Hereditary Hemolytic Anemia
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Where is the alpha globin gene cluster located?
On chromosome 16 (16p13.3)
What is the function of the zeta (ζ) globin gene?
It is an embryonic globin gene that substitutes for alpha-globin very early in development.
When is zeta globin expressed?
During the embryonic stage, specifically in the yolk sac phase (~first 6–8 weeks of gestation).
Which embryonic hemoglobin includes zeta globin?
Hemoglobin Gower I (ζ₂ε₂)
How many alpha globin genes does each person typically have?
Four total (two HBA1 and two HBA2—one set from each chromosome 16)
How are the alpha globin genes arranged on chromosome 16?
HBA1 and HBA2 are aligned one after the other in tandem.
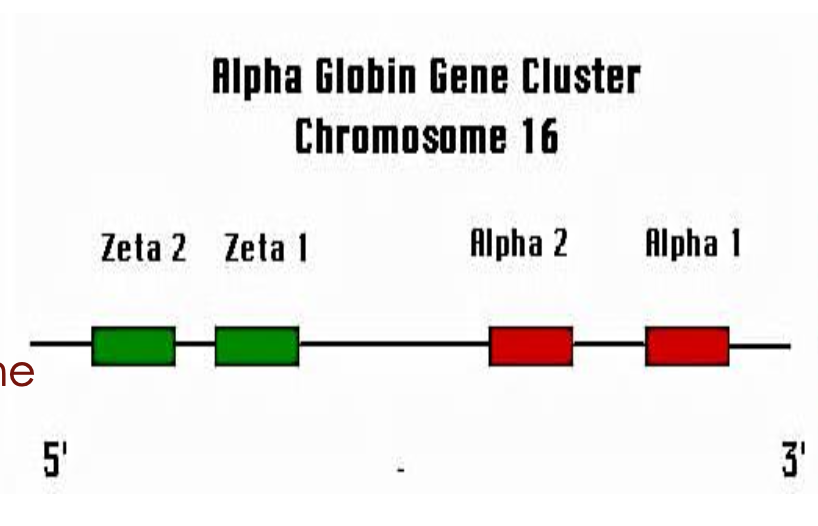
What proportion of alpha-globin chains is produced by each alpha gene?
Each gene contributes approximately 25% of the total alpha-globin chain production.
On which chromosome is the beta globin gene cluster located?
Chromosome 11
What is the sequence of genes in the beta globin cluster (from 5’ to 3’)?
Epsilon (ε), Gamma (Gγ and Aγ), Delta (δ), Beta (β)
Which gene in the beta cluster is expressed during embryonic development?
Epsilon (ε) globin
When is epsilon globin expressed?
During early embryonic development (approximately the first 12 weeks after conception)
Which gene is primarily expressed during fetal development?
Gamma (γ) globin
What type of hemoglobin does gamma globin form during fetal life?
Hemoglobin F (HbF), composed of α₂γ₂
Which gene in the beta cluster produces a small amount of globin in children and adults?
Delta (δ) globin
What hemoglobin is formed with delta globin?
Hemoglobin A₂ (HbA₂), composed of α₂δ₂
Which gene in the beta cluster is most active in adults?
Beta (β) globin, forming HbA (α₂β₂)
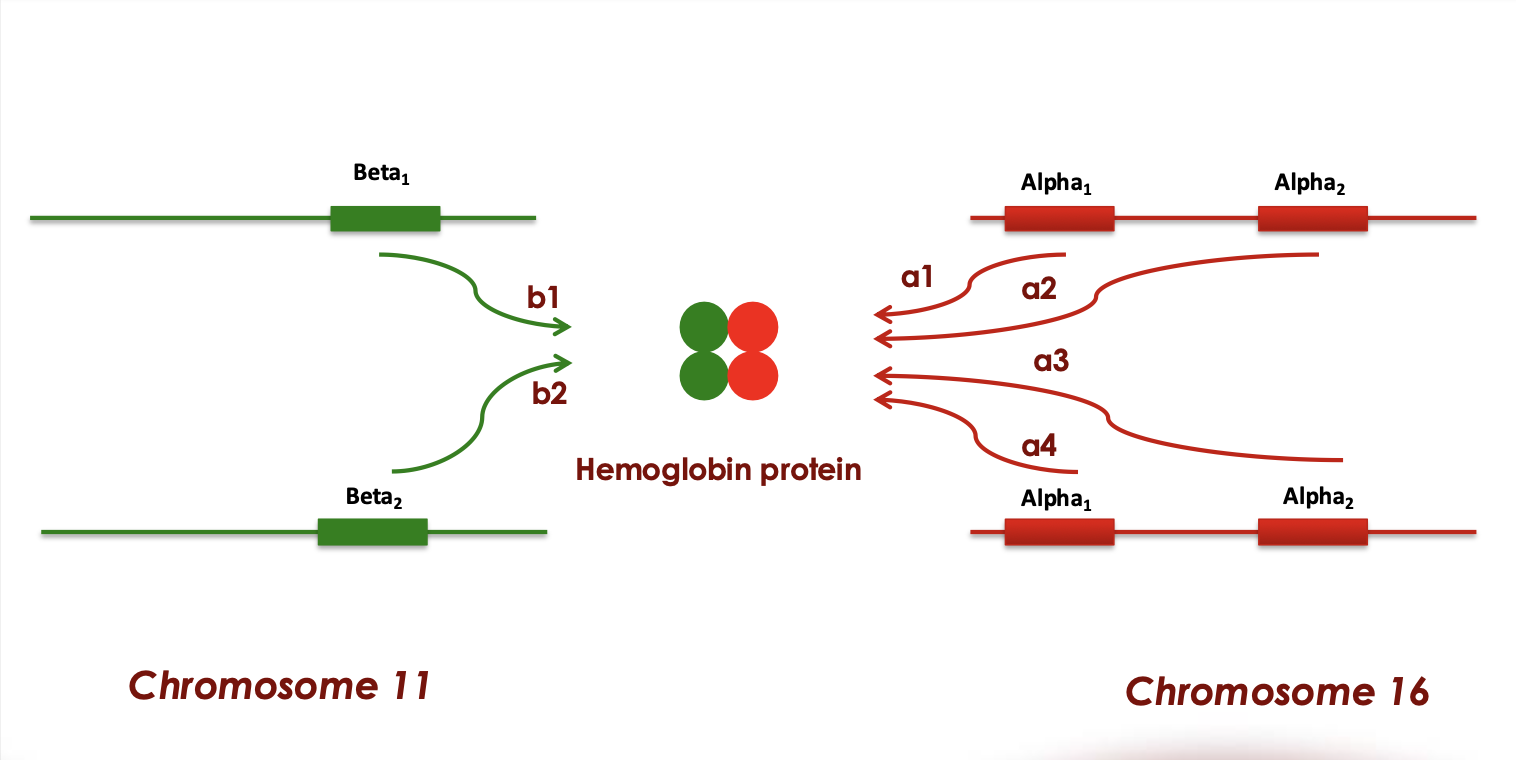
Embryonic hemoglobin
1st : zeta(2), epsilon(2)
2nd : alpha(2), gamma (2)
3rd : alpha (2), gamma (2)
Fetal hemoglobin
alpha(2),gamma(2)
Adult hemoglobin
Hemoglobin A :
alpha(2), beta(2)
Hemoglobin A2:
alpha(2), delta(2)
Human adult Hemoglobin coded by
Pathpopgenetic classification of anemia
-Decreased production
- Increased loss/ destruction
Decreased production
Nutrient deficiency
▪ Iron deficincy / megaloblastic
Hemopoietic cell defect:
▪ Anemia of chronic disorders
▪ Aplastic anemia
Increased loss/ destruction
▪ Blood loss anemia: acute/chronic bleeding
▪ Hemolytic anemia: congenital/acquired
congenital hemolytic anemia includes
Defective Hemoglobin: Thalassemia and Sickle cell
Defective Membrane: Spherocytosis
Deficient Enzyme: G6PD deficiency enzyme
Thalassemia
Inherited genetic disorder that results in reduced rate of synthesis or no synthesis of one of the globin chains that make up hemoglobin
A quantitative problem of too few globins synthesized
types of thalassemia
alpha thalassemia
beta thalassemia

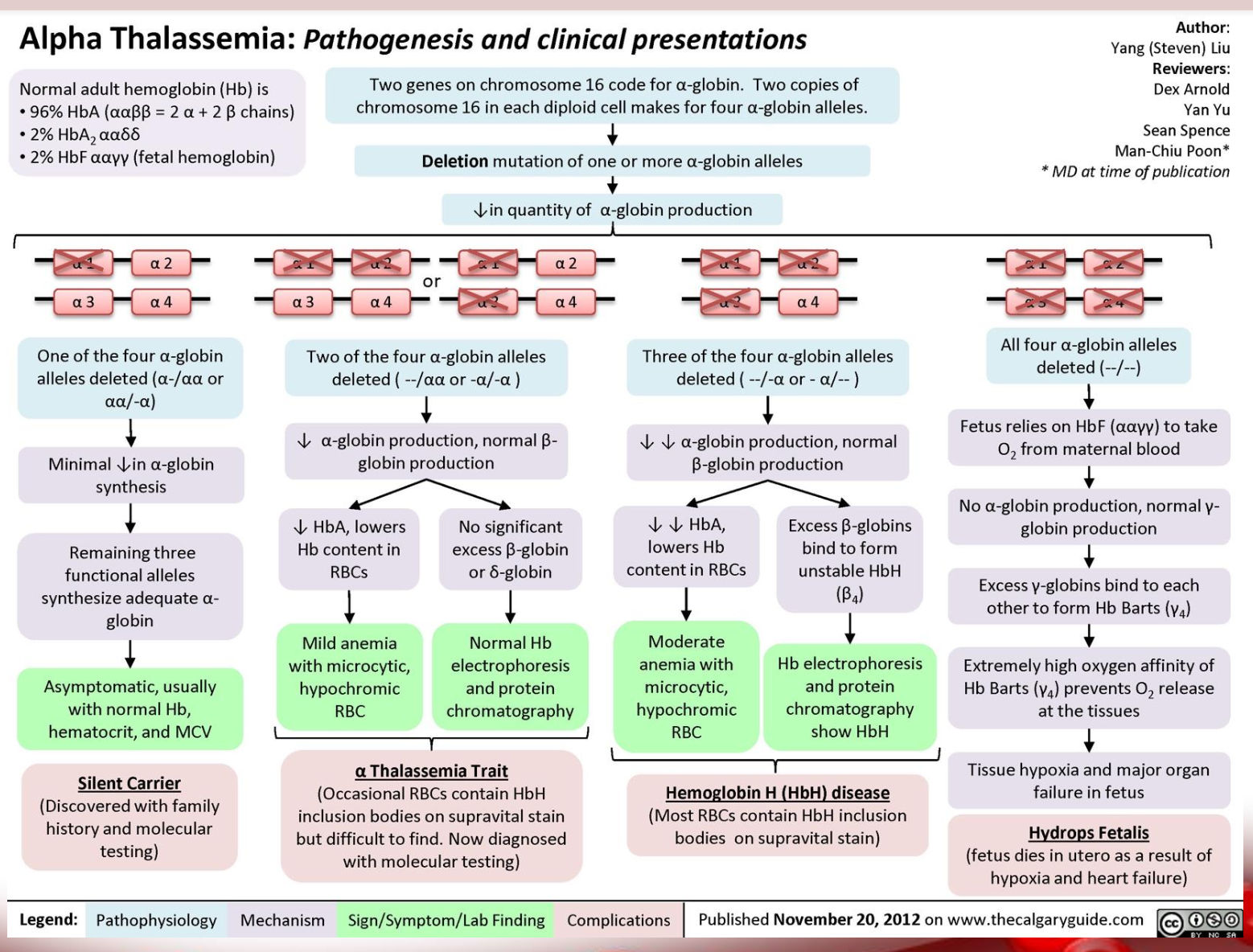
Alpha Thalassemia
Results from deficient or absent synthesis of alpha globin chain
Alpha Thalassemia genetic mutation
-HBA1 and HBA2 located on chromosome 16
-Mainly deletions, point mutations
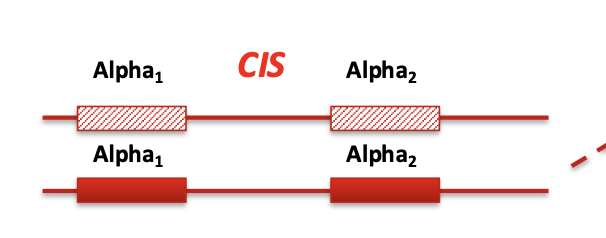
Trans
Each chromosome has one affected and one normal gene
(-α/-α)
(striped is affected, - is affected, a is normal)
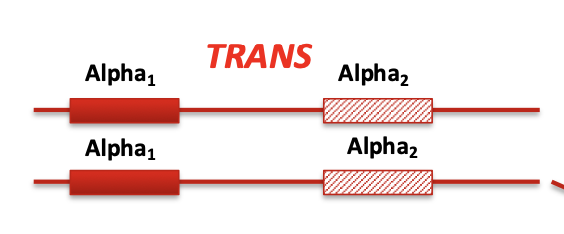
cis
Both deletions or mutations are on the same chromosome
(--/αα)
Trans X Cis
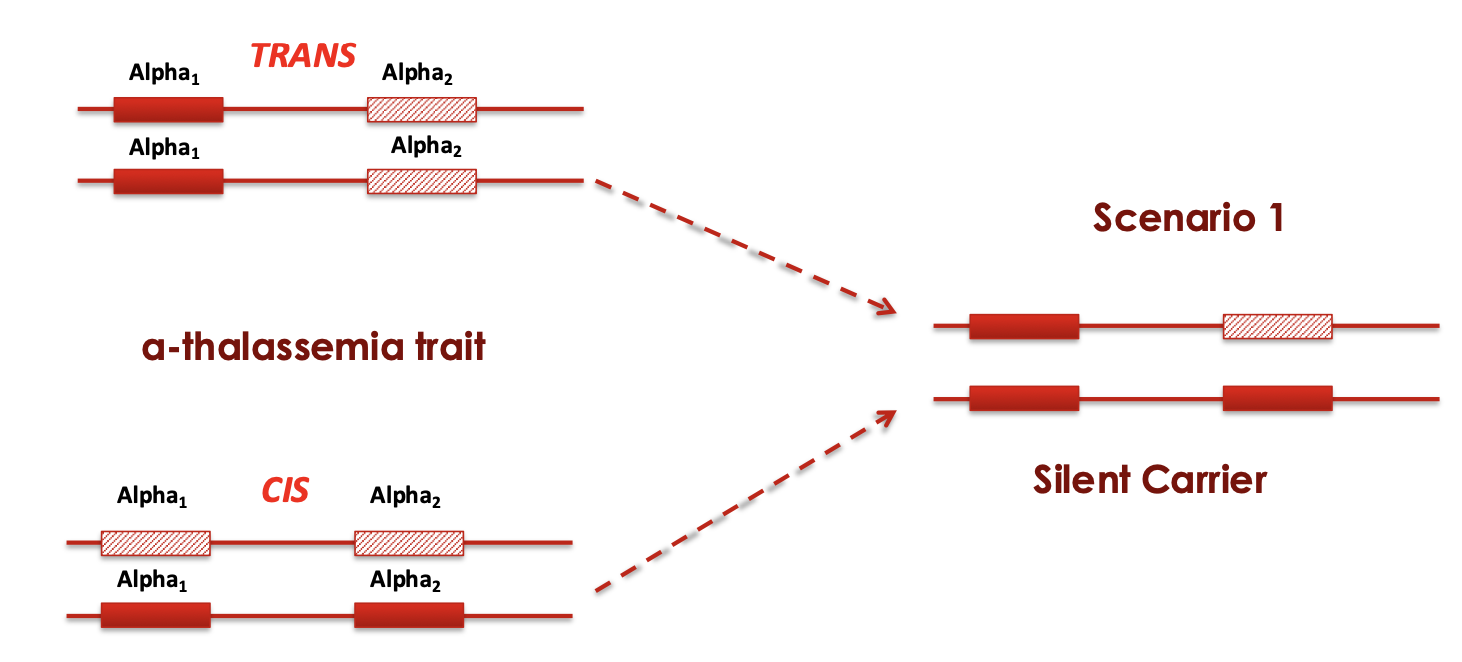
silent carrier
-/α α/α
Asymptomatic
slight reductions in MCV
and MCH or no changes
Trans X Cis
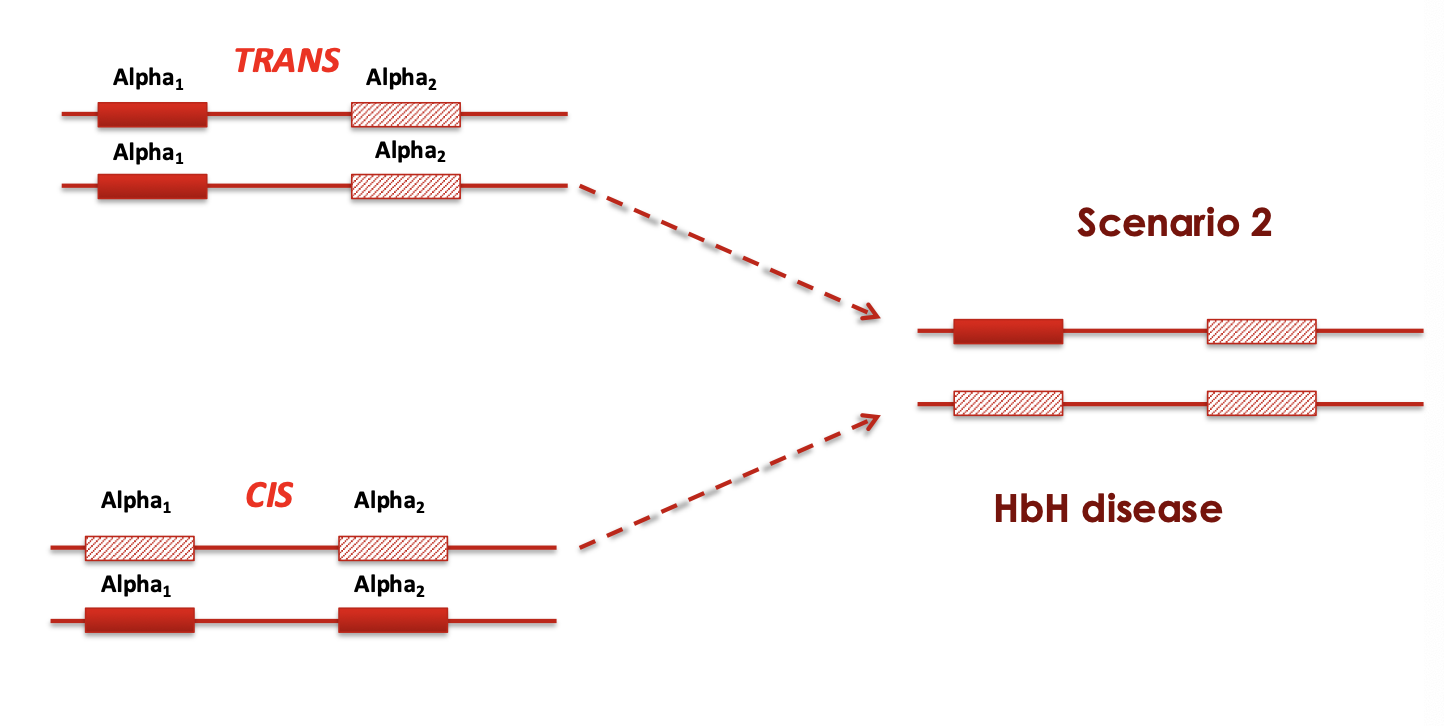
Cis X cis
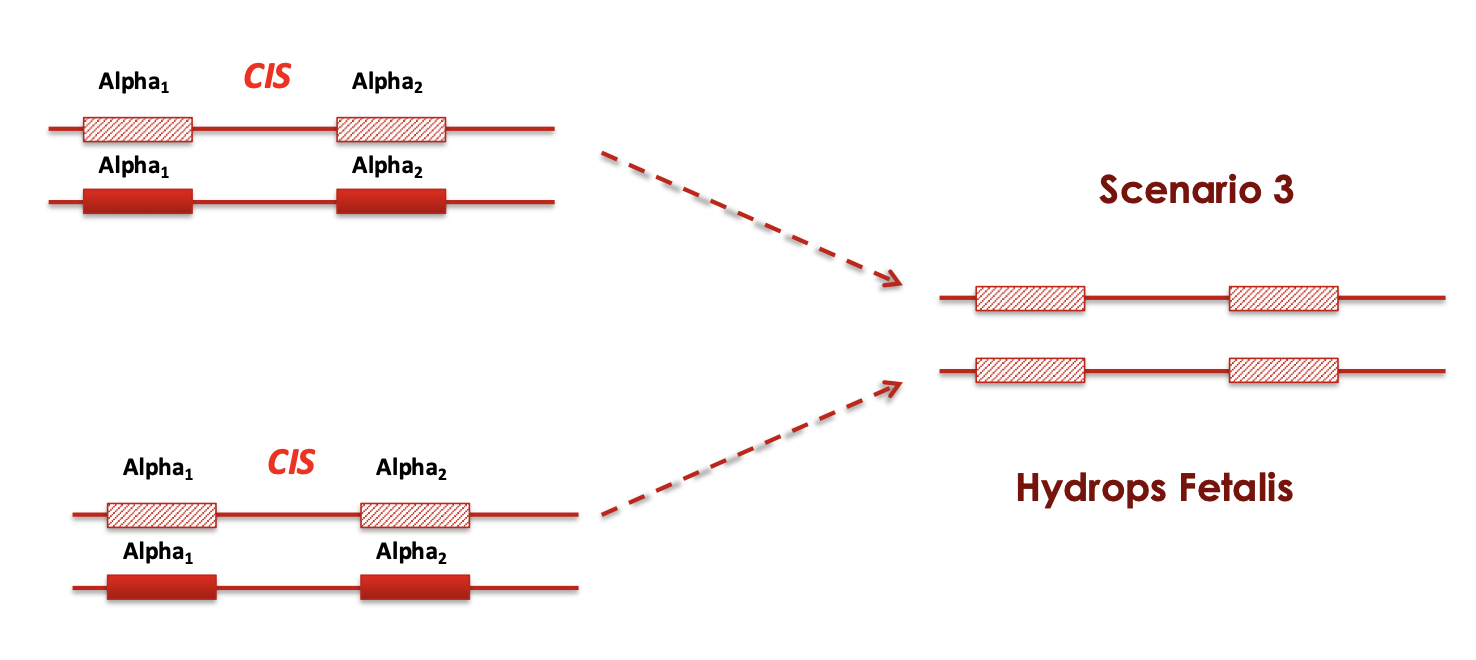
what disease happens if 2 genes are deleted
Alpha-thalassemia trait
-/α -/α
-/- α/α
Alpha-thalassemia trait
Asymptomatic
minimal anemia slightly
reduced MCV and MCH
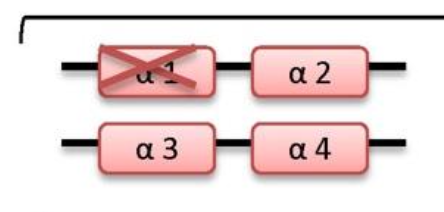
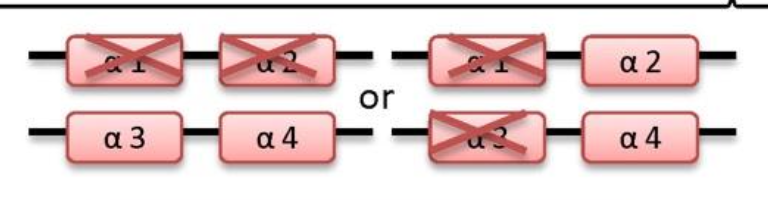
what disease happens if 3 genes are deleted
HbH disease
-/- -/α
HbH disease
microcytic hypochromic hemolytic anemia, splenomegaly, mild jaundice, and sometimes thalassemia-like bone changes
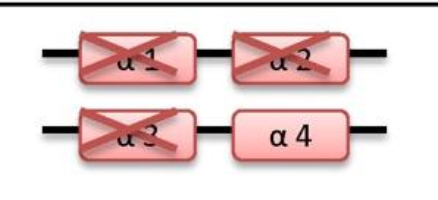
what disease happens if 4 genes are deleted
Hydrops fetalis
-/- -/-
Hydrops fetalis
Die either in utero or shortly after birth because of severe anemia
Alpha Thalassemia pathogenesis
Beta Thalassemia
Characterized by a genetic deficiency in the
synthesis of β polypeptide chains
Beta Thalassemia mutations
HBB gene on chromosome 11 provides instructions for making a protein called beta globin
Mutation in HBB prevent or reduce the production of beta globin
β0
The absence of beta globin is referred to as this
β+
A reduced amount of beta globin
Beta-thalassemia minor
beta-thalassemia trait genes
β+/β
βo/β
Beta-thalassemia minor
beta-thalassemia trait clinical features
-Asymptomatic
-Mild microcytic anemia
Beta-thalassemia
intermedia genes
β+/β+
βo/β+
Beta-thalassemia
intermedia clinical features
-Asymptomatic
-Minimal anemia reduced MCV and
MCH
may need occasional transfusions,
e.g., at times of illness or pregnancy,
depending on the severity of their
anemia.
Beta-thalassemia major
(Cooley's anemia) genes
βo/βo
Beta-thalassemia major
(Cooley's anemia) clinical features
presents at a few months of age
with progressive pallor and
abdominal distension; possibly with
poor feeding, decreased activity;
hepatosplenomegaly and bony
abnormalities most often of the skull
(frontal and parietal bossing, and
chipmunk facies).
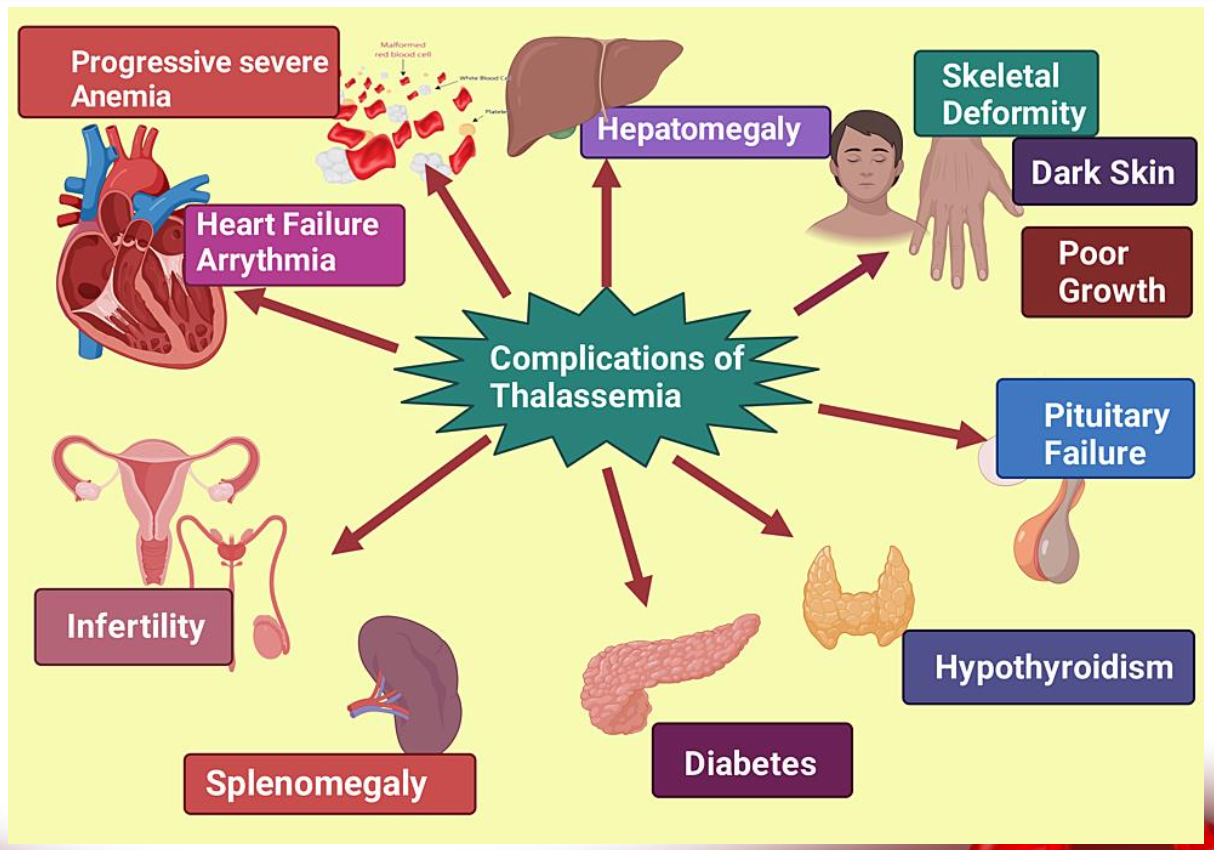
symptoms of thalassemia

complications of thalassemia
Sickle-cell disease
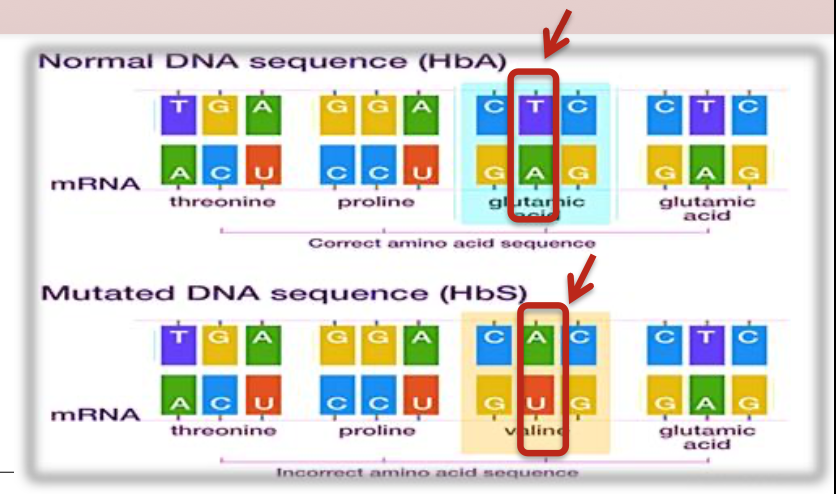
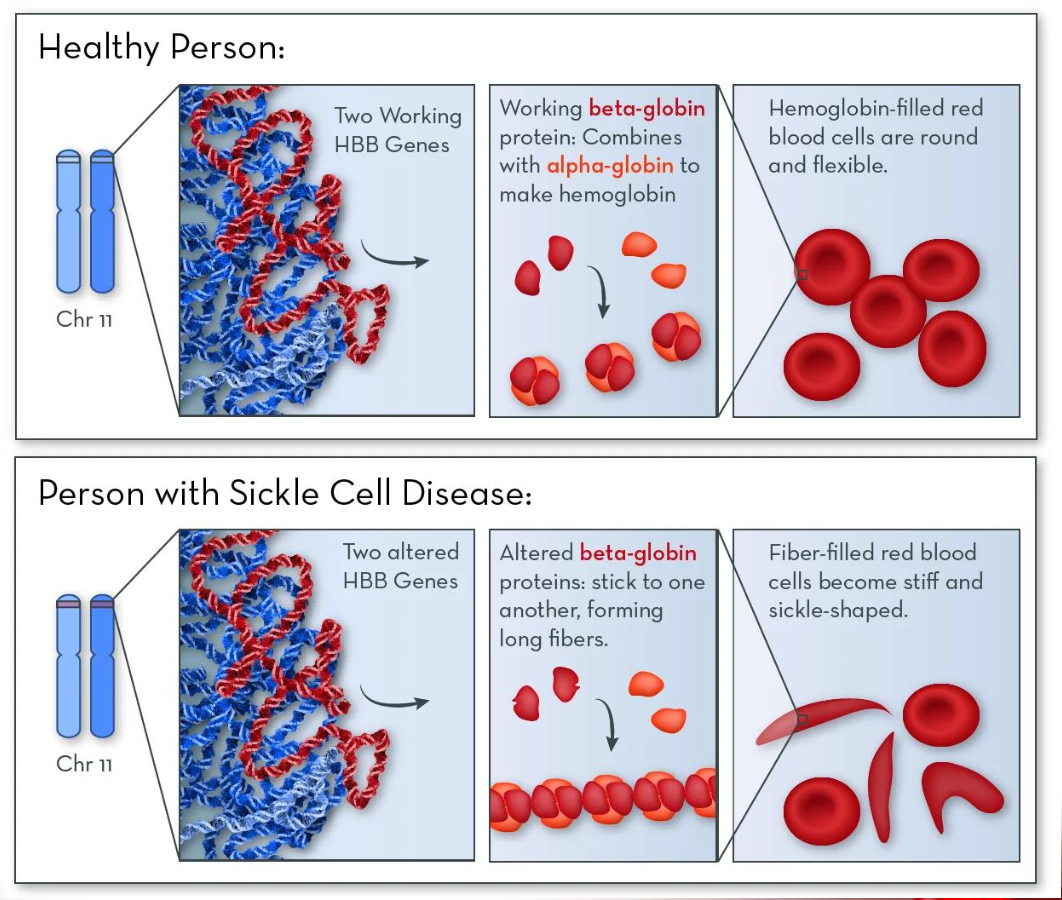
caused by a gene mutation that leads to the production of Sickle haemoglobin HbS
Qualitative :Production of abnormal chains
sickle cell mutation
Occur in beta globin gene of hemoglobin
Mutation on chromosome 11: single amino
acid change (Point mutation)
Inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern
point mutation
Monogenic disorder caused by an T-to-A point mutation in the 𝛽-globin gene that produces abnormal hemoglobin S (Hb S)
sickle cell disease pathogenesis

combinations
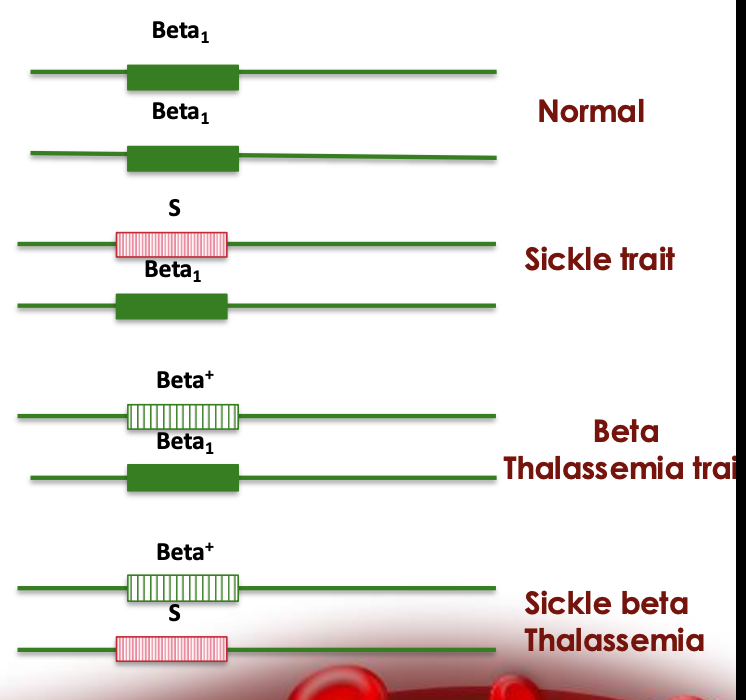
Sickle Cell Trait
HbA/S
~60% HbA, ~40% HbS
Sickle Cell Trait clinical
Carrier state; generally asymptomatic and live normal lives
Sickle Cell Anemia
HbS/S |
~100% HbS |
Sickle Cell Anemia clinical
Severe form of SCD; frequent vaso-occlusive crises, hemolytic anemia, organ damage
S/β⁰-thalassemia
HbS/β⁰
~100% HbS, 0% HbA, HbF ~1–10%
S/β⁰-thalassemia clinical
Clinically similar to sickle cell anemia (no HbA at all); often severe
S/β⁺-thalassemia
HbS/β⁺
~60% HbS, ~40% HbA
S/β⁺-thalassemia clinical
Milder symptoms than sickle cell anemia; variable severity depending on how much HbA is produced
HbSC Disease
HbS/C
~50% HbS, ~50% HbC, HbA 0%
HbSC Disease clinical
Milder sickle cell disease; fewer complications than HbSS, but still at risk for retinopathy, avascular necrosis
Hereditary Spherocytosis
Familial hemolytic disorder associated with a variety of mutations that lead to defects in red blood cell (RBC) membrane proteins
These proteins allow the cells to change shape without breaking when passing through narrow capillaries.
ANK1, EPB42, SLC4A, SPTA1 AND SPTB gens give the instruction to produce the proteins.
Dysfunctional membrane proteins interfere with the cell's ability to change shape when traveling through the blood vessels.
The misshapen red blood cells, called spherocytes, are removed from circulation and taken to the spleen for destruction.
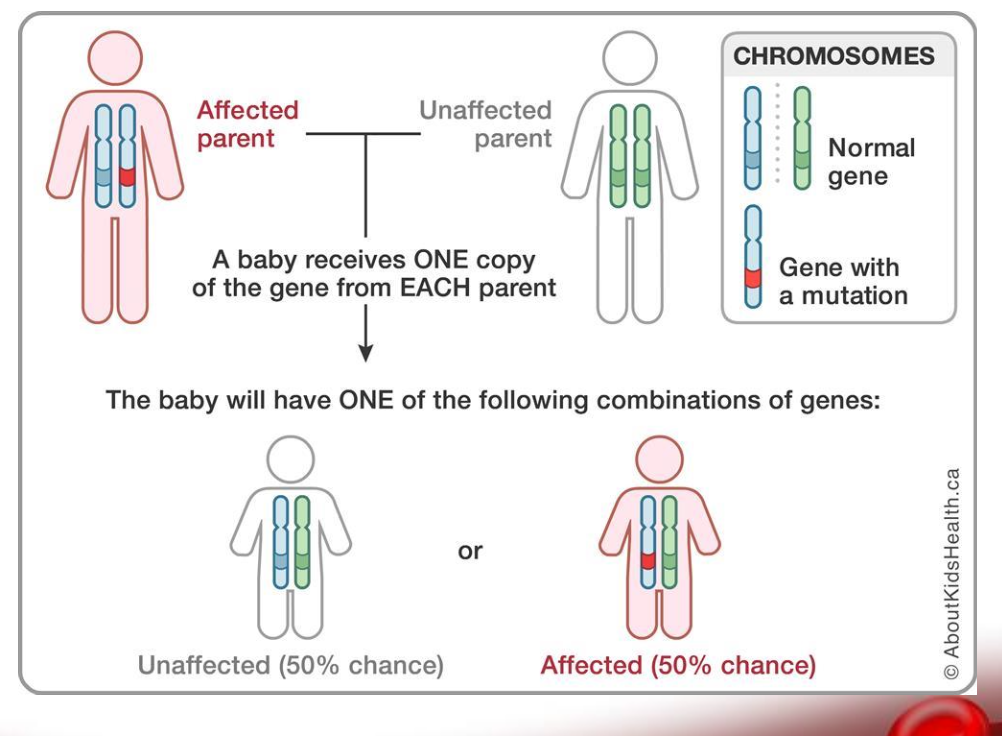
Spherocytosis inheritance
Inherited as autosomal dominant pattern

Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase
deficiency inheritance
X linked recessive disorder
G6PD gene
provides instructions for making an enzyme called glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase function
Beside carbohydrate metabolism, this enzyme involved in protecting red blood cells from the effects of potentially harmful molecules called reactive oxygen species.
If mutations in the G6PD gene reduce the amount of glucose-6- phosphate dehydrogenase or alter its structure, this enzyme can no longer play its protective role.
As a result, reactive oxygen species can accumulate and damage red blood cells.

Factors causing red blood cells to be destroyed faster than the body can replace them.
infections, certain drugs, or ingesting fava beans can increase the levels of reactive oxygen species