M&S Midterms
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
simuland
A __is the real - world item of interest.
simuland
It is the object, process, or phenomenon to be simulated
Schematic model
is a representation of a simuland.
Mechanical diagram
is used to develop a mathematical model for the car suspension system
Differential equations
are programmed for computer solution using a “continuous simulation” software tool
continuous simulation
Differential equations are programmed for computer solution using a “_” software tool
Simulation
is the process of executing a model over time
Attribute
. A significant or defining property or characteristic of a model or simulation.
• Fidelity • Resolution • Scale
Three important attributes
Fidelity
. Accuracy of model’s representation or simulation’s results.
Fidelity
AKA validity.
Reality Representation Requirements
Fidelity is relative to:
Reality
How consistent are the simulation results and the real world in the same scenario
Resolution
. The degree of detail with which the real-world is simulated. More detail is higher _.
Resolution
AKA granularity.
Scale
. Size of the overall scenario or event the simulation represents.
Scale
AKA level
Component Equipment
Typical scales for manufacturing systems:
Component-
System, subsystem, or single unit of a factory
Equipment
- 1, 10 or 100 machines
directly proportional
Fidelity and resolution relate
Indirectly proportional
Fidelity and scale relate
Indirectly proportional
Resolution and scale relate
Verification, Validation, and Accreditation
The process of determining if a model is correct and usable;
Verification, Validation, and Accreditation
the process of developing and delimiting confidence that a model can be used for a specific purpose
Verification
. The process of determining that a model implementation accurately represents the developer’s conceptual description and specifications
Verification
Is it coded right? Does the implementation match the design?
Verification
This is software engineering quality. General software testing methods apply.
Validation
. The process of determining the degree to which a model (and data) is an accurate representation of the real world from the perspective of the model’s intended usage.
Validation
Is the right thing coded? Does the model match reality (i.e., fidelity)?
Validation
This is modeling quality.
Informal
-Audit
-Desk checking
-Documentation Checking
-Face validation
-Inspections
-Reviews
-Turing test
-Walkthroughs
Static
-Cause-Effect Graphing
-Control Analysis
-Data Analysis
-Fault/Failure Analysis
-Interface Analysis
-Semantic Analysis
-Structural Analysis
-Symbolic Evaluation
-Syntax Analysis
-Traceability Assessment
Dynamic
-Acceptance Testing
-Alpha Testing
-Assertion Checking
-Beta Testing
-Bottom-up Testing
-Comparison Testing
-Statistical Techniques
-Structural Testing
-Submodel/Module Testing
-Visualization/ Animation …
Formal
-Induction
-Inductive Assertions
-Inference-Logical Deduction
-Lambda Calculus
-Predicate Calculus
-Predicate Transformation
-Proof of Correctness
Informal, Static, Dynamic, Formal
Verification and validation techniques
Accreditation
. Official certification by a responsible authority that a model is acceptable for a specific purpose.
For a specific purpose or function
Not a blanket or general-purpose approval
Authority is agency or person responsible for results or use of model, not developer
Accreditation notes
Authority
is agency or person responsible for results or use of model, not developer
state of a system
The _ at time t0 is the information required at t0 such that the output y(t), for all t>=t0, is uniquely determined from this information and from the input x(t) for t>=t0 .
state variables
This state information is usually represented by a vector q(t) whose components are called
state space
The __ of a system, denoted by Q, is the set of all possible values that q(t) may take
Static System
• A system in which the output depends only on the input and is independent of the system state
Static System
• A system without memory
Dynamic System
• A system in which the output depends on both the input and the system state • A system with memory
Dynamic System
event
With each state transition, we associate an __.
event
An __ is a specific instantaneous action or occurrence which results in an instantaneous change of system state. We call such systems “event-driven” systems
“event-driven” systems
An event is a specific instantaneous action or occurrence which results in an instantaneous change of system state. We call such systems __
“time-driven” systems
The system response varies as a continuous function of time, even when there is no change in the system input. Thus, the system state appears to evolve simply because time advances, We call these systems___
Deterministic System
: A system which will produce the same output from a given starting condition or initial state
Stochastic System
: A system in which one or more variables has uncertainty or variability.
Stochastic System
In this case, the system state becomes a random variable and a probabilistic framework is required to describe system behavior
Continuous-Time System
: A system in which the time variable is represented by a continuous variable; t ε R
Discrete-Time System
: A system in which the time variable is represented by a discrete variable, t ε I. Usually, the intervals between time values are equal.
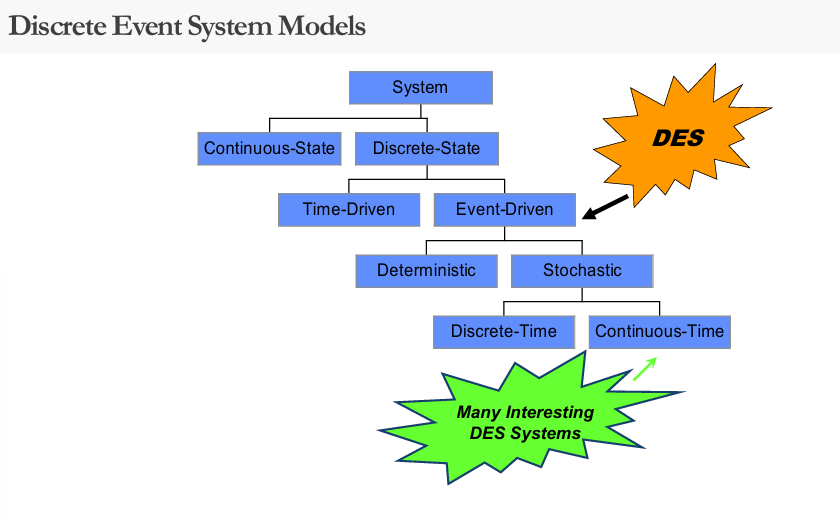
Discrete Event System (DES)
A __ is a discrete-state, event-driven system
Discrete Event System (DES)
state evolution depends entirely on the initial state of the system and the occurrence of asynchronous discrete events over time.
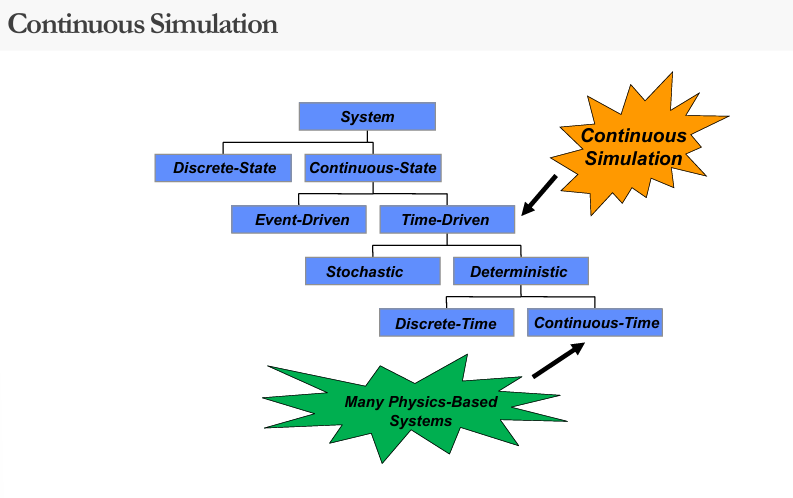
Continuous System
is a continuous-state, time-driven system
continuous
Many physics-based systems are modeled as _ systems.
Discrete Event Systems
PacMan movement of character
Discrete Event Systems
Water cycle phase
Continuous Systems
Projectile motion
Continuous Systems
Weather forecast system
• Static or Dynamic
• Continuous-State or Discrete-State
• Time-Driven or Event-Driven
• Deterministic or Stochastic
• Continuous-Time or Discrete Time
System Classification
DES, Continuous System
System Types
Monte Carlo Simulation
Discrete Event Simulation
Continuous Simulation
Agent-Based Simulation
Simulation Paradigms
Monte Carlo Simulation
• Static systems modeled using probability
• Simulation of a random experiment
• Implemented using spreadsheets and the relative frequency interpretation of probability
Discrete Event Simulation
• Dynamic systems modeled as queuing systems
• Implemented using spreadsheets or DES tools (Arena)
Continuous Simulation
• Dynamic systems modeled using differential equations
• Simulation of continuous-state, time-driven systems
• Implemented using spreadsheets or CS tools (Matlab-Simulink)
Agent-Based Simulation
• Generally a bottom up approach to represent human and social systems
• Usually stochastic in nature
• Implemented in various ways from a computational standpoint (ex. Netlogo)
Set
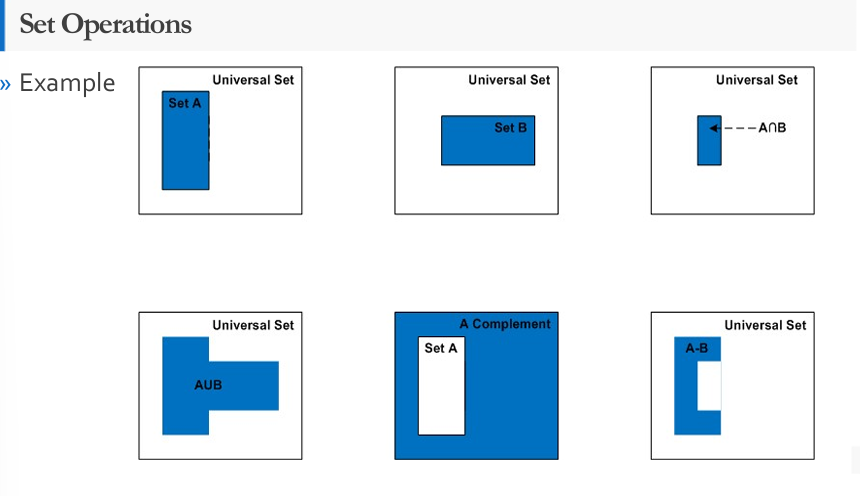
• a collection of objects
elements
• the objects are called __of the set and may be anything
Equality
set A and set B contain exactly the same elements
Union
the set consisting of all elements that are either in A or in B or in both A and B
Intersection
the set consisting of all elements that are in A and in B
Difference
the set consisting of elements in A that are not elements in B
Complement
The complement of set A, denoted A’, is the set Universal set - A
Common Probability Density Functions
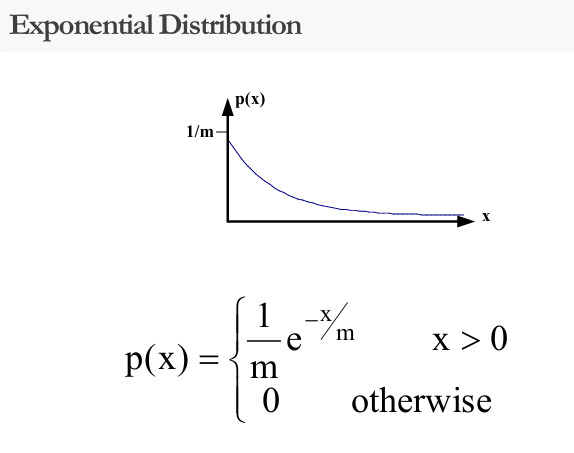
Common Probability Density Functions
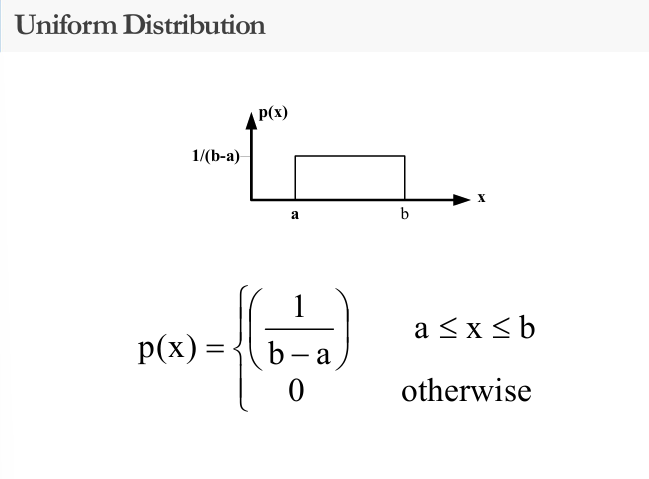
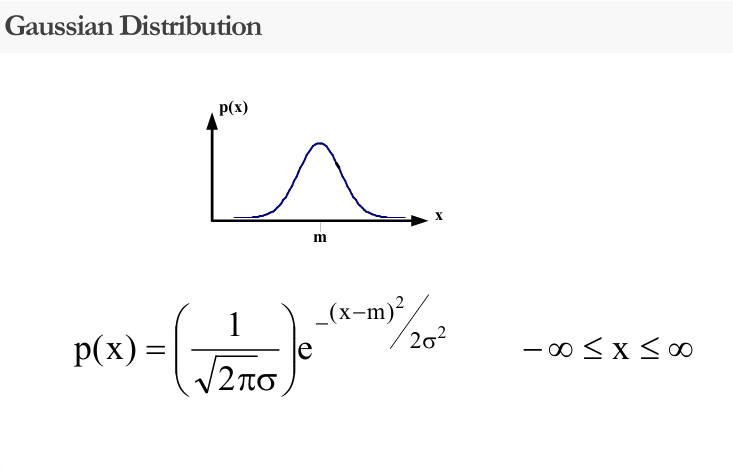
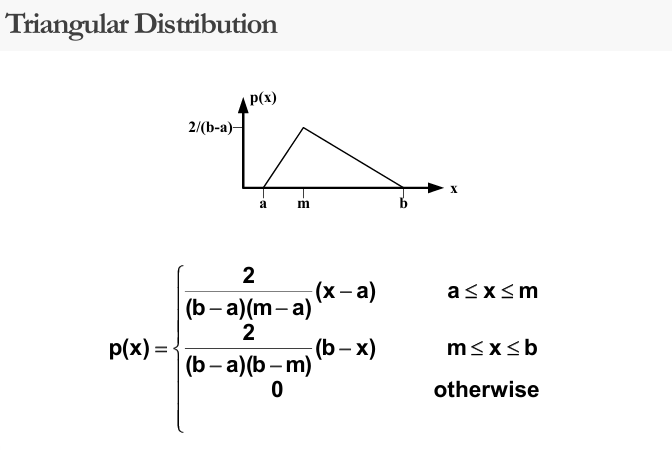
Random Number
is a sample, selected randomly, from the distribution UNIFORM (0, 1)
Random Variate
is a sample, drawn randomly, from a distribution other than UNIFORM (0, 1)
Inverse Transform Theorem
Used to generate random variate
Monte Carlo Simulation
Stochastic simulation of a real-world system modeled as a random experiment.
Modeling Approach of MCS
• System behavior is modeled using probability distributions
• Physics of system is not represented explicitly
Simulation Approach of MCS
• Utilize randomly generated parameter values
• Parameter values identify possible outcomes
• Usually conduct multiple trials and perform statistical analysis
• Simulation is static; there is no time advance feature
Simulation Results of MCS
• Utilize “relative frequency” definition of probability
• Conduct multiple trials to approximate limit operation
Generate a random number n = RAND( )
Determine the standard normal variate corresponding to n using Z(n)=NORM.S.INV (n)
Denormalize Z(n) to determine the point x
Repeat this process to find a point y
The point (x, y) represents the trial result
Check to see if this is a hit or a miss
Monte Carlo Solution Approach
Estimation
is the process of estimating a population parameter based upon knowledge of a sample statistic.
estimator
The sample statistic used in estimating a population parameter is called an __.
confidence interval estimate.
The most popular form of an estimate is the
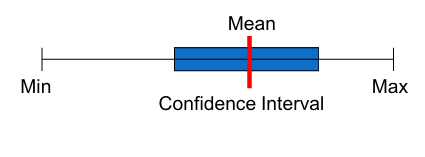
Precision
• refers to the accuracy of an estimate;
better/higher
the smaller the estimate interval, the __ the precision