week 14 virtual machines and networking
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
flashcards based on os slides from week 14
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
operating system
a layer of software between many applications and diverse hardware
what does the operating system do
hardware abstraction so an application doesn’t have to know the details about the hardwarre
arbitrates access to resources among multiple applications + sharing of resources
provides protections
what kind of protection does an OS provide
isolation protects app’s from each other
isolation also protects OS from applications
isolation limits resource consumption by any one app
OS prevents applications from writing into
privileged memory
OS prevents applications from invoking
privileged functions
privileged instruction examples
memory address mapping
flush or invalidate data cache
invalidate TLB (translation lookaside buffer) entries
load and read system registers
change processor modes from K to U
change the voltage and frequency of processors
halt/reset processor
perform I/O operations
unit of work for an OS
application
task
job
process
what does a TASK consist of
code — placed into memory
data — stored in memory
OS data for task — task descriptors
mode bit
hardware that identifies whether the system is in user mode or supervisor/kernel mode
requires extra support from the CPU hardware for this OS feature
supervisor or kernel mode (mode bit = 0)
can execute all machine instructions, including privileged instructions
can reference all memory locations
kernel executes in this mode
user mode (mode bit = 1)
can only execute a subset of non-privileged instructions
can only reference a subset of memory locations
all applications run in user mode
virtual machine
a simulated computer running within a real computer
virtual computer runs an OS that can be different than the host operating
in a virtual machine, all the requests to access real hardware are routed to the appropriate _________, then virtual os or applications don’t know they are _________
host hardware, virtual
a process is given the illusion that it has its
own memory, via virtual memory
own CPU, via time slicing
virtual extends this idea to give a process the illusion that it also has its own
hardware
moreover, extend the concept from a process to an entire os being given the illusion that it has its own memory, CPU, and I/O devices
virtual machine benefits
can run multiple os’s simultaneously on the same host
fault isolation if an os fails — doesn’t crash another VM. this is also useful for debugging a new os
easier to deploy applications — can deploy an app within a VM instance that is customized for the app, rather than directly deploying the app itself and worrying about compatibility with the target os — useful for cloud server deployments
a type 1 hypervisor provides a _____________ for guest OSs and resides just above the ___________
virtualization layer, hardware
virtual machine goal
create a virtual machine that executes at close to native speeds on a CPU, so emulation and interpreting instruction by instruction are not good options — too much software overhead
virtual machine solution
have the guest os execute normally, directly on the CPU, except that it is not in kernel mode
therefore, any special privileged instructions invoked by the guest os will be trapped to the hypervisor, which is kernel mode
when the guest os trapped to the hypervisor, the hypervisor
then emulates only these privileged instructions and when done passes control back to the guest OS, also known as a “VM entry”
with the hypervisor trapping, most ordinary (non-privileged) instructions operate at _________, and only privileged instructions incur the overhead of a trap, also known as a ________, to the hypervisor/VMM
full speed, “VM exit”
trap-and-emulate
Executable code from the guest can execute directly on the host CPU by the hypervisor. The hypervisor configures the CPU in such a way that all potentially unsafe instructions will cause a “trap”. A trap is an exceptional condition that transfers control back to the hypervisor
it is very easy to provision and deploy VM instances on the ______
cloud
amazon’s elastic compute cloud (EC2) uses ____________
Xen virtualization
different types of VMs or instances that can be deployed
standard, high-memory, high-cpu
users can create and reboot their own VMs
to store data peristently, need to supplement EC2 with an additional cloud service
amazon’s simple storage service (S3)
process VMs, e.g. Java VMs
differ from system VMs in that the goal is NOT to try to run multiple OSs on the same host, but to provide portable code execution of a single application across different hosts
java applications are compiled into __________ that can be run on any ________
Java byte code, Java VM
java VM acts as an interpreter of byte code, translating each byte code instruction into a local action on the host OS
______________ compilation can be used to speed up execution of java code
just in time
java byte code is compiled at run time into native machine code that is executed directly on the hardware, rather than being interpreted instruction by instruction
note Java VMs virtualize and abstract _______, not actual ________, unlike system VMs
machine, hardware
i.e. the target machine that Java byte code being compiled for is a software specifiction
applications today leverage the internet to __________________ data
send and receive data
internet service examples
web browser requests pages from a web server
P2P systems
streaming video
social networks
mobile apps
every networked application communicates to a remote process via a ___________
socket API
send(message)
recieve(message)
socket library talks via ___________ to OS kernel’s _____________
system call API, network stack
send(message)
receive(message)
the network stack’s architecture is organized into
multiple layers of protocols
each protocol performs a specific set of duties
web (HTTP), Email (SMTP, IMAP) reside in
application layer 5
TCP, UDP reside in
transport layer 4
IP (v4 and v6) reside in
network layer 3
ethernet, wifi, bluetooth reside in
data link/MAC layer 2
CDMA, OFDM reside in
physical layer 1
to send a packet of data to a remote destination
each layer first passes a packet of data down the stack to the next lowest layer
to receive a packet of data
each layer retrieves a packet of data from the layer below
and after processing the packet sends the packet to the layer above
to send, an application calls _____________
socket API’s send()
gives a pointer to the user space buffer containing the data to send
if file to be sent is large, the application
segments the file into smaller packets
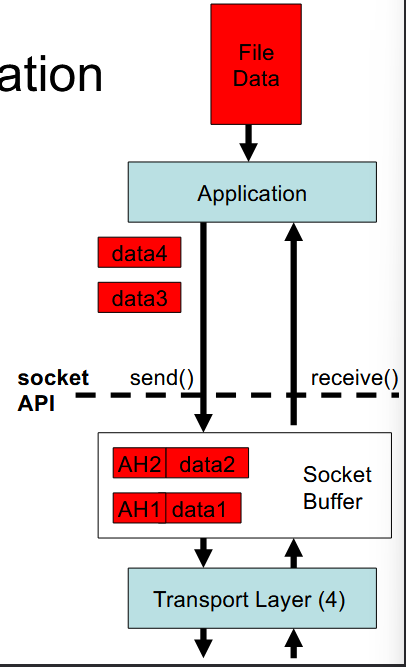
application layer prepend a ________ header to the user data, forming a __________
layer 5, packet
prepend the header AH1 to data1 forming packet 1
header info is useful at the remote receiver to decode the packet
when sending a packet
in general, at each layer N, a pack header NHx is prepended to data x and then set to a lower layer N-1
when sending a packet, packet grows as it __________ the network layered stack
descends
when receiving a packet
at each layer N, strip off the layer N header
when receiving a packet, packet shrinks as it _________ the stack
moves up
how to recover from a lost packet
retransmit lost packets
TCP, the transmission control protocol
transport layer’s job is _________________, if desired
end-to-end error recovery
how does the sender know if a packet was received correctly
receiver sends an Acknowledgement (ACK) packet back to sender
when does a sender know when to retransmit?
sets a timer
if it times out before ACK received, then retransmit
TCP ensures ____________
in-order delivery
many apps require TCP’s reliable and in-order packet delivery service
web, email, etc - can’t render a web page or read email if there are holes in the web page or email
changing order of web/email text also makes it unreadable
apps that use TCP can view the network connection as a __________________
pipe abstraction
any data sent into the pipe appears at the other end, hence it is reliable, i.e. pipes don’t lose data
a pipe preserves the order of the data sent into it at the output of the pipe — no reordering is possible
reliability comes at the cost of ________ due to retransmissions
delay
not all apps need/want TCP’s
reliability
interactive real-time apps like skype audio/video conferencing can’t wait for TCP’s retransmissions
must get packet delivered in real time, e.g. within 30 ms
real-time voice-over-IP (VOIP) apps like Skype and Facetime can tolerate
packet loss
may lose audio temporarily, but it’s OK
such apps are built on top of unreliable UDP (user datagram protocal) at layer 4, not TCP
the internet consists of many _______ that connect together to form a ___________
routers, network graph
the internet protocal (IP) network layer must route the
ip packet to the correct destination
network layer tries to find the ______________, e.g. using _________________
“shortest path”, dijkstra’s algorithm
the metric for shortest path may be minimum number of hops, shortest physical distance, lowest delay, minimum cost, etc
each router implements the
network layer
ip routing may _________
lose packets
any router or link may fail at any time. also congested router buffers may overflow
ok as long as TCP can retransmit them
each link between any two routers (endpoints) must be able to
transmit packets
data link layer is responsible for transmitting packets between any 2 neighboring nodes in the network
data link layer must define
the beginning and end of packets (packet framing)
packets may be lost, so this layer may also retransmit locally
along each link, the ___________ determines how 1’s and 0’s, i.e. digital bits, are transmitted
physical layer