Farm Animal Nursing - Equine Radiology
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
1 - Milliamperage (mA)
2 - Exposure time
3 - Kilovoltage
4 - Focal film distance
Identify the four factors that make up a radiograph
Milliamperage (mA)
Controls the amount of x-ray production at the target area
Degree of darkness on the image
What does radiographic density refer to?
Radiographic density increases
If you increase the mA setting, what happens to the radiographic density?
Radiographic density decreases
If you decrease the mA setting, what happens to the radiographic density?
Affects how long the x-rays are being produced for
What is exposure time?
To reduce blur caused by movement
Why would you want to decrease exposure time?
Kilovoltage potential (kVp)
Regulates the energy of the radiograph and is responsible for the contrast of the image
• Increases the density of the image
• Decreases the contrast of the image
What happens if you increase the kVp setting?
Focal film distance
The distance between the target and the radiographic film
• The number of x-rays reaching the film decreases
• Images are less detailed
• More scatter radiation
• If doubled, radiation intensity decreases by a factor of 4
What happens as you increase the focal film distance?
kVp
Which setting has the greatest influence on the quality of a radiograph?
Directed parallel to the ground and perpendicular to the midsagittal plane
Where should the beam be directed when shooting a radiograph?
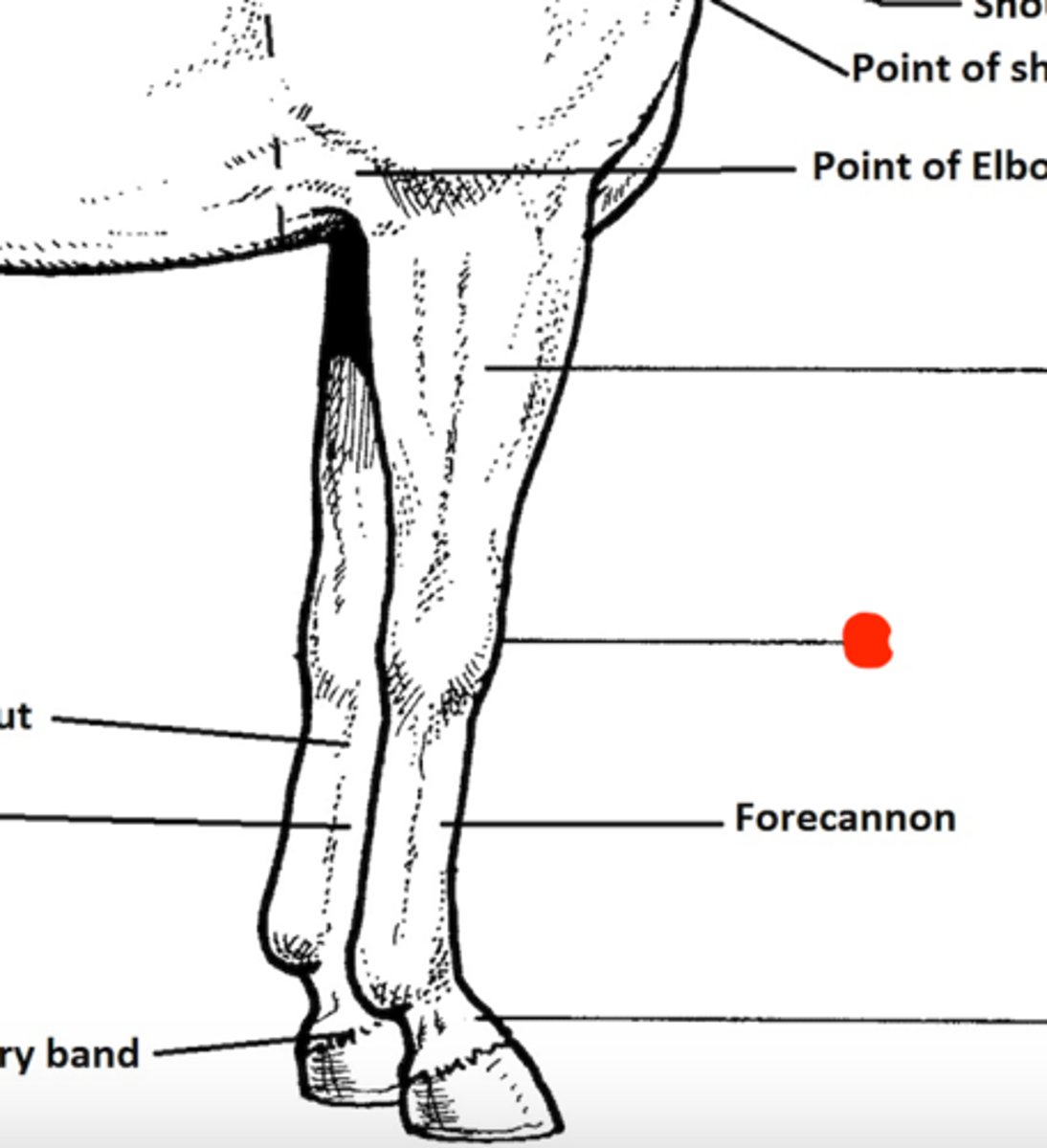
Carpus (knee, forelimb)
Identify the structure marked by the red dot
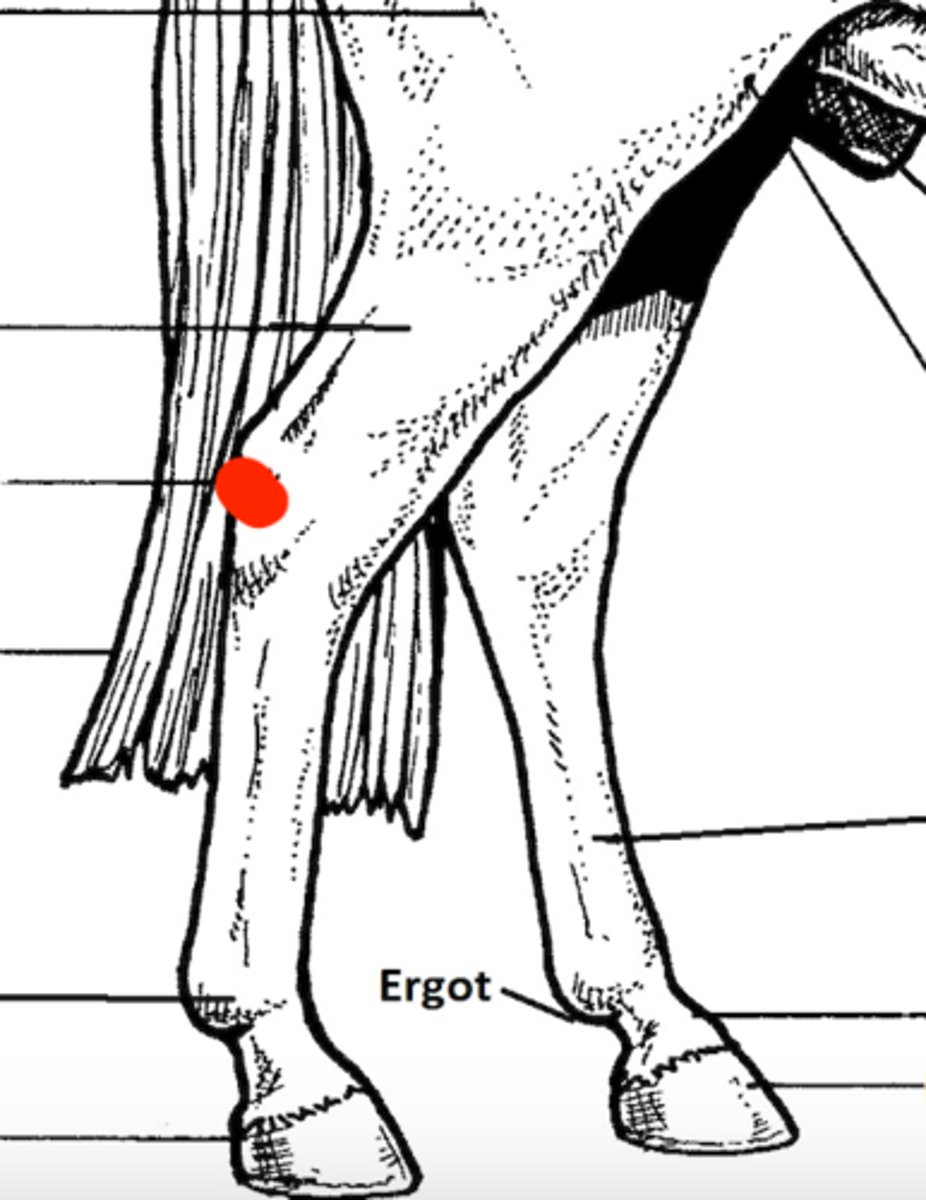
Tarsus (hock, hindlimb)
Identify the structure marked by the red dot
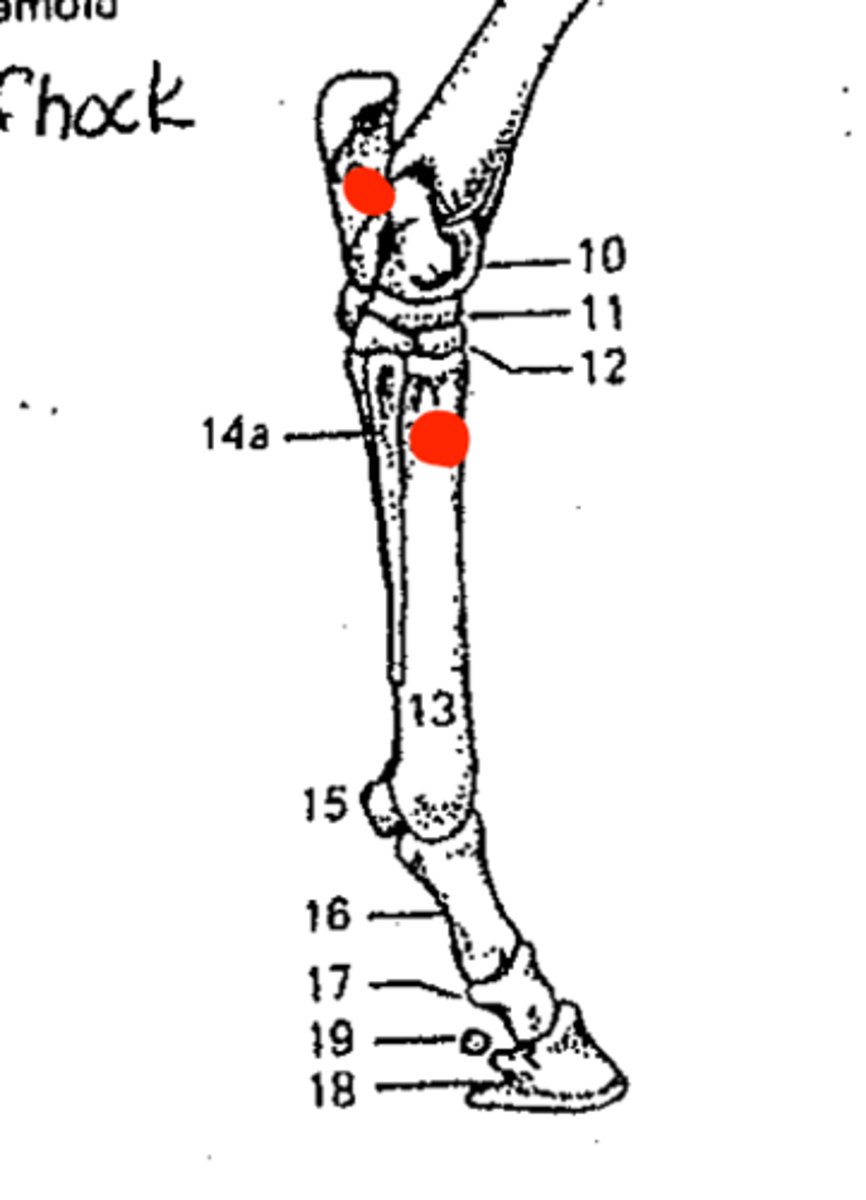
Top - Tarsus (hock)
Bottom - Metatarsus
Identify the structures marked in red from top to bottom
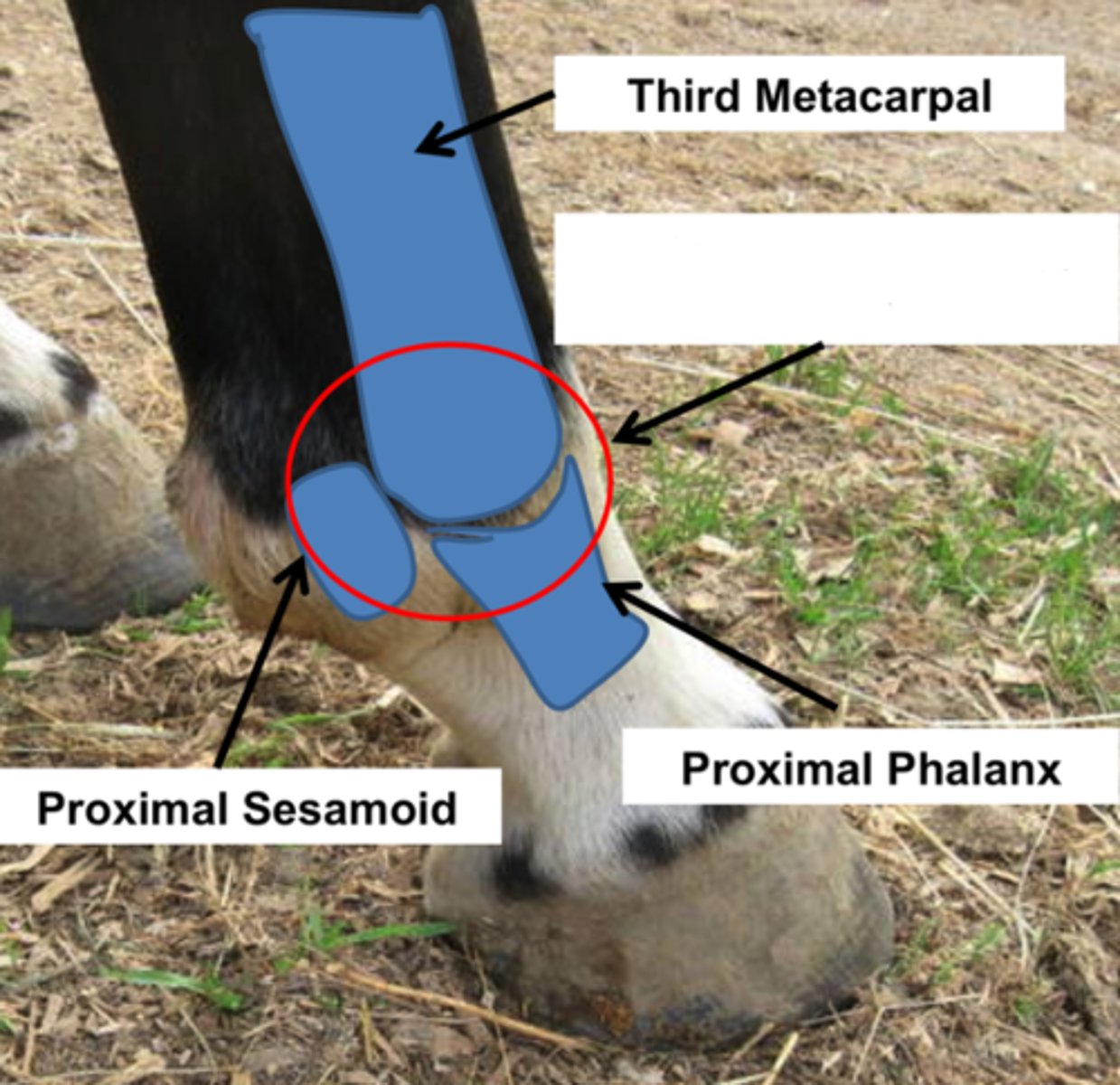
Metacarpophalangeal joint (forelimb)
Identify the structure circled in red
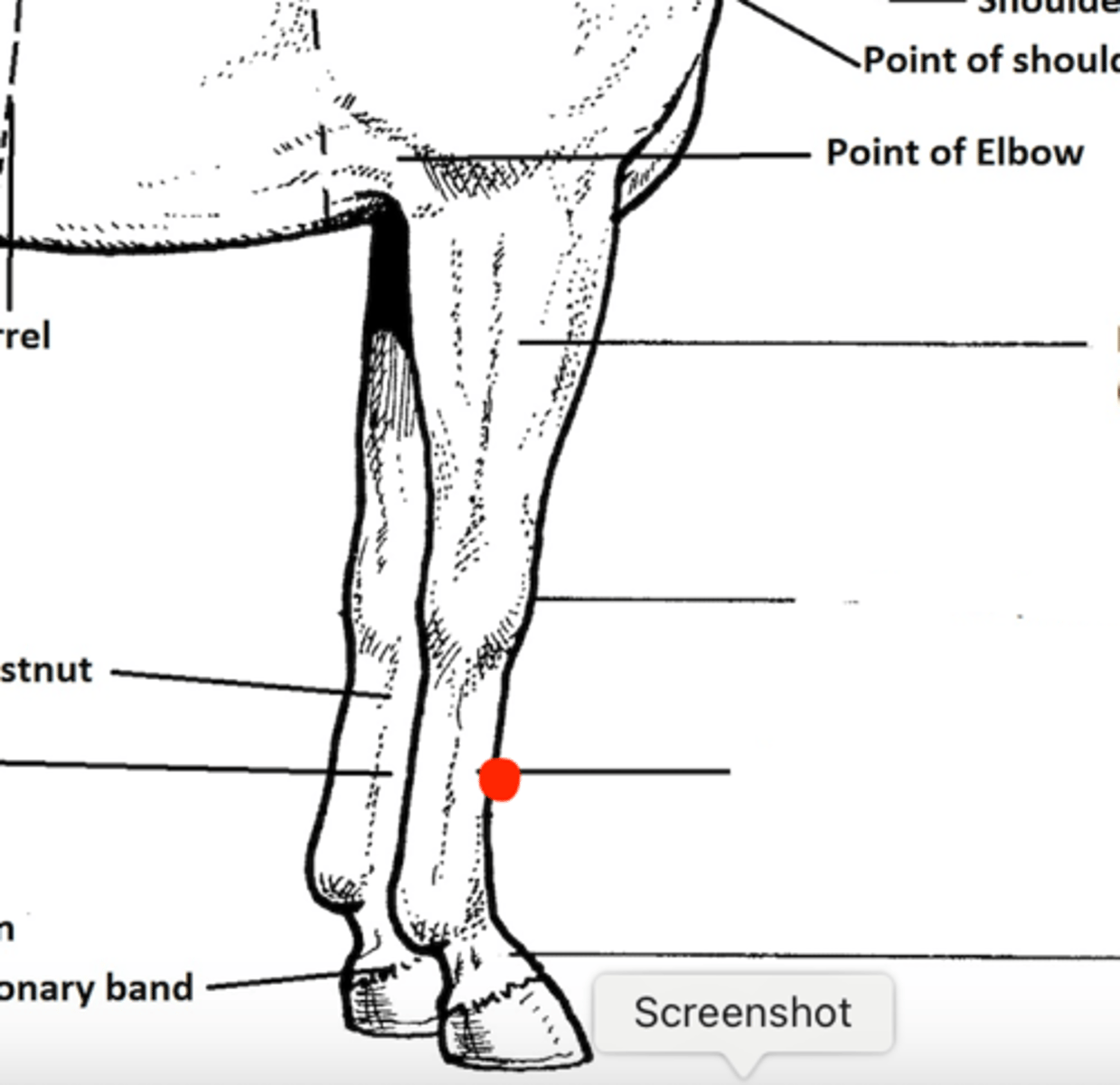
Metacarpus
Identify the structure marked by the red dot
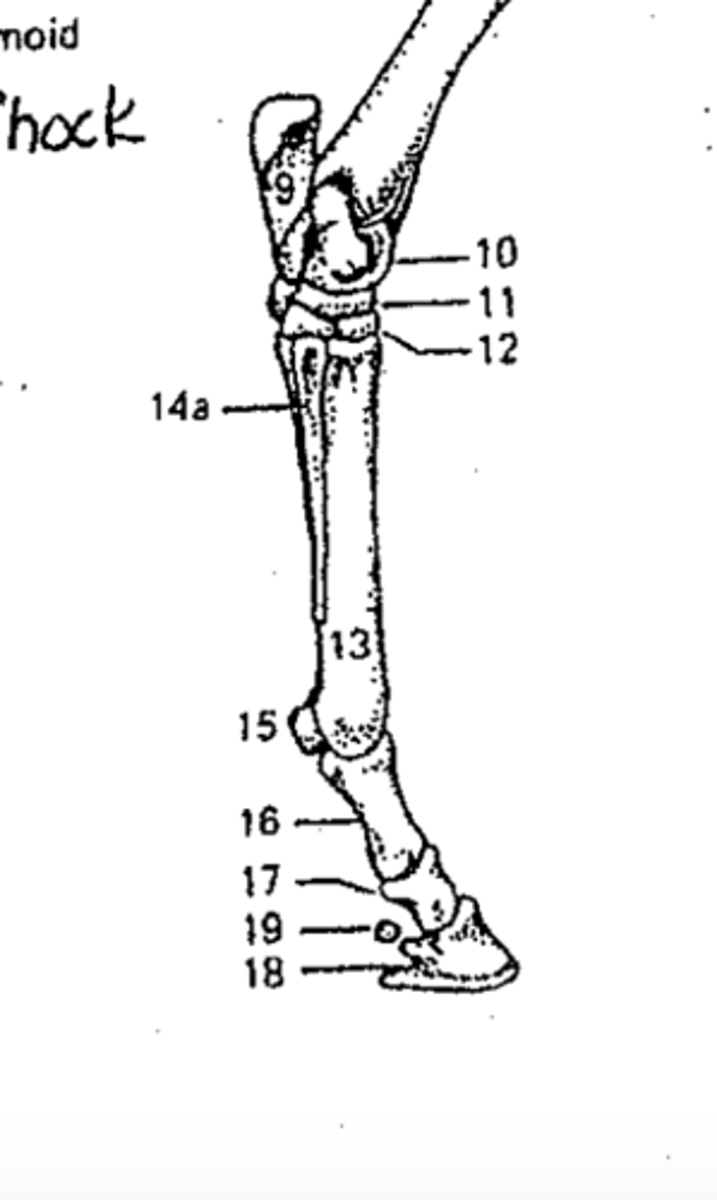
Distal sesamoid (navicular bone)
Identify the structure marked #19
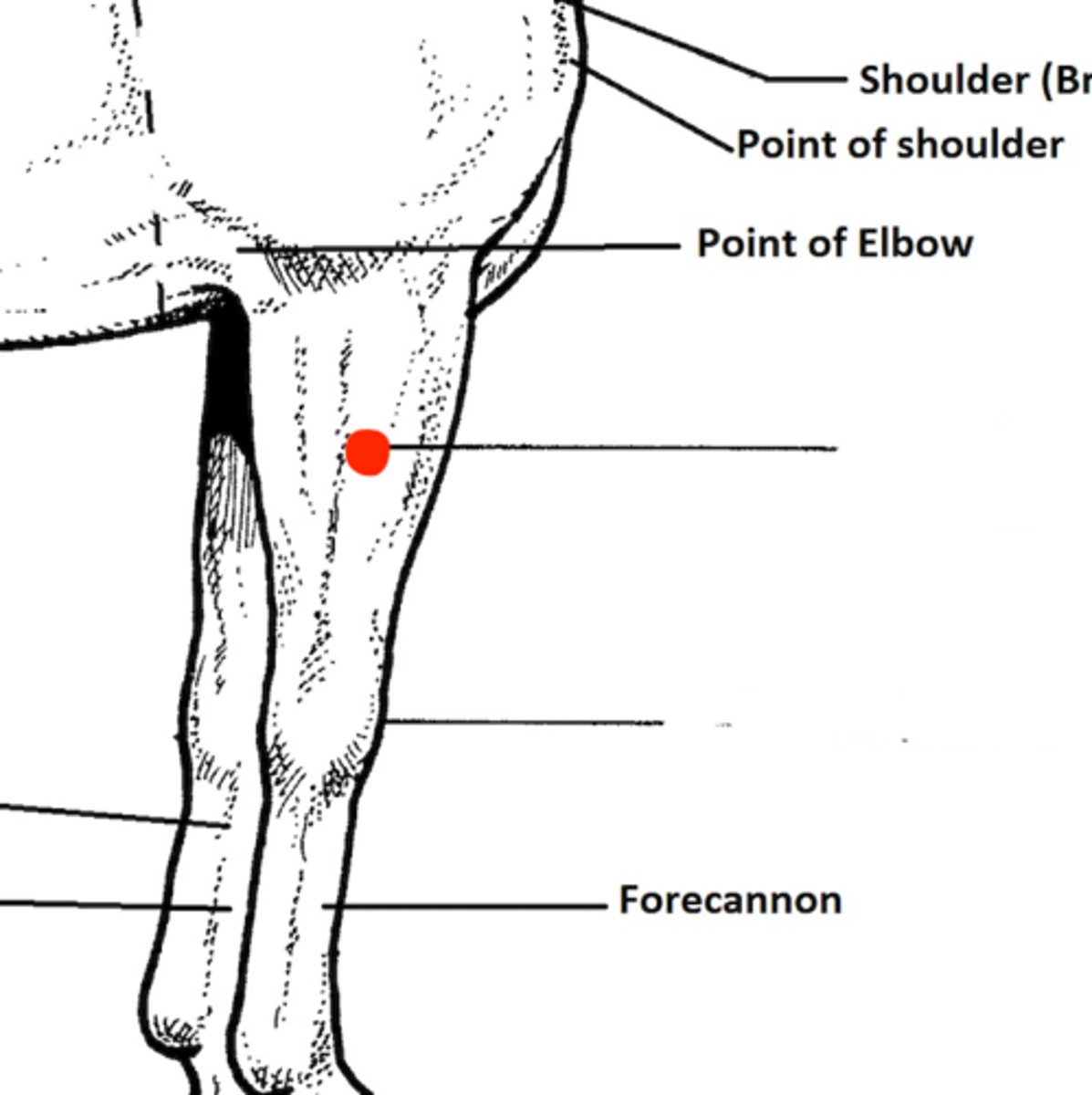
Brachioantebrachial articulation (between elbow and carpus)
Identify the structure marked by the red dot
Third phalanx (coffin bone or distal phalanx)
Identify the structure marked by the red dot

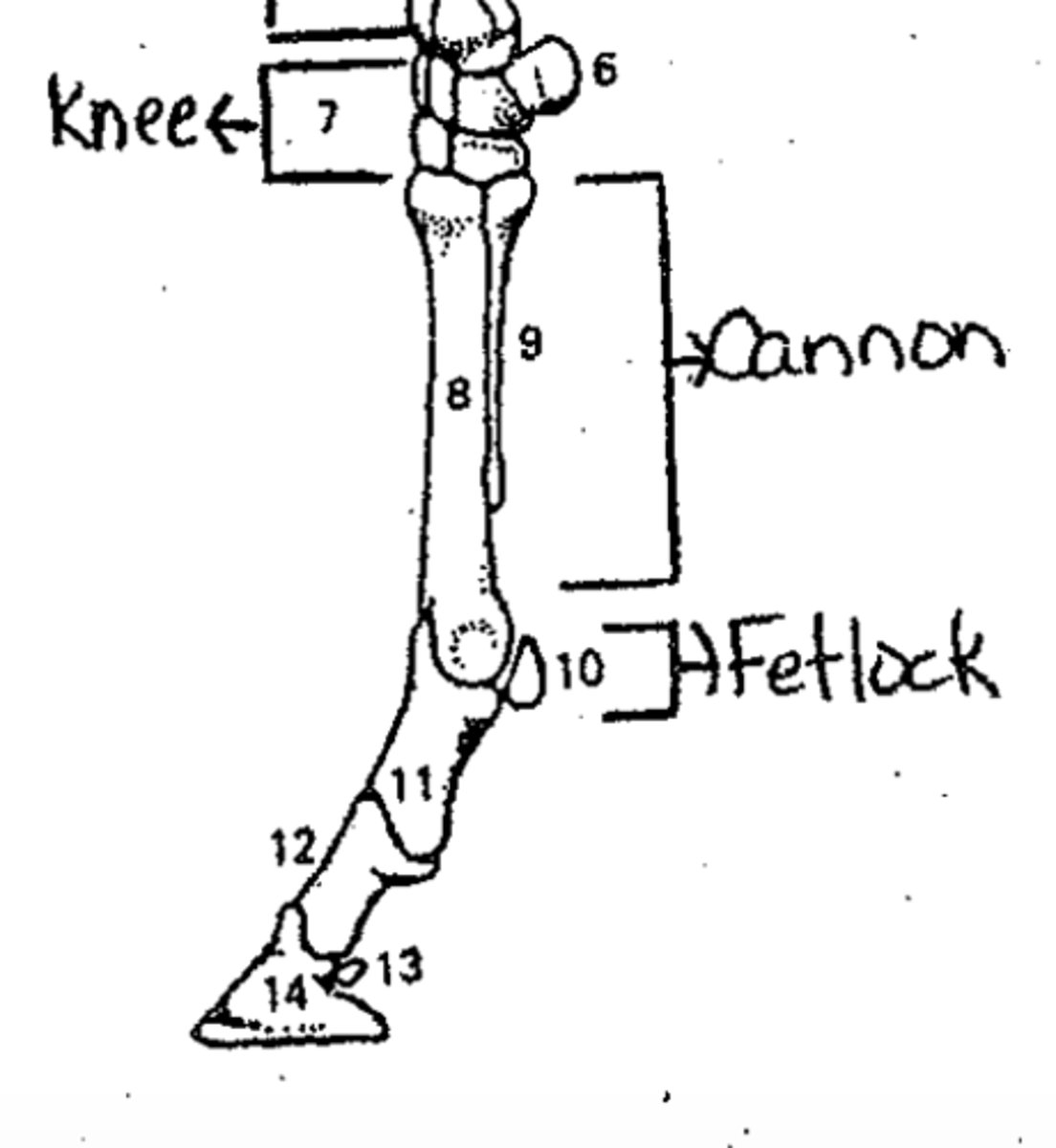
13 - Distal sesamoid (navicular bone)
14 - Third phalanx (coffin bone or distal phalanx)
Identify the names of structures 13 and 14
Diagonal view
What does oblique positioning refer to?
Palmar refers to back of front limbs
Plantar refers to the back of the hind limbs
What is the difference between palmar and plantar?
Front to back referring to structures below the knee
What direction does dorsal palmar refer to?
Front to back referring to structures above the knee
What direction does cranial caudal refer to?