Strategic Analysis Frameworks for Firm External & Internal Environment
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Strategic Analysis Frameworks for Firm External & Internal Environment
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
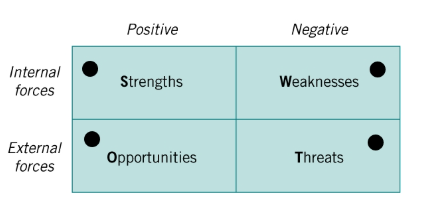
What is a SWOT analysis?
Strengths
Weaknesses
Opportunities
Threats
Which are internal and which are external forces?
Internal - Strengths & Weaknesses
External - Opportunities & Threats
What is Benchmarking?
Benchmarking is used as a means of understanding how an organisation compares with others.
What are the two approaches to benchmarking?
Industry/sector benchmarking. Insights about performance standards can be gleaned by comparing performance against other organisations in the same industry sector or between similar service providers against a set of performance indicators.
Best-in-class benchmarking. Best-in-class benchmarking compares an organisation’s performance or capabilities against ‘best-in-class’ performance – from whichever industry –and therefore seeks to overcome some of the above limitations.
What two potential limitations does Benchmarking have?
Surface comparisons. If benchmarking is limited to comparing outputs, it does not directly identify the reasons for relative performance in terms of underlying resources and capabilities
Simply achieving competitive parity. Benchmarking can help an organisation to develop capabilities and create value in the same way as its competitors and those best-in-class. However, the best performance that can be expected out of this exercise is to achieve a threshold level and competitive parity.
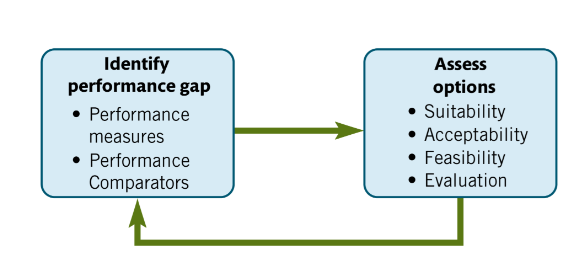
What does SAFE stand for?
SAFE stands for
Suitability,
Acceptability,
Feasibility,
Evaluation
What is SAFE analysis used for?
Gap analysis may expose organisational underperformance, either current or anticipated. To improve the situation, initiatives will be required and the acronym SAFE is a method to identify preferred strategic options
How to analyze Suitability in SAFE analysis?
A suitability analysis involves assessing the extent to which a proposed strategy:
exploits the opportunities in the environment and avoids the threats;
capitalizes on the organisation’s strengths and avoids or remedies the weaknesses.
How to analyze Acceptability in SAFE analysis?
Acceptability is concerned with whether the expected performance outcomes of a proposed strategy meet the expectations of stakeholders.
These can be of three types, the ‘3 Rs’: Return, Risk and stakeholder Reactions.
How to analyze Feasibility in SAFE analysis?
An assessment of feasibility is likely to involve two key questions:
Do the resources and capabilities currently exist to implement a strategy effectively?
If not, can they be obtained?
How to analyze Evaluation in SAFE analysis?
Evaluation is the process of identifying strategies that pass all the criteria of suitability, acceptability and feasibility. This is an important stage in the selection process as strategies that may appear excellent under one criteria may fail under another.
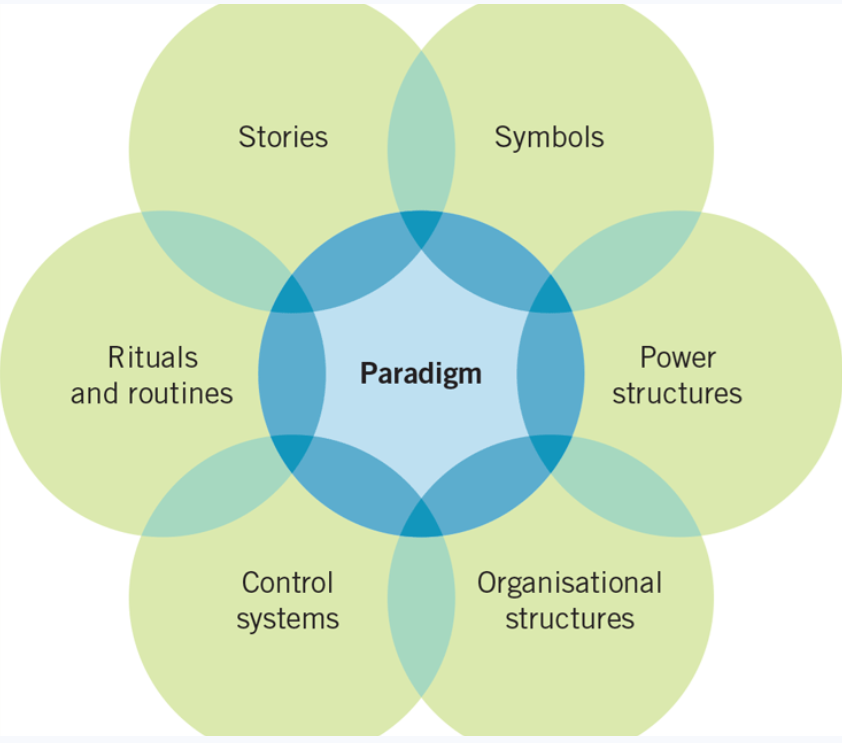
What is the Cultural Web?
The cultural web shows the behavioral, physical and symbolic manifestations of a culture that inform and are informed by the taken-for-granted assumptions, or paradigm (patterns), of an organisation.