cerebral cortex 4/1
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
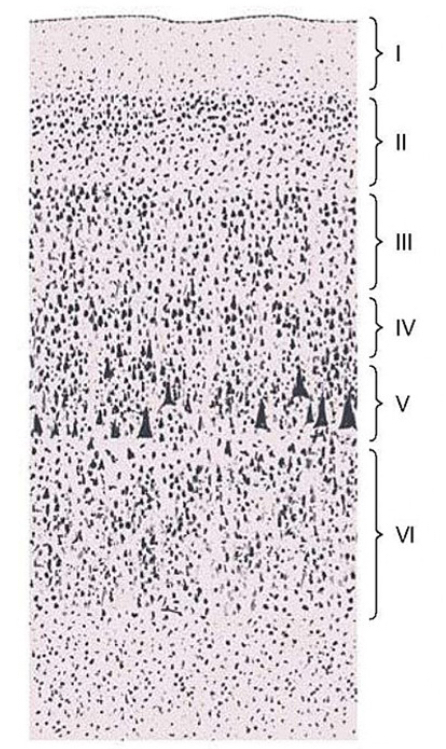
PI: which of the following cortical layers will be expanded if the sections as from the primary visual cortex?
layer I
layer II
layer III
layer IV
layer V
layer VI
4
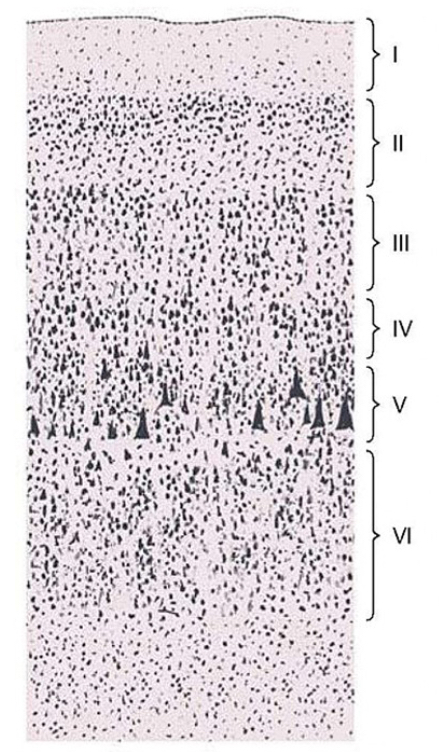
PI: which of the following layers chiefly gives rise to association and commissural fibers?
layer I
layer II
layer III
layer IV
layer V
layer VI
3
association fibers
connect gyri within same hemisphere
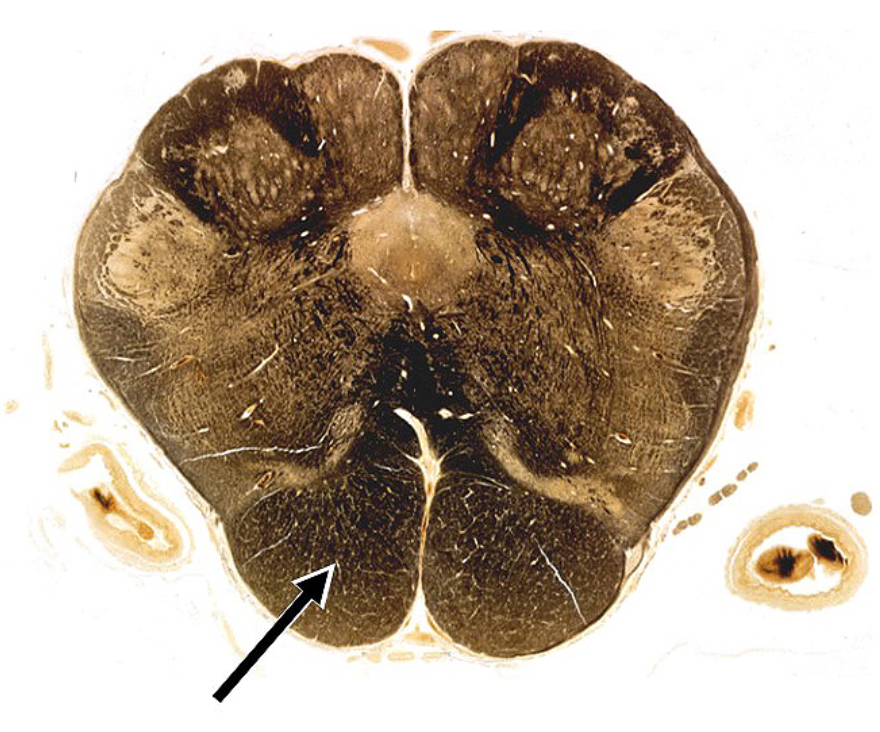
PI: axons of this structure originate chiefly from which cortical layer?
layer I
layer II
layer III
layer IV
layer V
layer VI
5
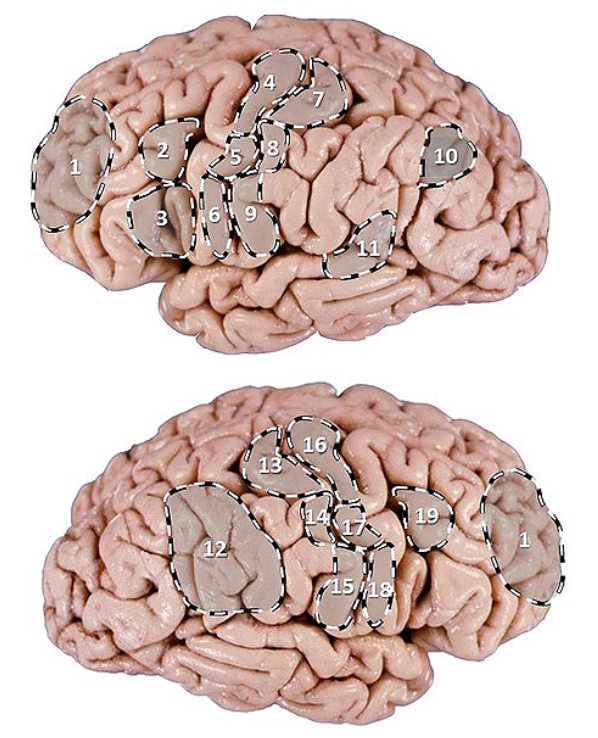
PI: which cortical area commands voluntary movements of the left forearm and shoulder?
16
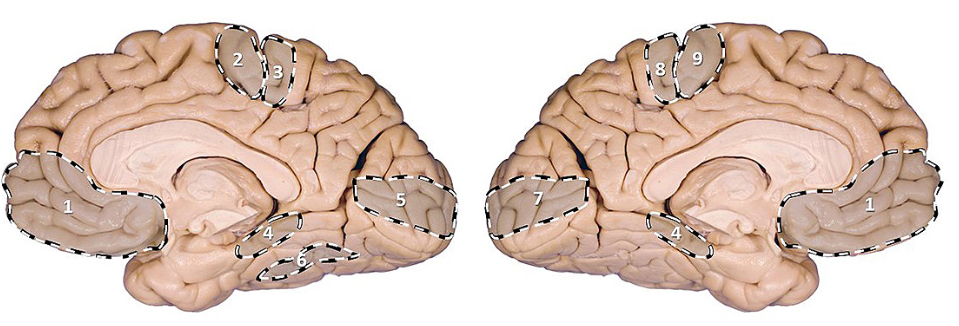
PI: which area is associated with voluntary movements of the right lower limb?
9
PI: which area when damaged is associated with impairment of graphesthesia in the left hand?
14
commissural fibers
connects gyri between two hemisphere (crosses midline)
PI: which area when damaged results in the following visual defect?
7
PI: a 72 y/o woman is brought to the ER by her daughter. the history of the current event, provided by the daughter, reveals that the woman complained of a sudden headache and, after lying down for a period of time, seemed very confused. the examination reveals an otherwise healthy woman who can see but is unable to recognize what she sees, which is probably contributing to her apparent confusion. this woman is most likely suffering from which of the following?
aphasia
anopsia
agnosia
apraxia
akinesia
3
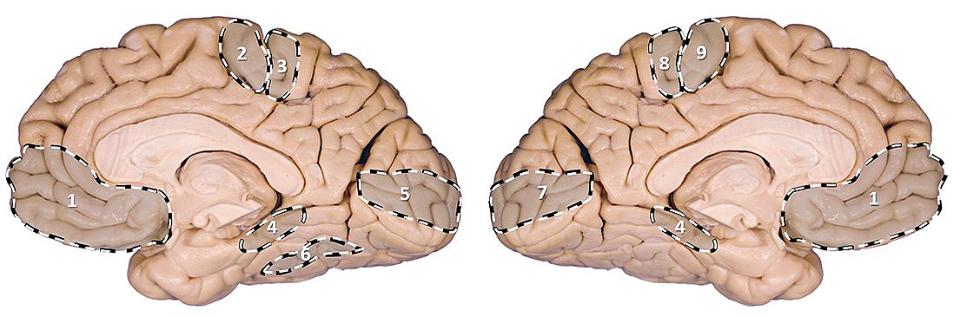
PI: which area when damaged results in the ability to recognize someone else’s or one’s own face?
6
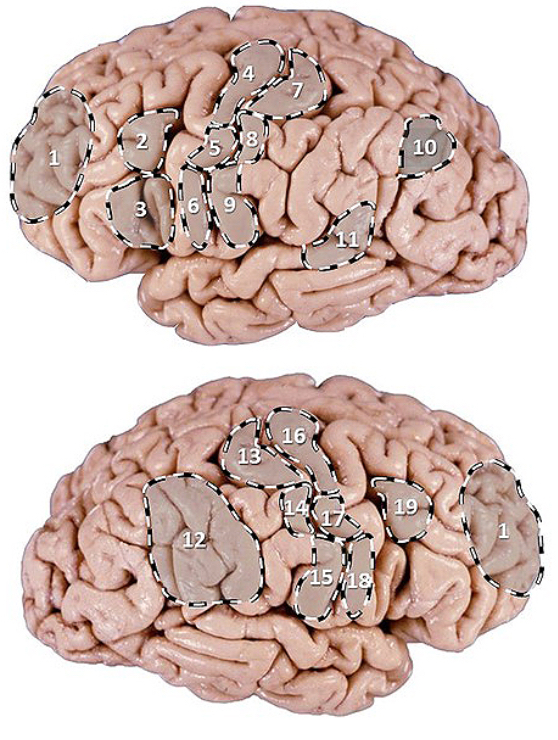
PI: which area is associated with programming the production of spoken words?
3
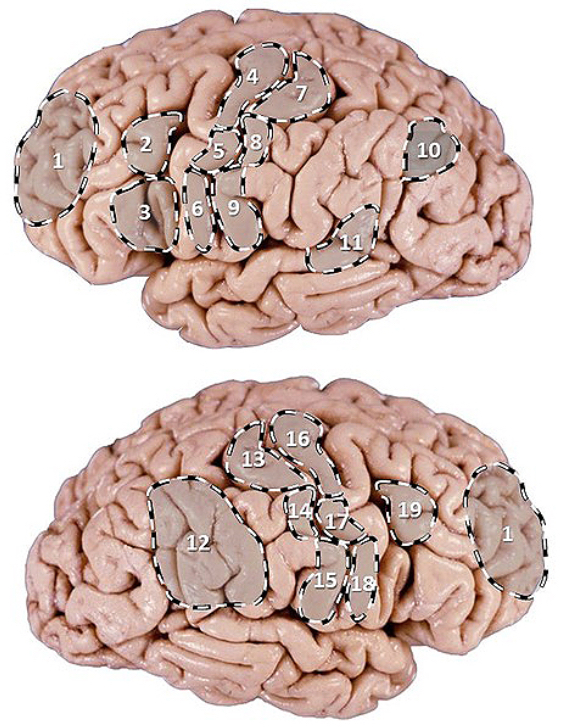
PI: which area when damaged is associated with impaired ability to concentrate, easily distracted, loss of initiative, apathy, cannot make decisions?
1
cerebral cortex
“highest center”
perceives sensations, commands skilled movements (UMNs), provides awareness of emotions and behavior (limbic system), necessary for memory and thinking (cognition), language abilities
older parts of the cerebrum
archicortex (found in hippocampus)
paleocortex (pyriform cortex) anterior to ^
neocortex
makes up 90% of cerebral cortex
6 histological layers
ex. primary motor cortex, primary visual cortex
layer 1 of neocortex
molecular layer
just deep to surface of cerebral cortex is (meningeal layer)
mostly devoid of neurons
some left to right myelinated axons
neighboring cortical columns have synapses
layer 2 of neocortex
external granular cell layer
interneurons with short axons
layer 3 of neocortex
external pyramidal cell layer
large pyramidal neurons
association fibers to white matter within same hemisphere, synapse on a cortical column in layers 2 & 3
commissural fibers to white matter, cross midline, synapse on cortical columns in layers 2-4
layer 4 of neocortex
internal granular cell layer
receptive in nature
input primarily from thalamus (corticopetal axons)
very thick in sensory cortex
layer 5 of neocortex
internal pyramidal cell layer
output layer
axons projects away from cortex (corticofugal)
thick in motor cortex, thin in sensory cortex
layer 6 of neocortex
multiform layer
various interneurons of various shapes
output layer (projection fibers to thalamus)
granule cells
chief input neurons of cortex
pyramidal cells
chief output neurons of cortex
functional/physiological arrangement of cerebral cortex
cortical columns
0.5-1mm wide
all neurons within a column work collectively for one particular function
cortical columns with the same function may not be adjacent to one another
frontal lobe
anterior to central sulcus
deep to frontal bone
parietal lobe
posterior to central sulcus
temporal lobe
inferior to lateral fissure
occipital lobe
posterior part of brain
brodman’s cortical areas
based on the thickness of different areas of the cerebral cortex
primary (unimodal) areas
processes single functions—primary motor cortex commands movements
association (polymodal) areas
integrates more than 1 function—parietal association integrates somatosensory, visual, hearing
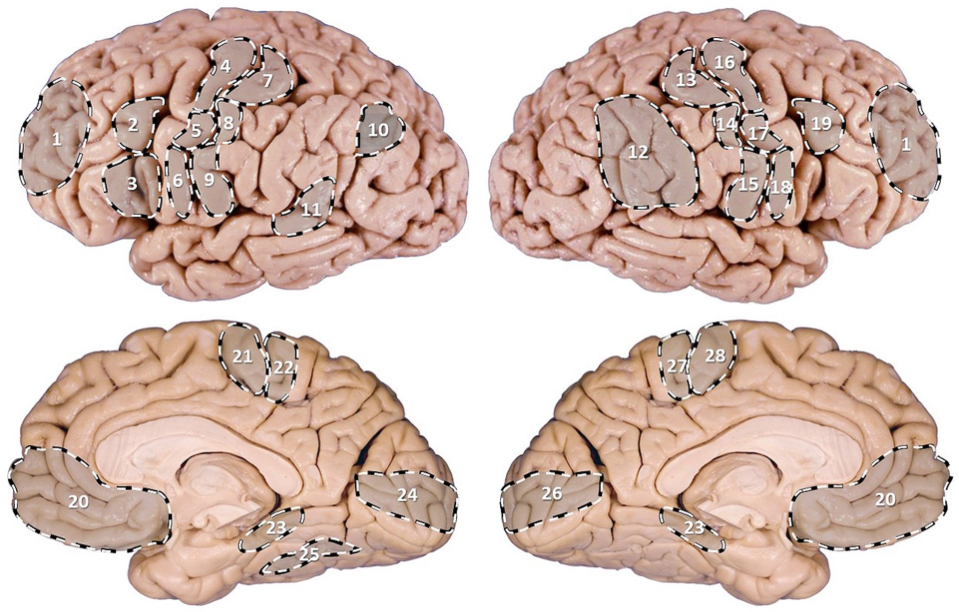
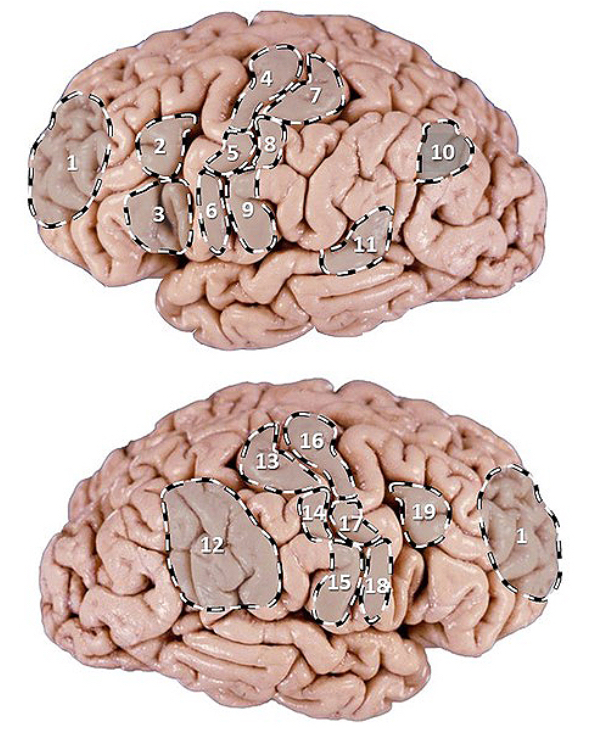
PI: a 72 y/o man presents with severe weakness of his R lower limb but has age-appropriate strength in both of his upper limbs. which of the following (pictured) might be the location of the lesion?
28
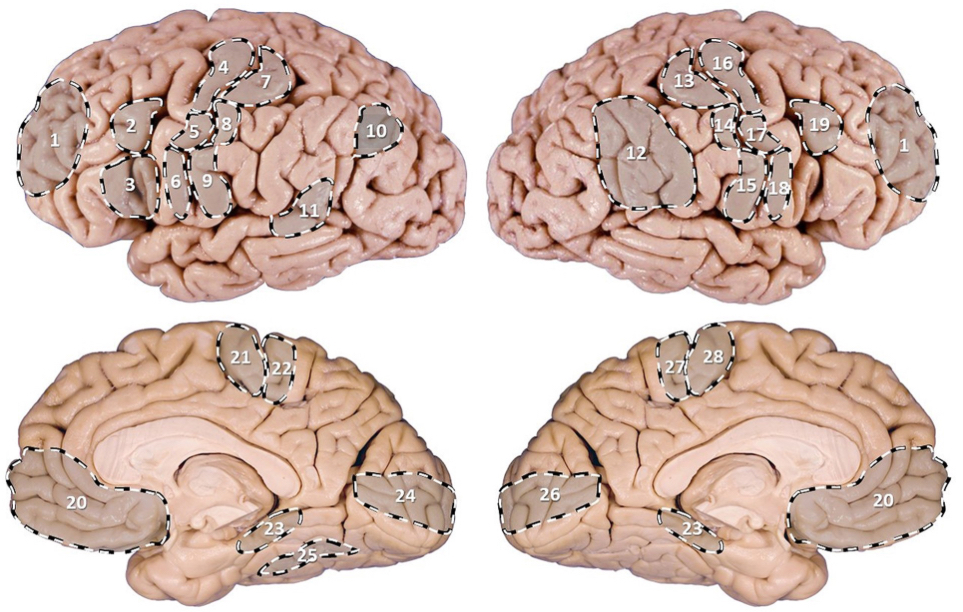
PI: a 67 y/o female patient is brought to the ER after her daughter noticed she has been having meaningless speech. when assessing the patient, she calls the chair a table, and at times would make up new words. she does not appear to be aware of her deficit and is carrying on an empty conversation. her speech is fluent, but with paraphasic errors. her repetition is impaired. on physical examination, a right upper quadrant field-cut is appreciated, with impairment in comprehension and repetition. which of the following (pictured) structures is most likely involved int his patient’s presentation?
11
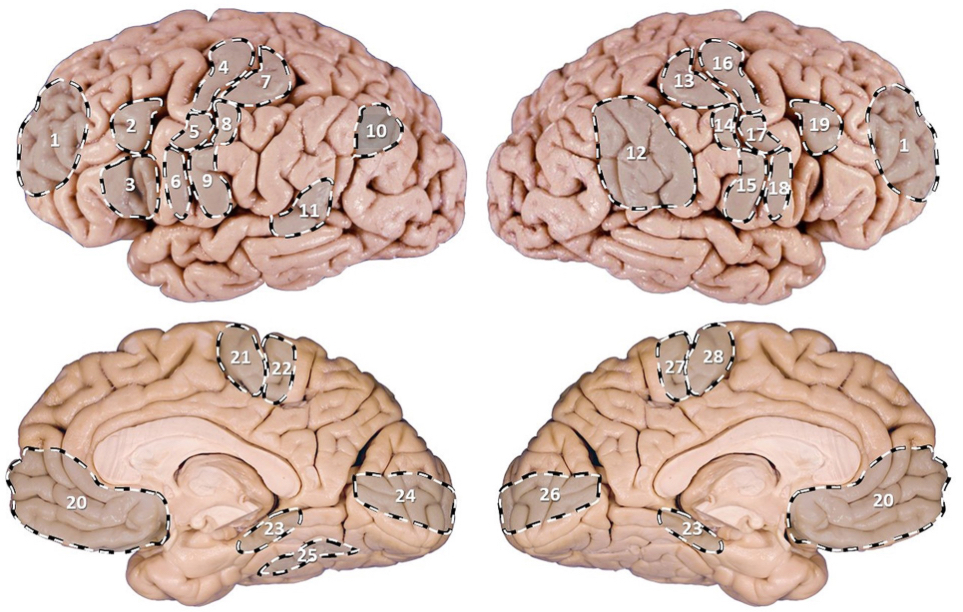
PI: a 66 y/o retired cartoonist with some reluctance was brought to the family physician by his wife who was “terribly concerned” about his recent behavior. she stated that her husband didn’t seem to know what to do with himself anymore. although his wife found this behavior tolerable since he was “getting old”, she became frightened by another peculiarity of his which was to go to bed leaving on his left shoe and sock. he would also leave on half of his shirt and trousers (left side). his left arm and leg were always seen to be hanging off the side of the bed. one night, she undressed his left side after he went to sleep only to discover that he refused to redress his left side when he got up the next morning. a scan reveals a cortical infarct. which of the following (pictured) structures is most likely involved in this patient’s presentation?
12