LASA Biotech I - Midterm
1/181
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Yes, there's redundant information on here. No, it's not by accident.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
182 Terms
What is Biotechnology?
Using living organisms, or the products of living organisms, for human benefit to make a product of solve a problem
What are some examples of traditional biotechnology?
Fermentation, Selective breeding
What are some examples of modern biotechnology?
Genetic engineering to make insulin
What is genetic engineering?
The manipulation of an organisms genes by introducing, eliminating, or rearranging specific genes.
What are some career options in Biotechnology?
Sales, marketing, regulatory, legal, financial, human resources, administrative staff
What are some examples of biotech jobs that can be obtained with different degree type?
Postdoctorate - Scientist
Doctorate - Scientist
Master’s Degree - Research Associate
Bachelor’s Degree - Research Associate
Certificate - Biotechnician
High School Diploma - Lab Assistant
What is a MSDS/SDS?
Material Safety Data Sheet / Safety Data Sheet
Legally required technical document, provided by chemical suppliers, describing the specific properties of a chemical.
What are the 8 sections of an MSDS/SDS?
Chemical identity
Hazard ingredients/identity
Physical chemical charcateristics
Fire and explosion hazard data
Reactivity data
Health hazards
Precautions for safe handling and use
Control measures
What does the blue section of the NFPA diamond show?
Health Hazard
What does a 0 mean for health hazard?
Normal material
What does a 1 mean for health hazard?
Slightly hazardous
What does a 2 mean for health hazard?
Hazardous
What does a 3 mean for health hazard?
Extreme danger
What does a 4 mean for health hazard?
Deadly
What does the red section of the NFPA diamond show?
Flammability
What does the 0 mean for flammabiblity?
Will not burn
What does the 1 mean for flammability?
flash point > 200F
What does the 2 mean for flammability?
flash point >100F
What does the 3 mean for flammability?
flash point <100F
What does the 4 mean for flammability?
flash point <73F
What does the yellow section of the NFPA diamond show?
Reactivity
What does a 0 mean for reactivity?
stable
What does a 1 mean for reactivity?
unstable if heated
What does a 2 mean for reactivity?
Violent chemical change
What does a 3 mean for reactivity?
Shock and heat may detonate
What does a 4 mean for reactivity?
may detonate
What is PPE?
Personal Protective Equipment
What does the uncolored section of the NFPA diamond show?
Specific hazards
What does “OX” mean in the uncolored section of the NFPA diamond?
Oxidizer compound
What does “ACID” mean in the uncolored sectino of the NFPA diamon?
Acidic compound
What does “ALK” mean in the uncolored section of the NFPA diamond?
Basic compound
What does “CORR” mean in the uncolored section of the NFPA diamond?
Corrosive compound
What does “W” mean in the uncolored section of the NFPA diamond?
use NO WATER
What does LD50 mean?
Dose is lethal in 50% of test animals
What does LC50 mean?
Concentration in the air is lethal in 50% of test animals
Examples of PPE for handeling reactive substances?
Lab coats, goggles, gloves.
Tips for handling corrosive substances
Always slowly dilute strong acids or bases by adding water, store strong acids and bases apart from one another.
How should solutions be labeled in the lab?
Identity of the contents and its concentration, owners initials, date and time, owners class period.
What is a microcentrifuge used for?
to seperate samples based on desity by spinning at high speeds.
What is a micropipette used for?
used to measure and transfer liquids by drawing the liquid into the tip.
What is a seroligical pipette used for?
transferring militers of liquid from less than 1ml to 50ml.
What is a spectophotometer used for?
measure absorbance of light in the ultraviolet region of the specturm (~100-700nm). Require halogen light bulbs that emit ultraviolet light and require cuvettes that don’t absorb UV lights.
What is a gel electrophoresis apparatus used for?
to seperate nucleic acids and proteins based on their size and charge. Used to run and compare DNA samples.
What is a vortex used for?
mixes the contents by rotating the bottom of a tube rapidly
What is a thermal cycler (PCR) machine used for?
used for amplification of a specific section of DNA by PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
Where can a picofuge be found in the lab?
in a cabinet to the right of your group table
Where can a microcentrifuge be found in the lab?
in a cabinet to the right of your group table & in the small room on a table
Where can a micropipette be found in the lab?
Top left on group tables shelves
Where can micropipette tips be found in the lab?
bottom level of the shelves on the table
Where can microtubes be found in the lab?
Right bottom shelf on table
How do you use a micropipette properly?
Never lay/hold it upside down/sideways. Set to the desired amount using the black wheel located near the handle. To draw up liquid press the plunger down until the first stop, place the tip in the liquid, and slowly release the plunger. Releasing liquid: place the tip in the container, and press the plunger down until the second stop.
How do you read a P-10 micropipettor?
Limits are 1-10μl. Bottom value (under red line) reads the 1/10th number, middle value reads the 1s number, top value reads the 10’s number.
How do you read a P-100 micropipettor?
Limits are 1-100μl. Bottom value reads the 1s number, middle value reads the 10s number, top value (above red line) reads the 100s number.
How do you read a P-1000 micropipettor?
Limits are 1-1000μl. Bottom value reads the 10s number, middle value reads the 100s number, top value (above red line) reads the 1000s number.
If you were pipetting with a P-10 that was adjusted to 089 what amount would you be pipetting in μl and mL?
8.9μl, 0.0089ml
If you were pipetting with a P-100 that was adjusted to 089 what amount would you be pipetting in μl and mL?
89μl, 0.089ml
If you were pipetting with a P-1000 that was adjusted to 089 what amount would you be pipetting in μl and mL?
890μl, 0.89ml
Conversion factor from μl to ml
1ml = 1000μl
How do you balance a microcentrifuge?
Match the exact amount of liquid used in the microtube for a dummy microtube and place the two directly across from one another to balance themselves out.
What are the four ways cheese can be made? (names only)
Control/No treatment method
Starter Culture/Buttermilk Method
Rennin/Rennet Method
GE Chymosin Method.
Rennin/Rennet Method
Protease that breaks down the protein casein is retrieved from the cells lining the stomach of calves. Examples include asiago, brie, and most cheddars.
GE Chymosin Method
Rennin cheese-making gene is cut out of the cow’s stomach and inserted into fungus cells. Fungus cells then read the cow DNA and synthesize the rennin enzyme, called “chymosin”. Benefits: cheaper, faster, larger yields. Examples include Jack, mozzarella, most Swiss chesses, etc.
Control/No treatment method
Milk is left to age, exposed to aid and naturally occuring bacteria within the milk.
Starter Culture/Buttermilk Method
New batches of cheese are started with specific cultures of selected bacteria that contain the enzymes that curdle milk.
What bacteria is used in buttermilk as a starter?
Lactobacillus
Casein
Milk protein that denatures and falls out of the solution because of lactic acid. Denatured casein lumps are called curds.
Whey
Liquid remaining when curds are pressed together
Proteases
Cleade proteins, such as casein, into smaller fragments that will also fall out of the solution
How is lactic acid produced during cheese production?
The naturally occuring bacteria in milk uses lactose (milk sugar) as an energy source and produces lactic acid as a waste product.
Curd
Lumps of denatured casien that are pressed together to form cheese.
How to calibrate a pH meter
Rinse electrode with DI water and blot it with lint-free tissue, place the electrode into the frist buffer and press Cal to start the calibration and record the final vpH value. Repeat these steps for all your buffer solutions. To recall the calibration results, press and hold the Cal button.
How to calibrate an electronic balance
Press and hold Menu until the menu is displayed, release the button and the display [C.A.L] will appear - press yes to accept. [SPAN] will be shown - press yes to begin the span calibration. The specified mass blinks on the display. Press the specified span calibration mass on the pan or press No to select an alternate weight. [—C—] will blink while the reading is stored. The display will show [done] if the calibration was successful. The balance returns to the precious application mode and is ready for use.
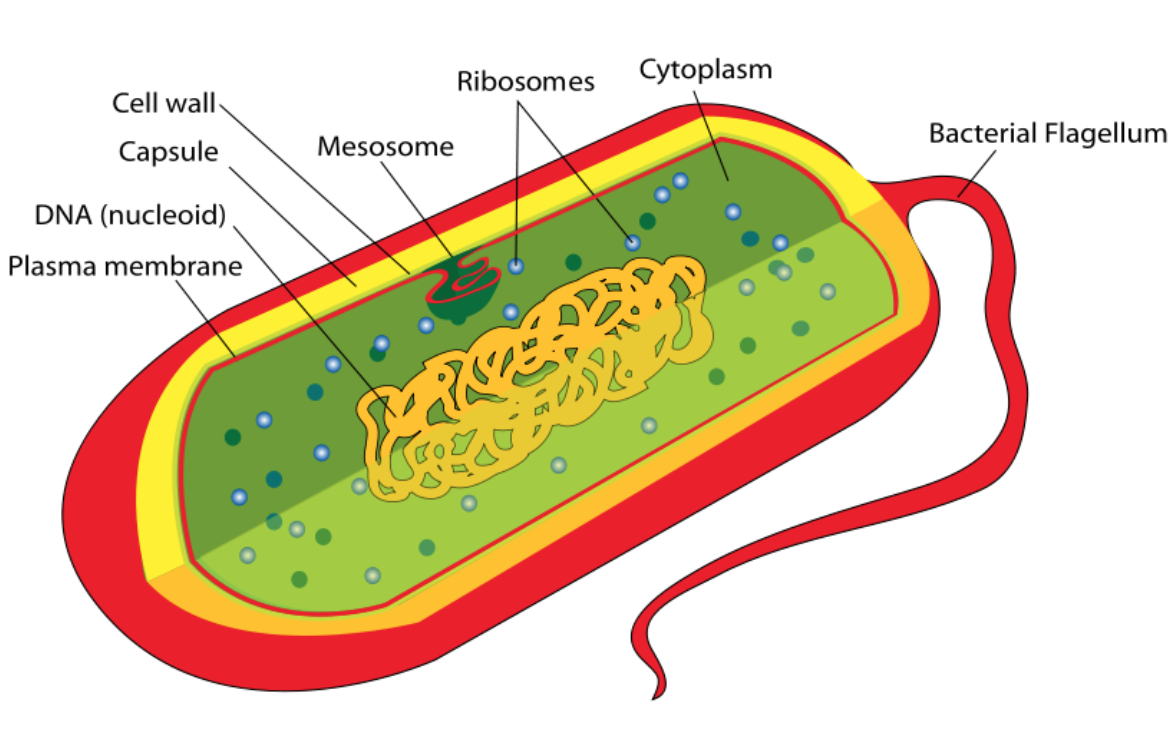
Prokaryotic cells
Contains a cell wall made of peptidoglycan that protects and provides structure to the cell.
Cytosol: liquid within cells that contains biomolecules and chemicals used in the cells.
Plasma membrane made of phospholipid bilayer and proteins, regulates transport in and out of the cell.
Ribosomes: protein synthesis, RNA to Proteins.
RNA attached to the cell membrane/floating in the cytosol.
DNA free-floating in the cytosol.
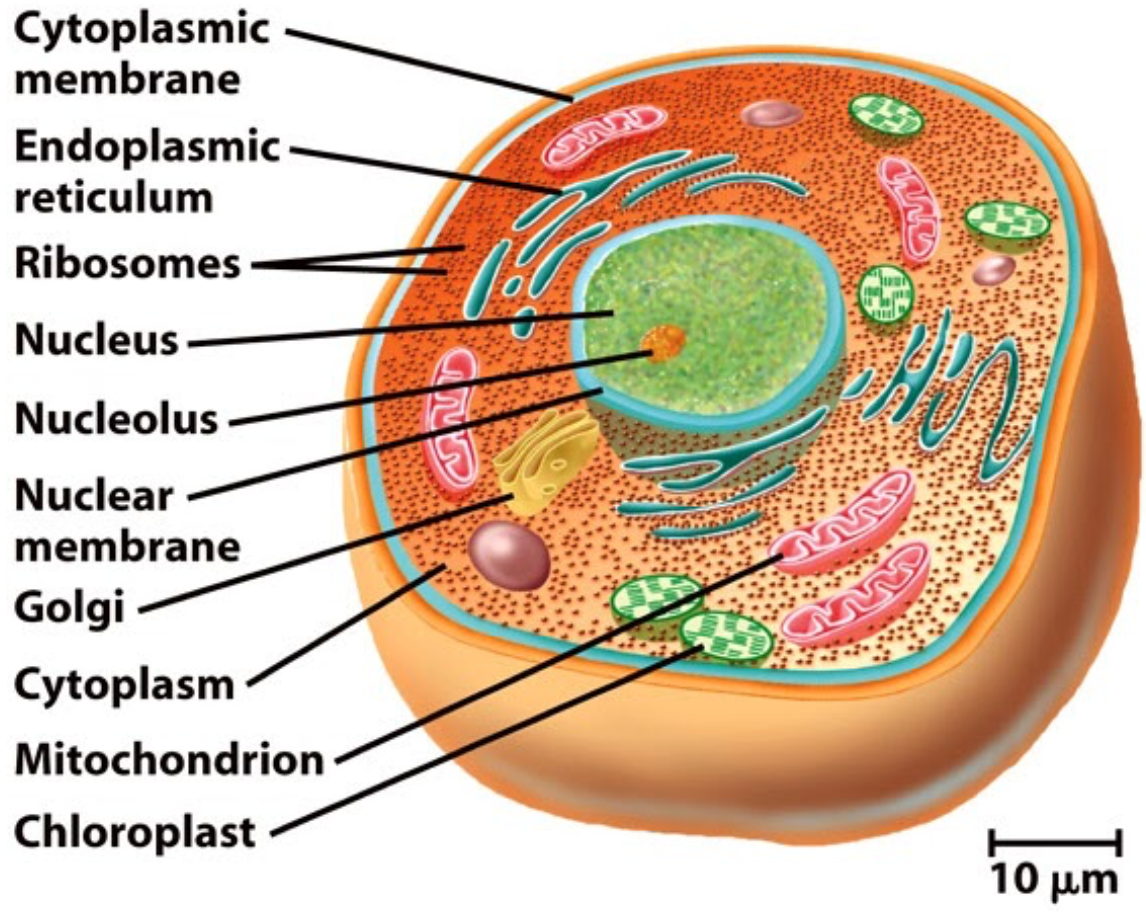
Eukaryotic cells
Contains membrane bound organells.
Cytoplasm: cytosol + organelles, specific to eukaryotes.
Mitochondria: “powerhouse of the cell” because it converts energy stores in nutrients into ATP whic his used for energy within the call.
Lysosome: digest enzymes used for intracellular digestion.
Ribosomes: protein synthesis, made of RNA and protein.
Nucleus: contains DNA, genetic info.
Rough ER containts ribosomes, Smother ER doesn’t. Lipid synthesis and metabolism.
Golgi apparatus packages/modifies proteins for secretion from cells or for somewhere within the cell.
Function of the Nucleus
Contains the genetic information in eukaryotic cells and acts as the cell’s control center.
Function of the Rough ER
Ribosomes attached to its surface. Mostly known to be involved in the synthesis and production of proteins.
Extra: Secretes proteins made by bound ribosomes that are then moved to the transitional ER where they are wrapped in a transport vesicle to head to the Golgi apparatus.
Function of the Smooth ER
Mostly known to be involved in the production of enzymes and lipids.
Extra: Performs synthesis of lipids, metabolism of carbohydrates, detoxification of drugs and poisons, and stores calcium ions.
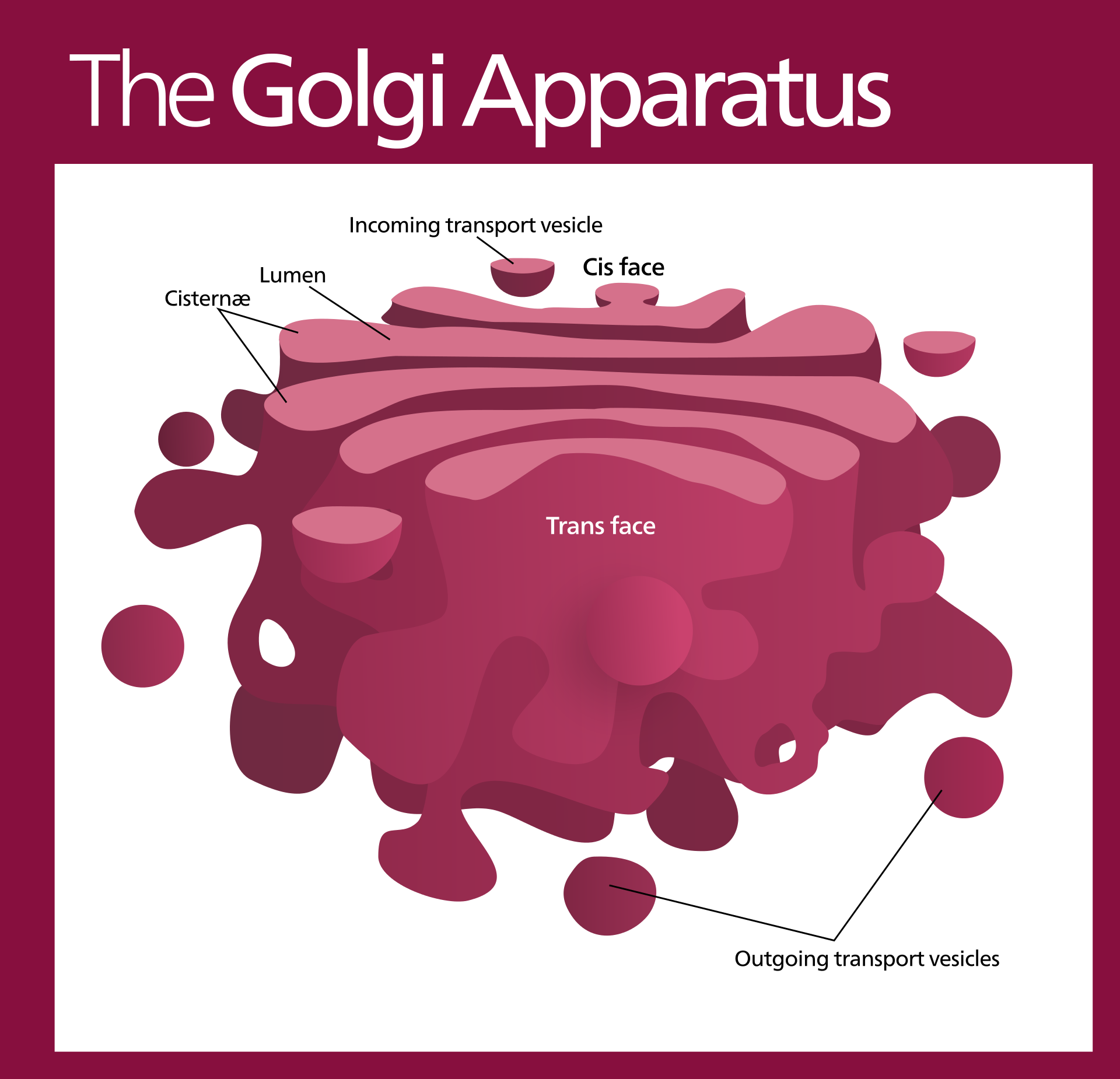
Function of the Golgi Apparatus
Packages proteins in little sacs called vesicles and distributes them around the cell to where they’re needed.
Extra: Modifies, stores, and sends proteins that come from the Rough ER.
2 sides to the Golgi Apparatus: cis and trans face. Vesicles enter via the cis face and depart via the trans face.
Also involved in the production of lysosomes.
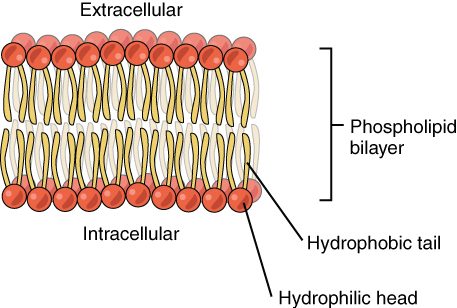
Function of the plasma membrane
Made of a phospholipid bilayer where the head is hydrophilic and the tail is hydrophobic. Very flexible. Provides protection and a fixed environment inside the cell. Controls what enters and exits the cell.
Function of the Vacuole
Large vesicles that store many different things like food and water. Many unicellular eukaryotes have contractile vacuoles to pump water out of the cell.
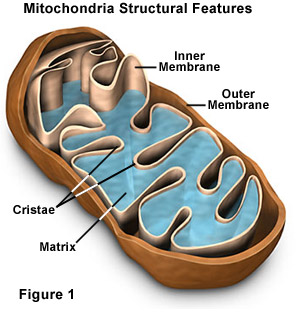
Function of the mitochondria
Creates ATP for the cell to use via cellular respiration. Contains an outer membrane and inner membrane, making up its double membrane.
Extra: inner membrane consists of folds called cristar which is where most of the ATP production happens. The folds increase the surface area and thus the efficiency. Inside the inner membrane is the mitochondrial matrix which is the site of the Krebs Cycle.
Function of the chloroplast
Site of photosynthesis. Contains a double membrane and has a green pigment calles chlorophyll that allows for the absorbtion of photons.
Extra: Chloroplast is made of the stroma, or lliquid fillind of the chloroplast, and the thylakoids, flat sacs of membranes that allow for the absorption of light.
Function of the lysosome
Trash can of the cell.
Breaks down most foods, amino acids, and other molecules. Inside of lysosome is extremely acidic.
Extra: in charge of apoptosis, which is programmed cell death. When the lysosome bursts, the acid inside causes the cell’s death.
Differnence between animal and plant cells?
Plant cells contain cell walls made of cellulose that acts as a protective outer layer other than the membrane, plasma membranes, nucleus containing DNA, and Ribosomes. They do not contain Centrioles
Animal cells contain plasma membranes, nucleus containingDNA, centrioles, and ribosomes. They do not contain cell walls.
Nucleosome
DNA wrapped around histones
Extra: Helps to supercoil the DNA, resulting in a greatly compacted structure that allows for more efficient storage of genetic information.
Histones
Packages DNA in small packets that fit inside nucleosomes. Also serves as a mechanism to control gene expression.
Central Dogma
DNA —> RNA —> protein
DNA to RNA through transcription
RNA to protein through translation
Purpose of Replication
When a double-stranded DNA molecule is copied to produce two identical DNA molecules. The passing of genetics to the next generation.
Essential because whenever a cell divides, the 2 new daughter cells must contain the same genetic information as the parent cell.
Purpose of Translation
When information encoded in mRNA directs the addition of amino acids during protein synthesis.
3 components of a nucleotide
Deoxyribose Sugar, Phosphate, Nitrogen Base
Deoxyribose Sugar
5 carbon ring (pentose sugar). Each carbon is numberd clockwise starting from oxygen: 1’, 2’, 3’, 4’, 5’. Lacks OH on 2’ carbon.
Phosphate group
comes off the 5’ carbon
Nitrogenous base
attached to 1’ carbon: these vary for each of 4 types of nucleotides: adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine (A, T, C, G)
DNA structure:
Double Stranded Helix
A - T: 2 H-bonds
C - G: 3 H-bonds
Complementary
Negatively charged sugar/phosphate backbone.
Antiparallel: 5’ to 3’, 3’ to 5’
Purines
One of the two nitrogenous bases.
Double rings, A and G.
Pyrimidines
One of the two nitrogenous bases.
Single rind, C and T (Uracil, U in RNA)
DNA base pairs
A - T, C - G
Adenine (A) to Thymine (T)
Cytosine (C) to Guanine (G)
RNA base pairs
A - U, C - G
Adenine (A) to Uracil (U)
Cytosine (C) to Guanine (G)
How are nucleotides linked together?
Covalently linked together in a chain through the sugars and phosphates
Purpose of DNA replication?
to produce 2 identical DNA molecules.