Brown Algae (Phaeophyta): Structure, Life Cycle, and Evolution
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What is the phylum of brown algae?
Phylum Phaeophyta
What are the two main types of diatoms based on their shape?
Centric and Pennate
What is the structure that forms the outer cell wall of diatoms?
Frustule
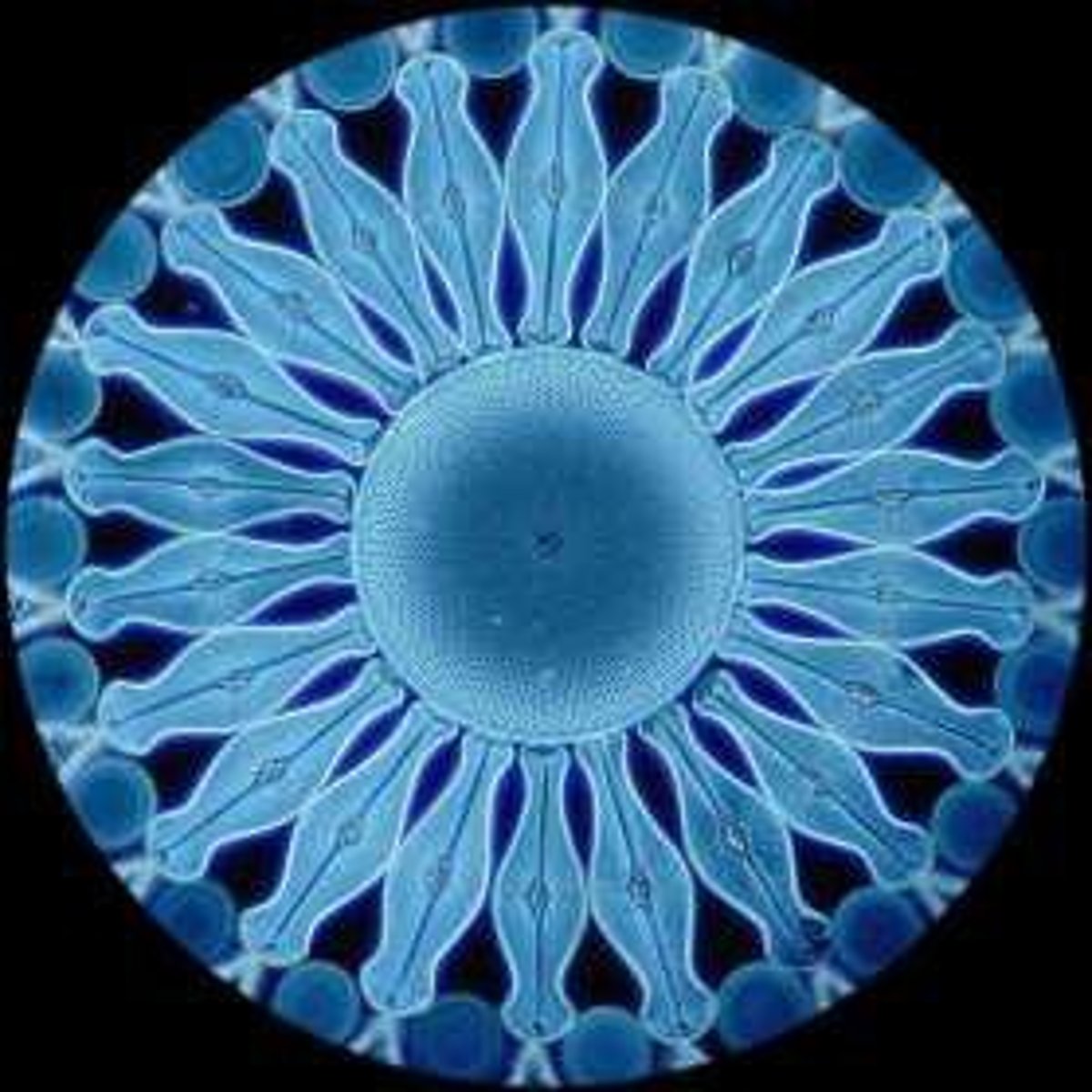
What are the two parts of a diatom's frustule?
Epitheca and Hypotheca
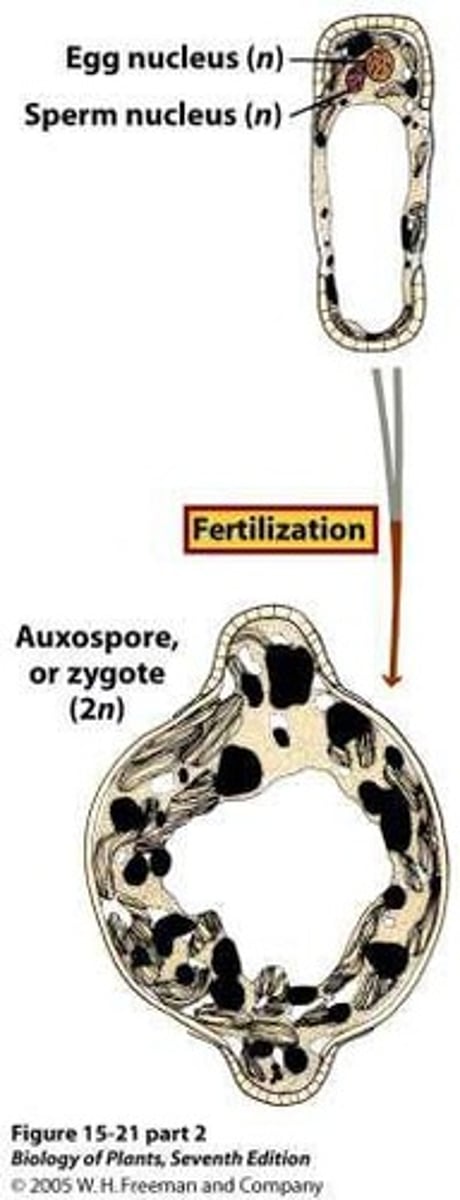
What is an auxospore?
A reproductive cell that can grow back to maximum cell size in diatoms.
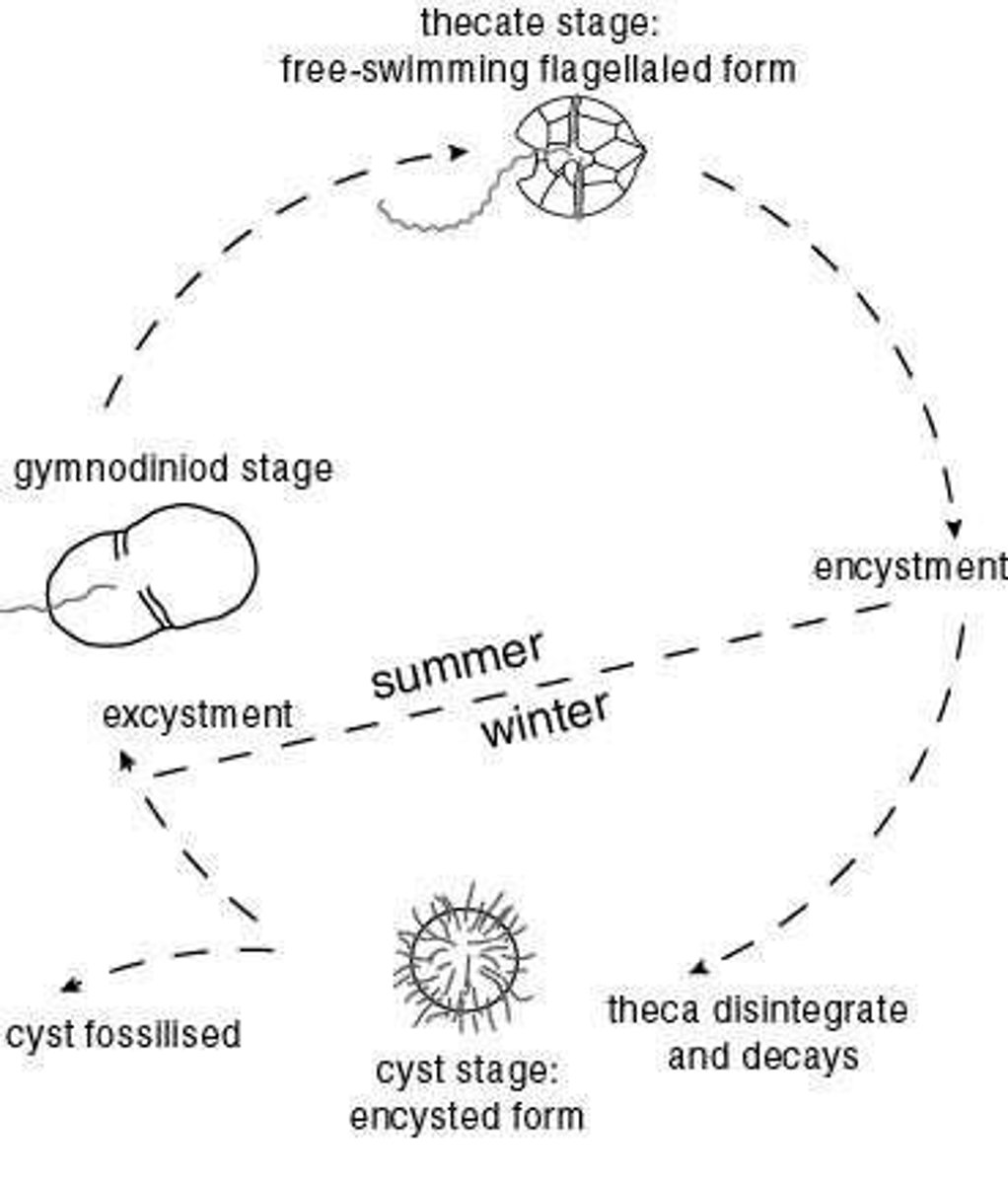
What type of reproduction is most common in dinoflagellates?
Asexual reproduction (cell divides in two)
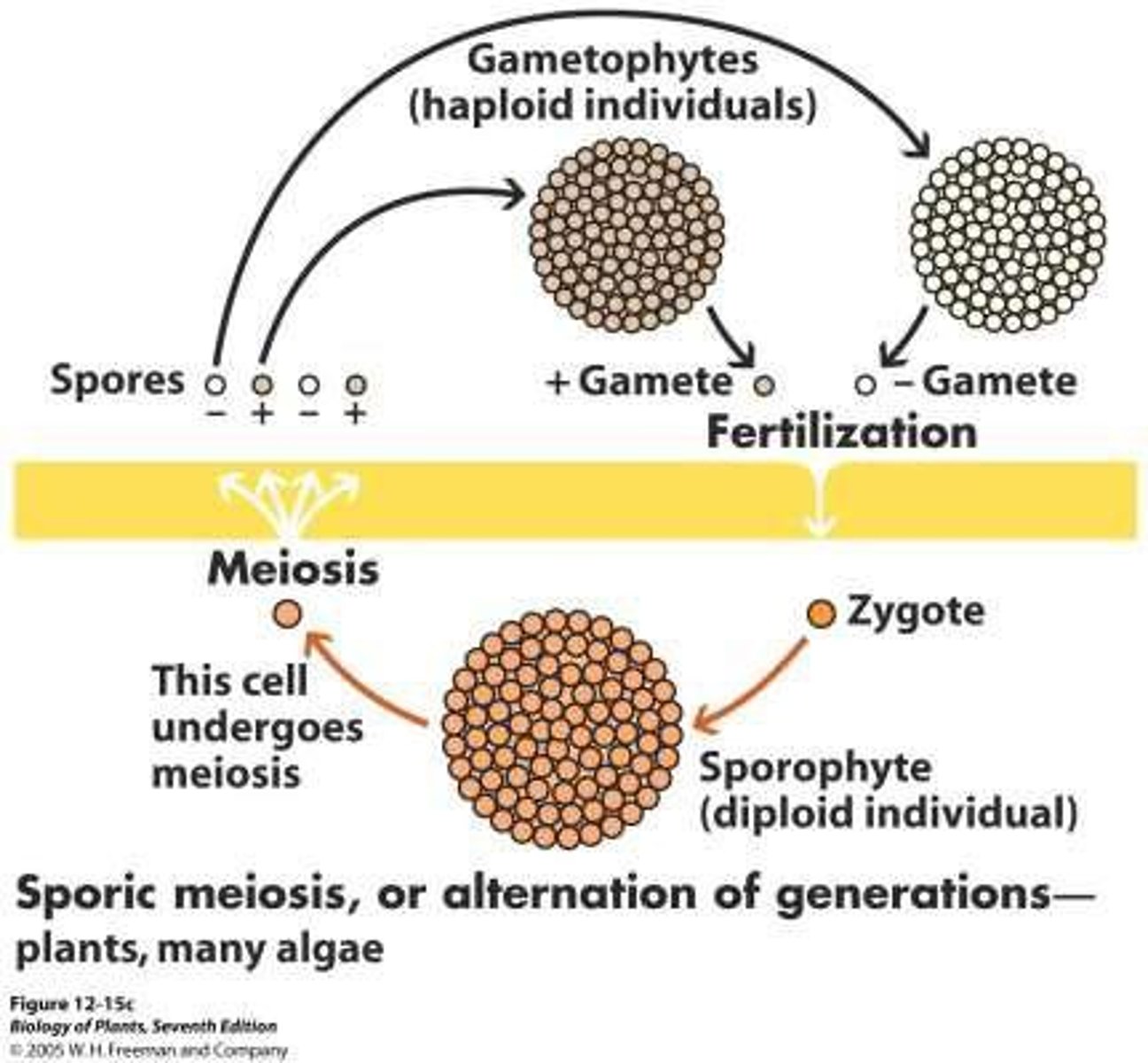
What is the haploid dominant life cycle called?
Haploontic
What is the difference between spores and gametes?
Spores are haploid cells capable of mitotic division; gametes are haploid cells that require fusion with another gamete to develop.
What is isomorphic alternation of generations?
When the gametophyte and sporophyte are identical.
What is heteromorphic alternation of generations?
When the gametophyte and sporophyte have different phenotypes.
What are the two main benefits of multicellularity?
Increased survival and reproduction through division of labor.
What is the primary cost of multicellularity?
Multicellular organisms require more oxygen than single-celled organisms of the same size.
What is the significance of diploidy in multicellular organisms?
Diploidy allows for masking of mutations, providing a survival advantage.
What is the main difference between multicellularity and coloniality?
Multicellularity involves differentiation of cells, while coloniality does not.
What is the basic form of brown algae called?
Thallus
What are the two types of flagella found in reproductive cells of heterokont algae?
Two dissimilar flagella
What is the storage molecule found in brown algae?
Chrysolaminarin and Lipid
What is Ectocarpus?
A simple, branched filamentous organism often growing on larger algae.
What is the life cycle of kelps characterized by?
Heteromorphic alternation of generations with a reduction of gametophyte.
What is the significance of gas bladders in Fucus?
They help raise kelp in the water column.

What recent advancement has been made regarding brown algae?
Genetically modified E. coli can digest carbohydrates in brown algae.
How much ethanol can seaweed yield per acre compared to sugar cane and corn?
1,500 gallons per acre, which is 50% more than sugar cane and triple that of corn.
What is the main advantage of multicellularity in terms of movement?
Multicellular organisms can move and divide simultaneously, unlike single-celled organisms.
What are the three life history variants in terms of ploidy?
Haploid, diploid, and alternation of generations.