test and quiz from sugars
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
name the 4 general classes of carbohydrate ad give a brief description for each
monosaccharides/ simple sugars- single ring, soluble in water
disaccharides- double ring, soluble in water
oligosaccharides- 3-9 rings, insoluble in water
polysaccharides/ complex sugars- multiple rings, insoluble in water
for each above class give 3 examples
M- glucose, fructose, galactose
D- maltose, lactose, sucrose
O- raffinose, stachyose, verbascose
P- starch, fiber/cellulose, glycogen
what are the 22 basic types of monosaccharides and how do they differ structurally and chemically
aldose- aldose functional group
ketose- ketone functional group
see pictures
What is the general molecular formula for monosaccharides
Cx(H2O)x
for a 5-carbon aldose, draw the general structure identifying the important parts and how the carbon is numbered
for a 5-carbon ketose, draw the general structure identifying the important parts and how the carbon is numbered
see pictures (5 and 6)
describe a fisher projection for a simple monosaccharide and how the different structural isomers are shown
number 1 carbon is on top, the horizontal line groups are always pointed above the page
look at picture
identify the anomeric carbo for the 2 types of monosaccharides and explain how they are identified
#1 carbon for aldose + #2 carbon for ketose
anomeric carbon has 2 oxygen bonded to it
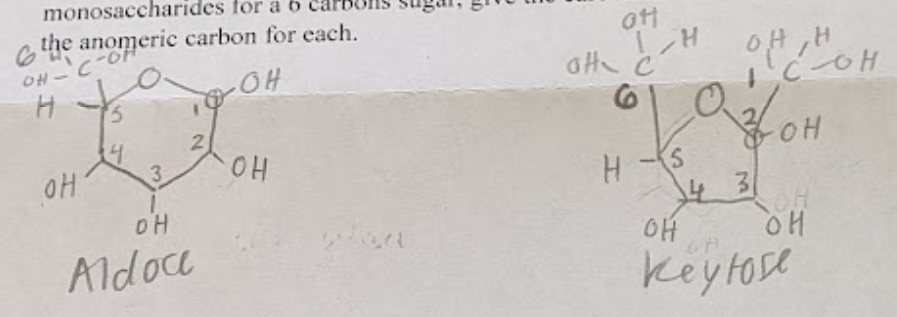
what is glycation and what health effect does it have
excessive glucose in the blood due to diabetes
leads to complications in diabetes
non enzymatic reaction where monosaccharides form a covalent bond protein molecule such as a fibrinogen, collagen, and protein which denature them
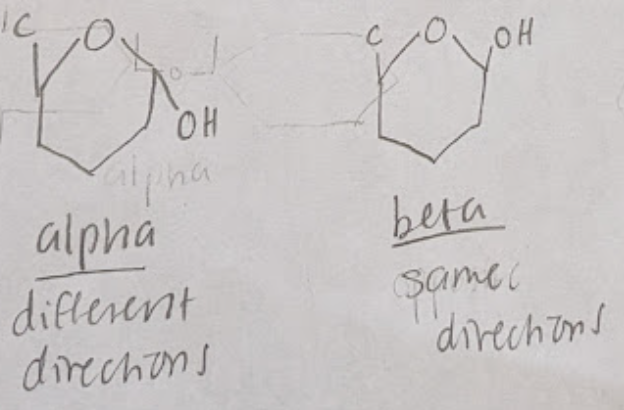
What is the difference between an alpha and beta monosaccharide ring structure isomer?
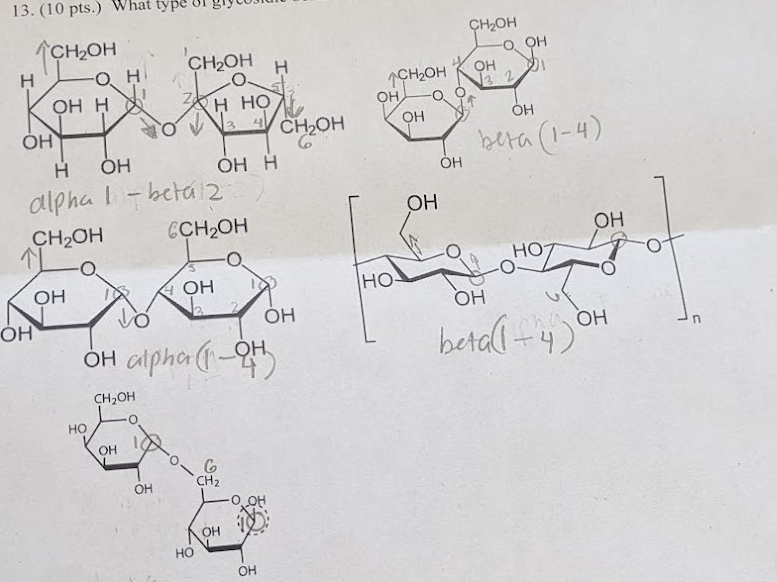
describe what a glycosidic bond is, the different types, and how they are named
glycosidic bond- condensation reaction (removal of water) between the anomeric carbon on one monosaccharides and any of the hydroxide groups on the second monosaccharides
alpha (1-4) because of the carbons bonded together
beta (1-4) because of the carbon bonded together
what type of glycosidic bond is shown for each molecule
which simple sugar is the sweetest
fructose- 173
what are the two type sof starch and how are they different
amylose- few/ no branches, softer
amylopectin- many branches, firmer
what is the difference between straight chain and branch glycosidic bonds in starch
branch- softer matrix (alpha 1-6)
straight- firmer matrix (alpha 1-4)
explain what ABO blood types are chemically and why they are important
AB- receive from anyone, only give blood to AB
O- universal doner, only receive from another O
important so that your immune system does not attack you
what kind of sugar is teh following
number the carbons correctly
what is glycation
give the name of the glycosidic bond formed for the following sugar