Tissues (epithelial, connective & muscle)
1/144
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
145 Terms
The three basic types of fibers that found in connective are
collagen, reticular, and elastic
The dominant fiber type in dense connective tissue is
collagen
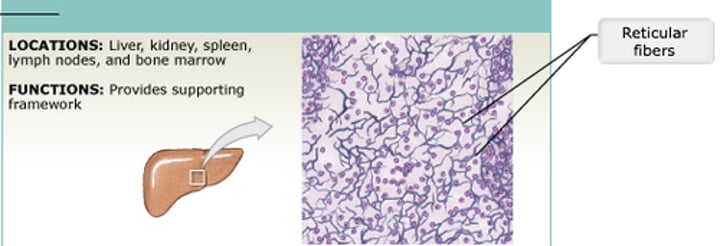
The framework of organs such as the spleen and liver is made up of _________ tissue
reticular tissue
The type of tissue that consists of living cells embedded in a non-living extracellular matrix is
Connective
Connective tissue
the most extensively distributed body tissue
consists of cells and the extracellular matrix those cells secrete
Examples of connective tissue
Cartilage
Adipose
Bone
Blood
areolar, and reticular tissue
tendons
The matrix of a connective tissue consists of _____.
Ground substance and fibers
extracellular matrix, which surrounds connective tissue cells, consists of a variety of different protein fibers and a ground substance. The type of fibers and components of the ground substance varies depending on the tissue type. Generally, the ground substance consists of
polysaccharides and proteins, which are secreted by the connective tissue cells. The ground substance can range from liquid (blood and lymph) to semi-solid (cartilage) to solid (bone).
The three types of protein fibers found in connective tissue are
collagen fibers, elastic fibers, and reticular fibers
Which of the following are NOT functions of connective tissue?
Performs absorption and secretion
Adipose tissue functions to
store triglycerides, protect internal organs, and insulate against heat loss
Tendons, which are formed by
dense regular connective tissue, attach muscles to bone.
elastic cartilage in the ear has what function
maintains shape while affording flexibility
Dense irregular connective tissue forms a
fibrous capsule found around organs and in the joints
blood functions to
transport gases, wastes, and nutrients as well as to provide immunity
fibroblast
immature cell found in loose and dense connective tissues that can still divide and secrete matrix
chondrocyte
mature cell found in cartilage. Wharton's jelly is an embryonic connective tissue found primarily in the umbilical cord
extracellular matrix
surrounds mature connective tissue cells
the extracellular matrix consists of a variety of different protein fibers and a ground substance. The three types of protein fibers found in connective tissue are
collagen fibers, elastic fibers, and reticular fibers.
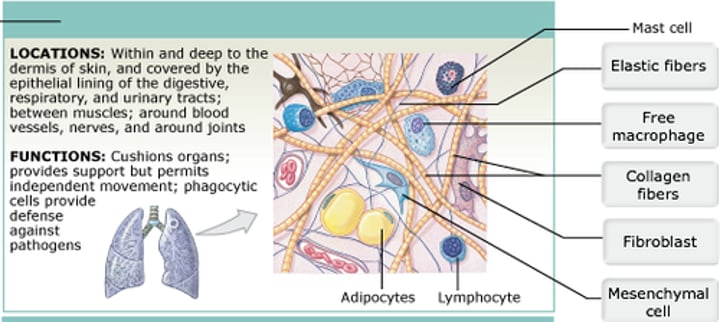
Areolar Tissue
(Loose Connective Tissue)
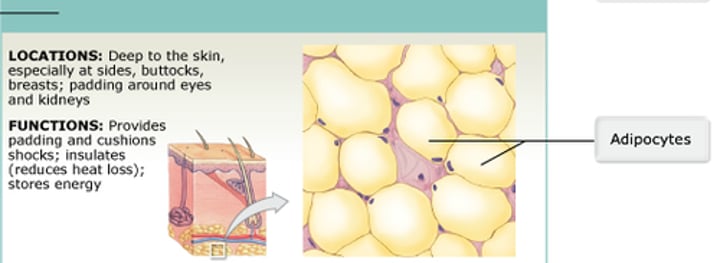
Adipose Tissue
(Loose Connective Tissue)
Reticular Tissue
(Loose Connective Tissue)
What are the Tree types of Loose Connective Tissues
Areolar
Adipose
Reticular
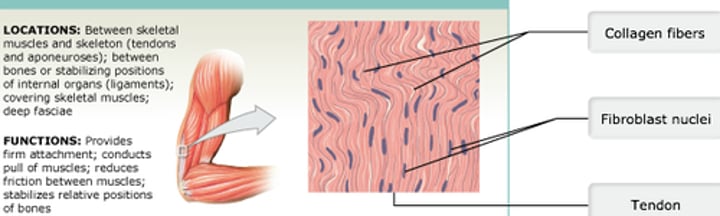
Regular
(Dense Connective Tissue)
Irregular
(Dense Connective Tissue)
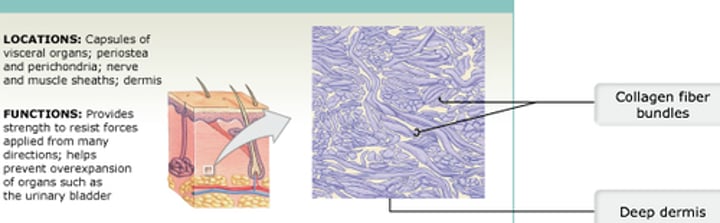
Elastic
(Dense Connective Tissue)
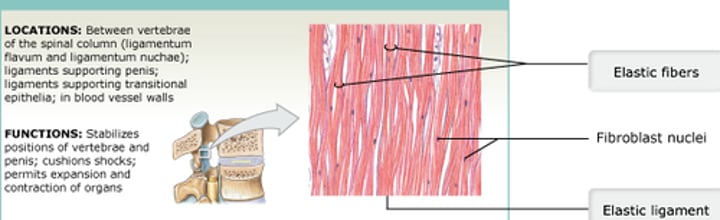
What are the Three types of Dense Connective Tissue
Regular
Irregular
Elastic
What is the correct statement which best describes adipose tissue?
It stores lipids.
All of the following are cell types of connective tissue proper
adipocytes
fibroblasts
macrophages
Which type of connective tissue stabilizes the positions of the vertebrae, cushions shocks, and permits expansion and contraction of organs?
elastic tissue
What type of connective tissue is found between skeletal muscles and skeleton?
dense regular connective tissue
Which of the following types of connective tissue stores triglycerides, prevents heat loss, and provides cushioning and support for internal organs?
Adipose tissue
what type of connective tissue functions to store triglycerides, protect internal organs, and insulate against heat loss.
Adipose tissue
Which of the following types of tissue forms the fascia, ligaments, and tendons?
Dense regular connective tissue
What kind of connective tissue consists of many thick (dense) collagen fibers arranged in primarily parallel bundles, forms tendons and ligaments, surrounds skeletal muscles, and forms the fasciae
Dense regular connective tissue
What is the most abundant fiber present in dense irregular connective tissue?
Collagen
What type of connective tissue consists of fibroblasts scattered throughout collagen fibers that have a random or irregular arrangement. This tissue type is typically found in the dermis of the skin, as well as in the fibrous capsule that surrounds organs and joints.
Dense irregular connective tissue
Elastic tissue is a type of ____ connective tissue.
dense
Elastic tissue has elastic fibers rather than __________ in the __________, which allow for stretching of various organs
collagen fibers ; extracellular matrix
Both blood and lymph are examples of
connective tissues.
The protein fibers of both blood and lymph are dissolved in the
matrix
The functions of bone include
support, protection, serving as the site of muscle attachment (thereby enabling movement), and housing the cells that form blood.
The solid matrix found in bone consists of
calcium salts crystallized on collagen fibers.
Compact bone is composed of long cylindrical columns called
osteons
The most common type of cartilage found in the body occurs at the end of most long bones in the joints, in the larynx, in the rings of the trachea (windpipe), and in the septum of the nose. Name this type of cartilage.
Hyaline cartilage
What is the most common type of cartilage?
Hyaline cartilage
What does the embryonic skeleton consists of that has a gelatinous matrix and provides flexible support, and latter ossifies to form bone
Hyaline cartilage
Which type of cartilage forms intervertebral discs, the pubic symphysis, and the meniscus in the knee?
Fibrocartilage
What type of cartilage is very strong rigid kind of tissue, is located where bone movement is limited and is used to provide support to joints that have great compressive forces working on it.
Fibrocartilage
Which statement best describes connective tissue?
usually contains a large amount of matrix
Connective tissue matrix is composed of __________.
ground substance and protein fibers
Which fiber type provides connective tissue strength?
collagen
Adipocytes
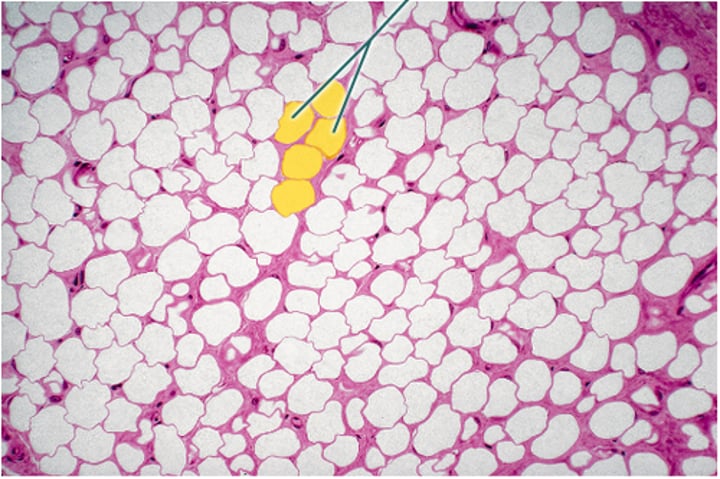
Osteoblasts
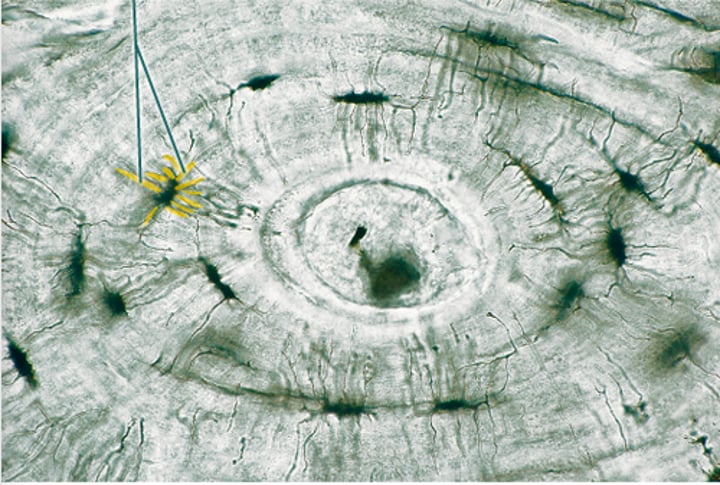

Chondrocytes
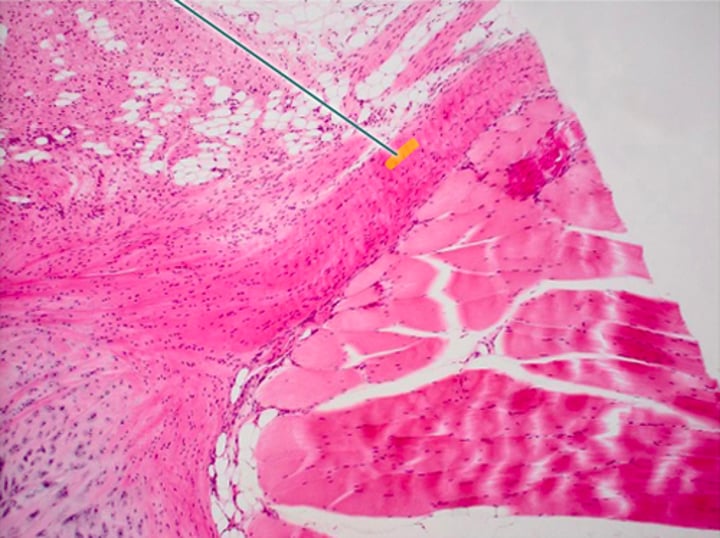
Collagen
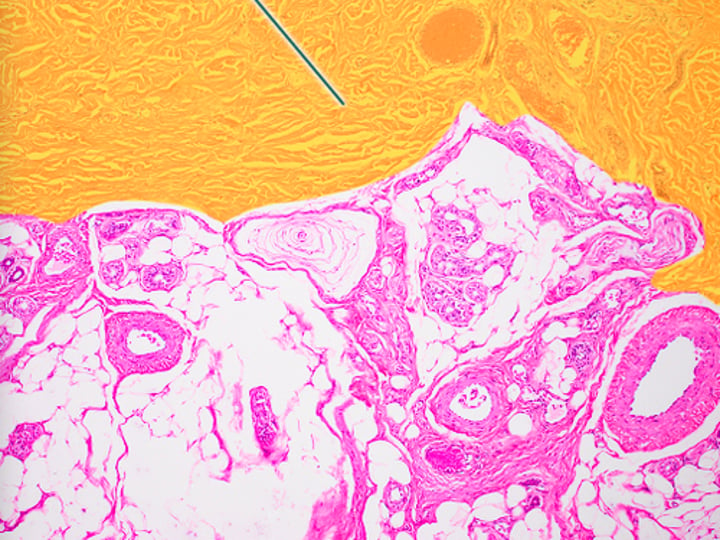
Fibrocartilage
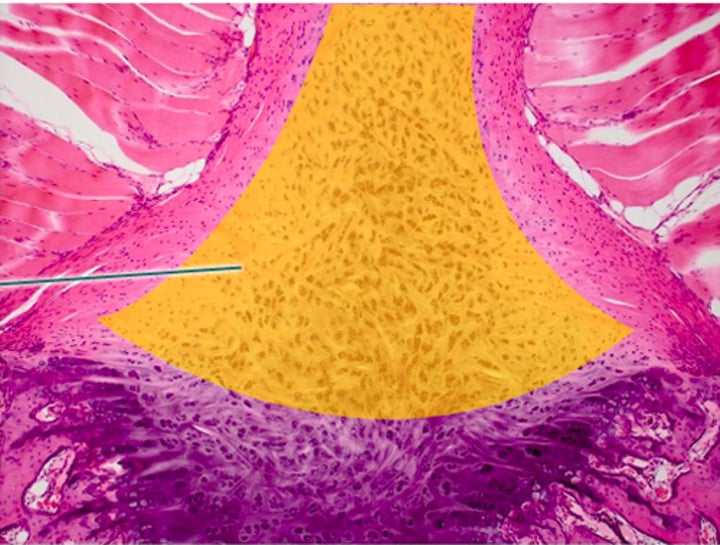
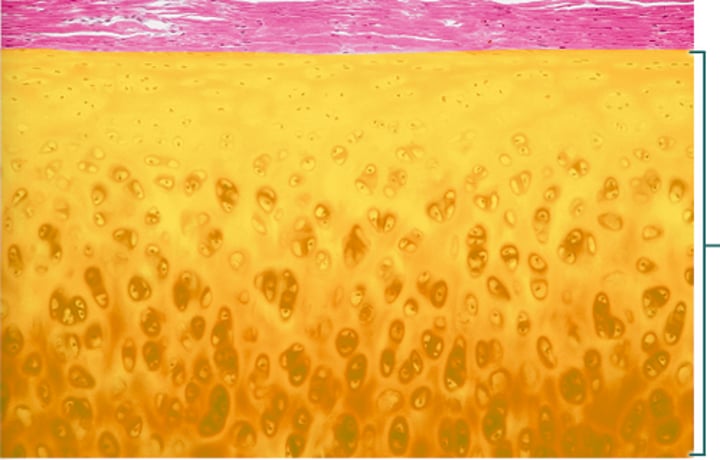
hyaline cartilage
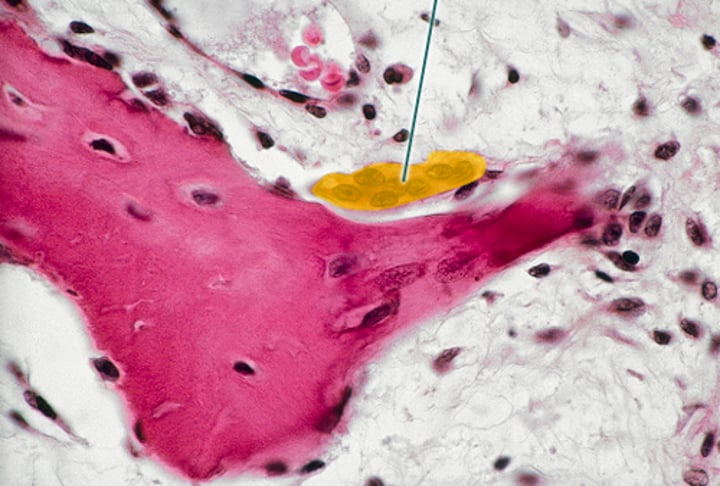
Osteoclast
reticular fibers
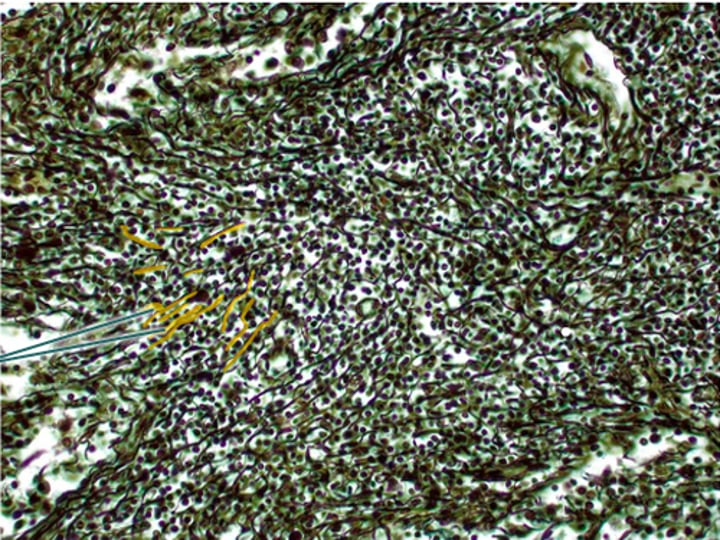
initiates an inflammatory response
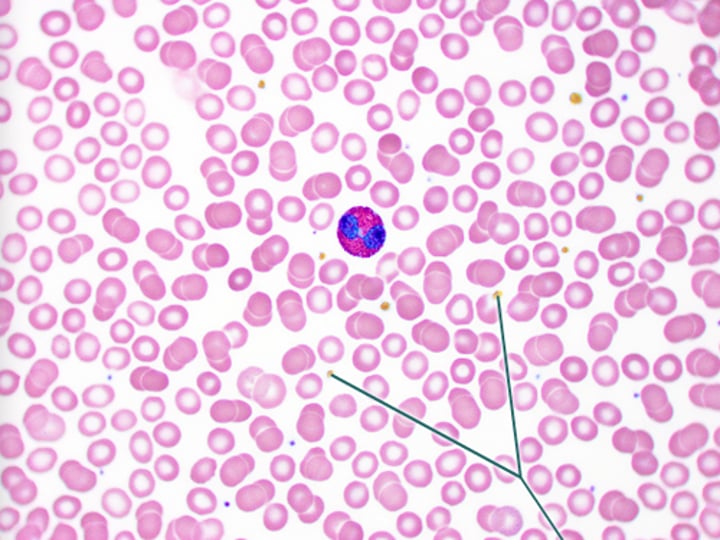
WBC
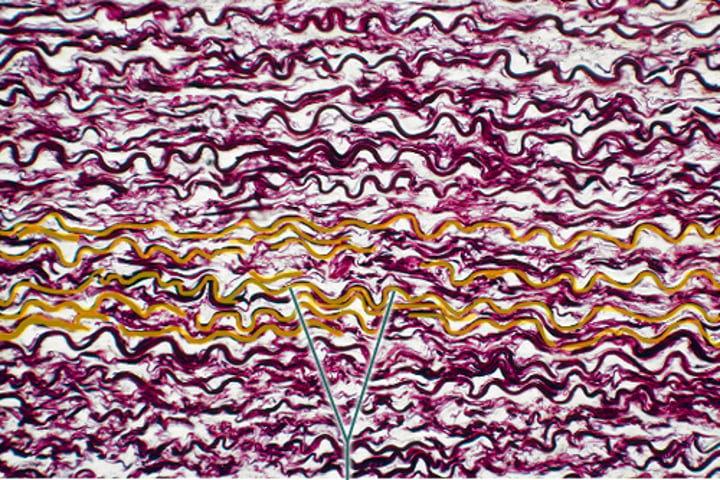
The highlighted fibers are produced by what cell type?
fibroblast
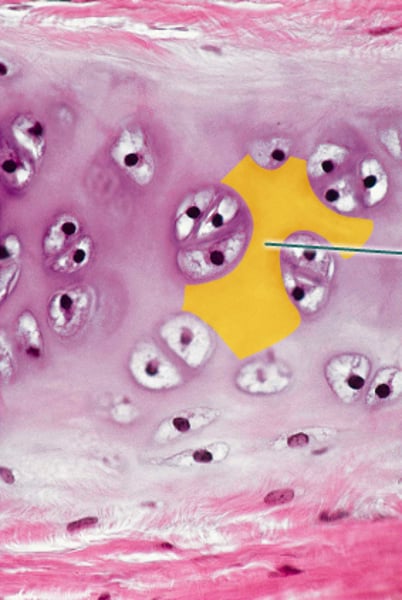
Which component of the connective tissue in this field of view is highlighted?
extracellular matrix
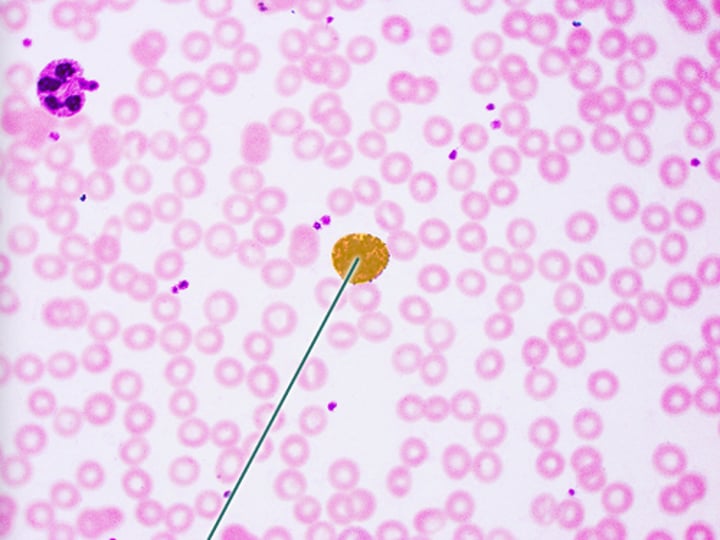
platelets
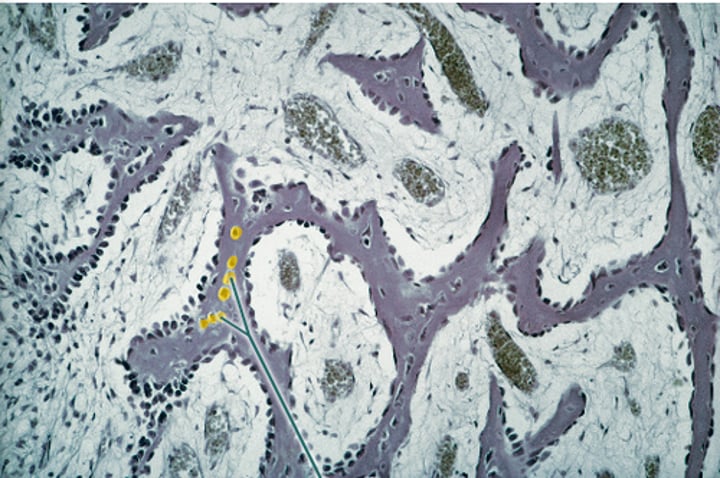
osteocytes in lacunae
Define tissues
A group of similar cells that performs a specialized function.
List the 4 major types of tissue.
1) epithelium
2) connective
3) muscle
4) nervous
Where is epithelial tissue generally found?
covering organs, lining body cavities, lining hollow organs, part of most glands
What are the 4 basic functions of epithelium?
1) protection
2) secretion
3) absorption
4) excretion
Types of epithelial membranes:
1) serous
2) mucous
3) cutaneous
Mucous epithelial membranes perform these functions:
1) line tubes and organs that open to the outside world
2) lining of the mouth, nose, throat, etc.
3) secrete mucus
Epithelial tissue is ______ (no blood vessels) and has to get all needed materials through _____.
avascular; diffusion
Epithelial tissue is classified according to
cell shape and the number of cells
What is a basement membrane?
a layer of nonliving tissue that anchors epithelium to underlying connective tissue.
What is the purpose of the basement membrane?
to anchor epithelial layer to the tissues beneath it
What is simple epithelium?
epithelium only one cell layer thick
List the 4 types of simple epithelium and give an example of each:
1) simple squamous (ex: air sacs in lungs)
2) simple cuboidal (ex: kidney tubules)
3) simple columnar (ex: inner lining of the digestive tract)
4) pseudostratified columnar (ex: inner lining of the respiratory tubes)
Characteristics of simple squamous epithelium:
single layer of flat cells
substances pass easily through
line the air sacs, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels
Characteristics of simple cuboidal epithelium:
single layer of cube-shaped cells
line kidney tubules, ducts of some glands, and cover the ovaries
Characteristics of simple columnar epithelium:
single layer of elongated cells
often have goblet cells
line the uterus, stomach, intestines
make mucus
sometimes possess cilia and microvilli
Clue: elongated nuclei
Characteristics of pseudostratified columnar epithelium:
single layer of elongated cells
appear striated
often have cilia and goblet cells
line respiratory passageways
What is stratified epithelium?
epithelium that is more than one layer thick
List the 3 types of stratified epithelium and give an example of each:
1) stratified squamous (ex: skin)
2) stratified cuboidal (ex: gland ducts)
3) stratified columnar (ex: line the male urethra)
Characteristics of stratified squamous epithelium:
many cell layers
top cells are flat
can accumulate keratin
outer layer of skin, line oral cavity, throat, vagina, and anal canal
Describe glandular epithelium and explain its function:
cells usually columnar or cuboidal
one or more cells = a gland
Function is to produce and secrete substances into ducts or body fluids.
What do exocrine glands do? give an example
secrete product into ducts. The ducts open onto some surface (internal or external).
ex: sweat glands
What do endocrine glands do? give an example
secrete product directly into tissue fluid or blood (ductless).
ex: hormone glands
List the exocrine glands classified by the way they secrete their product. Describe the way each secretes its product. Give an example:
1) Merocrine glands - release watery, protein-rich fluids by exocytosis. (ex: sweat and salivary glands)
2) Apocrine glands - small pieces of the cell containing product are pinched off into duct. (ex: mammary and ceruminous [ear wax] glands)
3) Holocrine glands - entire cells filled with product released into duct. (ex: sebaceous [skin oil] glands)
What is connective tissue's function?
1) bind structures (i.e. ligaments)
2) support and protection (conn. tissue around joint)
3) framework (skeleton)
4) fill spaces (loose conn. tiss. between muscles)
5) store fat
6) produce blood cells (bone marrow)
7) protect against infections (wht bld cells/immu. sys.)
8) help repair damaged tissue (scar tissue formation)
All connective tissue cells are surrounded by a substance (_______) they helped produce.
matrix
What is a matrix?
a mixture of :
1) connective tissue fibers
2) a ground substance (fluid/semisolid/solid)
__________ tissue is the most abundant tissue type.
Connective
List the 3 major types of connective tissue cells:
1) fibroblasts
2) macrophages
3) mast cells
Describe Fibroblasts:
-fixed cell
-large star-shaped
-most common type of connective tissue cell
-secrete protein fibers into matrix
Describe Macrophages:
-wandering cell
-important in defense
-specialized for phagocytosis (white blood cell)
-scavenge thru conn. tiss. for foreign particles
Describe Mast Cells:
-Fixed cell usually near blood vessels
-Releases Heparin (an anti-coagulant)
-Releases Histamines to help with inflammation and allergies.
List the 3 major types of connective tissue fibers:
1) Collagen
2) Elastin
3) Reticular Fibers
Describe Collagen fibers
-thick protein threads
-slightly elastic
-great tensile strength
-lots in the ligaments and tendons
-aka White Connective Tissue
Describe Elastin fibers
-thin elastic fibers
-form complex networks
-found in vocal cords
-aka Yellow Connective Tissue
Describe Reticular fibers
-very thin collagenous fibers
-delicate
-form complex networks
-support very delicate tissue like the spleen or tonsils