Sensorimotor Intergration
4.5(2)Studied by 6 people
Card Sorting
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:47 PM on 3/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
1
New cards
why have animals evolved brains?
to generate meaningful movement (behaviour)
2
New cards
the monosynaptic stretch reflex
1. Stretch of the mechanoreceptors in the muscle increase firing rate of the afferent sensory neuron.
2. Increased neurotransmitter release activates the motor neuron.
3. Contraction of biceps muscle.
3
New cards
what is contralateral movement?
voluntary movement
4
New cards
what is ipsilateral movement?
reflex movement
5
New cards
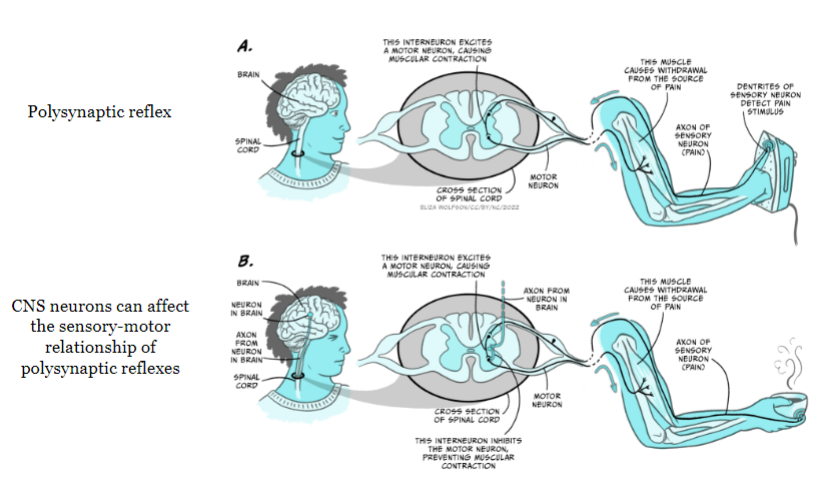
polysynaptic reflex and interaction with CNS
6
New cards
neural pathways and structures underlying voluntary movements
visual system (visual attention and saccades) → integration of visual information → trajectory prediction → movement control → movement precision → muscle contraction
7
New cards
how does the visual system detect stimuli?
* cones in the fovea detect the light bouncing off of the stimulus
* photoreceptors transduce the stimulation into neural activity
* bipolar cells change the activation state of ganglion cells → conveys visual info to the brain
* photoreceptors transduce the stimulation into neural activity
* bipolar cells change the activation state of ganglion cells → conveys visual info to the brain
8
New cards
how can the content of a person’s visual attention be traced?
from the course of that person’s saccades (neurons in the posterior parietal cortex fire more vigorously when the visual stimulus are the target of saccades)
9
New cards
what is the function of the saccade system?
to keep the image of the stimulus in the fovea (where vision is most accurate) (check slides for more info)
10
New cards
what are the two pathways involved in the integration of visual information?
geniculostriate pathway; tectopulvinar pathway
11
New cards
what occurs in the geniculostriate pathway?
* Perception of motion and depth by the dorsal visual stream (how).
* Perception of contrasts, contour and colour by the ventral visual pathway \n (what).
* Perception of contrasts, contour and colour by the ventral visual pathway \n (what).
12
New cards
what occurs in the tectopulvinar pathway?
* perception of the location by the pulvinar pathway (where)
13
New cards
what is trajectory prediction?
the integration of information over time; prior information about the stimulus is used (memory) as well as sensoria; integration to produce a likelihood about the situation
14
New cards
where does movement control occur in the brain?
basal ganglia
15
New cards
what does the oculomotor loop do?
controls eye movement and tracking of the stimulus
16
New cards
what does the skeletomotor loop do?
controls voluntary movements
17
New cards
what does the basal ganglia do (in terms of movement control)?
* action selection
* initiation and terminating actions
* relating actions with consequences
* initiation and terminating actions
* relating actions with consequences
18
New cards
how is the cerebellum involved in movement precision?
some regions of the cerebellum are activated when eye tracking and hand movement requires coordination
19
New cards
what happens during muscle contraction (neuromuscular junction)?
Acetylcholine release by the motor neuron axon terminal will contract fibres in the target muscle
20
New cards
how does the reward system affect behaviour/movement?
depending on the outcome of the behavioural reaction, it will either modulate the maintenance or modify the behavioural action