Carnegie 4
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Players of calcium homeostasis
Calcitonin (during childhood)
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)***
Vitamin D
Target of calcium homeostasis
GI tract
Bone
Kidneys
Goal of calcium homeostasis
Maintain blood calcium levels within a certain range, regardless of diet and bone density
99% of calcium in the body is stored where?
bone and teeth (majority in bone)
Hormones that increase bone deposition
Insulin
Growth hormone
IGF-1
Estrogen
Testosterone
Calcitonin (during childhood)
Hormones that increase bone resorption
PTH
Cortisol
T3 and T4
Bone is seen as a ______ by the body
bank of calcium
Bone is constantly remodeled via the actions of ___________
osteoblasts and osteoclasts
Mechanical stress of bones also encourages ______
bone deposition
Calcium storage
Of the 1% of calcium remaining (not in bones or teeth), 90% of it is inside cells, leaving only 0.1% of body calcium available in the ECF
Of the 0.1% in ECF, half is bound to proteins or phosphate
Osteoblast
derived from bone marrow stromal cells and deposit calcium in bone
Osteocytes
retired osteoblasts and maintain bone tissue
Osteoclasts
derived from macrophages and digest bone to release calcium into the circulation
0.05% of total body calcium as _______
free calcium
Free calcium available for essential functions such as
neuromuscular excitability (influences Na+ permeability)
excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac and smooth muscle
stimulus-secretion coupling
maintenance of tight junctions
blood clotting
absence of ___ is fatal within days due to lack of calcium to maintain stimulation of diaphragm contraction
PTH
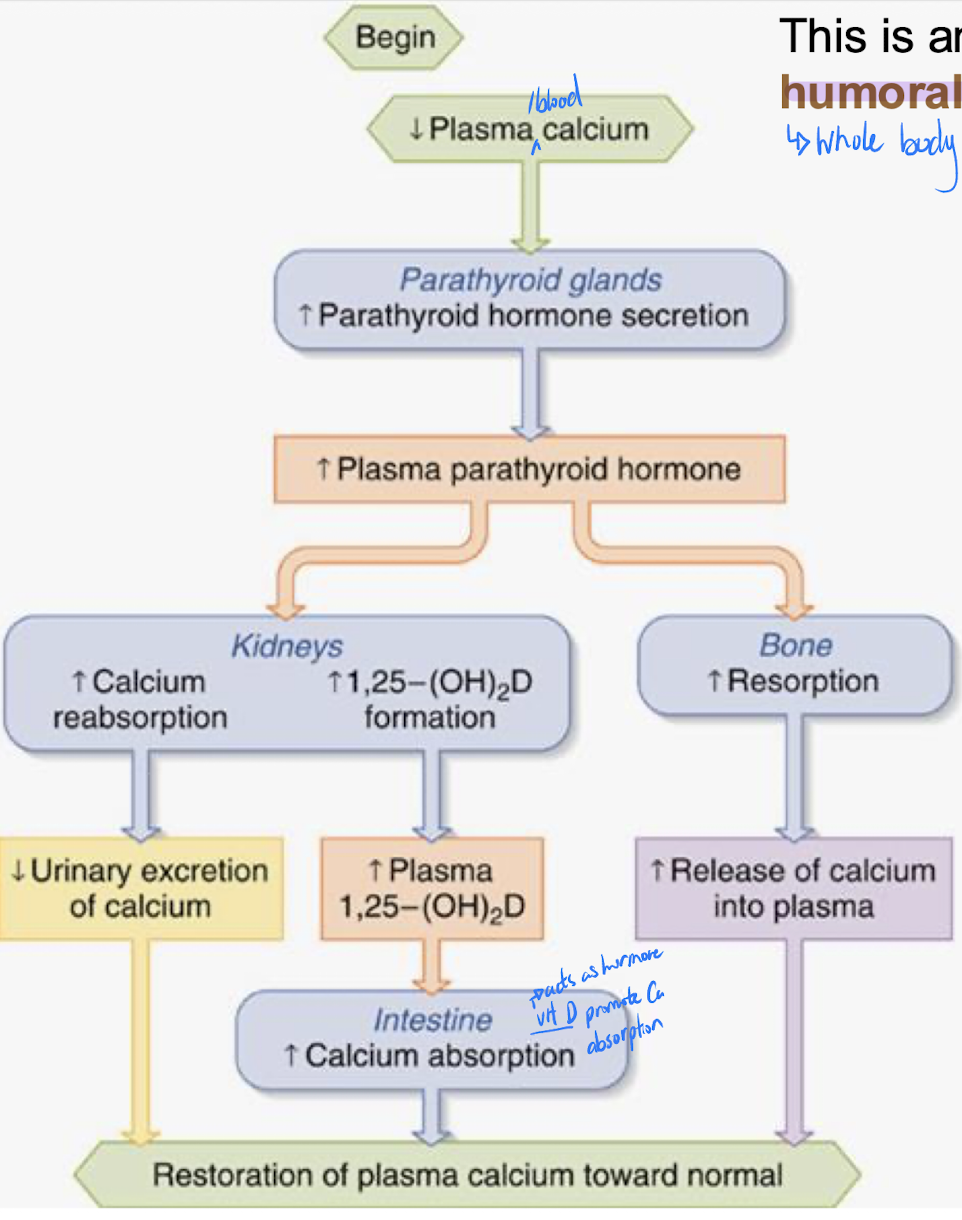
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Peptide hormone secreted in response to decreased blood calcium and will influence all 3 targets
Bone
GI tract
Kidney
Bone
stimulates resorption – fastest option to quickly raise blood calcium
GI tract
stimulates calcium absorption from diet (this is regulated)
Kidney
increases tubular calcium reabsorption to return it to bloodstream
Calcium is an excellent example of _________ of hormone release
Humoral regulation
Note that bone resorption moves both _________ and _______ into the bloodstream. This has the potential to be self defeating.
PTH deals with this by ______ excretion at the level of the kidneys so that the calcium remains as _______, available to various target cells.
calcium and phosphate
increasing phosphate
free calcium
Humoral regulation of calcium
Balance between osteoblast products
Osteoblasts and their precursors → RANK ligand (RANKL) → Macrophages/ osteoclasts → (triggered by binding of RANKL and RANK) Differentiation of macrophages into osteoclasts and Suppression of osteoclast apoptosis → increase Osteoclast action → Osteoclast action outpaces osteoblast action → decrease Bone mass
Osteoblasts and their precursors → Osteoprotegerin (OPG) → RANKL bound to OPG not available to bind with RANK → Blocks action of RANK → decrease Osteoclast action → Osteoblast action outpaces osteoclast action → Bone mass
Estrogen can help maintain ________ by activating the gene responsible for _______
bone density
OPG production
RANK
Receptor Activator of NF-k B (nuclear factor kappa NF-Kß - found on macrophages and induces them to differentiate into osteoclasts)
PTH activates ________ to promote ________ from the GI tract: Vitamin D is considered to be acting as a hormone in this context'
Two hydroxylations are required to get the active form: 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D
Vitamin D
calcium absorption
Calcitonin
a minor player
Secreted by thyroid parafollicular cells in response to elevated blood calcium
Inhibits osteoclasts (maximize osteoblast (increase bone growth))
Important during childhood growth
Not a key player in the day-to-day regulation of bone density in adults
Osteoporosis
Loss of matrix and minerals, especially in response to aging
More common in women because decreasing levels of estrogen after menopause
Osteoporosis treatment
anti-osteoclast drugs including calcitonin (nasal spray)
SERMS (selective estrogen receptor modulators)
newer drugs look at promoting osteoblasts rather than simply interfering with osteoclasts – possibly statins, also another type of estrogen signaling molecule
Bisphosphonates
they incorporate into calcium at the bone matrix
during resorption, they enter into the clasts by transcytosis
they induce apoptosis of excess clasts
they do not interfere in bone physicochemical properties
Adrenal glands
paired, pyramid-shaped organs on top of kidneys (suprarenal glands)
structurally & functionally, 2 distinct endocrine glands in one
adrenal medulla
adrenal cortex
adrenal medulla
nervous tissue forms core of gland; derived from neural crest and acts like part of sympathetic ns
adrenal cortex
encapsulates medulla & makes up most of glans; derived from mesoderm- 3 functional areas
3 functional areas of adrenal glands
adrenal cortex
zona reticularis- sex steroids
zona fasciculata- glucocorticoids
zona glomerulosa- mineralcorticoids
adrenal medulla- catecholamines
Adrenal medulla
composed of chromaffin cells which are modified postganglionic neurons
cells are clustered around capillaries; secrete E/NE (80/40) into ECS – then via blood stream to targets
Catecholamines
derivatives of the amino acid tyrosine
role is to prolong the body’s “fight or flight” response that was initiated by the SNS → constriction of blood vessels, increased blood sugar, faster heartbeat, diversion of blood to brain, heart & skeletal muscles
sympathetic nervous system stimulates medullary release of catecholamines; fast-acting but brief responses to stress
Release of E/NE
Hypothalamus → spinal cord → sympathetic fibers to adrenal medulla → release of E (mostly) and NE
Short-term stress response (reinforces response initiated by SNS)
Increased heart rate
Increased blood pressure
Liver: glycogenolysis & release of glucose to blood
Dilation of bronchioles
Redirected blood flow → increased alertness, decreased digestive system activity, reduced urine output
Increased metabolic rate
α1 and β1 adrenergic receptors tend to exert effects that are _____
stimulatory
α2 and β2 adrenergic receptors tend to be _______
inhibitory
α1
Location: Most sympathetic target cells
Affinity catecholamine for NE and E: NE > E
Typical response elicited: Excitatory
Example of responses elicited: Generalized arteriolar vasoconstriction (increase smooth muscle contraction)
α2
Location: Digestive system
Affinity catecholamine for NE and E: NE < E
Typical response elicited: Inhibitory
Example of responses elicited: Decreased motility in digestive tract (tsmooth muscle contraction)
β1
Location: Heart
Affinity catecholamine for NE and E: NE = E
Typical response elicited: Excitatory
Example of responses elicited: Increased rate and strength of cardiac muscle contraction
β2
Location: Skeletal muscle; smooth muscle of some blood vessels and organs
Affinity catecholamine for NE and E: E only
Typical response elicited: Inhibitory
Example of responses elicited: Breakdown of glycogen in skeletal muscle; bronchiolar dilation and arteriolar vasodilation in skeletal muscle and heart (I smooth muscle contraction)
Steroidogenesis in the adrenal cortex
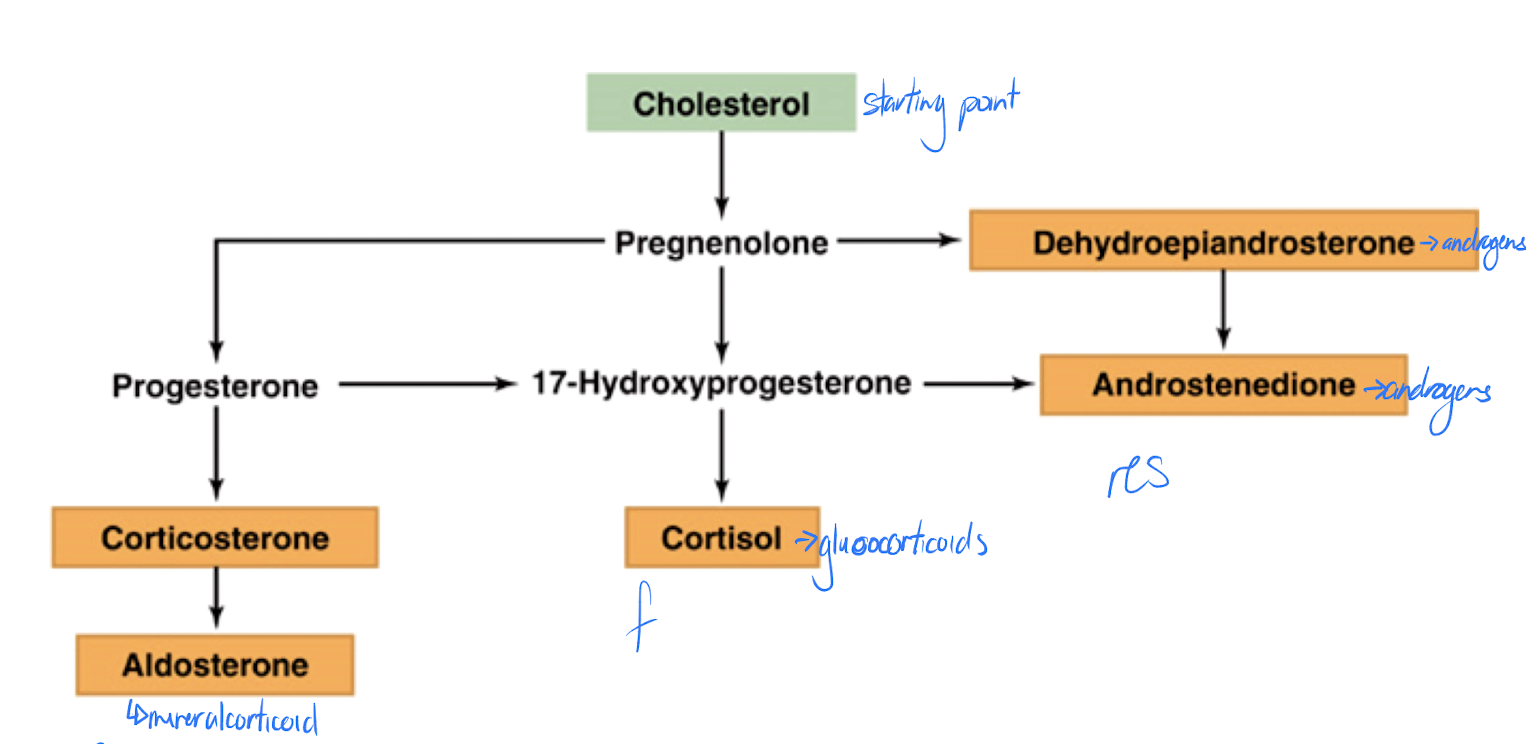
Aldosterone & cortisol are structurally very similar – consequence?
increase levels for long periods
can bind to other receptors
Reproductive Steroids pathway
Cholesterol → pregnenolone → DHEA
Glucocorticoids pathway
Cholesterol → progesterone → 17-OH-progesterone → cortisol
Mineralocorticoids pathway
Cholesterol → progesterone → corticosterone → aldosterone
Mineralocorticoids
hormones involved in balance of salts (Na+, K+) & water in body; essential to life to maintain adequate blood pressure
primary (95%) mineralocorticoid is aldosterone
Aldosterone
stimulates reabsorption of Na+ by kidney tubules (K+ out for Na+ in)
increases Na+ reabsorption from sweat, saliva, gastric juice
water follows Na+ if water channels are open (ADH!)
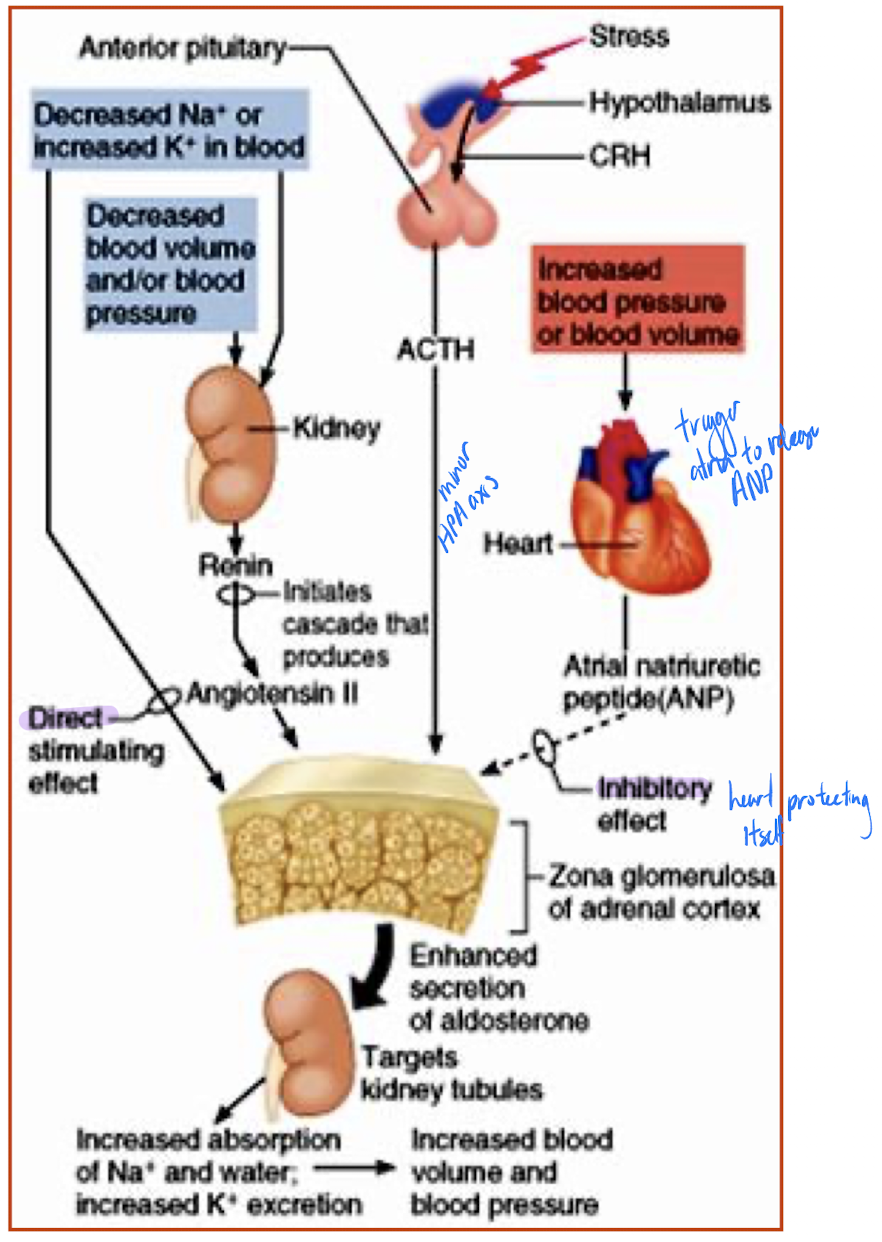
Conditions that increase aldosterone release
increased blood K+
low blood Na+
low blood volume/pressure
Mechanisms regulating aldosterone secretion
renin-angiotensin system
plasma Na+/K+
ACTH
plasma ANF (atrial natriuretic factor)
Renin-angiotensin system
major regulator of aldosterone secretion
angiotensinogen (from liver) -(renin from kidney)→ angiotensin 1 -(ACE)→ angiotenin 2
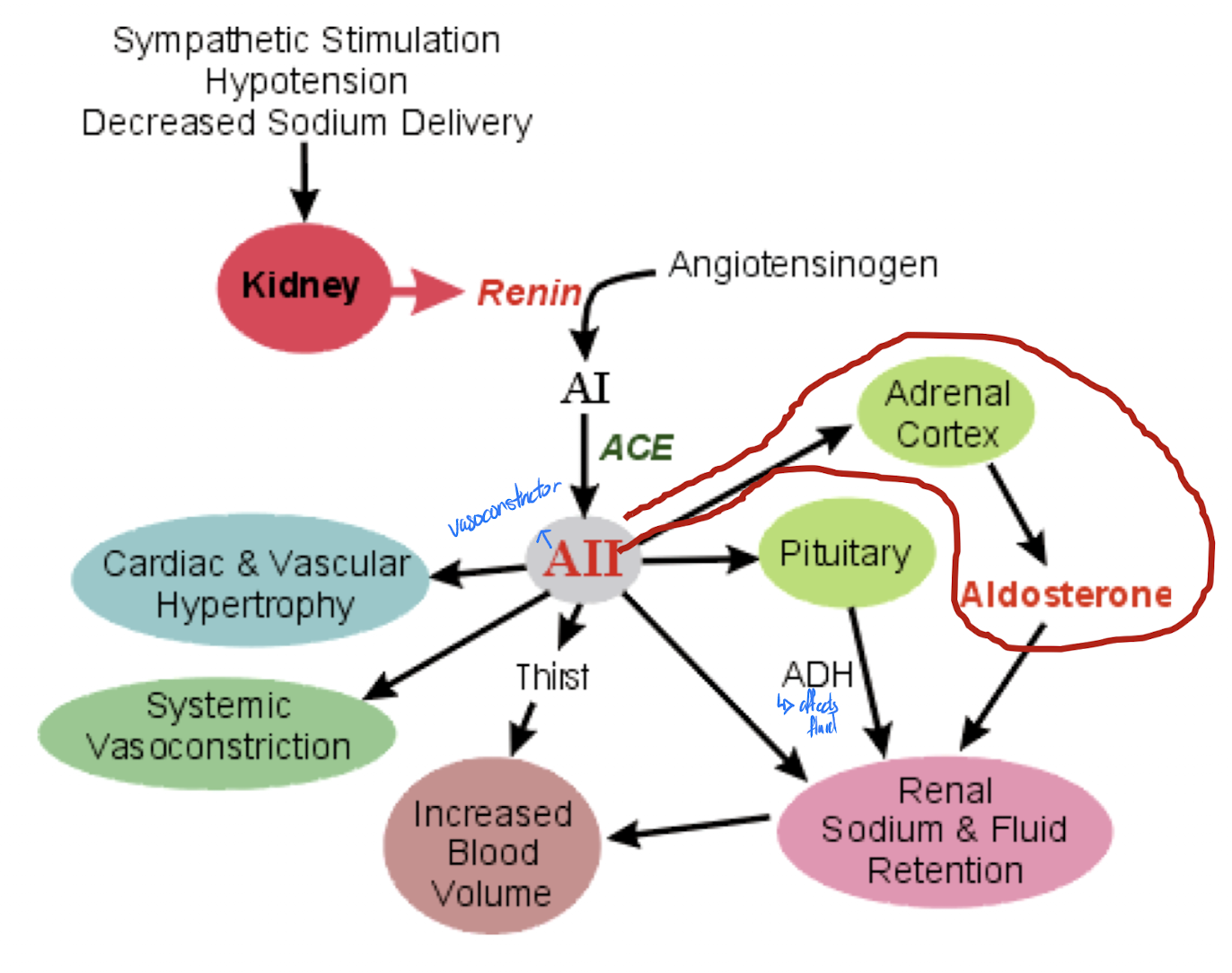
Plasma [Na+] or [K+]
low Na+ or high K+ stimulates aldosterone secretion
ACTH
Hypothalamic-Pituitary Axis
CRH (hypothalamus) → ACTH (anterior pituitary) → aldosterone (zona glomerulosa) usually ACTH (not specific to just aldosterone!!) a minor player - comes into effect if individual severely stressed
Atrial Natriuretic Factor (ANF)
released by heart when blood pressure rises
effects on aldosterone secretion are inhibitory; goal is to decrease blood pressure by allowing Na+ and water to leave body via urine
Zona Reticularis
primary product is DHEA (dehydroepiandrosterone)
much smaller amounts of estrogen produced in both males & females
amounts of both androgens and estrogens are insignificant compared to gonadal production of these steroids from late puberty on
Function of DHEA in females
onset of puberty to promote growth of pubic and axillary hair, enhance pubertal growth spurt and promote sex drive
important source of substrate for estrogen production post menopause (protect against osteoporosis)
Regulation of sex steroid secretion by the adrenals
not completely understood
can be stimulated by ACTH, but no negative feedback, so not really controlled by ACTH and levels rise markedly during puberty and this is not driven by ACTH
Hypersecretion of what can lead to masculinizing in females (e.g. hirsutism)
Hirsutism