Honors bio final study
1/208
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
209 Terms
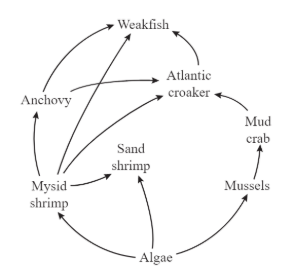
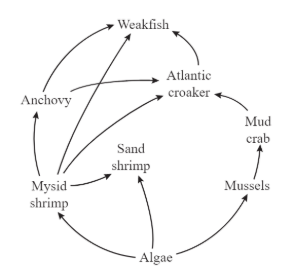
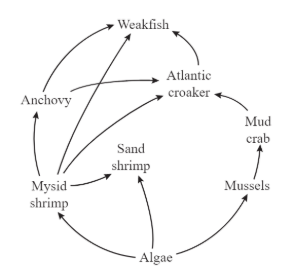
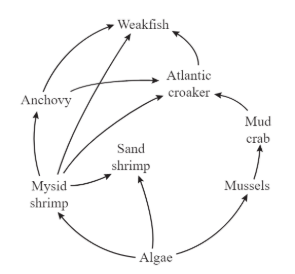
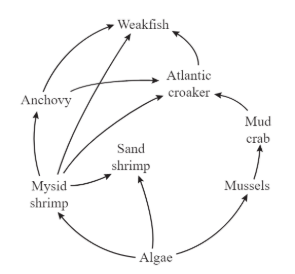
What happens to the remaining 90% of energy in the trophic levels because of the rule of 10%?
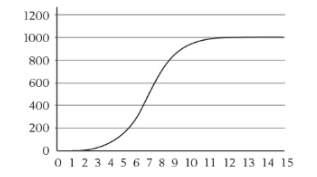
What are the independent, dependent variables, and title of the algae growth graph?
IV: Time (1-15 months), DV: Algae growth, Title: Algae Growth Over Time.


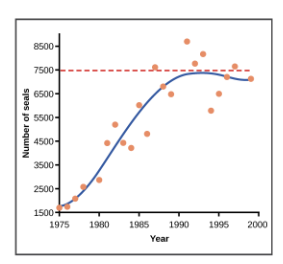
Label the following concepts within the graph: Exponential Growth, Logistic Growth, Carrying Capacity
CC: red dotted line, LG: entire blue line, EG: blue line from 1975-1985
What are examples for Carbs
Glucose, Sucrose, and cellulose
Monomer of Carb
Monosacharide
Polymer of a Carb
Polysacharide
Elements Of a Carb
CHO and 1:2:1
What are the sub units of lipids?
Glycerol and fatty acids (Lipids don’t have monomers or polymers)
Elements of a lipid
CHO and CH>O
functions of a lipid
Long term energy storage
insulation
Cell membranes
Examples of a lipid
triglyceride
phospholipid
steroids
What are the elements of a protein
CHON
What is the monomer for a protein
Amino acid
What is the polymer of a protein
Polypeptide chain
what are examples of proteins
enzymes
antibodies
muscles
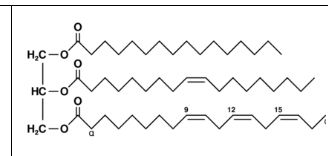
What is the macro molecule
Lipid—Evidence CHO, CH>O
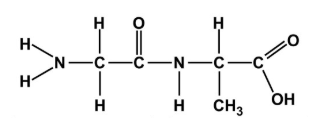
What is the macro molecule
Protein CHON, Amino group, Carboxyl group
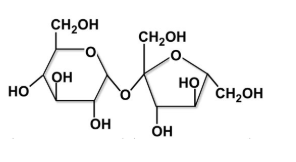
What is the macro molecule
carb—CHO, 1:2:1
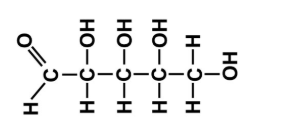
What is the macro melecule
Carb, CHO, 1:2:1
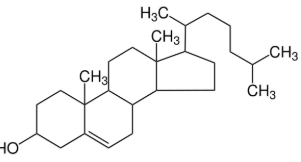
What is the macro molecule
Lipid, CHO, CH>O
Both carbs and lipids store energy, but lipids store more. Where is this energy stored?
Carbon-carbon bonds
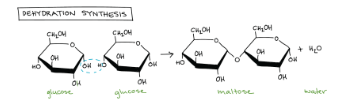
Draw a model that shows dehydration synthesis. Label the reactants and products.
R: glucose, P: maltose, water
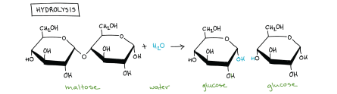
draw a model for hydrolysis
R: maltose, water - P: glucose
When an organism eats and digests food, is it doing dehydration synthesis or hydrolysis?
hydrolysis
When an organism builds muscle, is it doing dehydration synthesis or hydrolysis?
dehydration synthesis
What type of macromolecule are enzymes?
proteins
What is the function of enzymes?
Lowers activation energy in order to allow reactions to happen quicker.
What happens to an enzyme when it gets too hot, what is this process called? Will it continue to work in these conditions?
Denature, no the enzyme changes shape so the substrates will not bind at the active site to activate the enzyme.
What organelles are found in both plant and animal cells?
All eukaryotic organelles are found in both except: vacuoles (P), chloroplasts (P), lysosomes (A), centrioles (A)
Compare and contrast prokaryotes and eukaryotes (similarities AND differences)
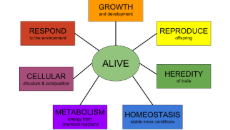
List the 8 characteristics of all living things and draw a picture representing each concept.
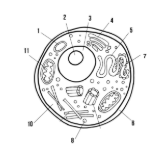
Label the parts of the cell and list their function below-1
Lysosome: contains enzymes that break down old cell parts and waste in the cell
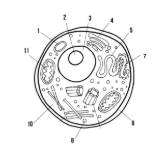
Label the parts of the cell and list their function below-2
Nucleolus: synthesizes ribosomes
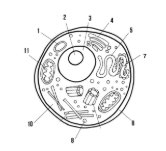
Label the parts of the cell and list their function below-3
Nucleus: contains genetic information
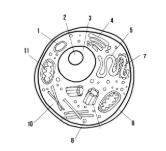
Label the parts of the cell and list their function below-4
Golgi apparatus: packages and ships finished proteins
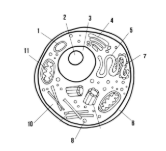
Label the parts of the cell and list their function below-5
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum: synthesizes lipids
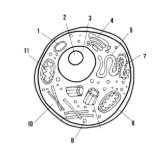
Label the parts of the cell and list their function below-6
Cell membrane: allows/keeps things from entering and exiting the cell
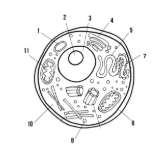
Label the parts of the cell and list their function below-7
Rough endoplasmic reticulum: modifies proteins
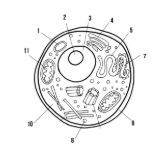
Label the parts of the cell and list their function below-8
Ribosome: synthesizes proteins
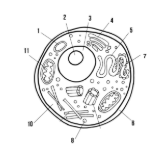
Label the parts of the cell and list their function below-10
Cytoplasm: fluid-like substance that holds organelles
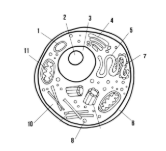
Label the parts of the cell and list their function below-11
Mitochondria: site of ATP synthesis
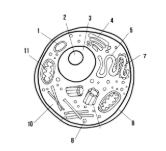
What type of cell is this? (Prokaryote or Eukaryote? Plant or Animal)?
eukaryote, animal
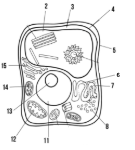
Label the parts of the cell and list their function below-2
Vacuole: water storage
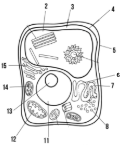
Label the parts of the cell and list their function below-3
Cytoplasm
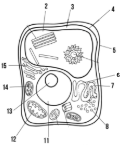
Label the parts of the cell and list their function below-4
Cell membrane
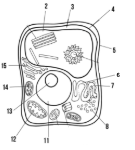
Label the parts of the cell and list their function below-5
Cell wall: maintains structure of the cell
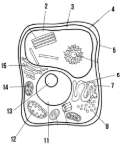
Label the parts of the cell and list their function below-6
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
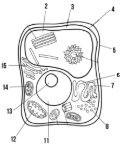
Label the parts of the cell and list their function below-7
rough endoplasmic reticulum
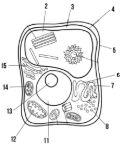
Label the parts of the cell and list their function below-8
ribosomes
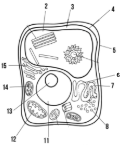
Label the parts of the cell and list their function below-11
Nucleus:
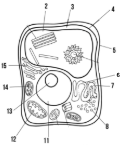
Label the parts of the cell and list their function below-12
Mitochondria
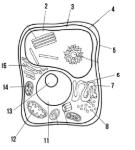
Label the parts of the cell and list their function below-13
Nucleolus
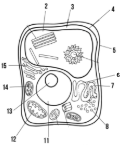
Label the parts of the cell and list their function below-14
Chloroplast: site of photosynthesis
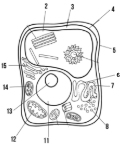
Label the parts of the cell and list their function below-15
Golgi apparatus:
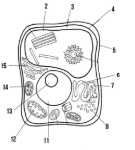
What type of cell is this? (Prokaryote or eukaryote? Plant or animal)?
eukaryote, plant

What is this diagram called?
Karyotype

What are the dark lines called AND How many total are there in THIS diagram?
Chromosomes, 10 total - 5 pairs of chromosomes
Where (in a cell) are these found?
nucleus
Why are they shown in pairs?
Organisms get one chromosome from their mother and one from their father

Does this diagram show a male or female? How can you tell?
Female: XX
What is a gene?
A section of a chromosome that codes for a specific trait (hair color, eye color, etc.)
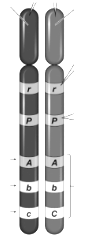
How many genes are shown?
5
What is an allele?
A version of a gene (hair color gene can have blonde, black, red, brown alleles)
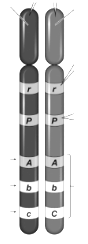
What are the alleles for the top gene?
r
Label each gene as homozygous or heterozygous.
Homozygous: rr, PP, AA, bb - Heterozygous: Cc
Define fitness
an organism’s ability to survive and reproduce in their environment

What is the variation in this scenario?
All 13 different beak sizes.

What was the selective pressure?
Drought which led to there only being large seeds available to eat

What type of finches were more fit?
Finches with larger beaks.

Describe the beaks that were found in this area 10 years after the drought. Why did this happen?
describe it yourself…
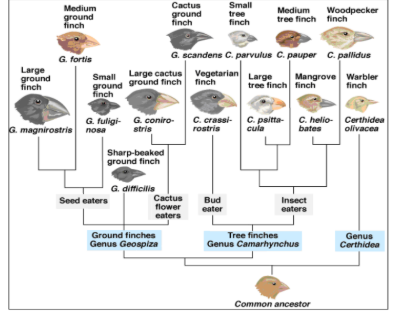
What is this type of diagram called?
Phylogenetic Tree
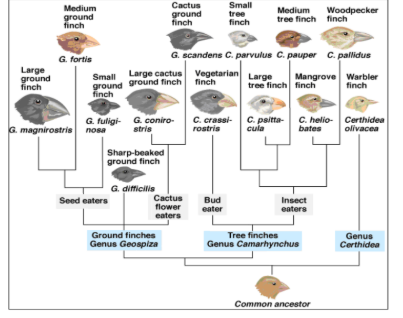
What does this type of diagram show?
Evolutionary relationships between different species of finches.
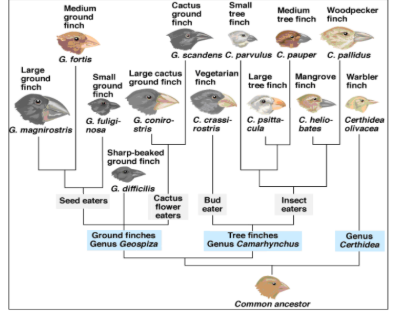
Are the ground finches more closely related to the Tree finches or to Genu Certhidea?
tree flinches
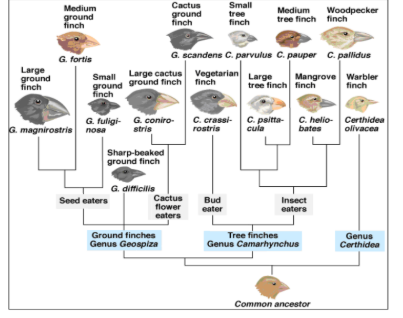
Who is the cactus ground finch most closely related to?
Large cactus ground finch
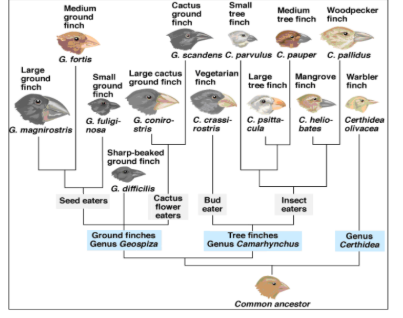
Does the large ground finch have DNA more similar to the Medium Ground finch or to the Warbler finch?
medium ground flinch
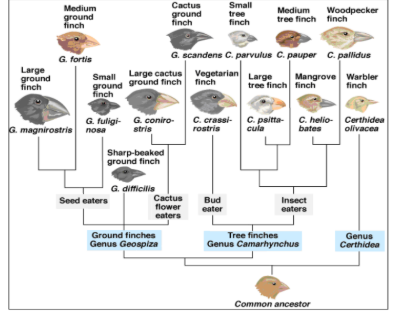
What type of finch is the most recent common ancestor for the Vegetarian finch and the Large tree finch
the very first common ancestor
Write the equation for photosynthesis.
Reactants: H2O, CO2, SE Products:O2, C6H12O2(glucose)
What are 3 conditions that will make the rate of photosynthesis increase?
Increased CO2, Increased Water, Increased Temperature, Increased Light Intensity
PSII purpose (light dependent)
Photosystem II (PSII) is a protein complex embedded in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, responsible for using light energy to split water molecules, releasing oxygen as a byproduct, and transferring electrons into the photosynthetic electron transport chain
PSI (Light dependent)
Photosystem I (PSI) is a large protein complex embedded in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, functioning as a key part of the photosynthetic electron transfer chain by capturing light energy and using it to transfer electrons to the production of NADPH
Chemiosmosis (Light dependent)
Chemiosmosis in photosynthesis refers to the process where a proton gradient is established across the thylakoid membrane within a chloroplast, allowing hydrogen ions (protons) to flow through ATP synthase, generating ATP (adenosine triphosphate) as a usable energy source for the plant cell
Light-Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle)
The Calvin cycle, also known as the light-independent reactions, is a series of chemical reactions that occur in the stroma of a chloroplast during photosynthesis, where carbon dioxide is converted into sugar molecules (glucose) using energy from ATP and NADPH produced in the light-dependent reactions.
what is glycolysis
Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway where glucose is broken down into two pyruvate molecules, generating a small amount of ATP and NADH energy in the process, occurring in the cytoplasm of a cell and considered the first step in cellular respiration, even without the presence of oxygen; essentially, it's the process of extracting energy from glucose by splitting it into smaller units.
What is Pyruvate Oxidation
Pyruvate oxidation is a biochemical reaction within cellular respiration where pyruvate, a three-carbon molecule produced during glycolysis, is converted into acetyl-CoA (a two-carbon molecule attached to coenzyme A by releasing a carbon dioxide molecule and transferring electrons to NAD+ to form NADH; essentially acting as a bridge between glycolysis and the Krebs cycle, allowing the acetyl-CoA to enter the next stage of aerobic respiration for further energy extraction
what is the Kreb cycle
The Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid, is a series of chemical reactions that occur in the mitochondria of cells, where acetyl-CoA (a two-carbon molecule) is completely broken down to produce carbon dioxide, generating energy carriers like NADH, FADH2, and ATP in the process; it's a key part of aerobic respiration, extracting energy from food molecules like glucose.
What is oxidation phosphorilation
Oxidative phosphorylation is a cellular process that generates ATP by transferring electrons from electron donors (like NADH and FADH2) through a series of protein complexes called the electron transport chain (ETC), ultimately reducing oxygen to water, while simultaneously pumping protons across the mitochondrial membrane to create a gradient that drives ATP synthesis via ATP synthase; essentially, it harnesses the energy released from electron transfer to create a proton gradient which then powers ATP production through chemiosmosis.