Neuro Lecture 9 (pt. 2): CN VIII, IX, X, XI, XII
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
What are the 2 divisions of the ear (CN VIII)?
- Bony labyrinth
- Membranous labyrinth
What does the bony labyrinth contain (CN VIII)?
Perilymph
What does the membranous labyrinth contain (CN VIII)?
Endolymph
What are the 3 components that the membranous labyrinth contains (CN VIII)?
- Cochlea
- Semicircular canals
- Otolith organs
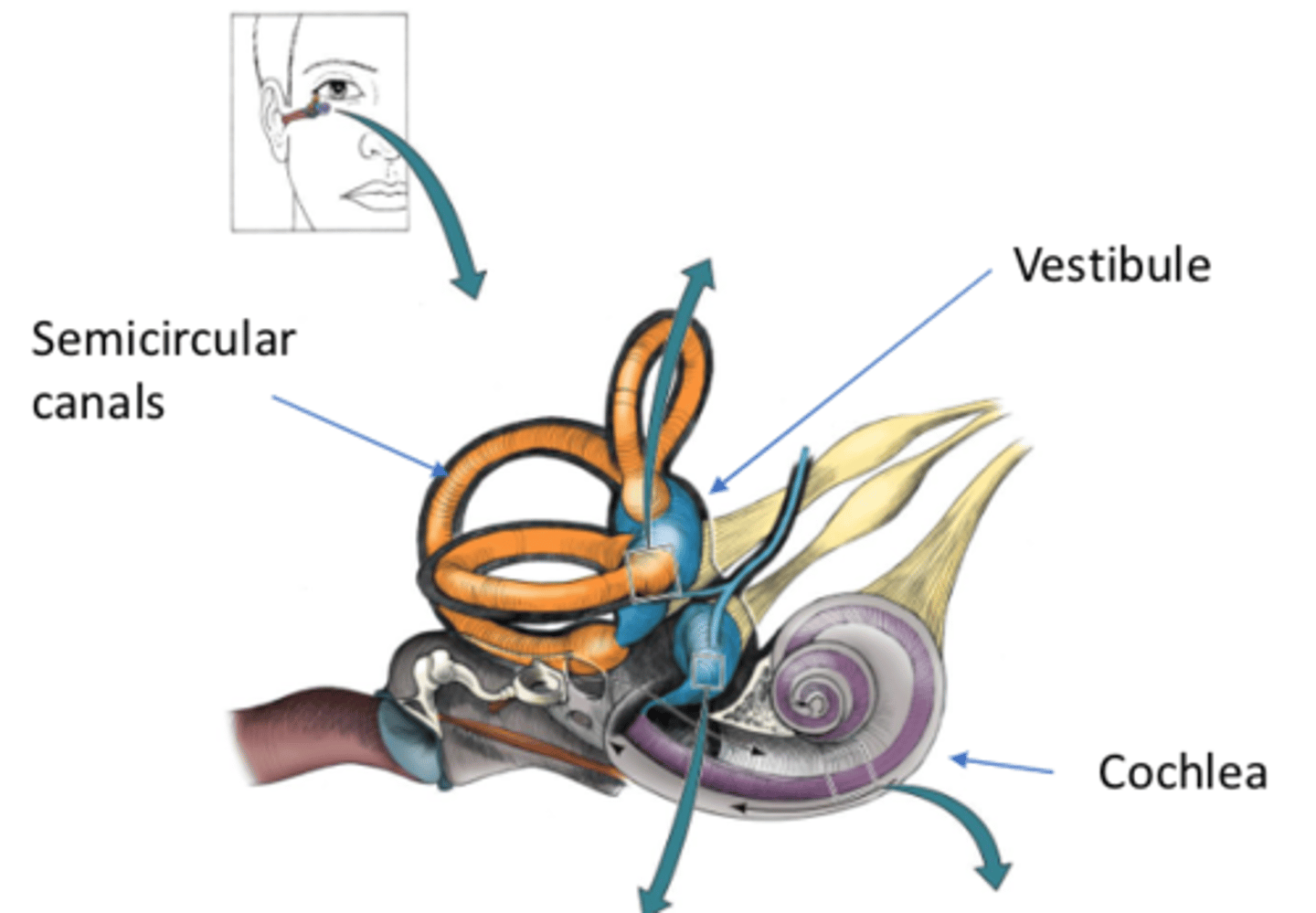
What does the cochlea contain (CN VIII)?
Hair cells (receptors) for hearing
What do the semicircular canals contain (CN VIII)?
Hair cells that respond to angular accelerations
What do the otolith organs contain (CN VIII)?
Hair cells that respond to linear accelerations
What does higher frequency sound/pitch activate (CN VIII)?
- Hair cells near oval window
- Birds, children, alarms
What does lower frequency sound/pitch activate (CN VIII)?
Hair cells near apex of cochlea
Where does the cochlear nerve synapse (CN VIII)?
Dorsal/ventral cochlear nuclei
How does auditory pathway cross (CN VIII)?
- Bilaterally at multiple points
- No unilateral hearing loss with lesions above cochlear nuclei
What are the 2 auditory pathways of the cochlear nerve (CN VIII)?
- Primary lemniscal
- Non-lemniscal
What is the primary lemniscal pathway responsible for (CN VIII)?
- Carries information from both ears to primary auditory cortex
- Conscious hearing and recognition of sounds
What is the first step of the primary lemniscal pathway (CN VIII)?
Primary sensory neurons in spinal ganglion send axons in cochlear division
What is the second step of the primary lemniscal pathway (CN VIII)?
Dorsal/ventral cochlear nuclei
What is the third step of the primary lemniscal pathway (CN VIII)?
Superior olivary nucleus
What is the fourth step of the primary lemniscal pathway (CN VIII)?
Inferior colliculus
What is the fifth step of the primary lemniscal pathway (CN VIII)?
MGN of thalamus
What is the sixth step of the primary lemniscal pathway (CN VIII)?
Auditory cortex (Heschl's gyrus)
What is the non-lemniscal pathway responsible for (CN VIII)?
- Unconscious perception of attention, awareness, auditory reflexes, emotional responses
- Via reticular formation
- Orients head and eye to location of sound
- Alerts to impending danger
What causes unilateral hearing loss (CN VIII)?
- Abnormalities of external auditory canal, middle ear, cochlea
- Injury of CN VIII, dorsal/ventral cochlear nuclei
What are 2 types of unilateral hearing loss (CN VIII)?
- Conductive
- Sensorineural
What is conductive hearing loss (CN VIII)?
Abnormalities of external auditory canal or middle ear
What causes conductive hearing loss (CN VIII)?
- Otitis
- Tympanic membrane perforation
What is sensorineural hearing loss (CN VIII)?
Disorders of cochlea or CN VIII
What causes sensorineural hearing loss (CN VIII)?
- Exposure to loud sounds
- Meniere's disease
- Tumor
Where can you find the vestibular anatomy (CN VIII)?
- Posterior to the cochlea
- Filled with endolymph
What does the vestibular anatomy consist of (CN VIII)?
- 3 semicircular canals
- Otolith organ
- Utricle and saccule
What structures are a part of the semicircular canals (CN VIII)?
Anterior/posterior/lateral semicircular canals
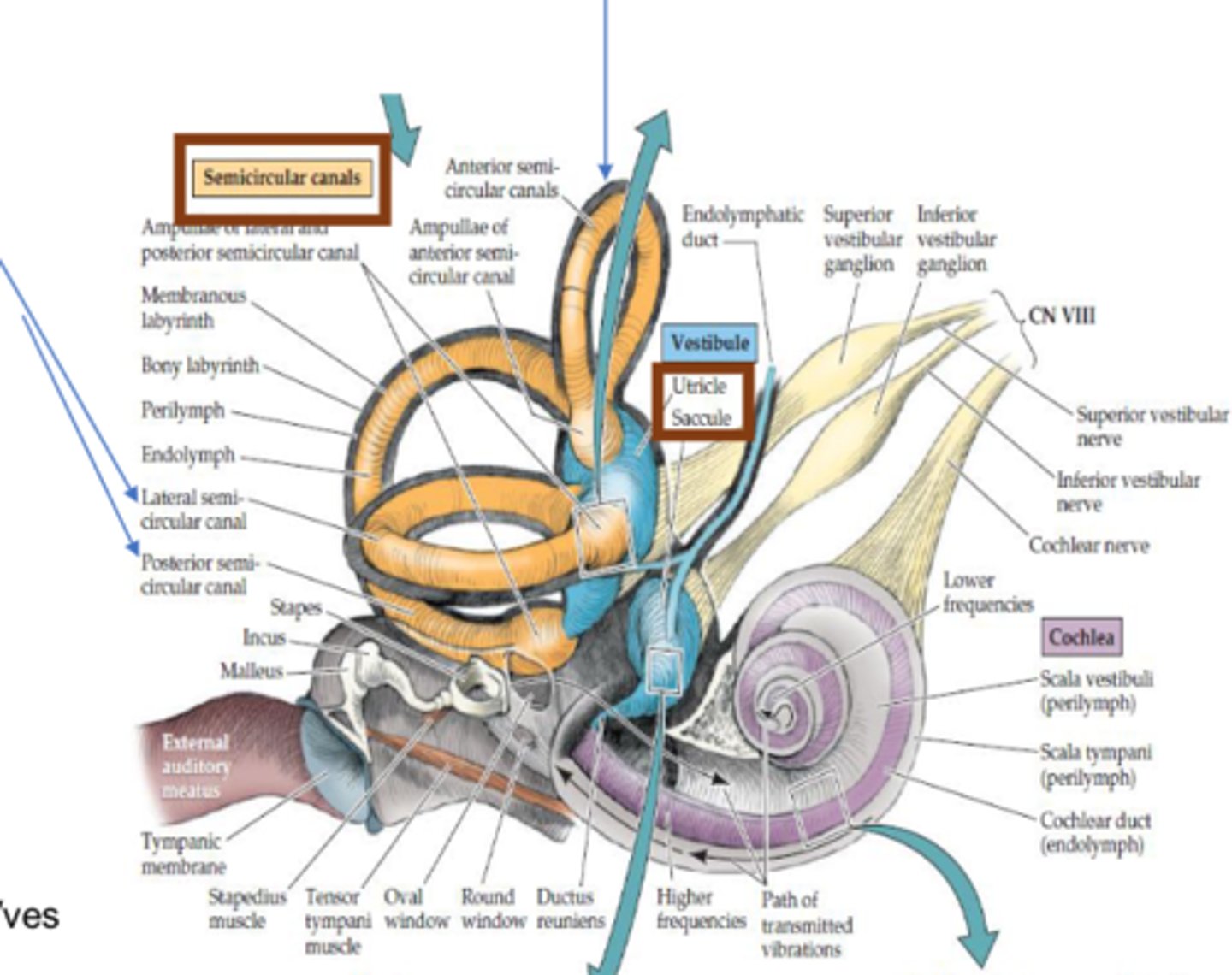
What sensory organ is a part of the semicircular canals (CN VIII)?
Ampulla
What is the function of the semicircular canals (CN VIII)?
- Sensing angular head motion in different directions
- Helps keep eyes steady when head is moving
- Vestibular ocular reflex (VOR)
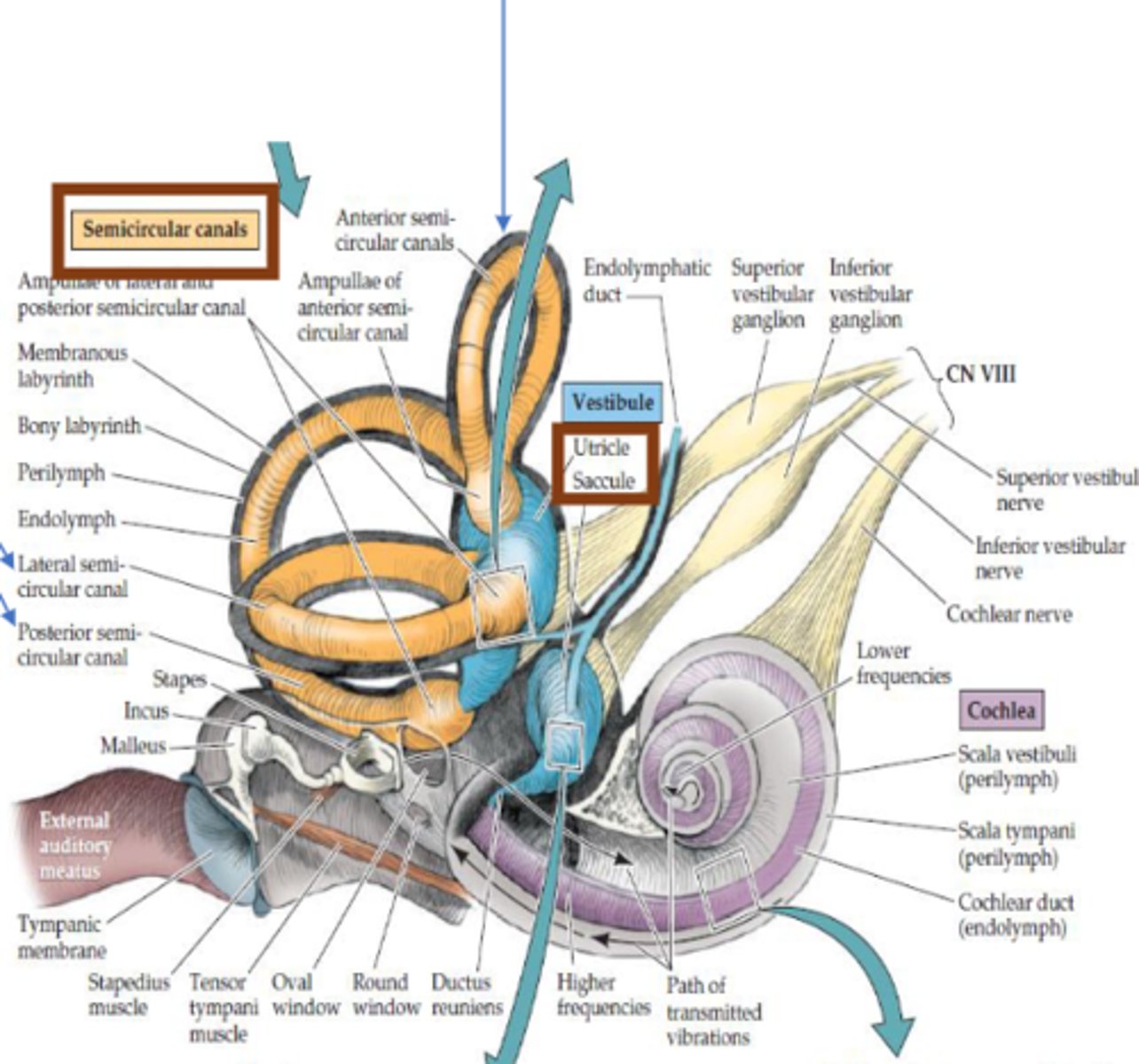
What is the ampulla (CN VIII)?
The structure in which hair cells are located
What is seen with increased activity in semicircular canals (CN VIII)?
- Complimentary
- Increased activity in one ear inhibits activity in the other
- Allows for better balance and stable vision
What structures are a part of the otolith organs (CN VIII)?
Utricle and saccule
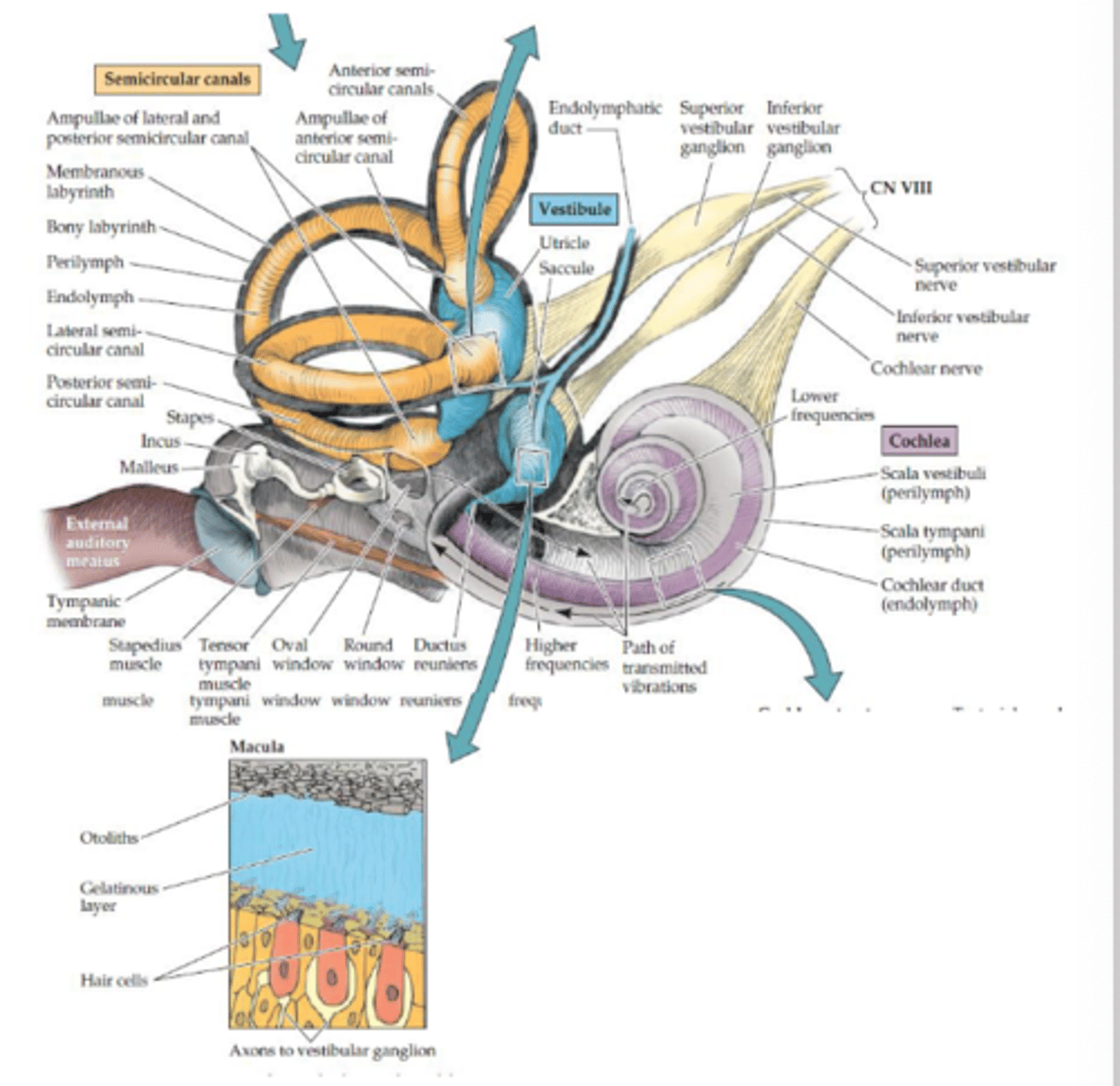
What sensory organ is a part of the otolith organs (CN VIII)?
- Macula
- Hair cells sensitive to movement in straight lines
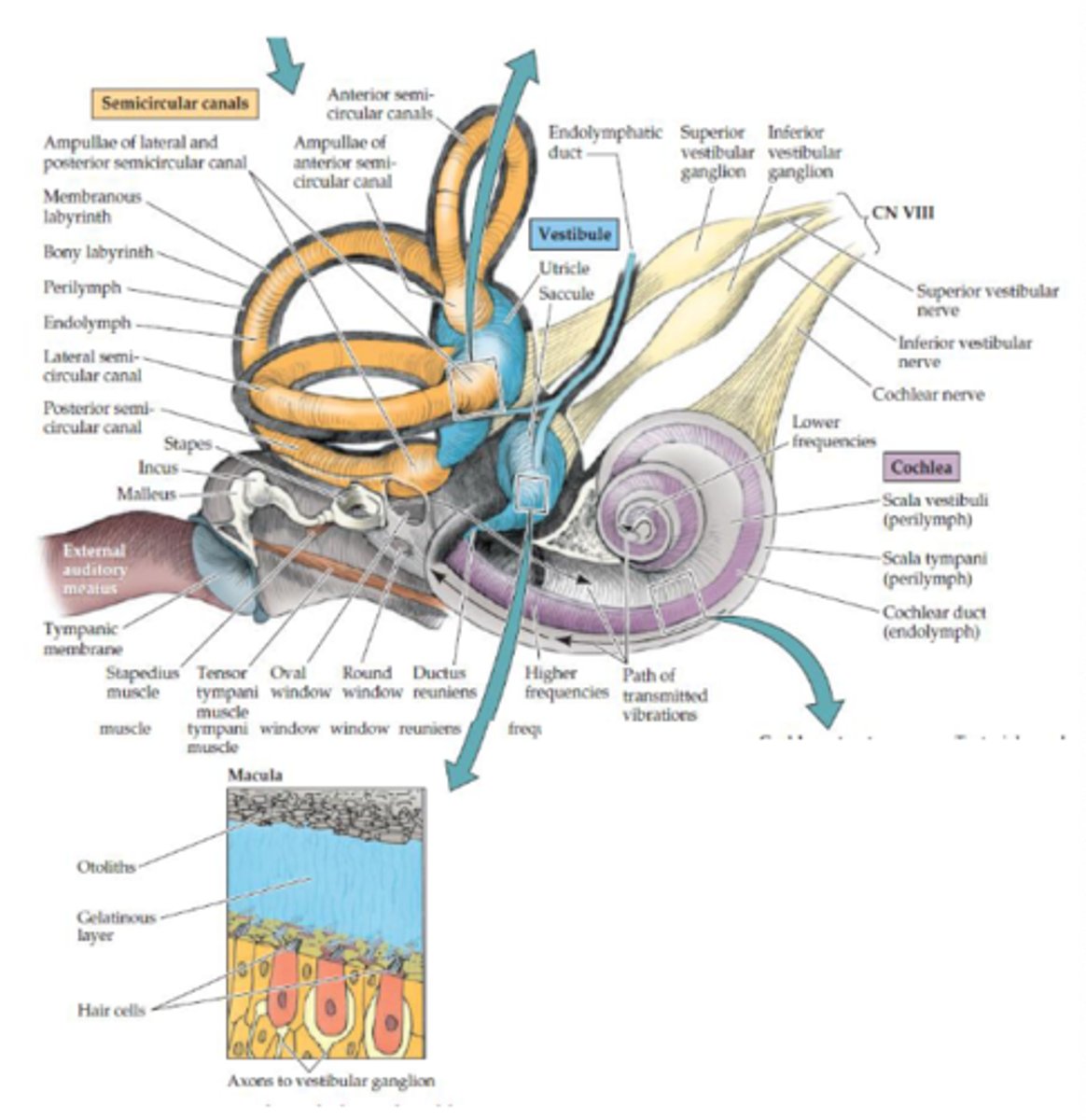
What is the function of the otolith organs (CN VIII)?
Sense position of the head with respect to gravity (linear acceleration)
What is the utricle sensitive to (CN VIII)?
Vertical acceleration, orientation, balance
What is the saccule sensitive to (CN VIII)?
Horizontal acceleration, deceleration of head in horizontal plane
What is benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (CN VIII)?
- Inner ear disorder
- Feeling that everything is spinning in/around
What causes benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (CN VIII)?
Otolith move out of place and enter semicircular canals
How do you test for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (CN VIII)?
- Dix-Hallpike (Nylén-Bárány) Test
- +ve with nausea and nystagmus
- -ve if dizzy but no nystagmus
What characteristics set apart peripheral vertigo (CN VIII)?
- Sudden and memorable onset
- Client will be able to give you a date/time
What characteristics set apart central vertigo (CN VIII)?
- Slow onset
- Client will not be able to tell you when symptoms started
What are the functions of the vestibular system (CN VIII)? (6)
- Proprioception
- Muscle tone and postural control
- Head positioning and movement in relation to gravity
- Balance
- Bilateral integration
- Alertness and arousal
What is proprioception responsible for (CN VIII)?
Awareness of body position and movement in space
What are muscle tone and postural control responsible for (CN VIII)?
- Influences proprioception
- Via medial/lateral vestibular spinal tract
What is head positioning and movement in relation to gravity responsible for (CN VIII)?
Head stability and midline orientation
What falls under the responsibilities of balance (CN VIII)?
- Gaze stability
- Gait stability
- Spatial awareness
What signs are associated with dysfunction of alertness and arousal in the vestibular system (CN VIII)?
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Altered consciousness
What muscle does the branchial motor neuron associated with the glossopharyngeal nerve innervate (CN IX)?
Stylopharyngeus muscle
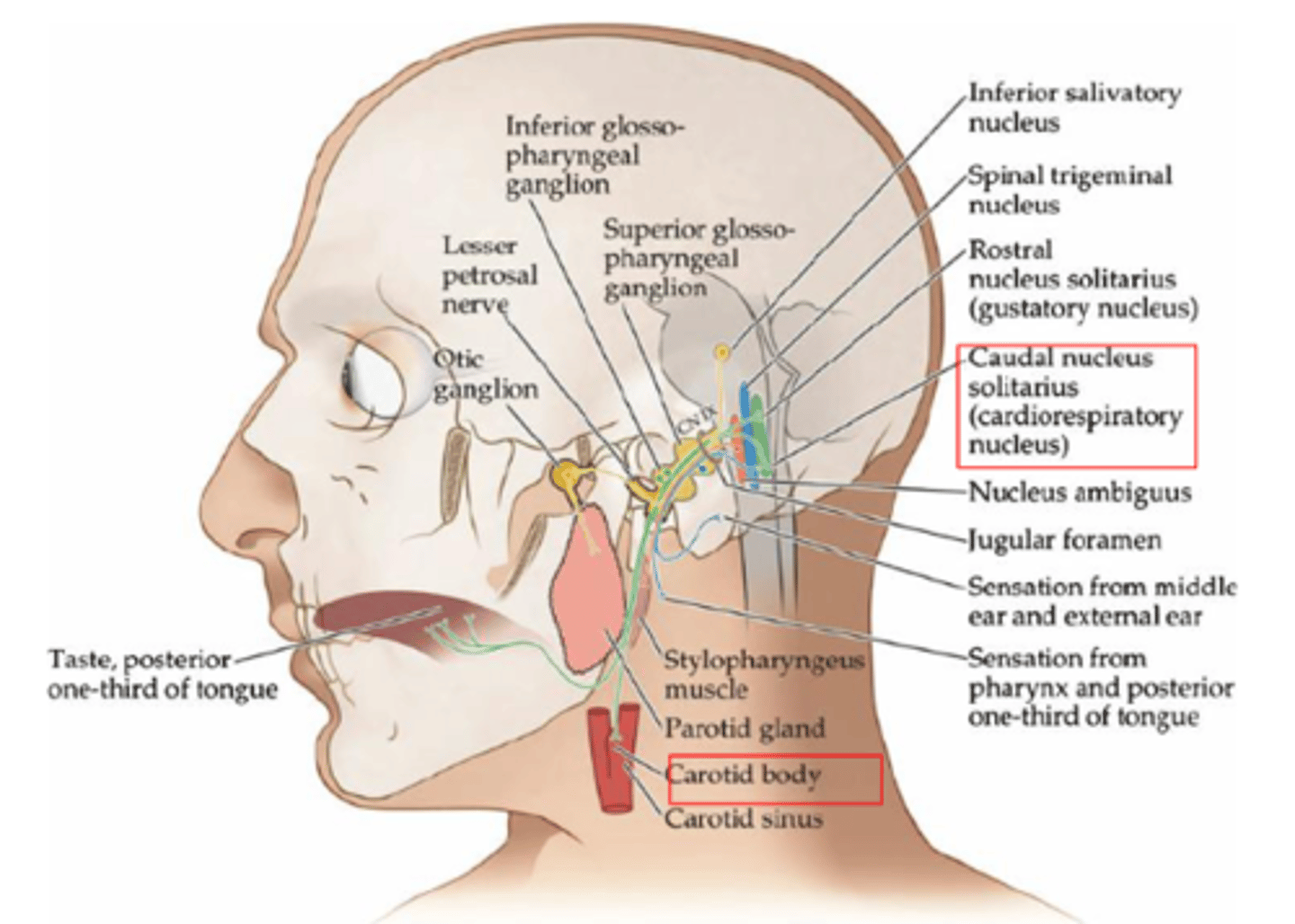
What gland is associated with the parasympathetic aspect of the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)?
Parotid gland (salivation)
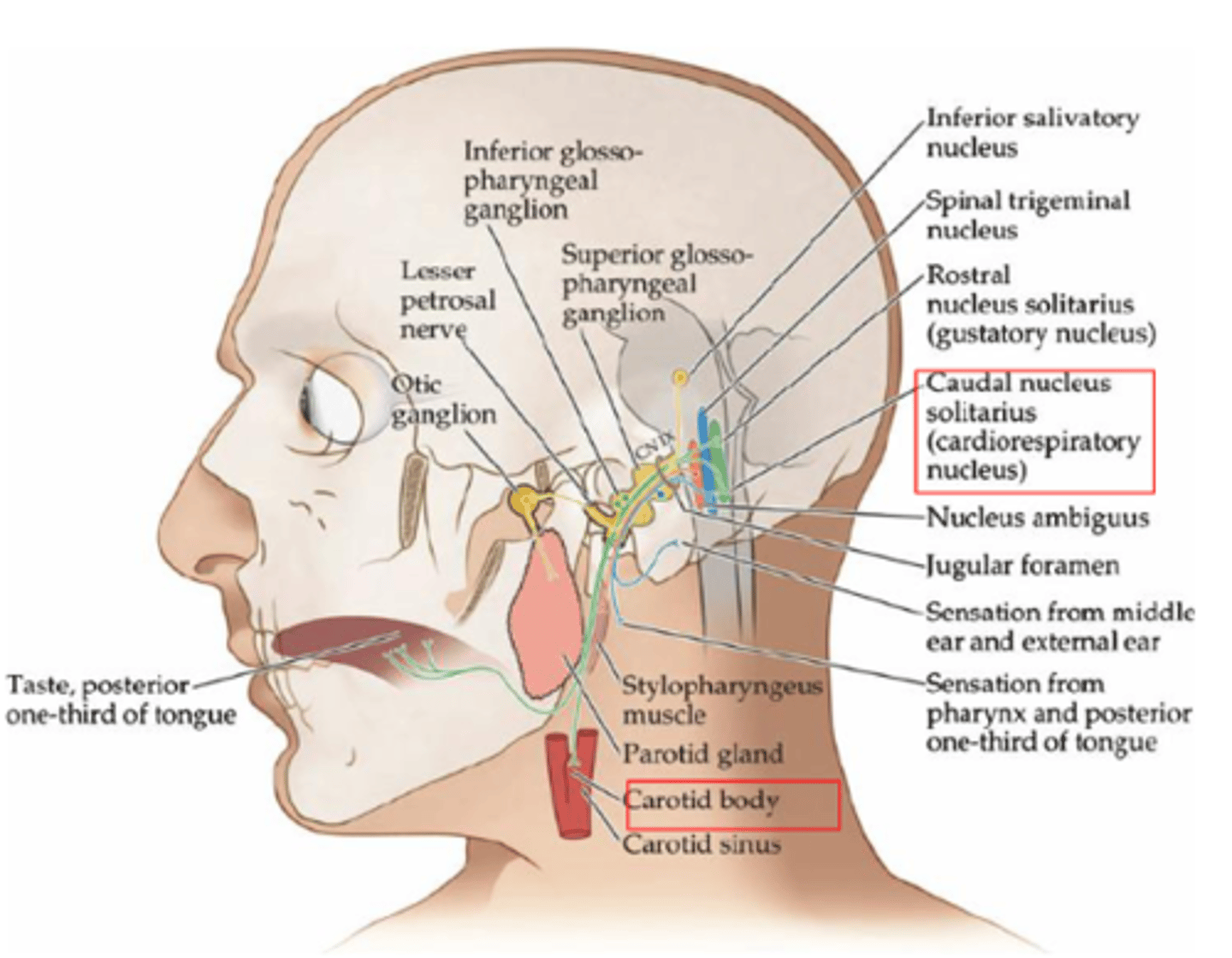
What does the general sensory neuron associated with the glossopharyngeal nerve innervate (CN IX)?
- Posterior 1/3 of tongue
- Pharynx
- Auditory meatus
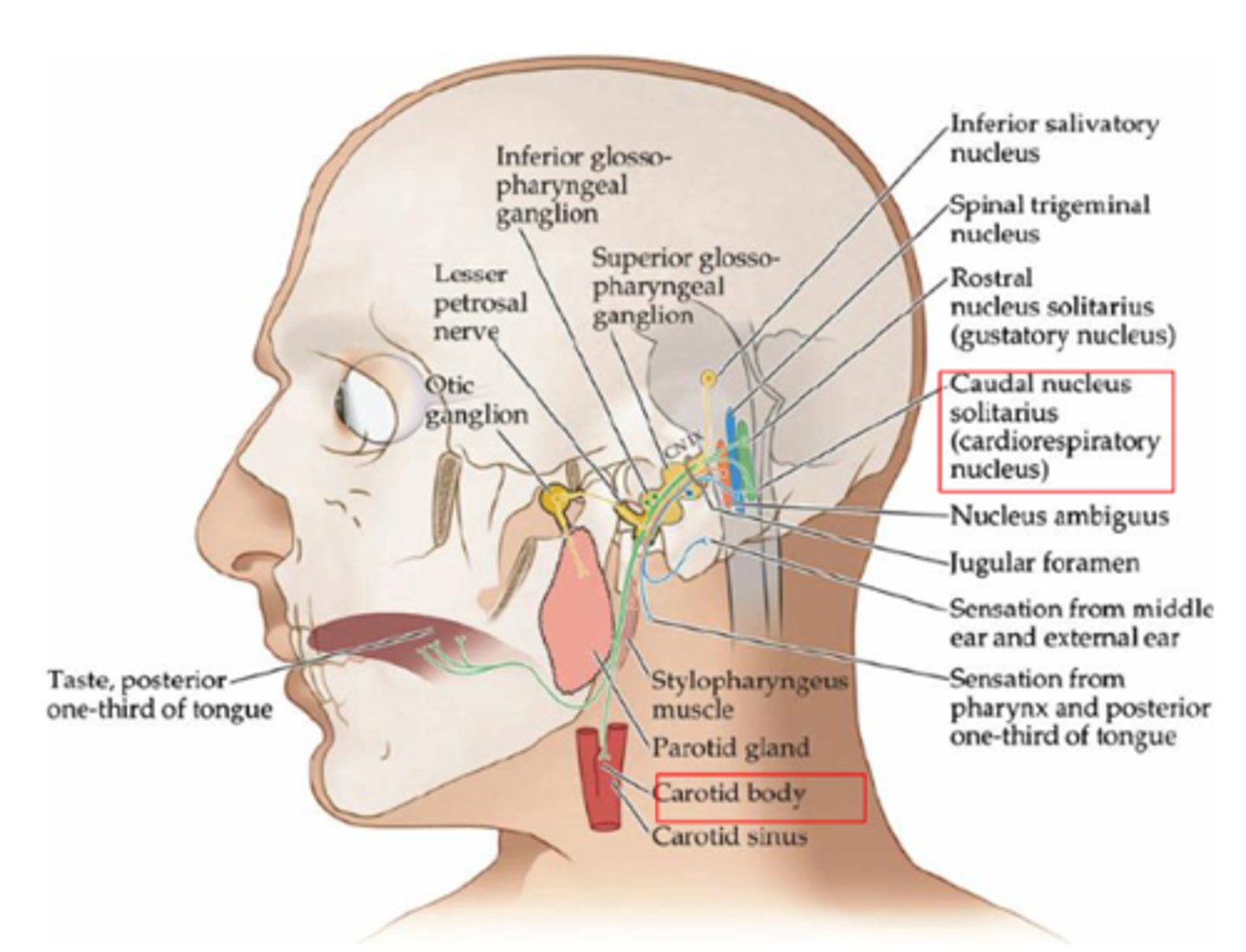
What is the special sensory neuron associated with the glossopharyngeal nerve responsible for (CN IX)?
Taste from posterior 1/3 of tongue
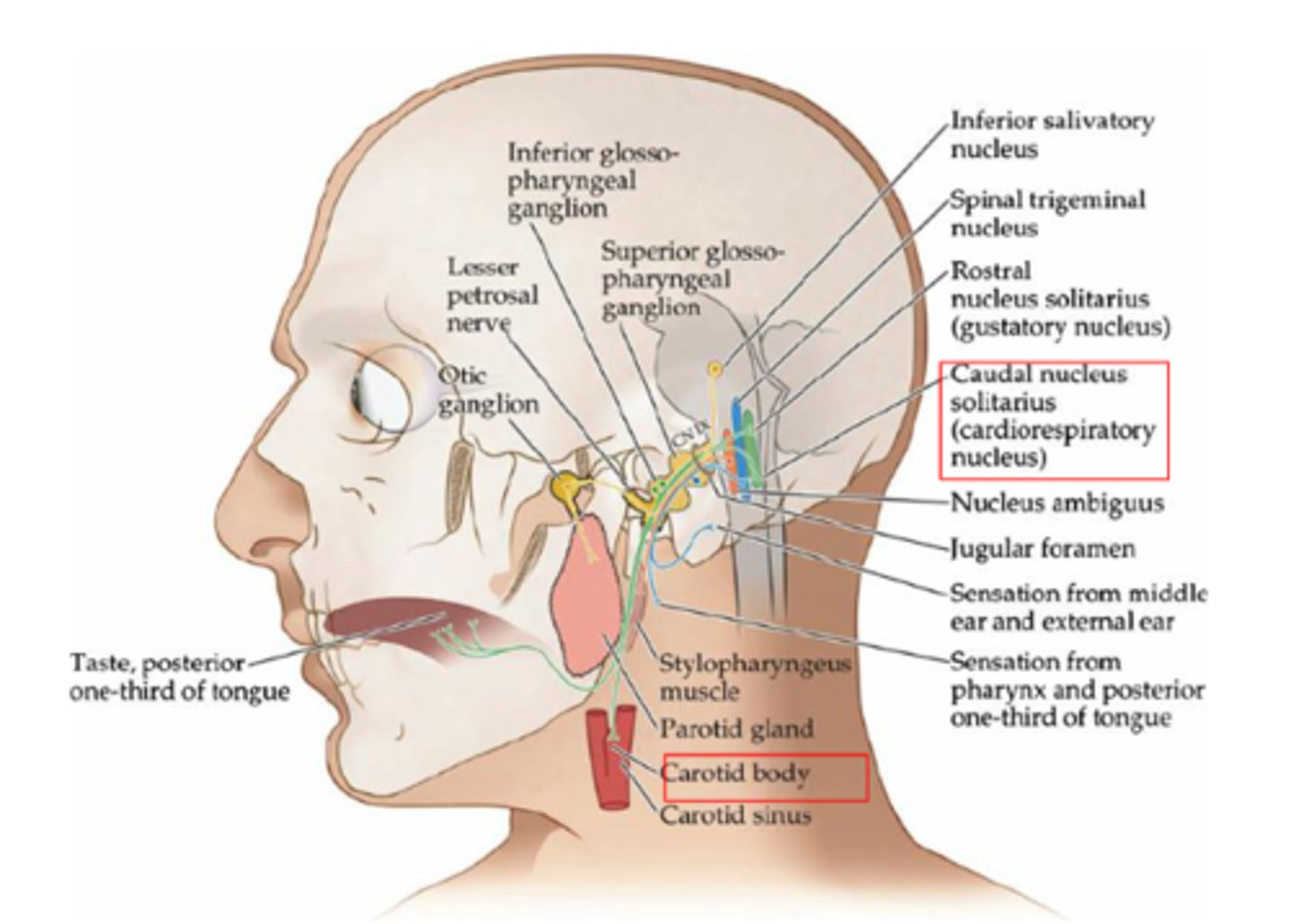
What receptors make up visceral sensory neurons associated with the glossopharyngeal nerve innervate (CN IX)?
Chemoreceptors and baroreceptors of carotid body
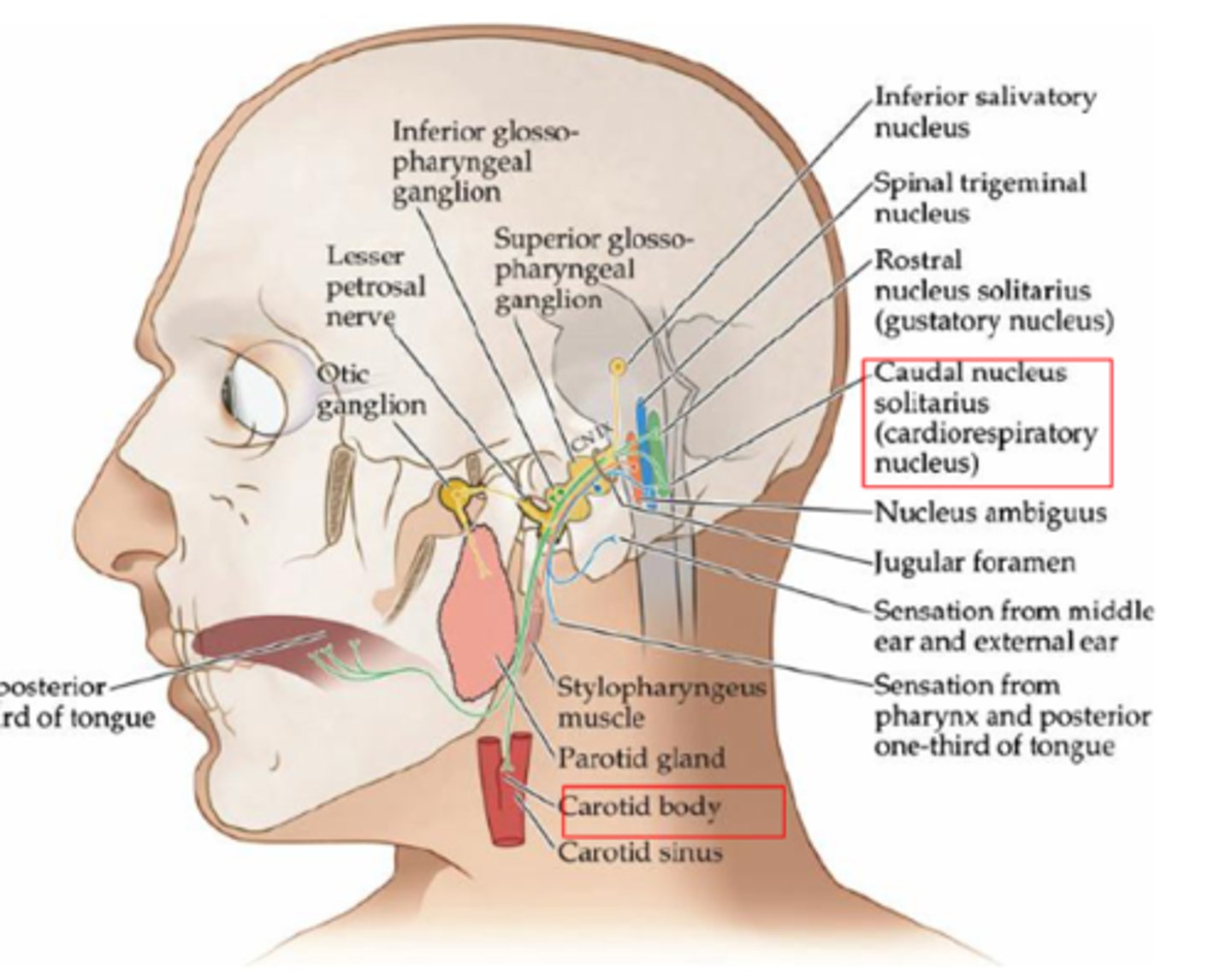
What are the important functions of CN IX?
- Special sensory
- Visceral sensory
- Other: gag reflex
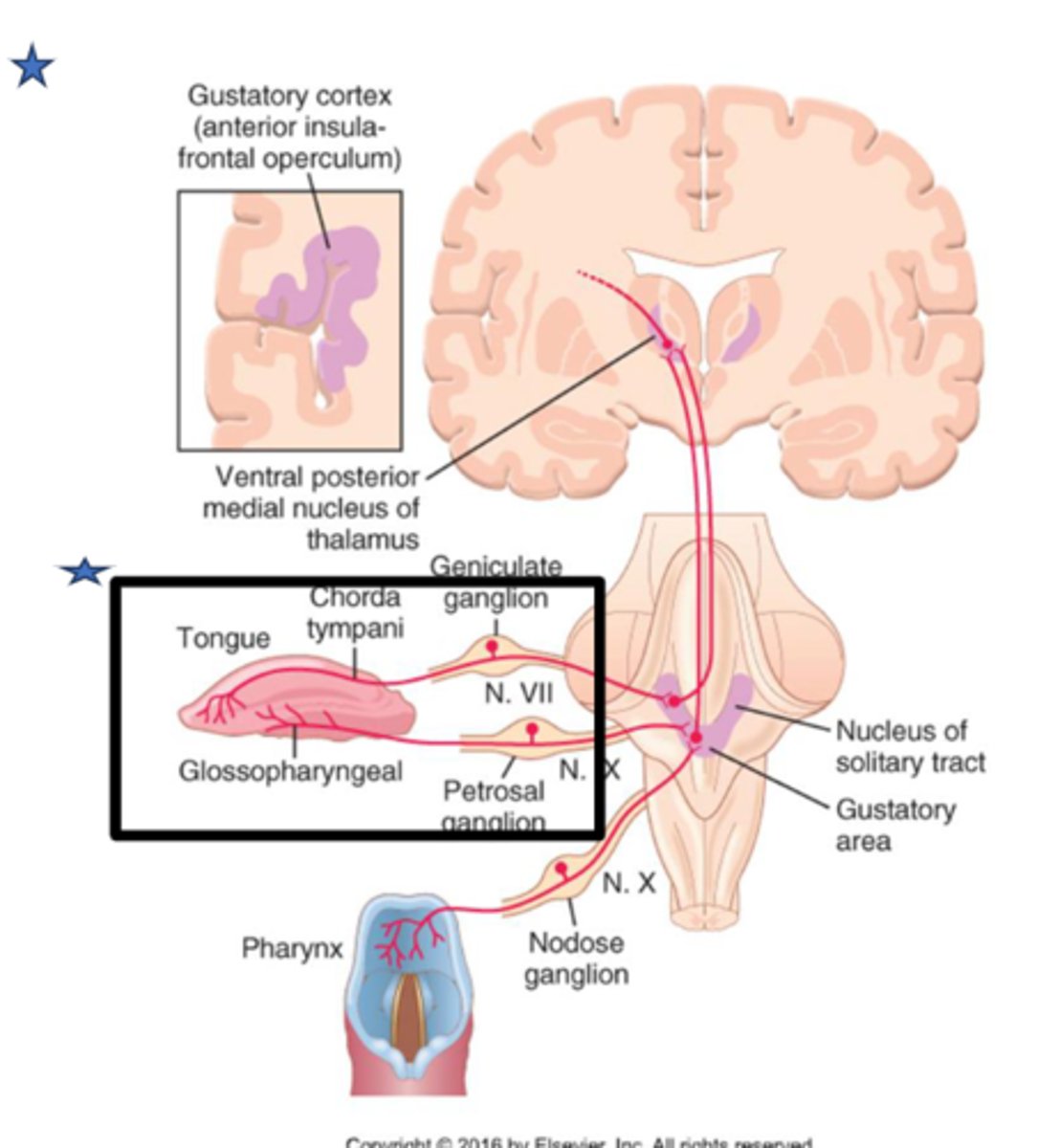
Which cranial nerve is also known as the "wandering nerve"?
CN X (vagus nerve)
What parts of the body are affected by CN X? (8)
- Larynx
- Trachea
- Bronchi
- Lungs
- Heart
- GI tract
- Liver
- Pancreas
Which organs receive parasympathetic innervation from the vagus nerve (CN X)?
- Heart
- Lungs
- Digestive tract
- Down to splenic flexure
Which muscles receive motor innervation from the vagus nerve (CN X)?
Pharyngeal and laryngeal muscles
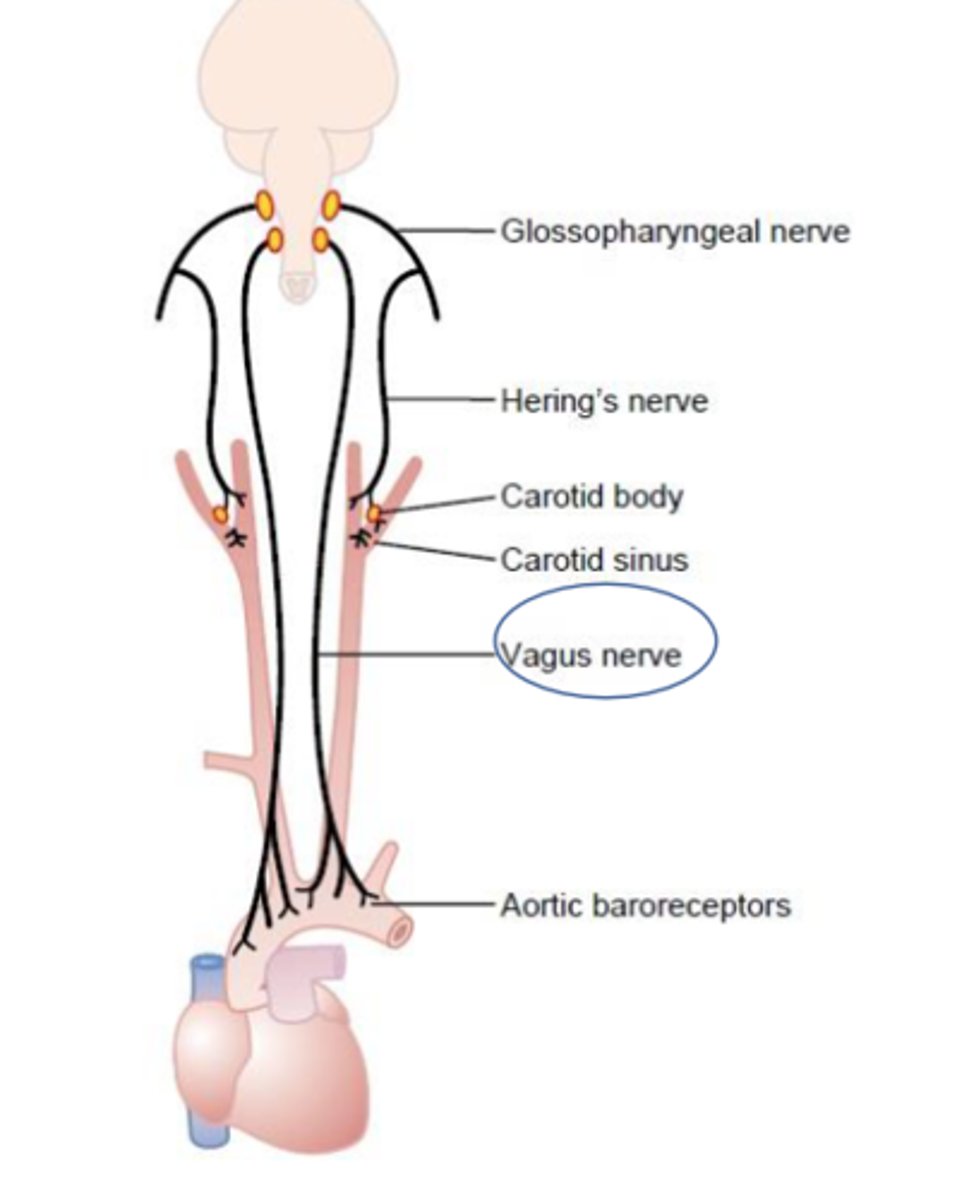
Which areas receive general sensory innervation from the vagus nerve (CN X)?
- Pharynx
- Meninges
- External auditory meatus
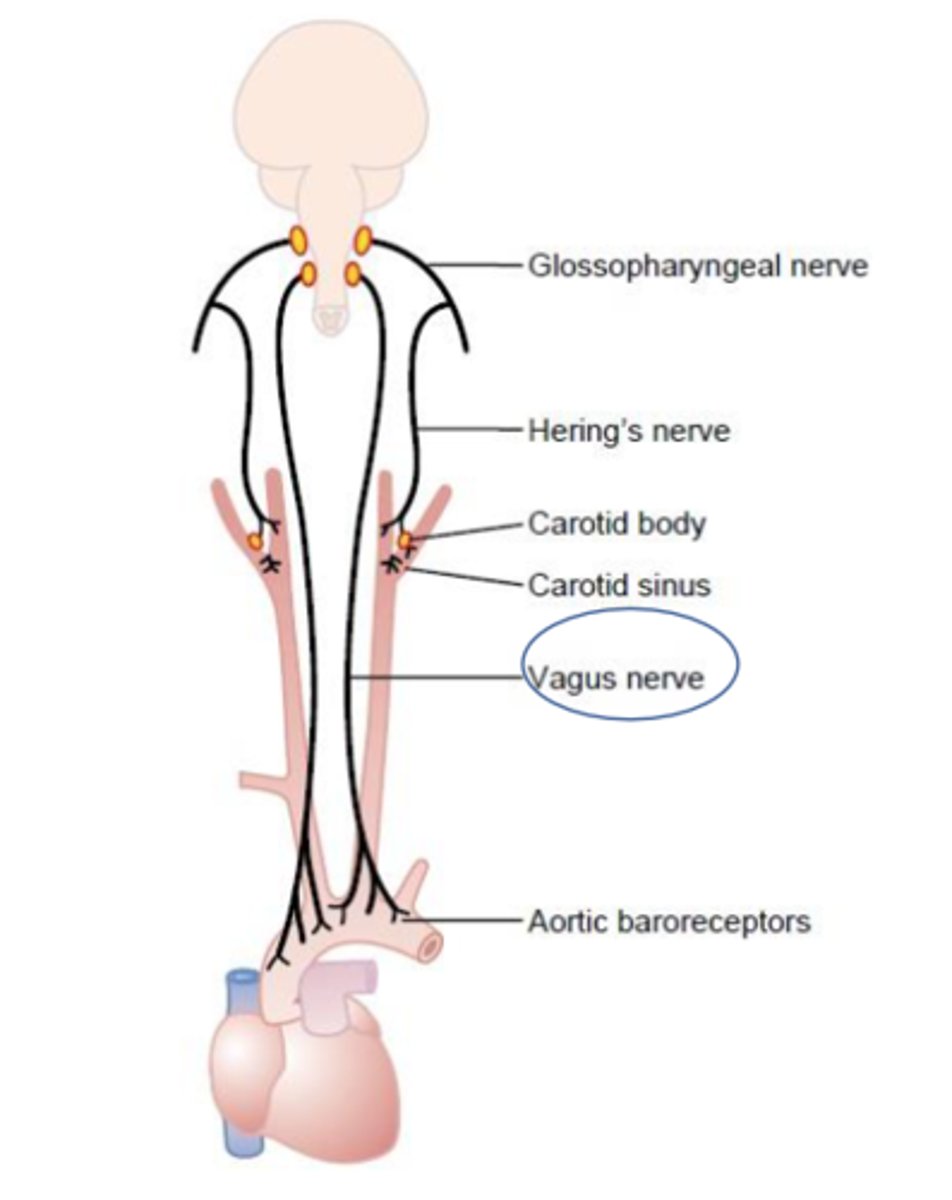
What is the special sensory innervation from the vagus nerve responsible for (CN X)?
Taste for the epiglottis and posterior pharynx
What makes up the visceral sensory innervation from the vagus nerve (CN X)?
Baroreceptor and chemoreceptor of aortic arch
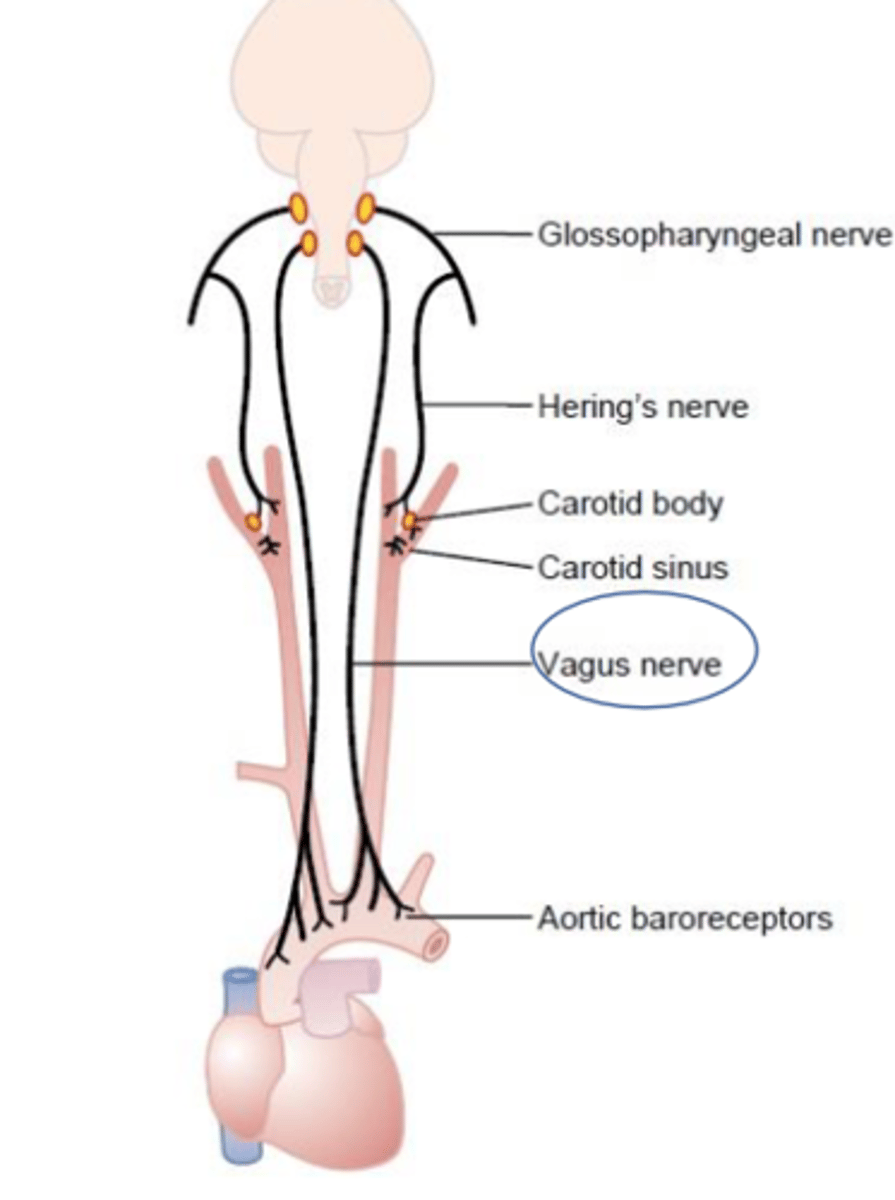
What tests can an OT do for CN IX and CN X?
- Palate elevation
- Gag reflex
What is dyspnea?
- Difficulty breathing if visceral branch of vagus nerve is damaged
- CN X pathology
What is dysphonia?
Hoarse voice
What is dysphagia?
Difficulty swallowing
What is dysarthria?
Difficulty enunciating words
What is the first step of the pathway of the spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)?
Arises in medulla and upper 5-6 cervical segments
What is the second step of the pathway of the spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)?
Ascend through foramen magnum to reach intracranial cavity
What is the third step of the pathway of the spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)?
Exits cranium via jugular foramen
What is the function of the branchial motor neurons associated with the spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)?
- Elevation of larynx with swallowing
- SCM for turning head in opposite direction
- Upper trapezius elevates shoulder and maintain head extension
Is the lower portion of the trapezius supplied by CN XI?
No, mainly supplied by cervical nerve roots C3 and C4
What are signs and symptoms of CN XI pathology? (5)
- Dysphasia
- Laryngeal elevation
- Weakness rotating head contralaterally
- Weakness flexing/extending head
- Difficulty elevating shoulder or involved arm above 90º
What is the function of the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)?
- Somatic motor
- Tongue movement
What is the first step of the pathway of the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)?
Motor pathway decussates and then synapses on hypoglossal nucleus
What is the second step of the pathway of the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)?
Exits between pyramid and inferior olivary nucleus
What does an UMN lesion of the hypoglossal nerve affect (CN XII)?
- Primary cortex
- Internal capsule (corticobulbar)
- Contralateral weakness of tongue
What does a LMN lesion of the hypoglossal nerve result in (CN XII)?
- Ipsilateral weakness of tongue
- Fasciculations
- Atrophy
What is an OT testing for with CN XII pathology?
- Tongue protrusion
- Unilateral weakness
- Tongue deviates toward weak side when protruded
What are signs and symptoms of CN XII pathology?
- Dysarthria
- Dysphagia
What are causes of dysarthria with CN XII pathology? (4)
- Infarct
- MS
- Brainstem lesions
- Lesions of cerebellar and basal ganglia pathways
What are causes of dysphagia with CN XII pathology? (5)
- Infarcts
- Neoplasms
- Esophageal strictures (narrowing)
- Neural components
- Aspiration pneumonia (serious!)
What is the cranial nerve combination involved in dysphagia?
- CN V
- CN VII
- CN XI (head control)
- CN X
- CN XII
What is the cranial nerve combination for innervation of the face?
- CN V (sensation)
- CN VII (movement of facial expression)
What is the cranial nerve combination for functions of the tongue and mouth?
- CN V mandibular division (general sensory)
- CN IX (general sensory)
- CN VII (special sensory)
- CN IX (special sensory)
- CN X (epiglottis and posterior pharynx)