Chem 109 Unit 2 Exam
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Terms for functional groups, isomers, polymers, biomolecules
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Carbonyl carbon/group
A carbon atom double bonded to an oxygen atom
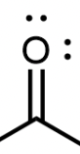
Aldehyde
A carbon atom double bonded to an oxygen atom and to a hydrogen atom
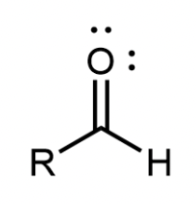
Ketone
A carbon atom partway along the chain is double bonded to an oxygen atom
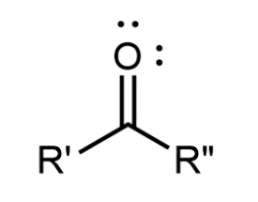
Ether
An oxygen atom found in the middle of the molecule, bonded to 2 different R groups (either or)
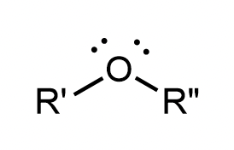
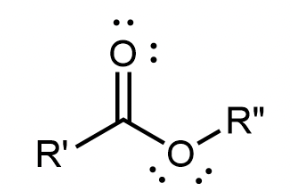
Ester
A carbonyl group with a second oxygen atom single bonded to the carbonyl carbon; found in the middle of the molecule, bonded to 2 different R groups
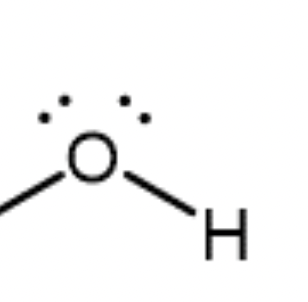
Alcohol/hydroxyl group
Contains an -OH group covalently bonded to a carbon atom
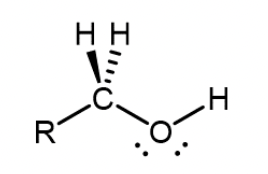
Primary alcohol
One alkyl group is attached to the carbon with the -OH group
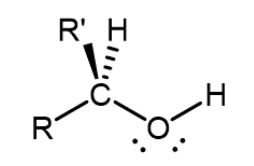
Secondary alcohol
Two alkyl groups are attached to the carbon with the -OH group
Tertiary alcohol
Three alkyl groups are attached to the carbon with the -OH group
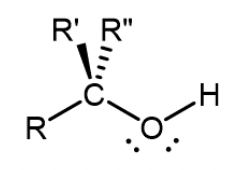
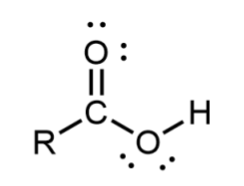
Carboxylic acid
Carbonyl carbon bonded to a hydroxyl group; found at the end of a molecule
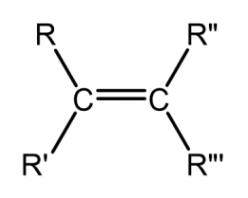
Alkene
A hydrocarbon containing one degree of unsaturation
Alkyne
A hydrocarbon containing 2 degrees of unsaturation
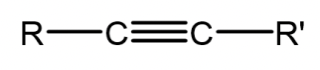
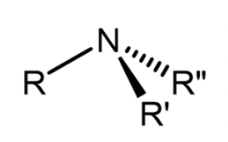
Amine
Derivative of ammonia; central nitrogen atom bonded to one or more hydrogens/R groups
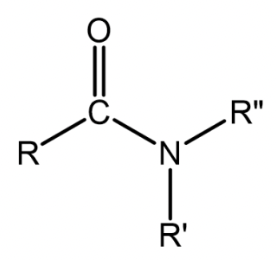
Amide
Nitrogen atom single-bonded to a carbonyl carbon and two other groups; R or hydrogens
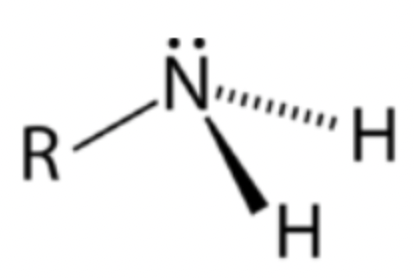
Primary amine
Nitrogen atom bonded to one R group and two hydrogens
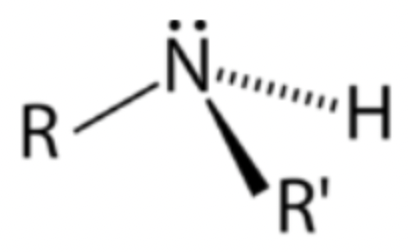
Secondary amine
Nitrogen atom bonded to two R groups and one hydrogen
Tertiary amine
Nitrogen atom bonded to three R groups
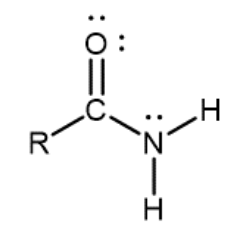
Primary amide
Nitrogen atom single-bonded to a carbonyl carbon and two hydrogens
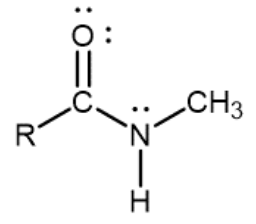
Secondary amide
Nitrogen atom single-bonded to a carbonyl carbon, one R group, and one hydrogen
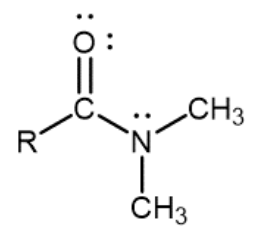
Tertiary amide
Nitrogen atom single-bonded to a carbonyl carbon and two R groups
Amides
Which functional group is always planar due to resonance and hybridization rules?
Structural/constitutional isomers
Molecules that share the same molecular formula but differ in the order of atom connectivity.
Stereoisomers
Molecules that share the same molecular formula and connectivity but differ in the 3D spatial arrangement of their atoms
Enantiomers
A pair of isomers that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other
Chirality
A property of a molecule that means it is non-superimposable onto its mirror image (like your left and right hand)
Diastereomers
Isomers that are non-superimposable, non-mirror images of each other
Geometric isomers
Isomers which have a different arrangement in 3D space due to a non-rotating bond or a ring structure
Cis isomer
An isomer where two identical groups are located on the same side of a rigid structure, such as a double bond or a ring
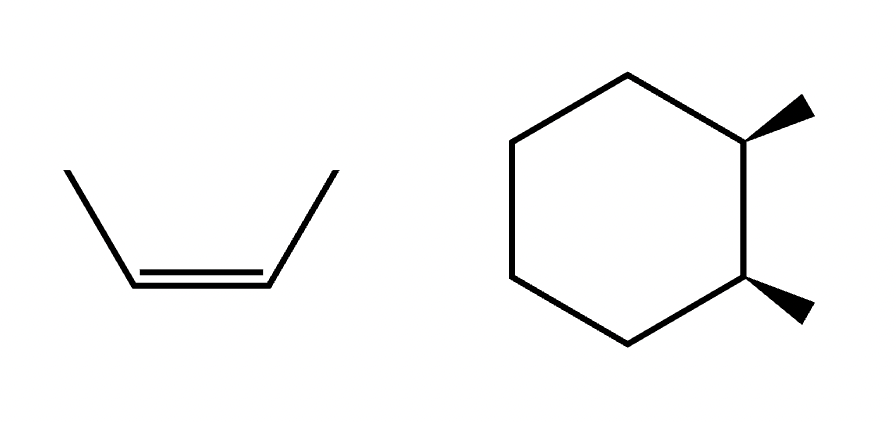
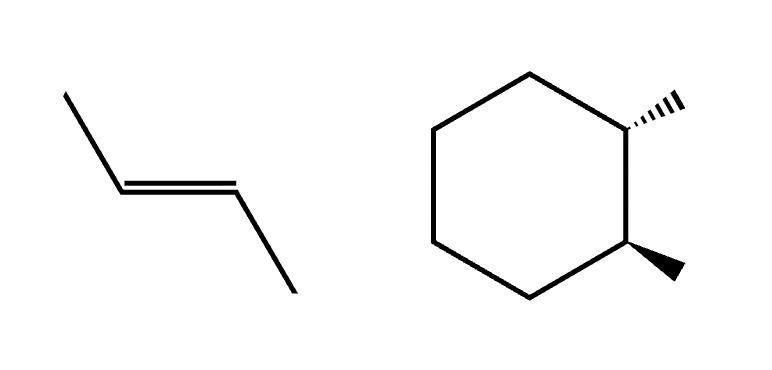
Trans isomer
An isomer where two identical groups are located on opposite sides of a rigid structure, such as a double bond or a ring
Addition polymer
A polymer formed by unsaturated monomers, typically with double bonds
Condensation polymer
A polymer whose formation releases a byproduct such as water; have functional group(s) in the polymer backbone (carboxylic acid, amide, or hydroxyl)
High-density polymer
Polymer with a LINEAR structure that allows for tight packing of molecules; has strong dispersion forces and is more rigid
Low-density polymer
Polymer with a BRANCHED structure that prevents tight packing of molecules; has weak dispersion forces and is more malleable
Cross-links
Covalent bonds between polymer chains that create a rigid, 3D network; enhance a polymer's strength, hardness, and resistance to heat and chemicals
Amino acid
A carbon atom (called the α carbon) bonded to a hydrogen atom, an amine group, a carboxylic acid group, and an R group (called the side chain)
Protein primary structure
The linear sequence of amino acids in a protein
Protein secondary structure
The local, 3D forms of polypeptide chain segments; determined by the pattern of hydrogen bonds between non-adjacent amine and carboxyl groups in an amino acid’s backbone
α-helix
A secondary protein structure consisting of a coiled polypeptide chain
β-sheet
A secondary protein structure consisting of a “pleated” sheet where the polypeptide chain connects side-by-side with itself
Protein tertiary structure
The overall 3D shape of a protein, formed by the folding and interactions of its secondary structures
Protein quaternary structure
The assembly of one or more polypeptides into a larger, functional protein complex; held together by intermolecular forces, not covalent bonds
DNA
Two polymer strands made up of nucleotide monomers that coil around each other in a double helix
Nucleotides
Monomers composed of a phosphate group and a nucleobase attached to a sugar
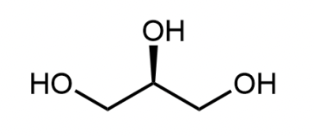
Glycerol
A chain of 3 carbon atoms, each bonded to a hydroxyl group
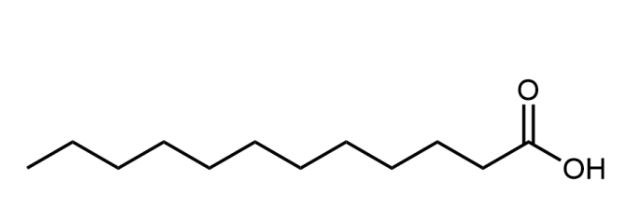
Fatty acid
A long, unbranched hydrocarbon chain with a carboxylic acid group at one end
Saturated glycerolipid
Has long, linear fatty acid chains that are easily stackable and have strong intermolecular forces
Unsaturated glycerolipid
Has fatty acid chains that are not as easily stackable and have weaker intermolecular forces