AP Gov Unit 1 Chapters 1-3
1/202
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
203 Terms
A nation's basic law. It creates political institutions, assigns or divides powers in government, and often provides certain guarantees to citizens. Can be written or unwritten.
Constitution

The document approved by representatives of the American colonies in 1776 that stated their grievances against the British monarch and declared their independence
Declaration of Independence
Rights inherent in human beings, not dependent on governments, which include life, liberty, and property.
Natural Rights
The idea that government derives its authority by the sanction of the people.
Consent of the Governed

The idea that certain government restrictions should be placed on government to protect the natural rights of citizens.
limited government

The first constitution of the United States, adopted by the United States, adopted by Congress in 1777 and enacted in 1781.
Articles of Confederation
A series of attacks on courthouses by a small band of farmers.
Shay's Rebellion

The document written in 1787 and ratified in 1788 that sets forth the institutional structure of US government and the tasks these institutions perform.
US Constitution
Groups such as parties or interest groups, which according to James Madison arose from the unequal distribution of wealth or property and had the potential to cause instability in government.
Factions
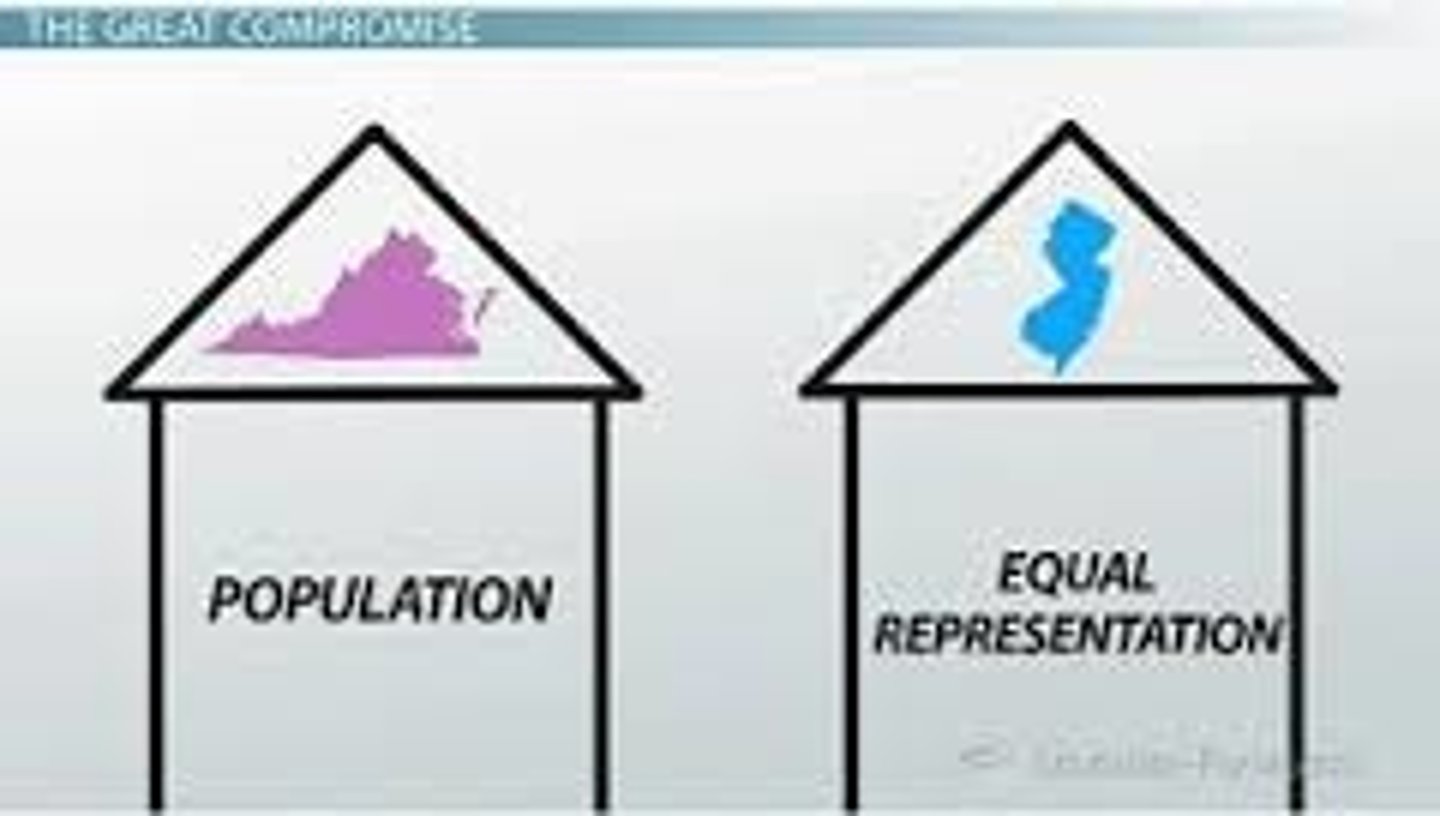
The proposal at the Constitutional Convention that called for equal representation of each state in Congress regardless of the state's population.
New Jersey Plan

The proposal at the Constitutional Convention that called for representation of each state in Congress in proportion to that state's share of the US population.
Virginia Plan
The compromise reached at the Constitutional Convention that established the two houses of Congress: the House of Representatives based on a state's share of the US population and the Senate in which each state has two representatives
Connecticut Compromise
A court order requiring jailers to explain to a judge why they are holding a prisoner in custody.
Writ of Habeus Corpus

A feature of the Constitution that requires each of the branches on government to be relatively independent of the others.
Separation of Powers
Features of the Constitution that limit government's power by requiring each branch to obtain the consent of the others for its actions.
Checks and Balances
A form of government in which the people select representatives to govern them and make laws.
Republic

Supporters of the US Constitution at the time the states were contemplating its adoption.
Federalists
Opponents of the US Constitution at the time when the states were contemplating its adoption
Anti-Federalists
A collection of 85 articles written under the name "Publius" to defend the Constitution in detail
Federalist Papers

The first 10 amendments to the Constitution, drafted in response to some of the Anti-Federalist concerns
Bill of Rights
A way of organizing a nation so that two or more levels of government have formal authority over the same land and people.
Federalism
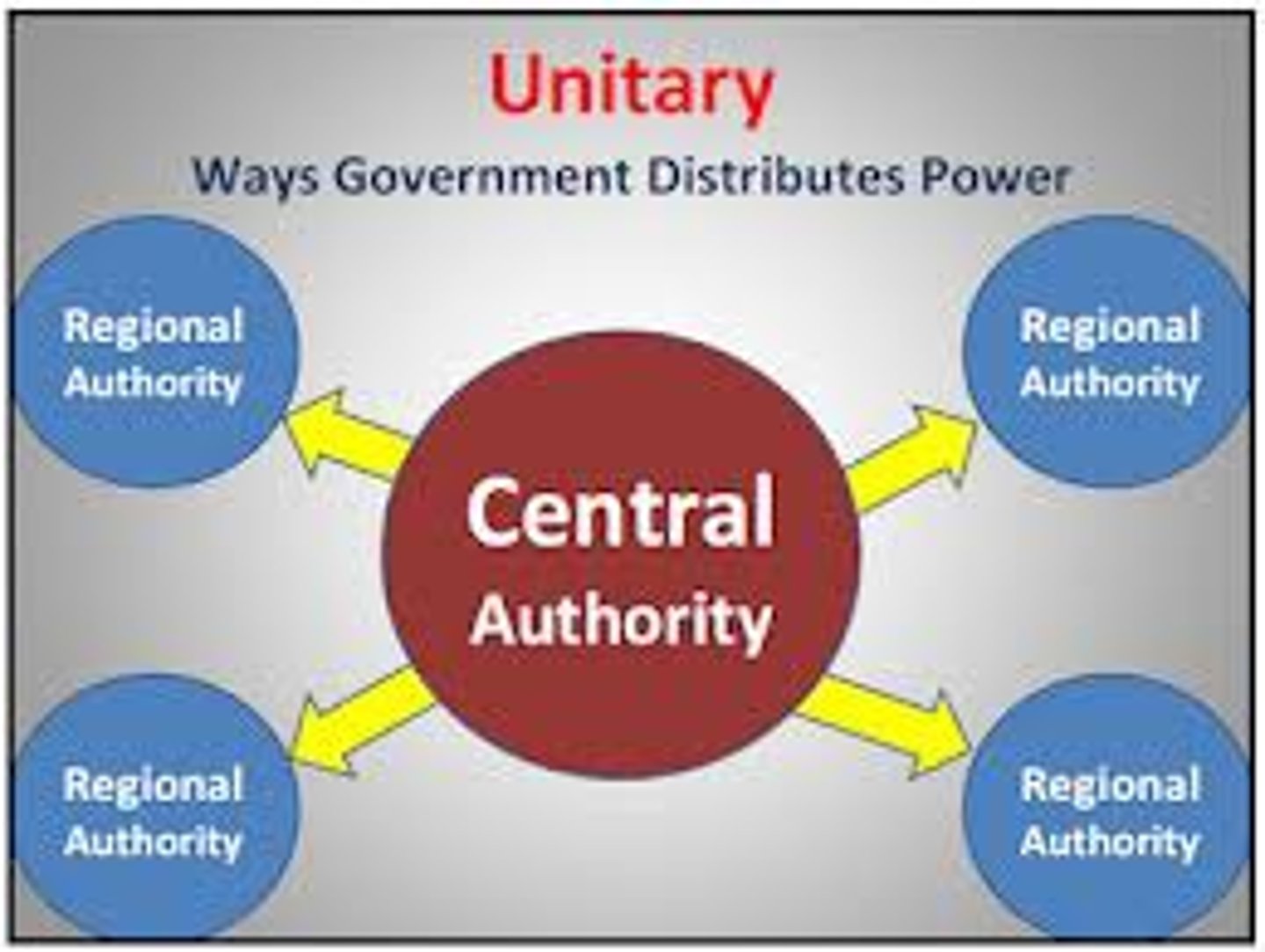
A way of organizing a nation so that all power resides in the central government.
Unitary Governments
The workings of the federal system- the entire set of interactionsamong national, state, and local governments, including regulations, transfers of funds, and the sharing of information.
Intergovernmental Relations
The clause in Article VI of the Constitution that makes the Constitution, national laws, and treaties supreme over state laws as long as the national government is acting within its constitutional limits.
Supremacy Clause
The constitutional amendment stating "The powers not delegated to the United Staes by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the states, are reserved to the states respectively, or to the people."
10th Amendment
An 1819 Supreme Court decision that established the supremacy of the national government over state governments and the doctrine of implied powers.
McCulloch v Maryland

Powers of the federal government that are specifically addressed in the Constitution
Enumerated Powers
Powers of the federal government that go beyond those enumerated in the Constitution
Implied Powers
The final paragraph of Article I, Secion 8, of the Constitution which authorizes Congress to pass all laws "necessary and proper" to carry out the enumerated powers
Elastic Clause (Necessary and Proper Clause)
A landmark case decided in 1824 in which the Supreme Court interpreted very broadly the clause in Article I, Section 8 of the Constitution giving Congress the power to regulate interstate commerce and encompassing virtually every form of commerical activity.
Gibbons v Ogden
A clause in Artivle IV on the Constitution requiring each state to recognize the public acts, records, and judicial proceedings of all other states.
Full Faith and Credit
A legal process whereby a state surrenders a person charged with a crime to the state in which the crime was alleged to have been committed
Extradition
The provision of the Constitution according citizens of each state the privileges of citizens of other states
Privileges and Immunities
A system of government in which both the states and the federal government remain supreme within their own spheres, each responsible for some policies
Dual Federalism
A system of government in which powers and policy assignments are shared between them and the national government
Cooperative Federalism
Transferring responsibility for policies from the federal government to state and local governments
Devolution
The pattern of spening, taxing, and providing grants in the federal system
Fiscal Federalism
Federal grants that can be used only for specific purposes; they come with strings attached
Categorical Grants

Fedral categorical grant given for a specific purpose and awarded on the basis of the merits of application
Project Grants
Federal categorical grants distributed according to a formula specified in legislation or in administrative regulations
Formula Grants
Federal grants given more or less automatically to states or communities to support broad programs in areas such as community development and social services
Block Grants

In Gibbons v. Ogden, the Supreme Court's decision created ________.
a broad definition of commerce to include every known method of commercial activity
The full faith and credit clause to the Constitution requires states to recognize each other's laws. Which of the following is an example of this?
a valid driver's license must be recognized in all states
Prior to the ratification of the new Constitution in 1789, the relationship between the national and state governments could best be characterized as ________.
a confederation
Grants that can be used only for subsidizing school meals, and that are calculated on the basis of the state's population of school-aged children who are living in families with incomes below the poverty line, are examples of ________.
formula grants
Seen as both controversial and costly to implement, what was an outcome of the No Child Left Behind Act on government?
An expansion of the federal government's power
Why did the Framers insert the interstate commerce clause into the Constitution?
To regulate all commercial activity between states
Crossover sanctions are a powerful tool of the federal government. Federal dollars in one program may be ________ in order to influence ________.
withheld; state policy
The constitutional provision which requires states to return persons charged with a crime to the state where the crime was committed is known as ________.
extradition
Under the Constitution, which of the following powers is reserved for the federal government?
Making treaties with foreign nations
To guarantee liberty, the Constitution embodies a form of government built upon which two structural concepts?
Federalism and separation of powers
Congress derives its implied powers from which clause in the Constitution?
The elastic clause
State constitutions protect liberty, but our biggest legal defense of freedom comes from ________.
the Bill of Rights
The Sixteenth Amendment allowed the national government the right to ________.
impose an income tax
Which amendment covers states' rights?
Tenth Amendment
A federal grant that would give states money for a new housing project, but that would require the states to make at least 50 percent of the housing available to low-income families, would be considered a(n) ________.
categorical grant
Federalism is more about ________ powers for Congress and ________ rights for state government.
implied; denied
A requirement the federal government imposes as a condition for receiving federal funds is called ________.
a federal mandate
While categorical grants provide states and local governments with federal funding for a specific purpose, block grants give state and local officials the ability to determine for themselves how to best spend federal grant money. One other advantage of block grants is ________.
they are given almost automatically without cumbersome paperwork
A form of governmental structure in which the national government is weak and most or all power is in the hands of its components (e.g., states) is known as ________.
a confederation
The Constitution grants citizens of one state comparable services to citizens of other states through the ________ provision.
privileges and immunity
The Founders adopted a federal (or shared) system of government because they feared ________.
tyranny for the states and limited voice in government
When the federal government requires that your local school district measure student performance with regularly scheduled tests, but does not provide any federal funding to meet this requirement, this is an example of ________.
an unfunded mandate
The Tenth Amendment reserves the powers that are not specifically delegated to the national government to ________.
state governments
Governmental authority in the United States is distributed according to a ________ system.
federal
The distribution of power between states and the national government concerning interstate commerce ________.
often depends on definitions and interpretations, rather than facts alone
McCulloch v. Maryland was the first Supreme Court decision to firmly uphold the ________ clause.
Necessary and Proper
The programs developed under President Franklin Roosevelt to expand the role of the federal government in providing employment opportunities and social services in the wake of the Great Depression were collectively referred to as the ________.
New Deal
Political scientists have devised terms to explain various kinds of federalism. Which of these forms of federalism works to aid and to influence states and localities?
Fiscal Federalism
The Constitution requires that states give ________ to the public acts, records, and civil judicial proceedings of every other state.
full faith and credit
The principal source of the national government's implied powers can be found in the Constitution's ________ clause.
necessary and proper
A provision of the Americans with Disabilities Act was made void by ________ who deemed it in conflict with the ________ Amendment.
the Supreme Court; Eleventh
American states are unitary governments as local governments receive authority from them; in turn, state authority is received directly from ________.
the Constitution
While the American system of government is characterized by federalism, most nations are governed by ______.
a unitary government
What is the basic intent behind fiscal federalism?
To use federal grants-in-aid to require states to take action
The necessary and proper clause is also known as the ________ clause.
elastic

Federalism is a constitutional arrangement in which power is ________.
divided between the national government and the states
Block grants were developed in 1966 in order to ________.
provide states with more flexibility to direct federal money toward specific local needs
National and state laws are clearly in conflict over the ________ Act.
Compassionate Use
The workings of the federal system are sometimes called ________ relations.
Intergovernmental
Under President Lyndon Baines Johnson's Great Society, the government took the unprecedented step of funding community groups directly. Which of the following choices best explains this unprecedented step?
It placed federal funds directly into the hands of community groups and circumvented state and local governments.
The powers of the federal government that are explicitly mentioned in the Constitution are called ________.
Enumerated powers
If you were living under a unitary (or undivided) system of government, ________.
all power would be concentrated at the central government level
The amendment that requires the states to adhere to fundamental guarantees of individual liberty is the ________ Amendment.
Fourteenth
The most clearly delegated powers, those actually written in the Constitution, are ________ powers.
Enumerated
The United States Constitution specifically lists ________.
what the national government can do
Since 1929, the national government's share of American governmental expenditures has ________.
grown rapidly
The debate about federalism in the United States ________.
has been ongoing for more than 200 years
Article VI of the Constitution, which states that the federal laws and the Constitution take precedence over state laws and constitutions, is known as ________.
the supremacy clause
In cooperative federalism, in order to qualify for federal grant money, cities and states must ________.
follow federal guidelines for adopting and enforcing federal laws
In implementing civil rights legislation in the 1960s, the federal government relied on a combined application of the commerce clause and the equal protection clause in the Fourteenth Amendment. How did the combined usage of these constitutional provisions enable the federal government to force the states to comply with civil rights legislation?
The federal government used its power to regulate interstate commerce as a means of enforcing the equal protection clause on behalf of all U.S. citizens involved in commercial activities carried on between states.
Powers not specifically spelled out in the Constitution are reserved for ________.
the states or the people
Under a system of ________ federalism, state governments and the national government are equally authoritative; neither is regarded as superior to the other.
dual
Which of the following statements best describes a federal system? It is a system of government in which ________.
significant governmental powers are divided between the central government and smaller units
In a ________ system, all ruling authority rests in a single central government.
unitary
Powers exercised by both the national government and state governments are called ________ powers.
shared
Beginning in the 1990s, the Supreme Court began making a series of rulings that reinterpreted the commerce clause more narrowly than it had been interpreted since the late 1930s. The reason for this change in interpretation of the commerce clause by the court was an attempt to ________.
limit the power of the federal government that had become too powerful at the expense of the states
In 1787, federalism was a compromise between centrists, who supported a strong national government, and those who ________.
favored decentralization
Since the ratification of the Constitution, American federalism has gradually changed from ________.
dual to cooperative federalism
________ require or direct states to provide additional services under threat of penalties or as a condition of funding.
Mandates