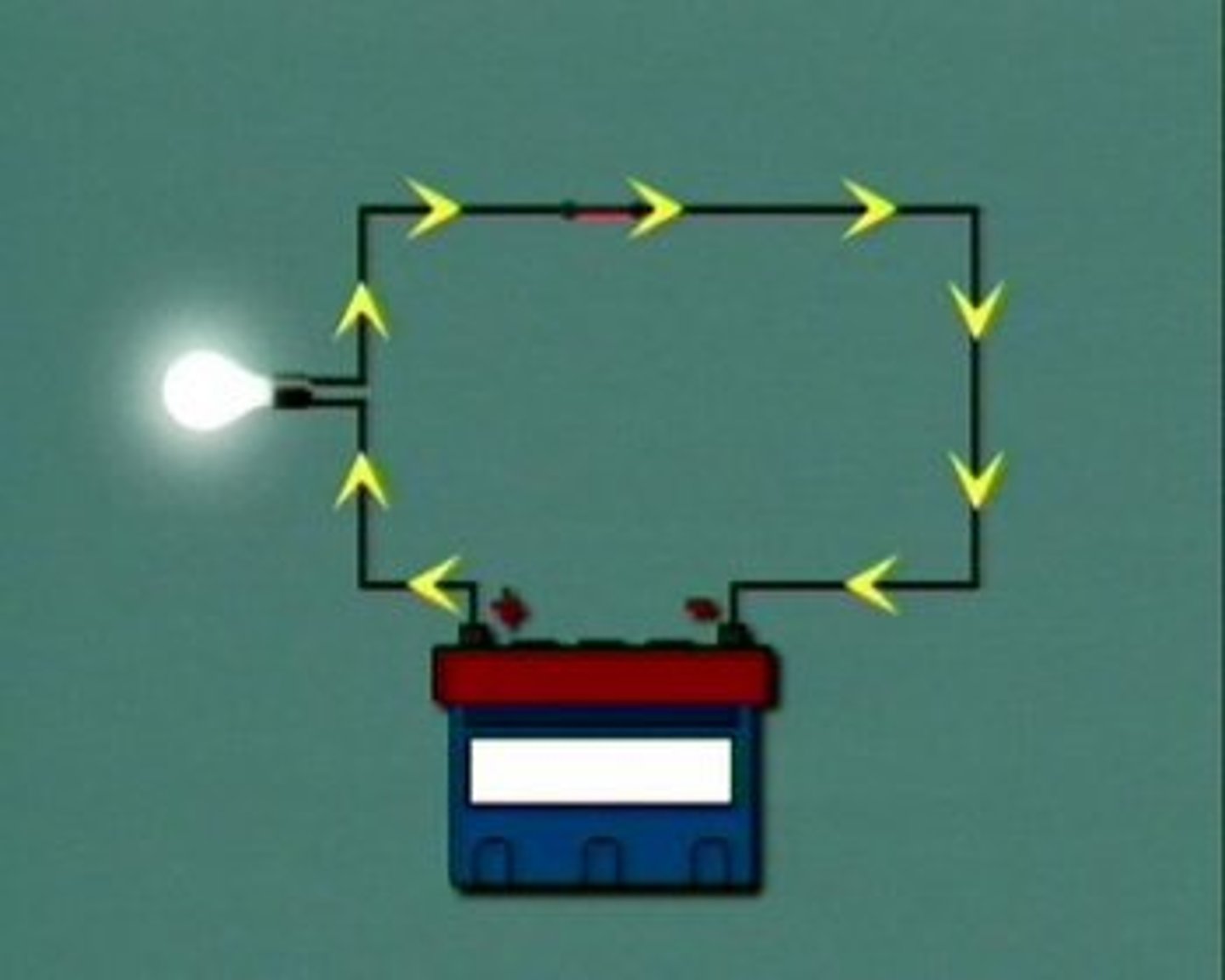
complete circuit
The path of an electric current from the generating source through conductors and back to its original source; needs an energy source, conducting wires, and load (resistance)
static electricity
A buildup of charges on an object.

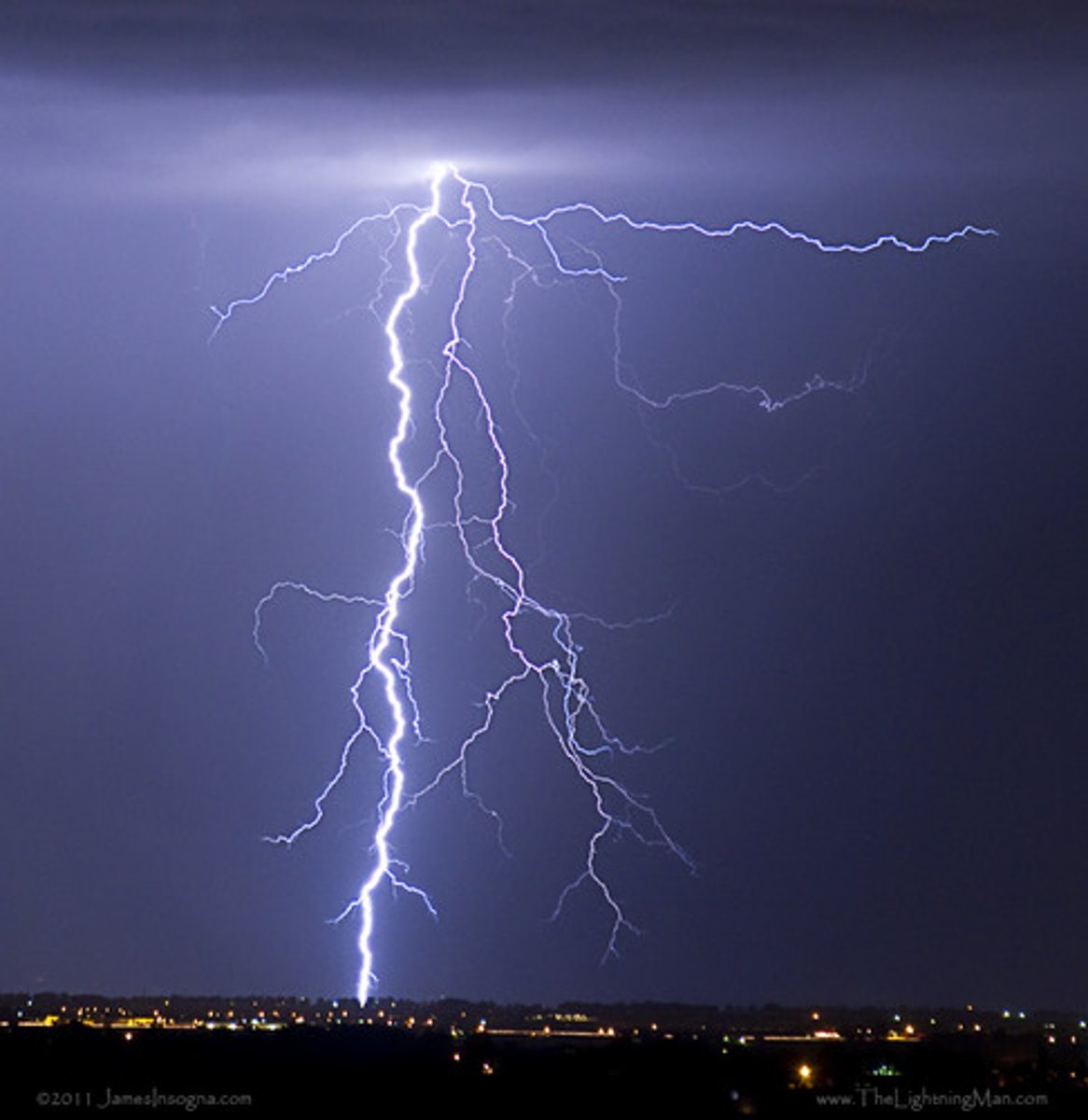
lightning
large scale static discharge

Ohm's Law
the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance

Complete circuit
3 things needed: power source, conducting wires, and a load (electrical component)
Renewable energy sources
Solar, wind, geothermal, hydroelectric, biomass

Non-renewable energy sources
Coal, natural gas,