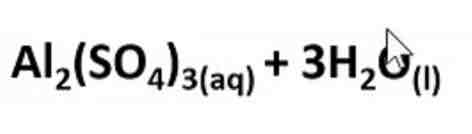Structure + bonding/ ionic oxides/ simple covalent oxides
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What does the graph for the melting points of group 3 oxides look like?
Like this

Why do Na2O, MgO and Al2O3 all have high melting points?
Because they form giant ionic lattices which have lots of strong attractive forces which require a lot of energy to break the bonds
Why does MgO have a higher melting point than Na2O?
Because magnesium forms 2+ ions which are more strongly attracted to the oxygen so requires a lot more energy to break
Why does Al2O3 have a lower melting point than MgO?
The Al3+ ions distort the electron cloud of oxygen this means there is some covalent character, which requires less energy to break bonds
Why does SiO2 have a higher melting point than the rest of the non metal oxides?
SO2 forms a macromolecular (giant covalent structure) which has many strong covalent bonds that require lots of energy to break
Why do P4O10 and SO2 have lower melting points than SiO2?
Because they form simple molecular structures which have weaker intermolecular forces, therefore less energy is required to break the bond
What type of solutions are formed when ionic oxides are added to water?
Alkaline solutions are formed because the Ionic oxides contain the O2- ion which accepts protons from the water molecules when dissolved in solution
What pH is formed when sodium oxide dissolves in water? And does it dissolve readily or sparingly
12-14 and it dissolves readily
What pH is formed when magnesium oxide dissolves in water and does it dissolve readily or sparingly?
9-10 and it dissolves sparingly in water so the alkaline solution is not as strong
What is formed when simple covalent oxides (P and S) are added to water?
Acidic solutions are formed
What product is formed when phosphorus oxide is added to water?
Phosphoric ( V) acid, H3PO4
What product is formed when sulfur dioxide is added to water?
Sulfurous oxide (H2SO3)
What product is formed when sulfur trioxide is added to water?
Sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
Why is silicon dioxide insoluble in water?
Because they form giant covalent structures which have many strong covalent bonds that require large amounts of energy to break
Why is aluminium oxide insoluble in water?
Because it is amphoteric and is insoluble in water
What does amphoteric mean?
It has both covalent and ionic character
What is silicon dioxide classed as? Because it reacts with a base to form a salt.
Silicon dioxide is classed as an acid
When period 3 oxides react with acids/bases what do they form as products?
Salt and water
How do you deduce the formula of a salt?
By joining the negative and the positive ion from two of the compounds
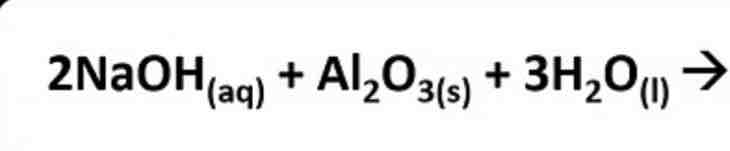
What products are formed in this reaction?
2NaAl(OH)4

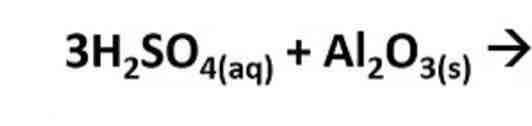
What products are formed in this reaction?
Al2(So4)3 + 3H2O