Chapter 7: Audition (Hearing)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
1
New cards
Sound
Produced by objects that vibrate and set molecules of air into motion
2
New cards
700
Sound travels ___ mph, with a range of 30-20k Hz
3
New cards
Waves
Stimulate receptor cells in ears, perceived as sounds
4
New cards
Pitch, loudness, timbre
3 perceptual dimensions of sound
5
New cards
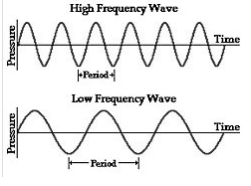
Frequency
Pitch
6
New cards
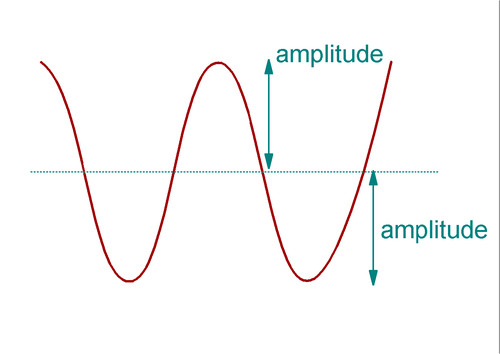
Amplitude
Loudness
7
New cards
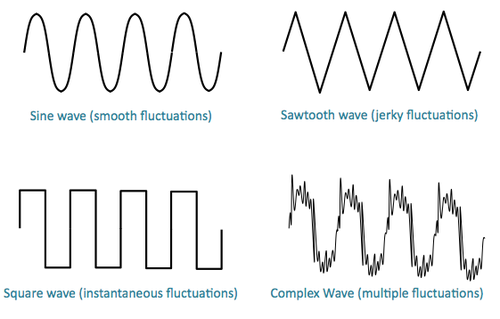
Complexity
Timbre
8
New cards
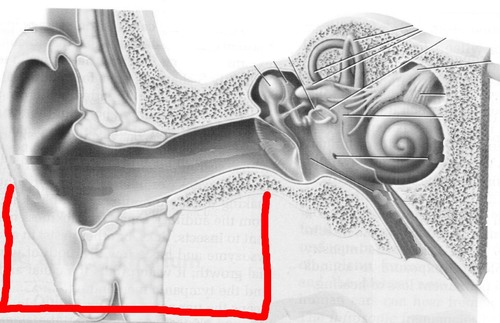
Outer Ear
Pinna, ear canal, tympanic membrane
9
New cards
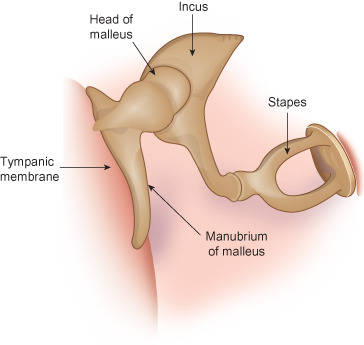
Middle Ear
Ossicles
10
New cards
Hammer, anvil, stirrup
Order of the ossicles
11
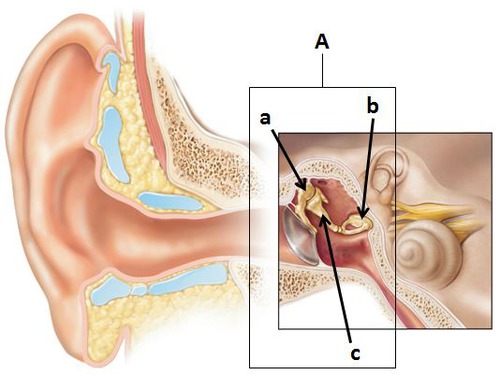
New cards
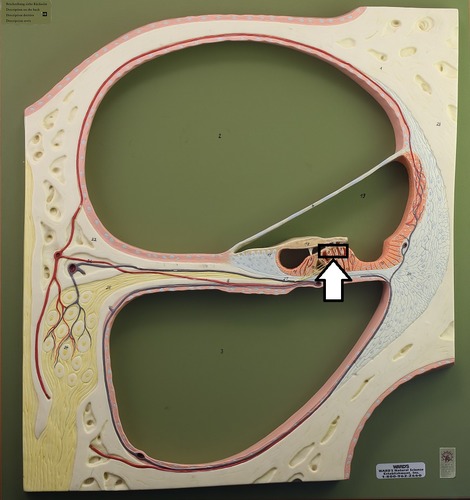
Inner Ear
Eustachian tube, cochlea, oval, round window
12
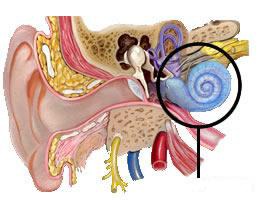
New cards
Cochlea
Snail-shaped structure of inner ear that contains auditory transducing mechanisms
13
New cards
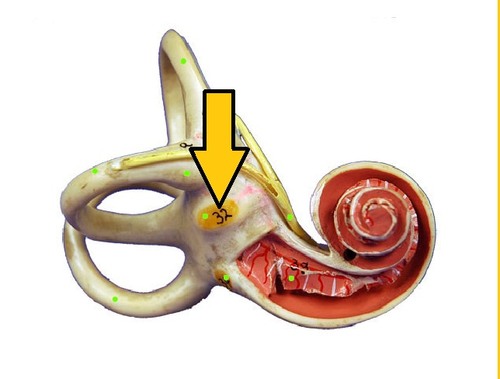
Oval Window
Opening in bone surrounding cochlea with membrane that transmits sound vibrations from ossicles into fluid of the cochlea
14
New cards
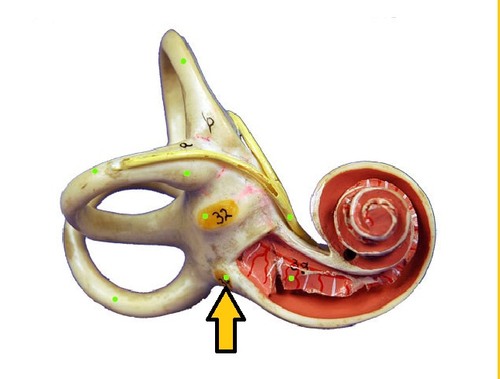
Round Window
Membrane-convered opening in bone surrounding cochlea that releases sound vibrations from the cochlea
15
New cards
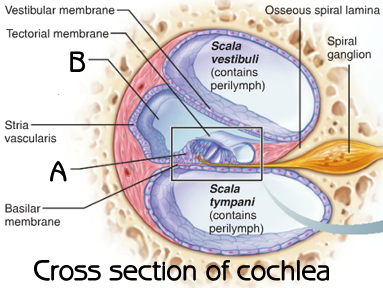
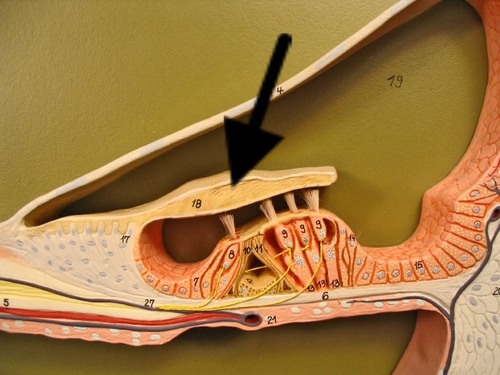
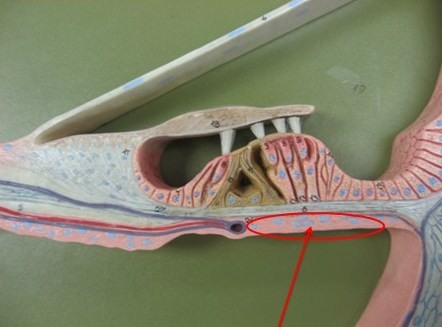
Organ of Corti
16
New cards
Tectorial Membrane
T for top
17
New cards
Basilar Membrane
B for base/bottom
18
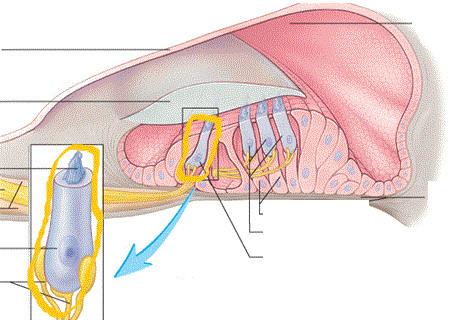
New cards
Inner Hair Cells
Responsible for normal hearing
19
New cards
Outer Hair Cells "Effector Cells"
Influence mechanical characteristics of basilar membrane
20
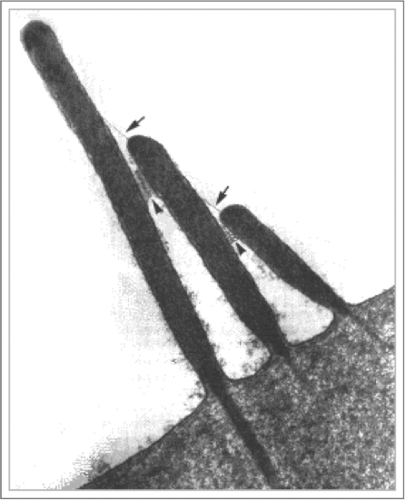
New cards
Tip Link
"tugs" on cation channels of hair cells; floods K+ and Ca2+
21
New cards
Hyperpolarized
0% probability of opening the cilia; from bending to smallest cilia
22
New cards
At rest
Slightly depolarized 10% probability of opening the cilia
23
New cards
Highly Depolarized
100% probability of opening the cilia; from bending to tallest cilia
24
New cards
First
___ (first/second/third/fourth/fifth/sixth), air molecules vibrate
25
New cards
Second
___ (first/second/third/fourth/fifth/sixth), tympanic membrane oscillates these vibrations
26
New cards
Third
___ (first/second/third/fourth/fifth/sixth), ossicles push on the oval window
27
New cards
Fourth
___ (first/second/third/fourth/fifth/sixth), liquid inside the cochlea moves from the upper to lower region
28
New cards
Fifth
___ (first/second/third/fourth/fifth/sixth), basilar membrane flexes to sound, depends on frequency
29
New cards
Higher, closest
___ frequencies flex the basilar membrane ___ to the oval/round window
30
New cards
Sixth
___ (first/second/third/fourth/fifth/sixth), hair cells located in the region where basilar membrane flexes are pushed toward the more rigid tectorial membrane
31
New cards
Cochlear Nucleus
Nuclei in medulla that receive auditory information from 8th cranial nerve
32
New cards
Superior Olivary Nucleus
Nuclei in medulla that receive auditory information from the cochlear nuclei
33
New cards
Lateral Lemniscus
Band of fibers carry auditory information through the medulla and pons
34
New cards
Medial Geniculate Nucleus
Nucleus in thalamus that relays auditory information to the primary auditory cortex
35
New cards
Ipsilateral, contralateral
Sound is processed via ___ , and then ___.
36
New cards
Hierarchal
Auditory cortex is organized in a ___ manner.
37
New cards
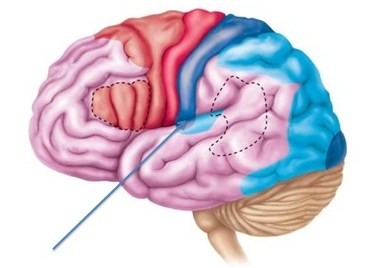
Primary Auditory Cortex
Processes pure tones (core region)
38
New cards
First
The ___ level of auditory association cortex is a belt region that processes complex sounds
39
New cards
Highest
The __ level of auditory association cortex is a parabelt region that processes complex sounds
40
New cards
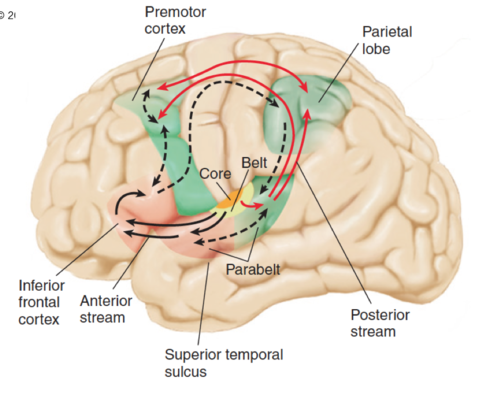
Anterior Stream
Analysis of complex sounds (what) TO THE FRONTAL LOBE
41
New cards
Posterior Stream
Involved with sound location (where) TO SPACE-FOCUSED AREAS

42
New cards
Tonotopic Organization
Higher frequencies are located near each other and further away from lower frequencies
43
New cards
Rate Coding
Rate of depolarization determines LOW frequencies
44
New cards
Place Coding
Basilar membrane bends to determine MODERATE TO HIGH frequencies
45
New cards
Low
Number of axons active at the same time determine __ loudness
46
New cards
High
Rate of hair firing and level of tympanic membrane depressions determine __ loudness
47
New cards
Antibiotics
High doses may damage hair cells at base // difficulty with higher frequencies
48
New cards
Loud Sounds
Damage to hair cells at base
49
New cards
Bone Growth
Hearing loss from this over the round window
50
New cards
Amusia
Perception of music facts (rhythms)
51
New cards
Patient LR
Damaged left superior temporal gyrus; unable to perceive or produce rhythmic aspects of music
52
New cards
True
(T/F) Patient LR could perceive emotional aspects of music