The Phosphorus Cycle and Nitrogen Cycle
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
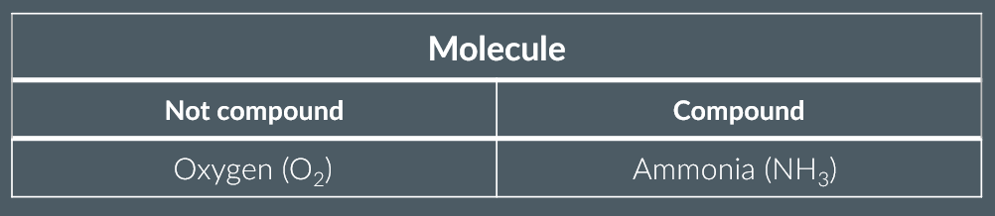
compounds
molecule of oxygen……….
contains more than one element
isn’t classed as a compound since it only contains oxygen atoms.
Plants absorb phosphorus in the form of…
phosphoric acid.
phosphate.
phosphide.
phosphine.
B
The waste of both plants and animals is broken down by…
mycorrhizae.
saprobionts.
decomposers.
phosphate-fixing bacteria.
B
Phosphate is commonly found in…
rocks.
the atmosphere.
salts.
A
Due to harsh …….. conditions, causing whethering of rock, phosphate ions are relased into ……… whcih can be taken up y …….. eatern by ……. re relased into soil through defication/dead animals or is …………../……….. into bodies of water (eg sea) and over thousands of years, used to form ……… rocks
weather
soil
plants
animals
transported/leeches
new
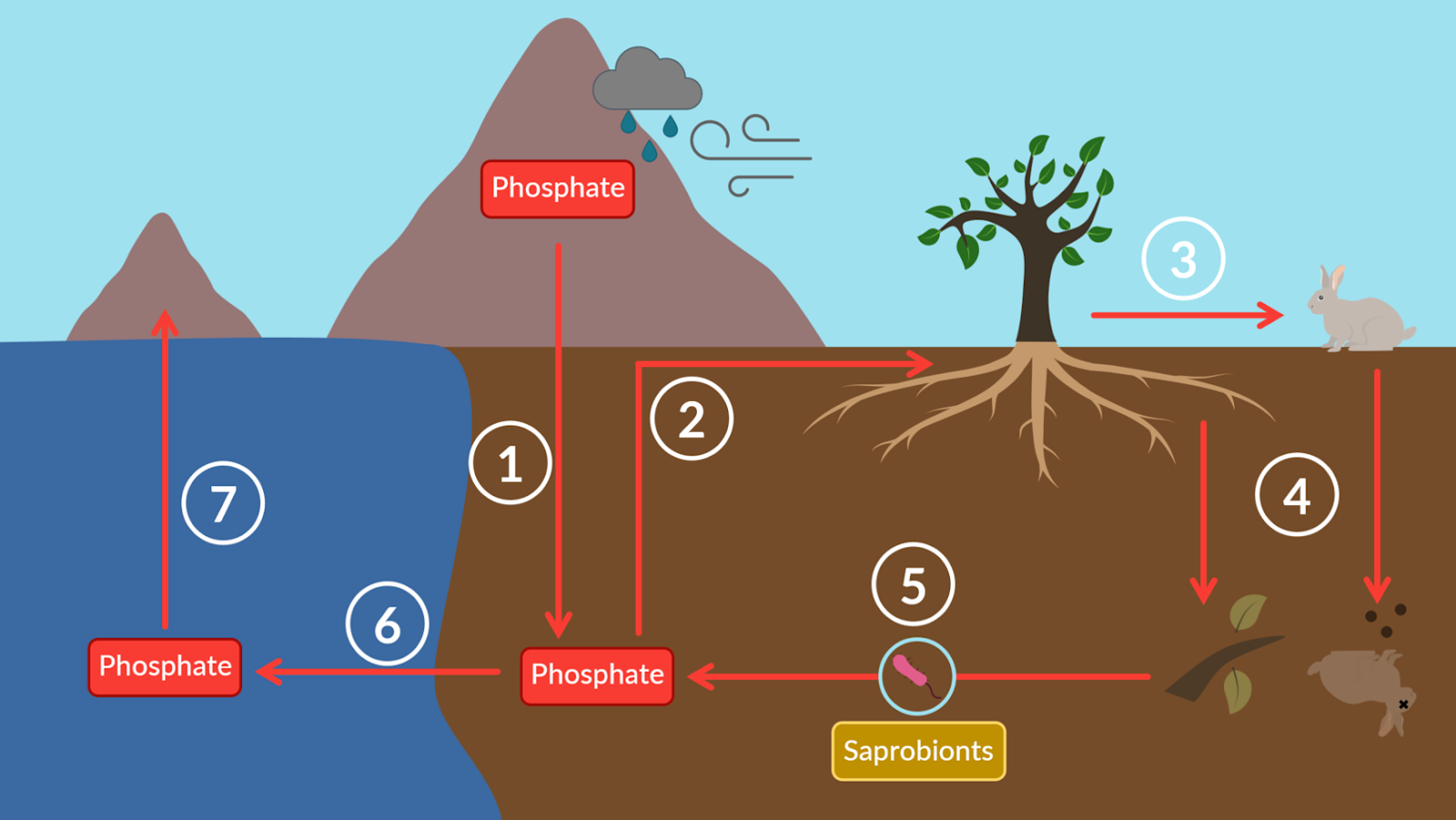
Everything you need to know about the phosphorus cycle is summarised in the diagram below:
Rocks contain phosphate. Harsh weather conditions break down rocks, releasing phosphate into the soil.
Some phosphate is absorbed by plants to make phosphate-containing compounds like ATP.
Plants are eaten by animals, which can then make their own phosphate-containing compounds.
Both plants and animals die, and animals also excrete.
The waste of animals and plants is broken down by saprobionts, releasing phosphate back into the soil.
Some phosphate moves throughout the soil to bodies of water, like the sea.
Over thousands of years, phosphate is used to form new rocks.
Phosphate originates from…
the oceans.
plants.
rocks.
urine and faeces.
C
The waste of animals and plants is broken down by ……… -bionts.
sapro
Saprobionts release phosphates into the soil. What happens to these phosphates?
Select all that apply
They move throughout the soil to bodies of water, like the sea.
They are reabsorbed by plants to make phosphate-containing compounds.
They are used to further decay animal and plant waste.
They are reabsorbed by saprobionts to make phosphate-containing compounds.
A B
Describe the stages of the phosphorus cycle
Rocks contain phosphate.
Harsh weather conditions break down rocks, releasing phosphate into the soil.
Some of this phosphate is absorbed by plants to make phosphate-containing compounds like ATP.
Plants are eaten by animals, which can then make their own phosphate-containing compounds. Plants and animals die, and animals also excrete. The waste of animals and plants is broken down by saprobionts, releasing phosphate back into the soil.
Some phosphate moves throughout the soil to bodies of water, like the sea.
Over thousands of years phosphate is used to form new rocks - after which the phosphorus cycle repeats.
Plants absorb phosphate to form biological molecules containing phosphorus. Which of the following might the plant make?
Select all that apply
Cellulose
Triglycerides
ATP
DNA
C D
A natural event occurs that causes weathering to local mountains and produces rockfalls. Some time later, nearby crops start to grow better than identical crops further away.
Suggest why, using your knowledge of the phosphate cycle.
Rock contains phosphate.
The area near rock weathering and rockfalls is likely to receive additional phosphate into the soil.
As a result, nearby crops are able to absorb more phosphate (compared to crops further away).
If all other conditions are the same, crops that absorb more phosphate will be able to produce more ATP to grow. In contrast, identical crops further away will receive less phosphate and grow at a slower rate.
Describe how dead organisms are utilised in the phosphorus cycle.
Dead organisms within the soil attract saprobionts.
These saprobionts break down phosphorus-containing compounds to phosphate.
The phosphate is either moved into bodies of water to form rocks, or directly absorbed by plants through the soil.
The majority of plants obtain nitrogen in the form of…
ammonium ions.
nitrite.
nitrate.
nitriles.
C
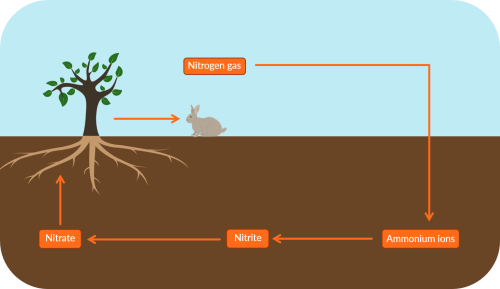
To get from nitrogen gas in the atmosphere to nitrate in the soil, nitrogen gas is first converted to…
nitrate.
nitrite.
nitriles.
ammonium ions.
This is/these are then converted to…
nitrate.
nitrite
nitriles.
ammonium ions.
D
B
What’s needed for these conversions in the nitrogen cycle to take place?
Saprobionts
Bacteria
Fungi
B
Bacteria in the roots of some plants convert nitrogen gas to the same nitrogen-containing compound as their free-living counterparts.
So, they convert nitrogen gas to…
ammonia.
ammonium ions.
nitrate.
nitrite
A
The process of converting nitrogen gas into ammonia is known as…
ammonification.
nitrogenation.
nitrogen fixation.
nitrification.
C
There are two types of nitrogen-fixing bacteria. These are…
Select all that apply
mutualistic.
soil-living.
free-living.
root-dwelling.
A C
fREE living nitogen fixing bacteria:
exist in the soil
convert nitrogen gas → ammonia→ ammonium ions
MUTUALISTIC nitrogen fixing bacteria:
exist in teh plant roots
convert nitorgen gas to be immedicately used by plant to make nitorgen containing compounds eg DNA
and receives carbohydrates from plant in return