monoclonal antibodies exam q corrections
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are usually made using mouse lymphocytes.
Candida albicans infection produces serious symptoms in patients with a poor
immune system.
Recently scientists have produced mAbs to Candida albicans using human
lymphocytes produced naturally after an infection.
(a) Candida albicans lives in the throat of infected patients.
A sample is taken from the throat of a patient with a suspected Candida
albicans infection.
The sample is transferred onto a microscope slide.
Describe how the mAbs and a fluorescent dye could be used to see any
Candida albicans pathogens on the slide.
bind fluorescent dye to mAbs
1
put (bound) fluorescent mAbs on the slide (and rinse off)
ignore add mAbs and dye to slide
(unbound)
1
mAbs will bind to Candida albicans / pathogens and show up under
the microscope
allow mAbs will bind to Candida
albicans / pathogens and show up
under UV (lamp)
In a laboratory the human lymphocyte mAbs were injected into animals infected with Candida albicans.
The mAbs caused increased phagocytosis of the Candida albicans pathogens.
Doctors intend to start a trial to give the mAbs to patients severely ill with Candida albicans.
(b) Explain how increased phagocytosis of the Candida albicans pathogen will
help the patient.
more Candida albicans / pathogens will be engulfed / killed by phagocytes /
white blood cells
allow Candida albicans / pathogens will
be engulfed / killed by phagocytes /
white blood cells more quickly
do not accept white blood cells produce
antibodies
do not accept lymphocytes engulf
Candida albicans
1
therefore less damage to cells / tissues / organs
ignore less toxin released (by Candida
albicans)
A virus called RSV causes severe respiratory disease.
(a) Suggest two precautions that a person with RSV could take to reduce the
spread of the virus to other people.
any two from:
• regular hand washing
or
use hand sanitiser / alcohol gel
• cover nose / mouth when coughing / sneezing
allow wear a face mask
• put used tissues (straight) in the bin
• don’t kiss uninfected people
allow isolate patient from others
or
don’t share cutlery / cups / drinks with uninfected people
• clean / disinfect / sterilise surfaces regularly
ignore responses referring to infected people
Scientists have also used human lymphocytes to make mAbs to other
pathogens and to some types of cancer cells.
Suggest one reason why these new mAbs have been more successful in
treating diseases in humans than mAbs made using mice.
any one from:
• (the body will) not reject the mAbs
or (the body is) less likely to reject the mAbs
do not accept idea of rejection of cells
• mouse mAbs are (more likely to be) rejected
• the human lymphocytes have already responded to that
infection / cancer cell so they are known to work against the
disease
A trial was carried out to assess the effectiveness of using monoclonal
antibodies to treat patients with RSV.
Some patients were given a placebo.
(d) Why were some patients given a placebo?
as a control
or
to see / compare the effects of the treatment (vs. no treatment)

Evaluate how well the data in the table above supports the conclusion:
‘monoclonal antibodies are more effective at treating RSV than a
placebo’
(supports the conclusion because)
over double the number / % of patients (in the trial) were hospitalised with
the placebo (compared to MAB)
(does not support the conclusion because)
no information on patients not hospitalised / still unwell at home
or
other factors may have affected those admitted to hospital
allow correct named factor e.g. age / gender / other
illness
or
don’t know if it was a double blind trial
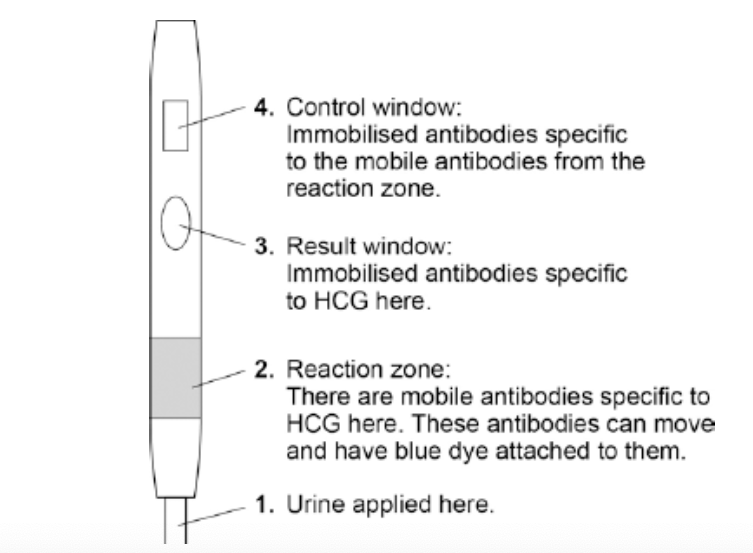
Figure 2 shows the parts of a pregnancy test strip.
The pregnancy test strip will show a positive test result when a woman is
pregnant.
Explain how the pregnancy test strip works to show a positive result.
(as) urine passes through reaction zone
HCG hormone binds to the mobile HCG antibody (in the reaction zone)
(passes up the stick) HCG hormone binds to the immobilised HCG
antibodies in the results zone
(the other) antibodies which do not attach to HCG
bind to antibodies in control zone
blue dye appears in both control and results zones (to show positive result)