Circular Motion
1/24
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What is the equation for critical speed for circular motion in a vertical plane?
v = √(gr)
Critical speed = √(acceleration of free fall × radius)
How do you derive equation for critical speed for circular motion in a vertical plane?
Weight = centripetal force, W=mv2/r
mg=mv2/r
g=v2/r
v2=gr
v=√(gr)
For circular motion in a vertical plane, what is the centripetal force equal to at the critical velocity?
The weight is equal to the centripetal force
Why are some sharp bends in the road are banked?
When a vehicle rounds a bend on a flat road, the centripetal force required is provided by friction between the tyres and the road. The friction available on a flat corner determines how fast the corner can be ‘taken’.
The sharper the bend, the smaller the radius and the greater the centripetal force which needs to be provided for the car to follow the bend.
If friction is not enough additional centripetal force can be provided by banking the road so that the horizontal component of the Normal Contact force acts towards the centre of the bend.
Why do aeroplanes bank their wings to turn?
When 𝜃 is the angle of banking
The horizontal component of the lift 𝐿𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃 is unbalanced and provides a centripetal force so the plane will follow a horizontal circular path.
The vertical component 𝐿𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜃 is balanced by the weight.
What is centripetal force?
The constant force that acts perpendicular to the velocity and keeps a body moving with constant speed in a circular path
Define Uniform Circular Motion
When an object is moving and:
The resultant force (the centripetal force) is acting inward
The resultant force (the centripetal force) is equal in magnitude at all points
Definition of Angular velocity
The rate of change of angle for an object moving in a circular path
Derive ω = 2π/T
Angular velocity is the rate of change of angle, so ω = θ/t
In a time t equal to one period T, the object will move through an angle θ equal to 2π radians.
Therefore ω = 2π/T
Derive ω = 2πf
ω = 2π/T and f = 1/T, so ω = 2πf
What equation links the angular velocity to the rate of rotation in rpm?
Derivation v = rω
For a constant speed v = distance travelled / time taken = x / t
When x = circumference of circle = 2πr, t = time period = T
v = x/t = 2πr/T = r × 2π/T
Angular velocity = 2π/T, so v = rω
What are the 2 equations for centripetal force?
Draw a diagram of a body moving in uniform circular motion, showing the direction of the velocity, centripetal force, centripetal acceleration.
How can a body moving at a constant speed be accelerating?
Why does the centripetal force not do any work?
A ball is attached to a string and whirled in a vertical circle. Draw a freebody diagram of the ball at the top of this circle and derive the expression for the Tension at this position.
Centripetal force F = mg + T
T = F - mg = mv²/r - mg

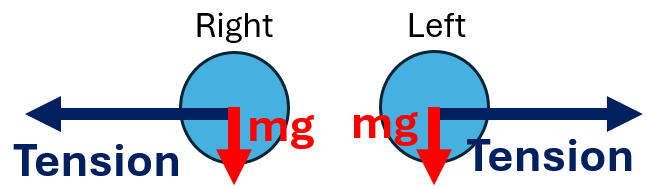
A ball is attached to a string and whirled in a vertical circle. Draw a freebody diagram of the ball at the side of this circle and derive the expression for the Tension at this position.
Centripetal force F = T
T = F = mv²/r
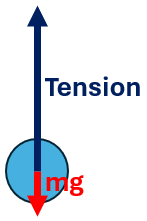
A ball is attached to a string and whirled in a vertical circle. Draw a freebody diagram of the ball at the bottom of this circle and derive the expression for the Tension at this position.
Centripetal force F = T - mg
T = F + mg = mv²/r + mg
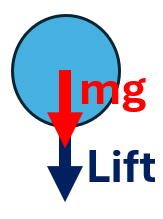
A plane is flying in a vertical loop. Draw a freebody diagram of the plane at the top of this loop and derive the expression for the lift force at this position.
Centripetal force F = mg + L
L = F - mg = mv²/r - mg
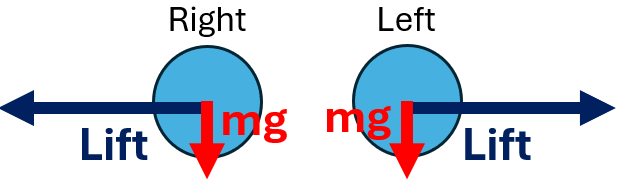
A plane is flying in a vertical loop. Draw a freebody diagram of the plane at the side of this loop and derive the expression for the lift force at this position.
Centripetal force F = L
L = F = mv²/r
A plane is flying in a vertical loop. Draw a freebody diagram of the plane at the bottom of this loop and derive the expression for the lift force at this position.
Centripetal force F = L - mg
L = F + mg = mv²/r + mg
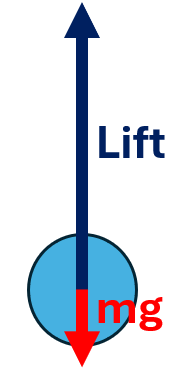
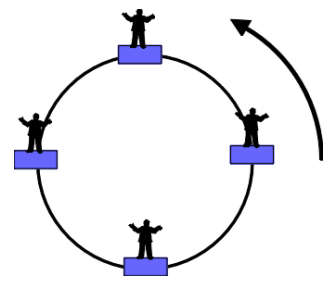
A person stands on a Ferris wheel. Draw a freebody diagram of the person at the top of this loop and derive the expression for the normal contact force at this position.
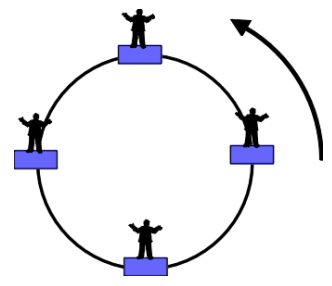
A person stands on a Ferris wheel. Draw a freebody diagram of the person at the side of this loop and derive the expression for the normal contact force at this position.
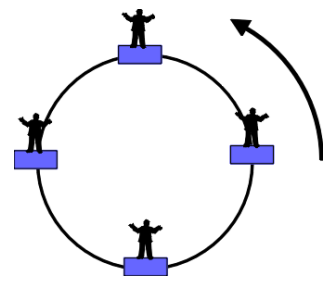
A person stands on a Ferris wheel. Draw a freebody diagram of the person at the bottom of this loop and derive the expression for the normal contact force at this position.