Glycolysis, Gluconeogenesis, Krebs Cycle, Oxidative Phosphorylation
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
186 Terms
Glycolysis
- exergonic reaction pathway
- convert glucose into pyruvate
- releases ATP and NADH
Phases of glycolysis
- preparatory phase : consumes 2 ATP, first 5 steps
- pay off phase: produce 2 ATP and 2 NADH
Net ATP and NADH produced
- 2 ATP and 2 NADH
Steps of Glycolysis
1. Glucose
2. Glucose-6-phosphate
3. Fructose-6-phosphate
4. Fructose 1-6-bisphosphate
5. glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate
6. 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
7. 3-phosphoglycerate
8. 2-phosphoglycerate
9. phophoenolpyruvate
10. pyruvate
Glucose to Glucuse-6-phosphate
- glucose is phosphorylated (to trap it since G^P negative charge prevents it from going to the cell cytoplasm)
- enzyme: hexokinase
- cost: 1 ATP
- requires Mg2+ as a cofactor
GLUT protein
- family of glucose transport
Glucokinase
- isozyme of hexokinase found in the liver
- has a lower affinity fro glucose allowing the liver to continue metabolism of glucose even at high intracellular glucose concentration
Glucuse-6-phosphate to Fructose-6-phosphate
- rearrange G6P to F6P by enzyme glucose-6-phosphate isomerase
- easy to reverse
glucose-6-phosphate isomerase other names
- phosphoglucose isomerase, phosphohexose isomerase
Fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-1,6-biphosphate
- FGP is phosphorylated by phosphofructokinase-1 PFK-1
- needs ATP and Mg2+
- rate limiting step of glycolysis and key regulatory point in the pathway
fructose-1,6-biphosphate to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate
- fructose-1,6-biphosphate is destabilized by the electrostatic repulsion between its two negatively charged phosphate groups.
- aldolase is able to easily split the hexose ring into two trioses sugars glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate are what
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate= adolse
dihydroxyacetone phosphate =ketone
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate to dihydroxyacetone phosphate
- enzyme trisephsphate isomerase converts DHAP to GADP
- final step of preparatory phase
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
-GADP undergoes dehydrogenation and phosphorylation (DHAP) via glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase (GADP)
- form 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (1,3-BPG)
- Hydrogen used to reduce two molecules of NAD to NADH and a proton
1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to 3-phosphoglycerate
-phosphoglycerate kinase transfers a phosphate group from 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (1,3-BPG) to ADP, forming 3-phosphoglycerate (3PG) and ATP
- sensitive to ATP consentration
- needs Mg2+
3-phosphoglycerate to 2-phosphoglycerate
Phosphoglycerate mutase catalyzes the isomerization of 3-phosphoglycerate (3PG) to 2-phosphoglycerate (2PG)
2-phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolpyruvate
- Enolase, (a lyase,) then catalyzes the conversion of 2-phosphoglycerate (2PG) to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)
- needs 2 MG 2+
Phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate
- pyruvate kinase, with Mg 2 converts phosphoenolpyruvate into pyruvate
- yields ATP
Glycolysis diagram
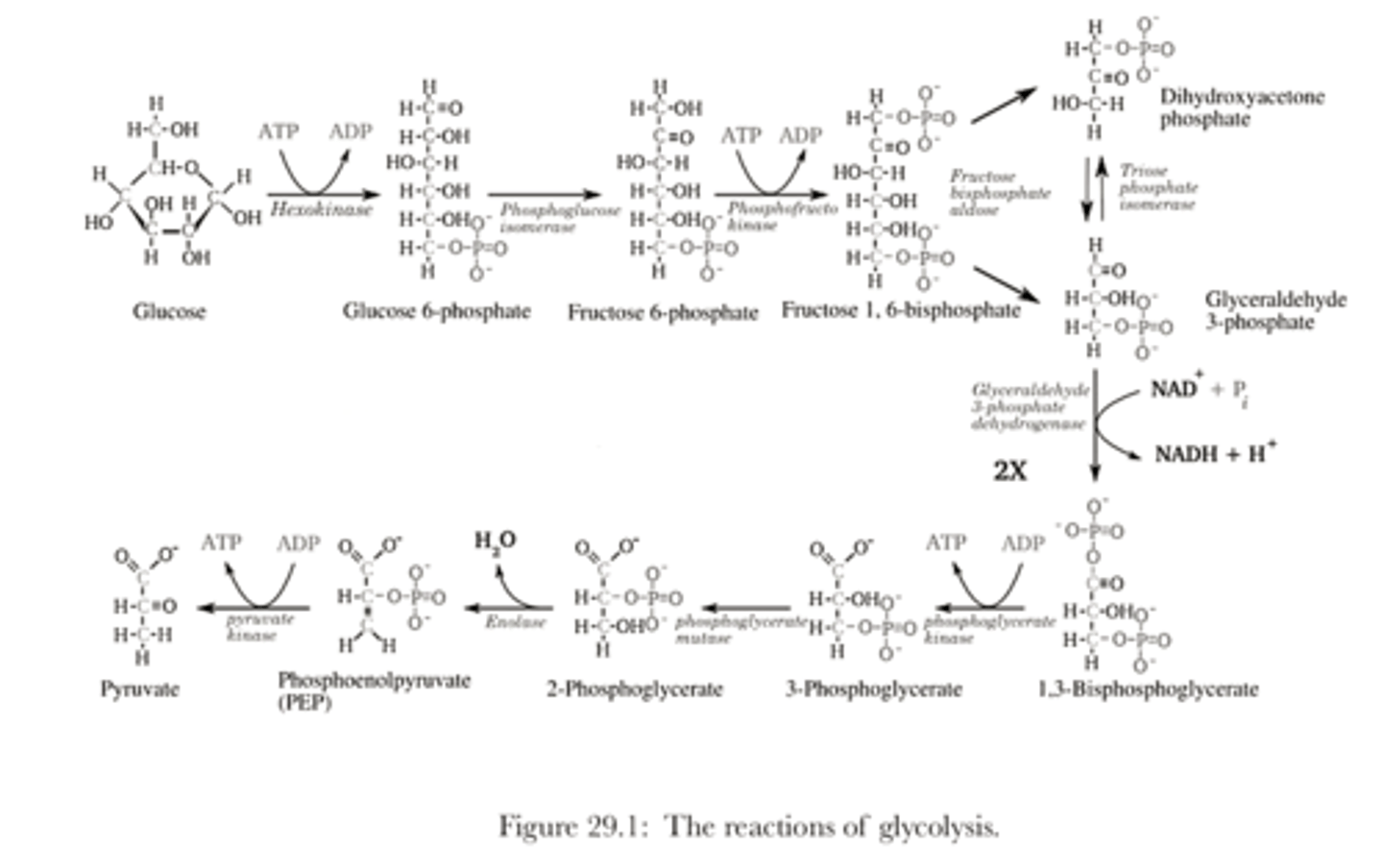
Next equation of Glycolysis

What happens if NAH if not regenerated?
- glycolysis stops
- go to lactic acid fermentation
Net equation for lactic acid fermentation
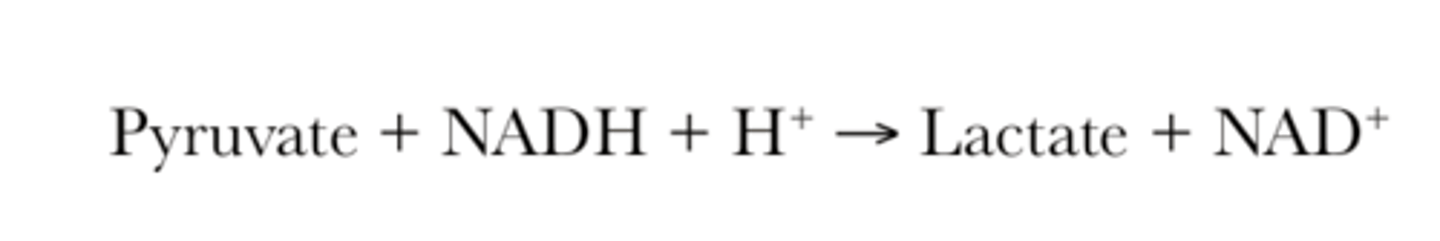
Lactic acid fermentation diagram and description
- convert pyruvate to lactate
- anaerobic
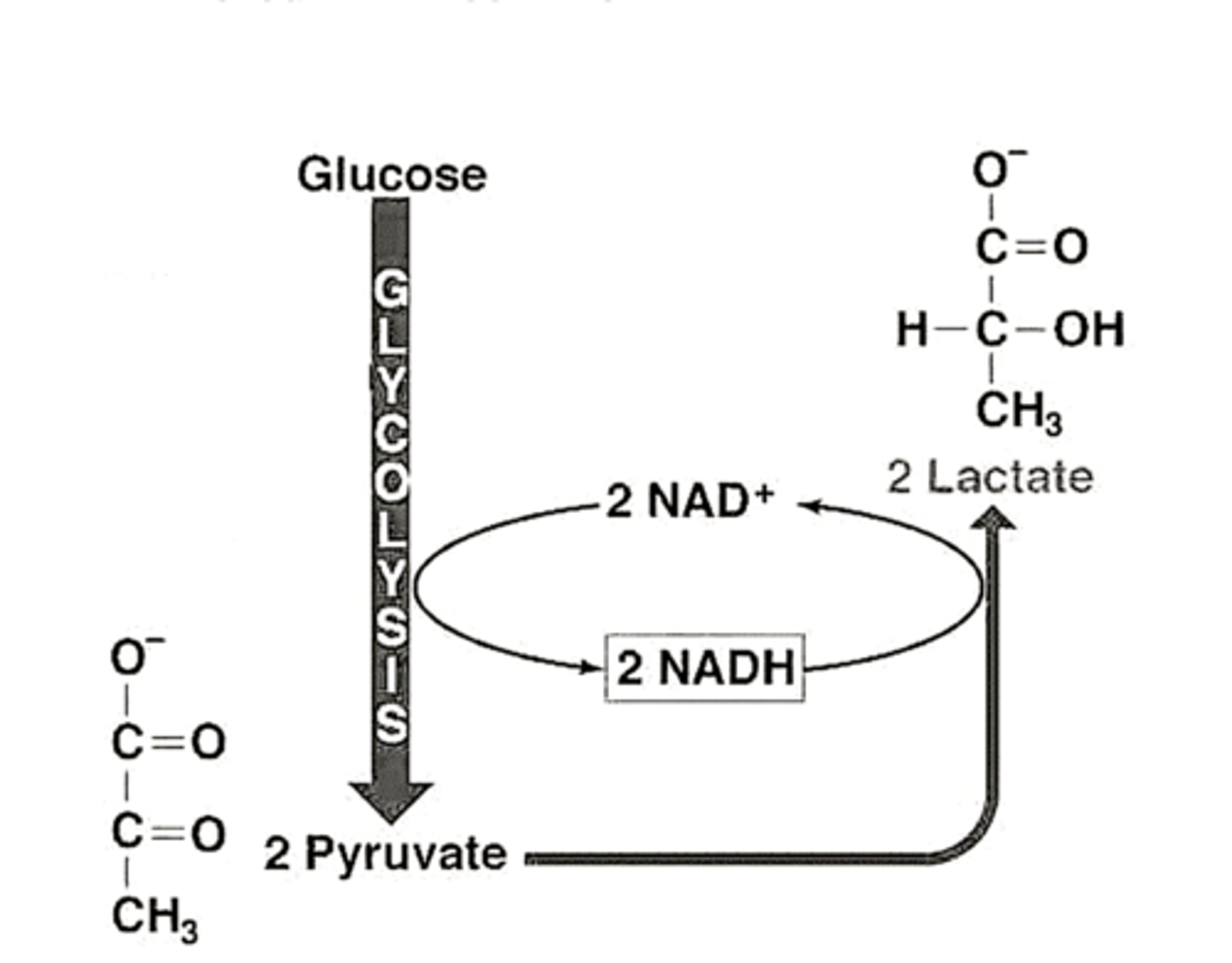
Ethanol fermentation steps
- pyruvate is cleaved producing acetaldehyde and carbon dioxide. The acetaldehyde produces ethanal
- anaerobic
Pyruvate decarboxylation
- Pyruvate is converted to acelty - CoA and CO2
- enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase
Acetyl-Co A other uses
- can be an building block for fatty acids.
Carboxylyted Acelty-Co A
- done by pyruvate carboxylase,
- replease the intermediates of the citric acid cycle adn serves as gluconeogenic substrate
Glyconeogenesis
- metabolic pathway that synthesizes glucose from non-carbohydrate carbon substrates
- 1 of 2 mechanism by which humans provide glucose to tissue types that consume it constitutively and which prevents glucose levels from droping alot during fasting
What can be used to synthesize glucose -5
- pyruvate, glycerol, lactate, odd chain fatty acids, and the glycogenic amino acids
Where does gluconeogensis occur?
- liver and a little on the cortex of the kidneys
If one is fasting how does this affect kidney contribution to gluconeogenic/?
increases it
Primary substrates of gluconeogenesis
- lactate, glycerol, and glucogenic amino acids
Glucogenic amino acids
- under go transamination and deamination to produce alpha keto acids
- enter the krebs cycle which is converted to oxyloacete (gluconeogenic reactant)
Lactate
- in the liver convert lactate to pyruvate via lactate dehydrogenase during the Cori cycle
Acetly-CoA and non-glucogenic amino acids convert to glucose
-Acetly-CoA and and substances that produce it, as well as non0glucogenic amino acids can not be converted to glucose
- reason, irreversibility of the pyruvate dehydrogenase reactions
Ketogenic amino acids/non-glucogenic amino acids
Leucine and lysin
non-glucogenic amino acid!
Know this chart
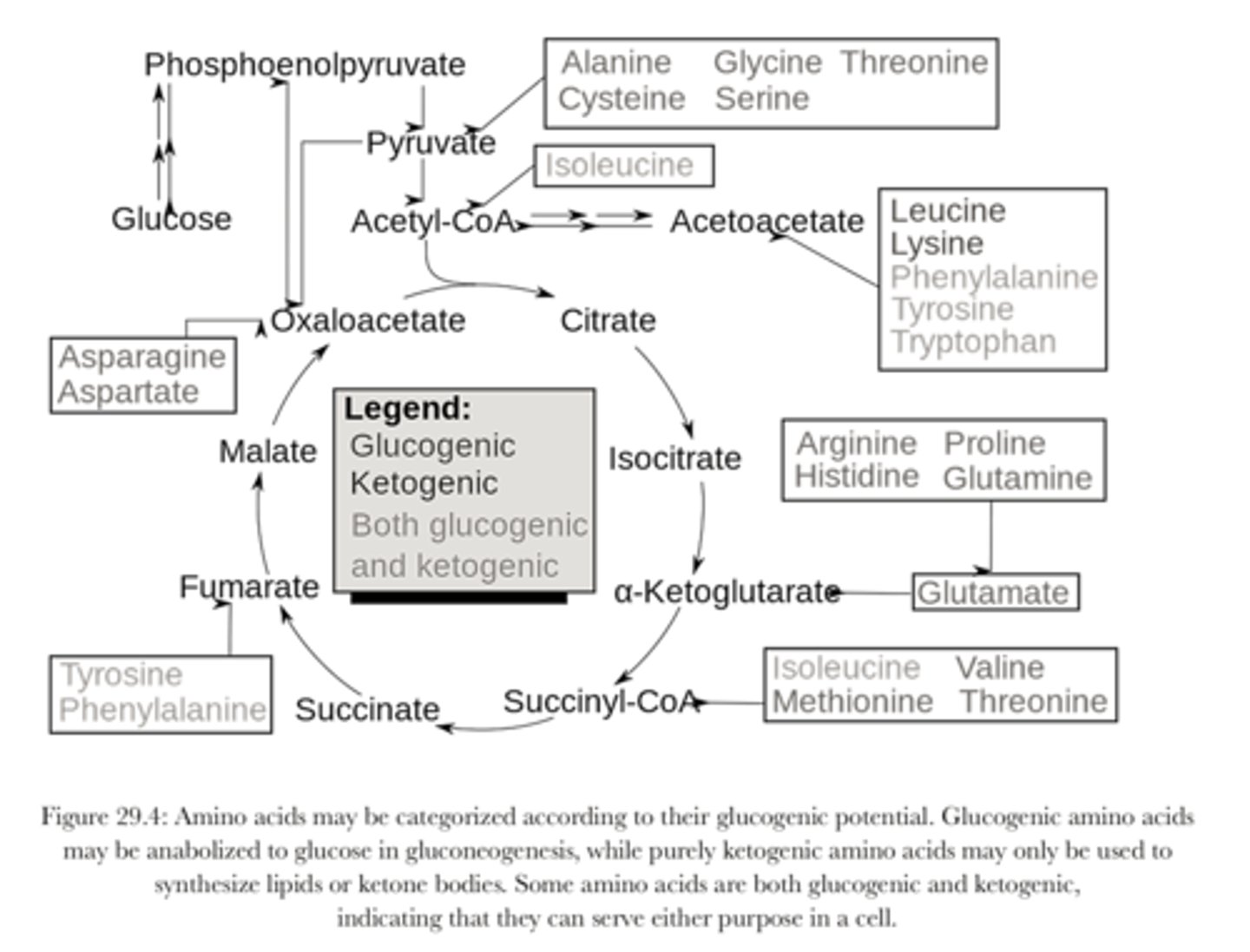
How many steps if Gluconeogenesis? Where does it happen
- 11 steps
- depends on what substrate it comes from... wither cytosol or mitochondria
Gluconeogensis: Pyruvate to oxyloacetate
- carboxylation reaction,
- happens in the mitochondria
- via pyruvate carboxylase
- need the hydrolysis of ATP
- ocyloacetate is tempory reduce to ma
Gluconeogensis: Pyruvate to oxyloacetate - When does it happen
- happens when there are high levels of acety-coA produced by the beta oxidation of fatty acids
Gluconeogensis: oxyloacetate to malate
- is temporarily reduced to malate by NADH so it can get exported out of the mitochondria. Once out it can be reoxidizes to oxalacetate using NAD+ in the cytosol
Gluconeogensis: oxyloacetate in the cytosol
- now makes phosphoenolpyruvate via decarboxylation and phosphorylation
- requires inorganic phophate via GTP to GDP and is catalyzed by phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase
Gluconeogensis: Fructose 1,6-biphosphate to Fructose 6-phosphate
- uses fructose 1,6-biphosphatase as the enzyme not PFK
- consumes h20 and releases a phophate
- rate limiting step of gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogensis: Glucose 6-phosphate to Glucose
- uses glucose 6 phosphatase
- irreversable
Glycolysis vs Gluconeogensis
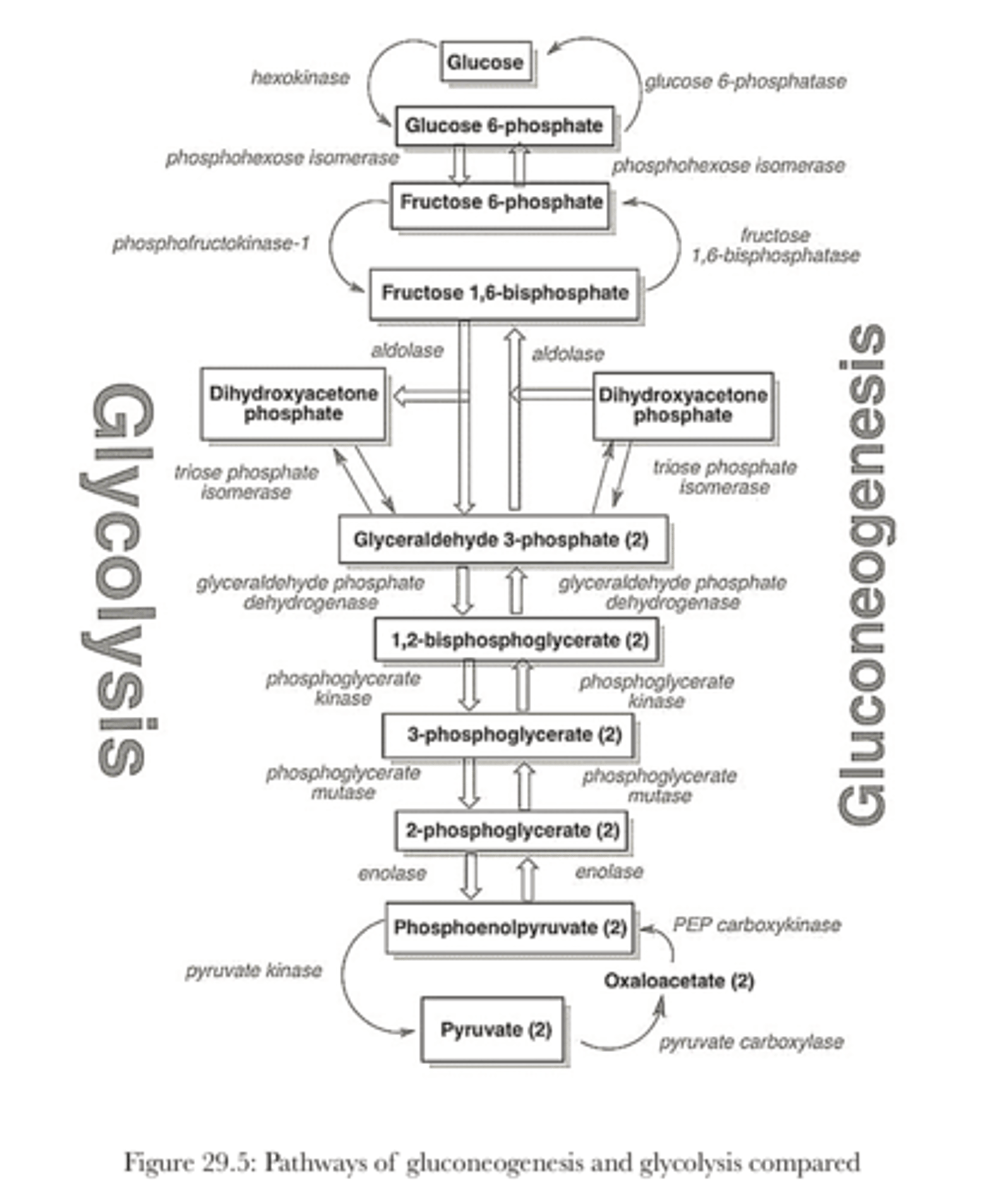
Where is Glycolysis regulated?
- hexokinase, phosphofructokinase and pyruvate kinase
- they are irreversible enzymes of glycolysis with large negative free energy changes
How is regulation of glycolysis happens?
- hexokinase, phosphofructokinase and pyruvate kinase are activated or inhibited
What dictates the regulation of glycolysis?
-the balance of ATP in the body, need for glycoltoc intermediates and blood glucose levels
What maintains blood homeostasis
- liver and pancrease
Liver cell can convert?
Convert glucose-6phosphate to glucose 1-phosphate and polymerized to form glycogen. or can send them to glycolysis to be converted to pyruvate
Where is excess citrate sent to?
- to the cytosol where the ATP citrate lyase will cleave citrate to regenerate acetyl-Coa and oxaloacetate
- the acetyl-Coa can be used to make fatty acids or cholesterol q
hexokinase vs glucokinase
- both in liver
- glucokinase is not inhibited by high glucose 6 phosphate concentration. allowing the conversion of glucse to fatty acid, glycogen and cholesteral when blood glucose and intra-hepatic glucose 6 phosphate concentrations are high
- glucokinase due to a high Km will not rephosphorylate glucose to glucose-6-phosphate at low glucose concentrations
What happens when the [glucose] decerase
- glycolysis in the liver decreases while gluconeogensis increase
What modifies the activity of phosphofructosekinase?
- two allosteric effectors: AMP and fructose 2-6-bisphosphate
- are intracellular signals regarding the abundance of available glucose in cells
fructose 2-6-bisphosphate
- mad when F6P is phosploated by a second bi-functional phosphofructosekinase enzyme (PFK2)
- as an allosteric acticator of the glycolytic enzyme PFK-1
Glucagon levels
- high when blood sugar levels are low
- causes cAMP concentration to increase, which increases the activity of protein kinase A,
Protein kinase A
- Phosphorylates pFK2
PFK
- bifunction enzyme
- can contains both kinase and phosphatase activity
Phosphorylation of PFK2
- makes it inactive, and allows fructose biphosphatase-2 (FBPase-2) to be activated
(FBPase-2)
- dephosphorylase F2,6BP generating F6P and deceases PFK activity
Epinephrine
- catecholamine hormone
0 can cause cAMP levles in the liver to rise
-
Low levels of fructose-2,6-biphosphate
- decrease PFK1 activity and increase fructose 1,6 biphosphate activity
- this favors glucogenesis
Well fed state
- insulin and glucagon levels decrease
- increase F2,6BP present in the liver and increase in hepatic glycolysis
Diagram: Regulation of PFK-1 by fructose-2-6, bisphosphate
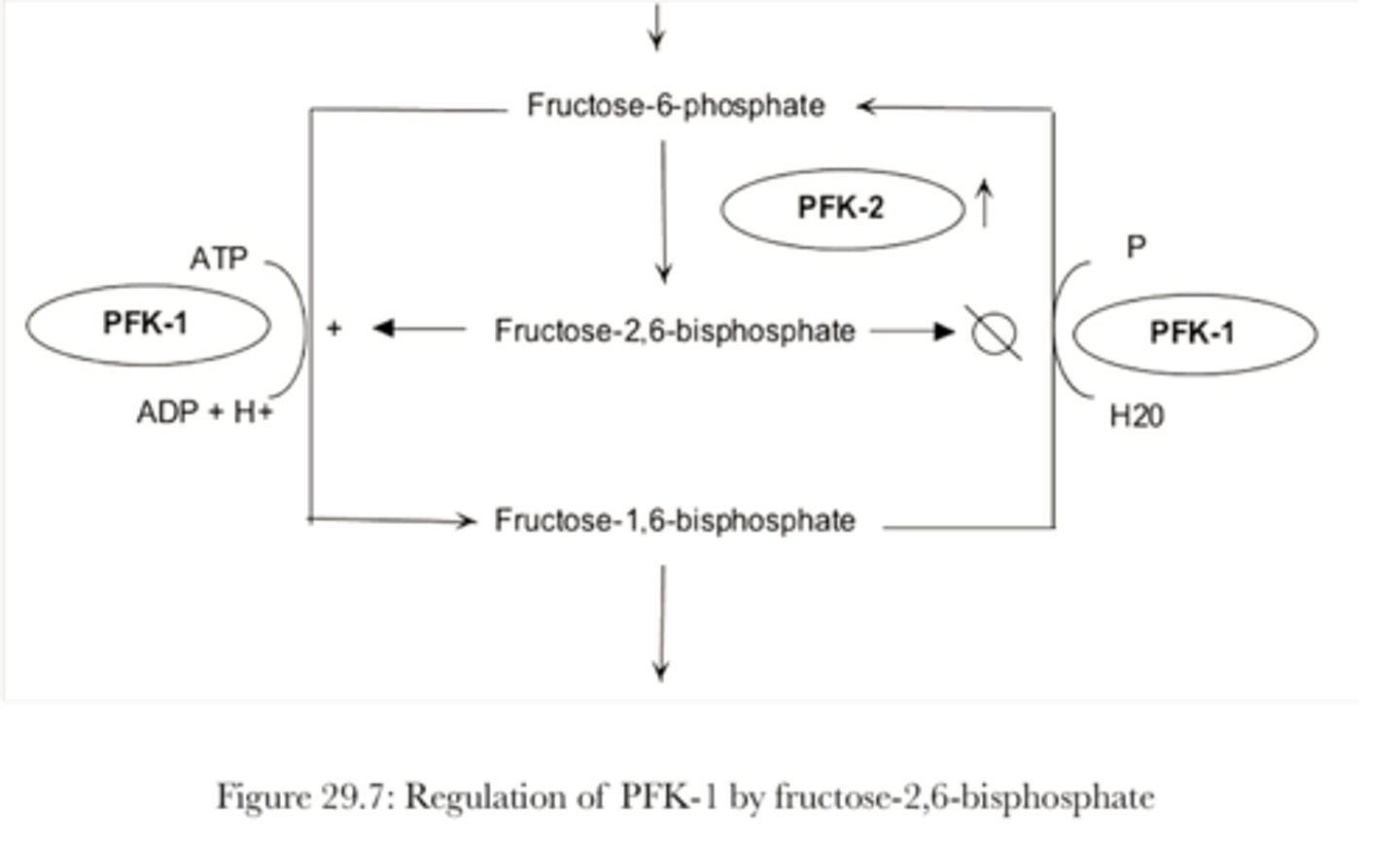
What regulates PFK-1
- High levels of ATP, inhibit
- AMP and citrate: positive allosteric effectors
Pyruvate kinase regulation (liver)
- negativley allosterically regulated by ATP and alanine
- liver pyruvate kinase is indirectly regulated by glucagon and epinephrine (both hormones cause elevation of cAMP which would inactivates the pyruvate kinase)
- are inactive when PEP carboxykinase and pyruvate carboxylase are active
Muscle pyruvate kinase
- is not inhibited by protein kinase A and is insensitive to epinephrine
- this happens becuase the body needs to inhibit glycolysis in the liver when fasting but continue it in the muscles
Insulin and blood glucose levels
- when BG levels increase so doo insulin levels
Insulin
- activates phophoprotein phosphatase 1
phophoprotein phosphatase 1
- dephosphorylates and activates pyruvate kinase
What enzymes regulate Gluconeogensis?
- G6P, F1,6BP, PEP carboxykinase
What determines the regulation of gluconeogensis
- glucagon levels
What happens when blood glucose levels are low?
- Glucagon is released by the alpha-cells of pancreas, cAMP levels rise, increasing the activity of protein kinase A
- When the target of protein kinase A becomes phosphorylated, gluconeogensis is stimulated and glyoylysis is inhibited
What effect does Glucagon have on F 1,6-BP and PFK-1
- stimulates F 1,6-BP inhibits PFK-1 by decreaseing fructose 3-6 biphoophate through its interactions with PFK-2 and FBPase-2
What effect foes Glucagon have on hepatic pyruvate kinase
- converts it to its inactive phosphorylated form through cAMP induced stimulation of protein kinase A which decreases the rate of pyruvate production
Glucagon effect on PEP carboxykinase
- increases the enzyme's availability when the pool of gluconeogenic substrates grow
What inhibits and activates FBPase-1
- high [AMP] inhibits, high [ATP] activates
What activates PFK-1
- AMP
What affect does acetly Co A have on pyruvate carboxylase?
- it allosterically activates it during fastomg
- since rapid catabolism of fats in adipose tissue happens when faster there are more acetyl Co A available this activates the PDH kinase and inhibited pyruvate dehydrogenase. This increase pyruvate going through gluconeogeneisis and decese its rate going to the krebs
Pentose phosphate pathway
- aka phosphogluconate pathway, and hexose monophophate shunt
- cytosolic pathway that operates to produce the reducing equivalent NADPH and the pentose sugares needed for nucleotide biosynthesis .
NADPH
-major reductant involved in the biosynthesis of fatty acids and cholesterol and lipids
- important in anabolic mechanism
- also provides the cell a measure of protection against the damaging effects of reactive oxygen species generated from hydrogen peroxide
NADPH and glutathione
NADPH provides the reducing equivalents by which reduced glutathione may be regenerate by glutathione reductase
Glutathion disulfide
- have glutathione from NADPH
- glutathione peroxidase converts hydrogen peroxide to water via oxidation of monomeric glutathione to glutathione disulfide

Phases of the pentose phosphate pathway
- divided into two phases:
- initial oxidative phase : NADPH is synthesized
- Final non-oxidative phase: Pentose synthesis
Oxidative phase of pentose phosphate pathway
- two NADP+ are reduced to NADPH, while G^P is oxidized to produce ribulose 5 phosphate and a carbon dioxide
- 1st molecule of NADPH produced while G-6-P is oxidized to 6-phosphogluno- 𝛿-lactone (this is catalyzed by G-6-P dehydrogenase)
- the 2nd NADPH is synthesized during the conversion of 6-phosphogluconate to ribulose-5-phosphate
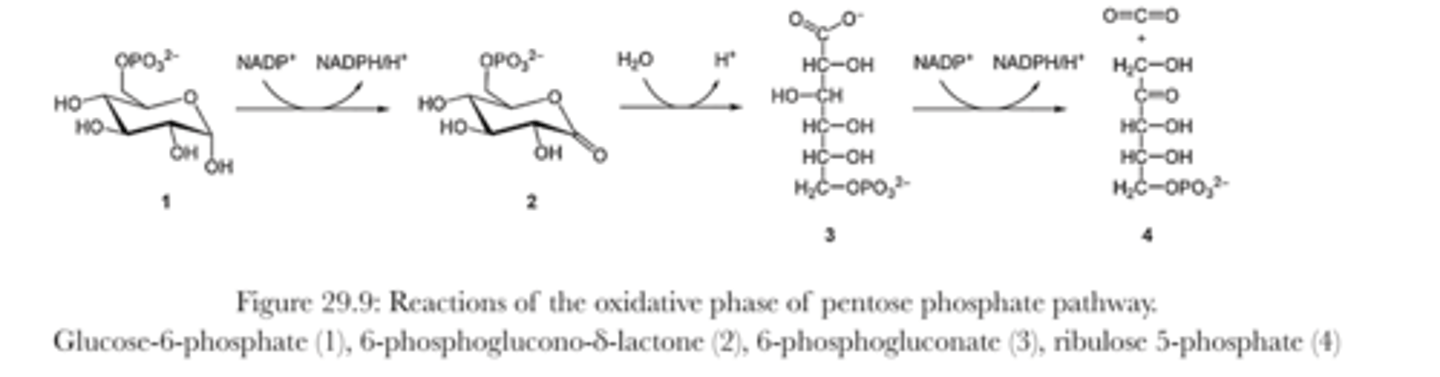
Non-oxidative phase of pentose phosphate pathway
- ribulose-5-phosphate produced during the oxidative phase can be converted to ribose-5-phosphate required for the synthesis of nucleotides or to the glycolytic intermediates glyceraldehyde-3-phsophate or fructose-6-phosphate

What if the cellular need for NADPH exceeds that of ribose-5-phosphate?
- thiamine dependent enzyme transketolase and aldolase enzyme convert ribulose-5-phosphate to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and fructose-6-phosphate via transfer of 2 or 3 three- carbon units.
What happens when the need for ribose-5-phosphate is more than NADPH?
- ribose-5-phosphate can be synthesized from glyceraldhyde 3-phosphate and fructose-6-phosphate without passing through the oxidative phase of the reaction
What is the reate limiting enzyme of the pentose phophate pathway?
- G6P dehydrogenase
G6P dehydrogenase
- allosterically inhibits NADPH
- stimulated by NADP+
Ratio of NADPH/NADP+
- normally high and the pentose phosphate pathway process is inhibited
- decreases when NADPH increases and increase the pathway
What does NADP+ do?
- stimulates glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase to make more NADPH
How does acetyl CoA effect NADPH production
- it inhibits it
Other names for the krebs cycle
-tricarboxylic acid cycle TCA or citric acid cycle
Krebs cycle overview
- Generates high-energy compounds through the oxidation of fats, carbohydrates and proteins
Where does the Krebs cycle happen
- in the mitochondrial matrix
What is Acetyl-CoA
- two carbon substrate of Krebs
How can Acetyl-CoA be produced
- From pyruvate
- B-oxidation of fatty acids in the mitochondrial matrixs
- directly from the carbon backbone of ketogenic amino acids freed from protein catabolism
- ketone bodies and certain alcohols
Ketogenic and glucogenic amino acids
- only ketogenic leucine and lysine
- ketogenic and glucogenic: isoleucine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, tyrosine and threonine
Transamination of ketogenic amino acids
- will produce acetyl-CoA
- amine group of the amino acid is transferred to a keto acid forming a keto acid
- required enzyme pryrioxal 5' phosphate PLP and depend on available alpha keto acids