Lecture 3 - Newton's Laws of Motion and Friction
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Newton’s First Law
An object at rest remains at rest unless a net force acts on it
An object moving with constant velocity continues to move with same speed and in the same direction unless a net force acts upon it
Free Body Diagrams
a diagram that shows all the forces acting on the object only and not by the object
Newton’s Second Law
When a net force acts on an object it experiences acceleration (F=ma)
If acceleration is 0…
F = 0
Tension
mass x gravity
Tension and Newton’s Second Law Equation
T - mg = ma
A 75kg person is standing on a bathroom scale in an elevator, calculate the scale reading in the elevator when it is stationary, ascending with acceleration of 1.2 m/s² and descending with acceleration of 1.2 m/s²
stationary: N - mg = 0
N = mg
N = 75×9.8 =735 N
ascending: N - mg = ma
N = mg + ma
(75×9.8) + (75×1.2) =825 N
descending: N - mg = -ma
N = mg - ma
(75×9.8) - (75×1.2) =645 N
NOTE: if elevator was free falling, scale would read 0 as person feels weightless
when you push down on the desk, what do you feel
the force of the desk pushing up on you
Whenever one body exerts a force on a second body…
The second body exerts an equal and opposite force on the first body
What is Friction
Whenever two surfaces slide across each other there is a force resisting the motion - called frictional force
Static Friction
There is NO relative motion between the two surfaces
Kinetic Friction
There is relative motion between the two surfaces
static friction vs kinetic friction
static friction is inclined upward until it reaches a peak, then it transitions to kinetic friction where it drops and plateaus
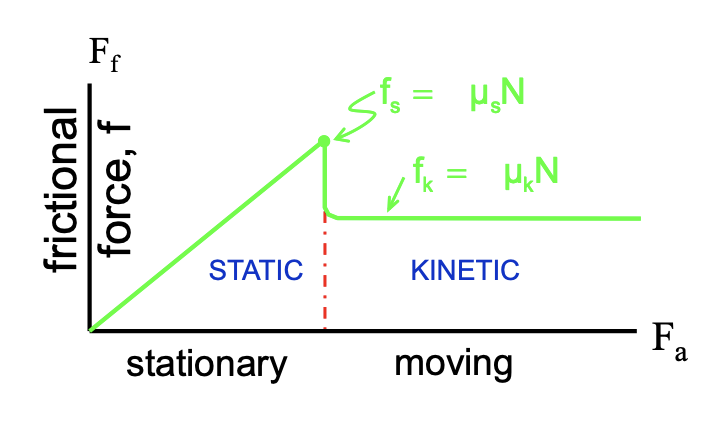
Frictional Force
.
Newton’s Third Law
Every action has an equal and opposite reaction