GIT 1 (Oral Cavity)
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Pathology of the Alimentary System
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Parasite migration
Portal of Entry of Pathogen
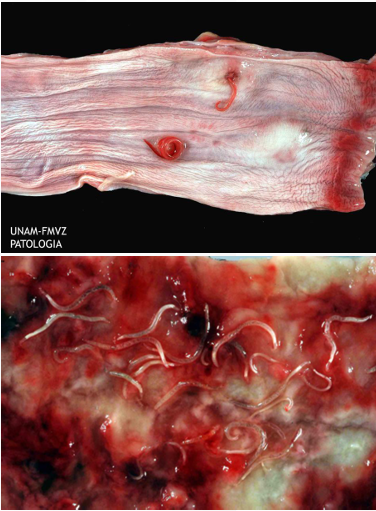
Ingestion (most common)
Portal of Entry of Pathogens
Cheiloschisis (Harelip)
Identify which Congenital Anomaly
- Failure of the fusion of the upper lip along the midline or philtrum
- Steroid administration in humans and primates are observed

Palatoschisis
Lateral palatine process
Genetic, Steroid administration, Toxic plants
Starvation, Aspiration Pneumonia, Death
Identify which Congenital Anomaly
Result of failure of fusion of the?
Predisposing factors (GST)
Results to? (SAD)
Epitheliogenesis imperfecta
Tongue & Esophagus
Bovine
Stratified Squamous epithelium
Bacterial infection, Dehydration
Disease
Organ
Spp
This is the incomplete development of the _____ of skin, adnexa, and/or mucosa
May lead to? [BD]
![<ol><li><p>Disease</p></li><li><p>Organ</p></li><li><p>Spp</p></li><li><p>This is the <strong>incomplete development of </strong>the _____ of skin, adnexa, and/or mucosa</p></li><li><p>May lead to? [BD]</p></li></ol><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/19074dde-f7ca-447a-a7a8-704db0d28f72.png)
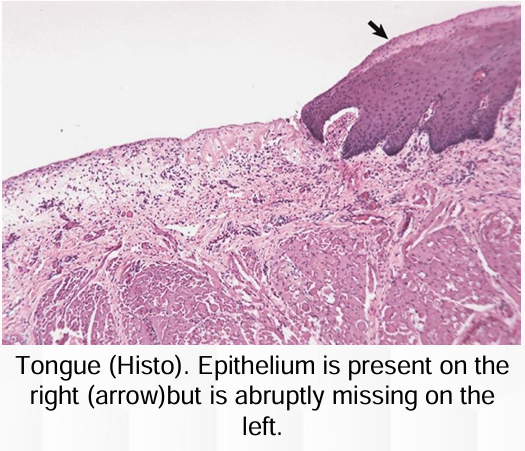
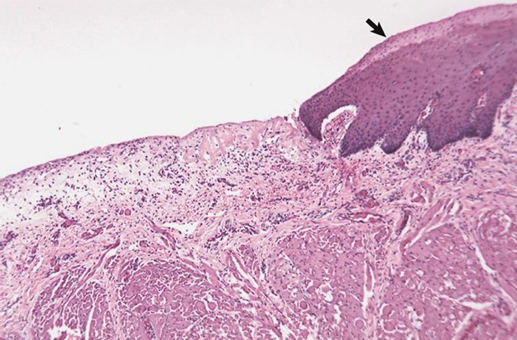
Epitheliogenesis imperfecta
Tongue
Disease
Organ
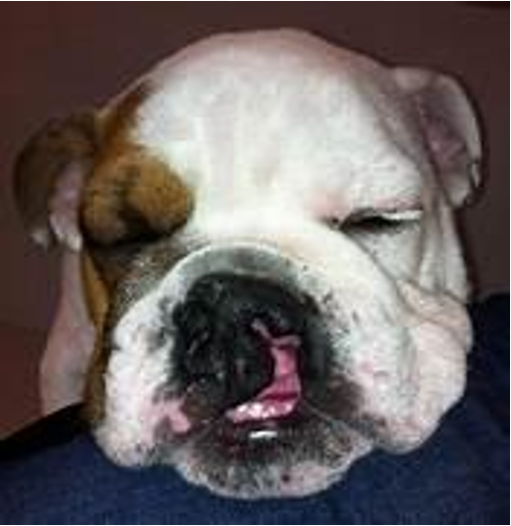
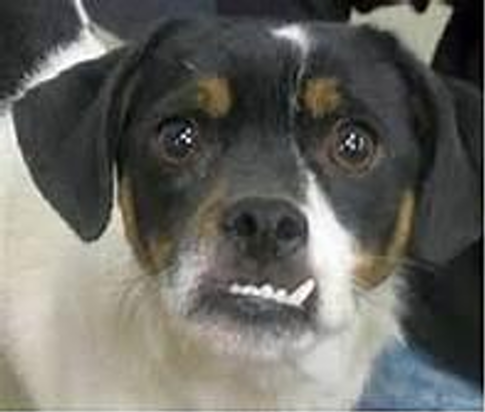
Prognathism (underbite/sow mouth)
Skull conformation
Disease
In dogs, it is dependent on

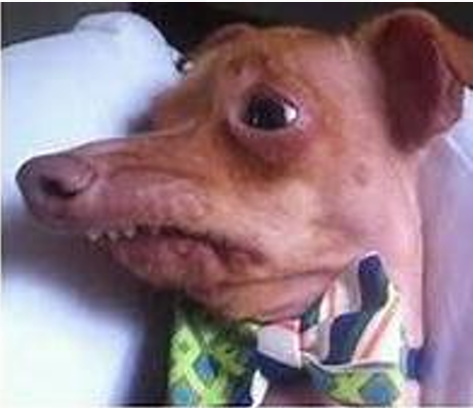
Brachygnathia (Overbite/Parrot mouth)
Skull conformation
Disease
In dogs, dependent with

Stomatitis
Important indicator of some systemic diseasse
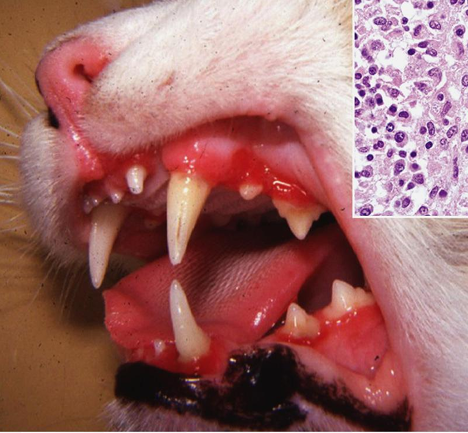
Vesicular Stomatitides
Refers to oral vesicles and blisters
The term is generally reserved for those lesions caused by epitheliotropic viruses
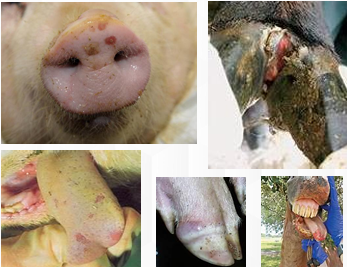
Vesicular Stomatitis
Apthae (white spots)
Bullae
Raw ulcerated areas on the tongue and lips
Fever
Anorexia
Vesicles
Attached epithelium
Salivation
Lameness
Disease
Clinical Signs
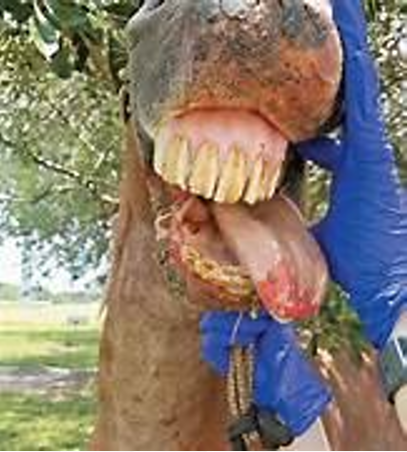

Bovine
Mouth, gingiva
Focal, oral ulcer
Vesicular stomatitis
Raised epithelial ruptured blister over a raw surface
Spp
Tissue
Morphologic Dx
Etiologic Dx
Lesion Description
Cow
Hoof
Interdigital Dermatitis
Vesicular Stomatitis Virus
Interdigital ulceration & vesicles
Spp
Tissue
Morphologic Dx
Etiologic Dx
Lesion Desc.
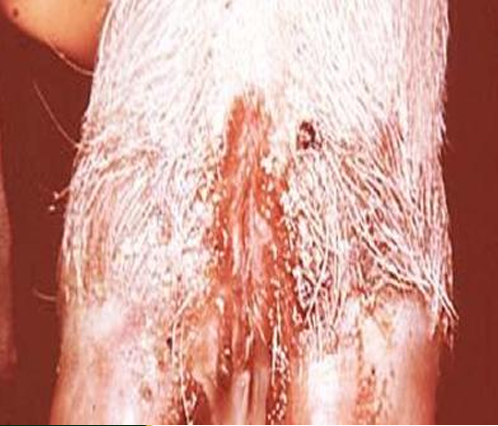

Vesicular stomatitis
Porcine
Large vesicle (Bullae) on Dorasl snout
Disease
Spp
Desc
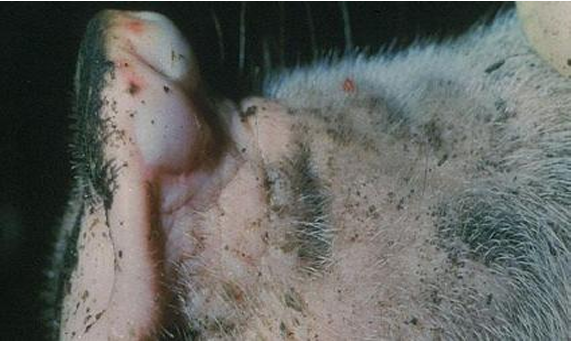
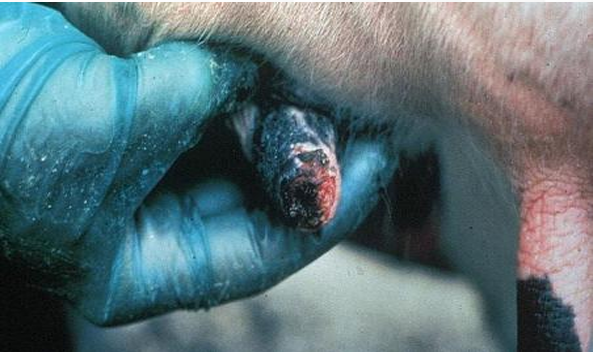
Vesicular stomatitis
Bovine
Distal teat severely eroded & hemorrhagic
Disease
Spp
Desc
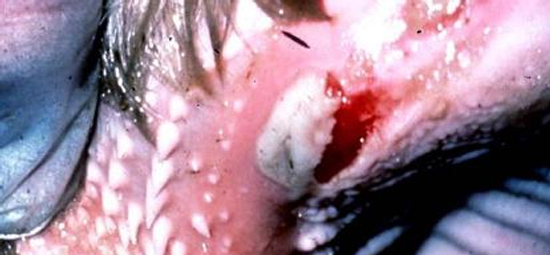
Vesicular stomatitis
Bovine
Extensive ulceration of the dental pad & Severe salivation
Disease
Spp
Desc
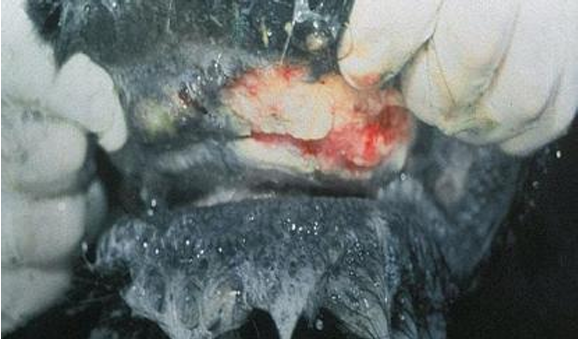
Vesicular stomatitis
Equine
Extensive erosion of the lip at the mucocutaneous junction
Disease
Spp
Desc
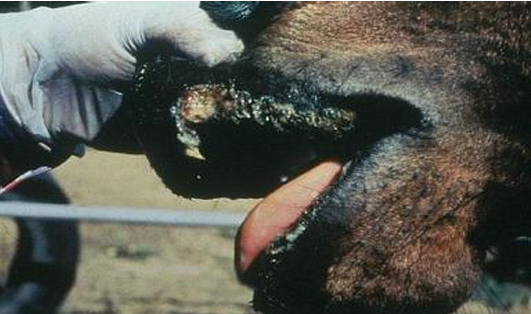
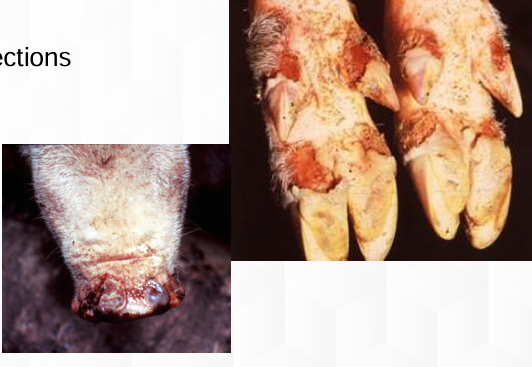
Food & Mouth Disease
Disease
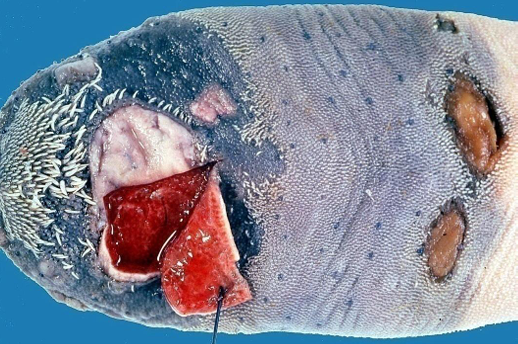
Food & Mouth Disease
Disease

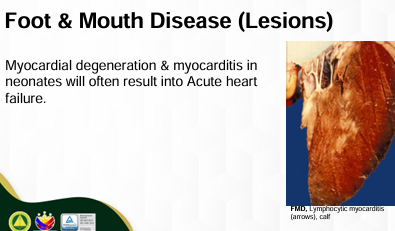
Food & Mouth Disease
Lymphocytic myocarditis
Bovine (Calf)
Disease
Lesion
Spp
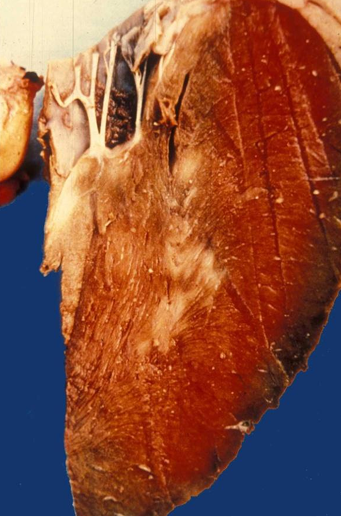
Food & Mouth Disease
Secondary bacterial infection, Hoof separation
Disease
Possible Sequelae
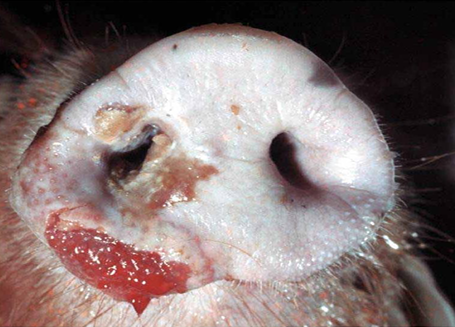
Swine Vesicular disease
Enterovirus (Picornaviridae)
True
Disease
Etiology
T/F, this is only present in Swines
Vesicular Exanthema (VE)
Calicivirus
VE serovars
Disease
Etiology
____ are variants of San Miguel Sea Lion Virus

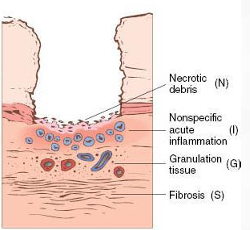
Erosive & Ulcerative Stomatitides
Papular Stomatitides
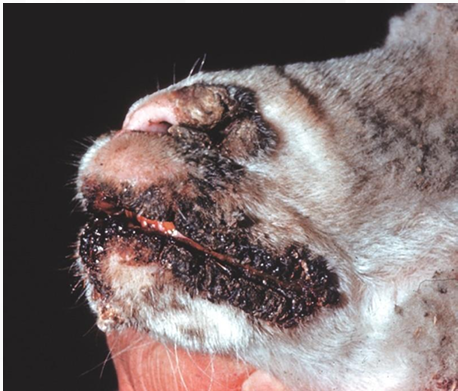
Ovine (Sheep, Adult)
Nose & lips, Skin, Gross
Chronic pustular dermatitis
Contagious Ecthyma Parapoxvirus
Contagious Pustular Dermatitis, Sore mouth, Orf
Several proliferative scabs
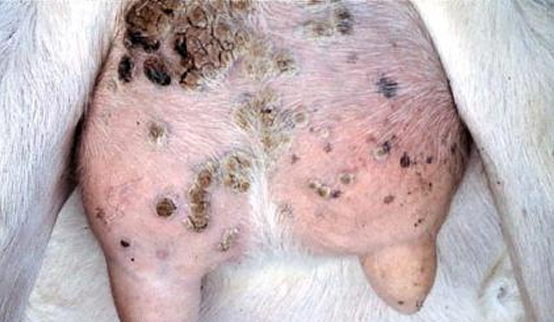
Spp
Tissue
Morphologic Dx
Etiologic Dx
Lesions or Dx name
Lesions Descr.
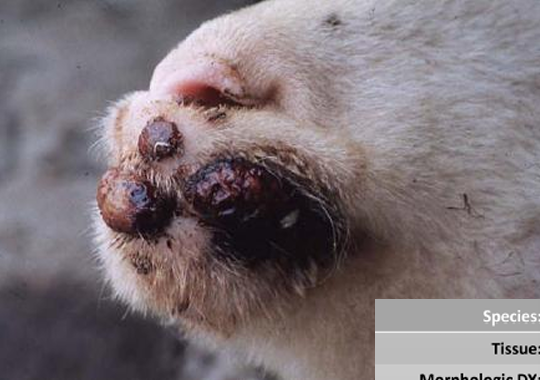
Caprine (Goat, adult)
Udder, Skin, Gross
Chronic Pustular Dermatitis (Orf)
Parapoxvirus
Numerous round lesions w white swollen periphery & dark centers & large proliferating areas of necrotic surface debris more dorsally confluent
Spp
Tissue
Morphologic Dx
Etiologic Dx
Lesions Descr.
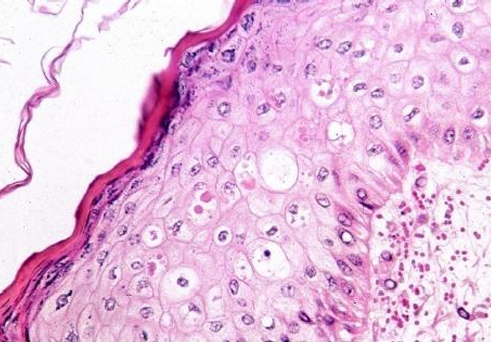
Papular Stomatitis
Ballooning degeneration & Intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies
Bovine (Cow)
Disease
Desc.
Spp.
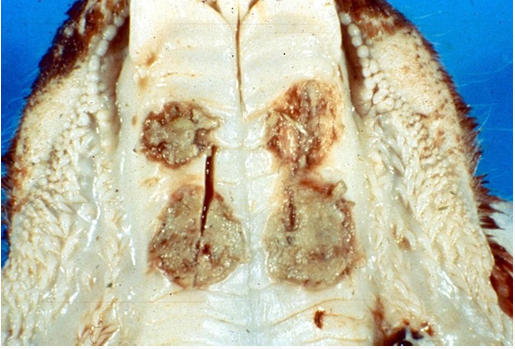
Calf Diphtheria
Fusobacterium necrophorum
Hard palate
Necrotizing stomatitis (Hard palate), ulcers are covered by a diphteric membrance
Pigs
Disease
Etiology
Organ
Desc.
This animal can also be affected w this disease
Calf diphtheria
Necrotizing glossitis
Fusobacterium necrophorum
Disease
Lesion desc.
Etiology
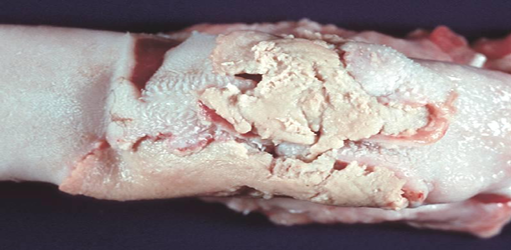
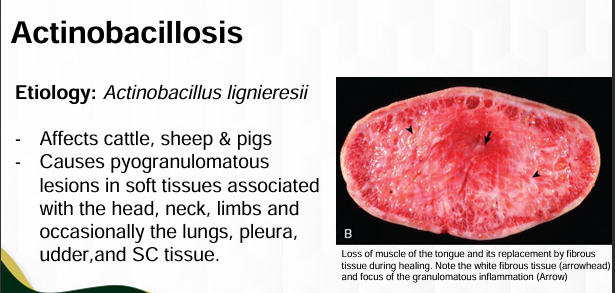
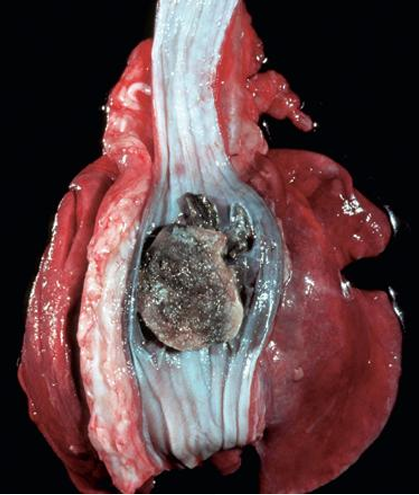
Actinobacillosis
Actinobacillus lignieresii
White fibrous tissue
Granulomatous inflammation
Disease
Etiology (SN)
Arrowhead
Arrow
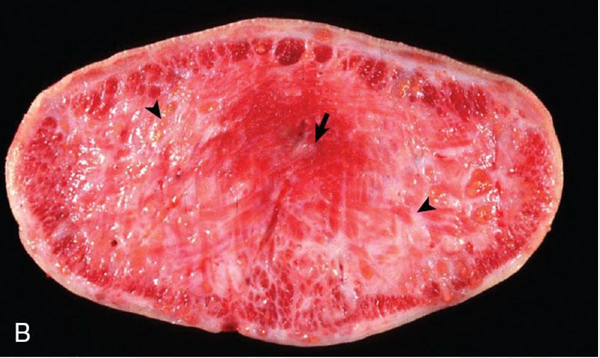
Actinobacillosis
Actinobacillus lignieresii
Submandibular LN & Soft tissues
Clinical signs
Wooden tongue
Abnormal tongue position
Salivation
Partial anorexia
Disease
Etiology
Organ affected
Clinical signs

Bovine
Tongue
Diffuse sclerosing actinobacillosis
Actinobacillosis - Actinobacillus lignieresii
Wooden tongue
Tongue is enlarged, white, and firm as a result of severe proliferation of connective tissue which replaces the muscular tissue
Spp
Tissue
Morphologic Dx
Etiologic Dx
Lesions or Dx Name
Lesion Desc
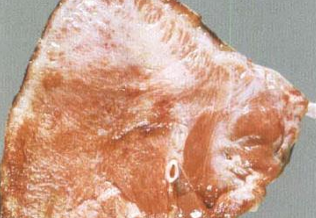
Actinobacillosis
Bacterial colonies & radiating clubs & suppurative inflammation
Disease
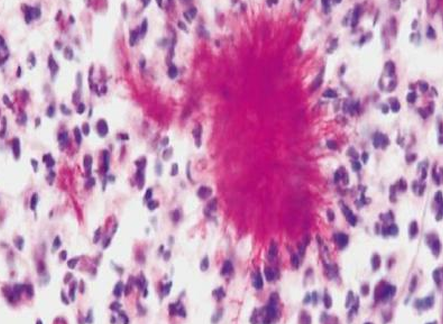
Actinomycosis
Actinomyces bovis
Pyogranulomatous stomatitis & Osteomyelitis, Lumpy jaw
Bovine
Disease
Etiology (SN)
Characterized by
Spp.
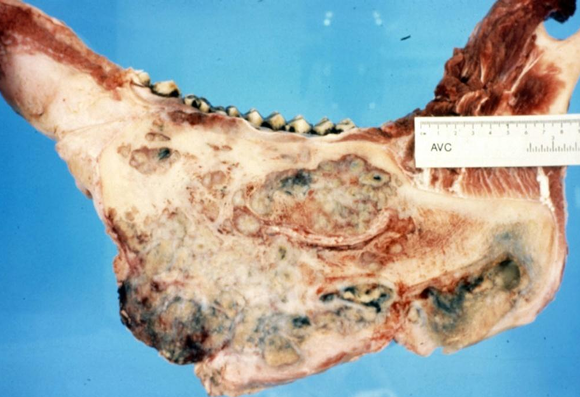
Actinomycosis
Actinomyces bovis
Pyogranulomatous stomatitis & Osteomyelitis, Lumpy jaw
Bovine
Disease
Etiology (SN)
Characterized by
Spp.
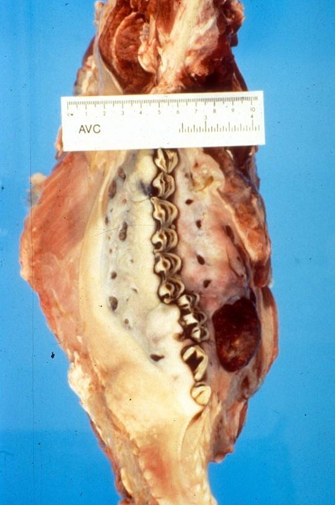
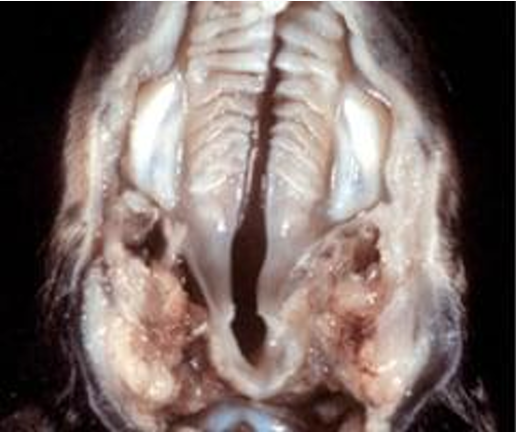
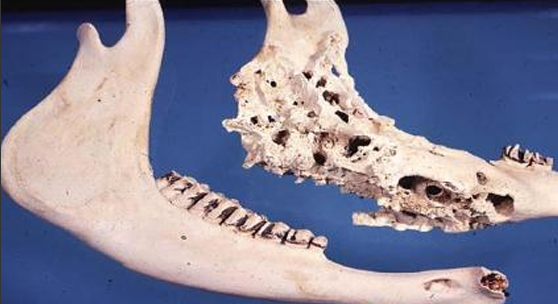
Bovine (Cow), Adult
Jawbone
Chronic Infectious Osteomyelitis
Actinomyces Bovis Infection
Actinomycosis, Lumpy jaw, ACTI
Jawbone is deformed by irregular bone proliferation of most other ramus w large spongy cavities
Spp
Tissue
Morphologic Dx
Etiologic Dx
Lesion or Dx
Lesion description
Actinomyces bovis
SN
Note the characteristic branching nature of these slender gram+rods
Eosinophillic granuloma
Skin
dX NAME
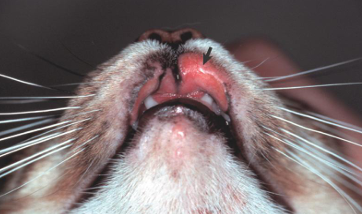
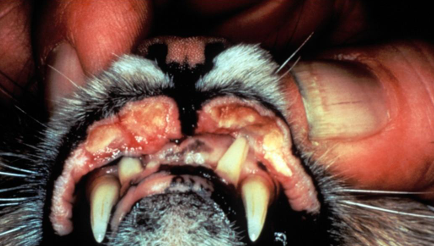
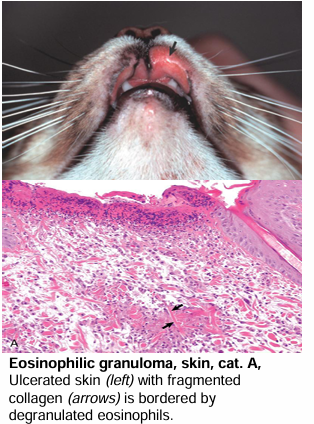
Eosinophilic Granuloma
Disease name
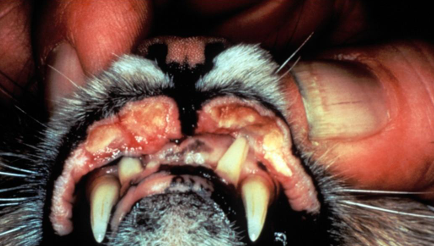
Eosinophilic granuloma
Skin
Feline
Fragmented collagen
Disease name
Tissue
Spp.
Arrow
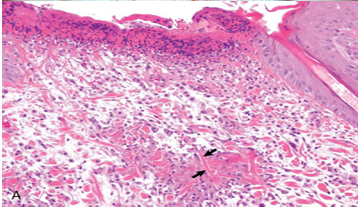
Eosinophilic granuloma
Skin
Feline
Fragmented collagen
Macrophages
Multinucleated giant cells
Degranulated Eosinophils
Flame figure
Disease name
Tissue
Spp.
Arrow
M
G
E
E resembles ?
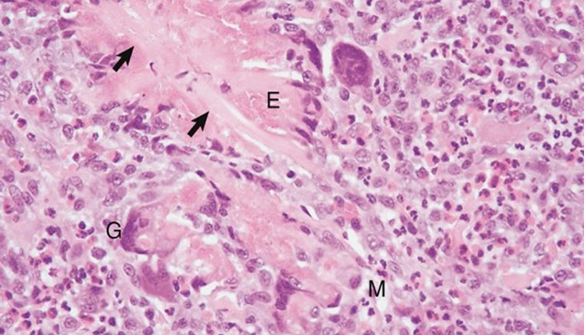
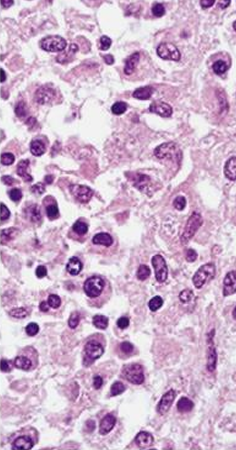
Lymphoplasmacytic Stomatitis
Disease
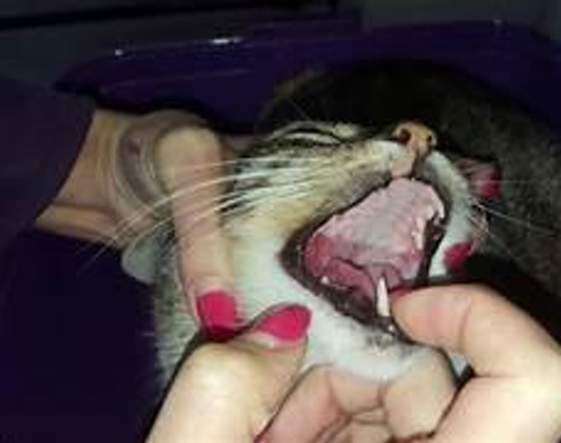
Lymphoplasmacytic Stomatitis
Disease
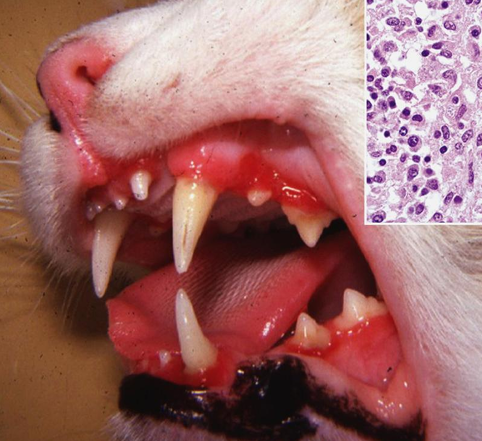
Lymphoplasmacytic stomatitis
Feline
Disease
Spp
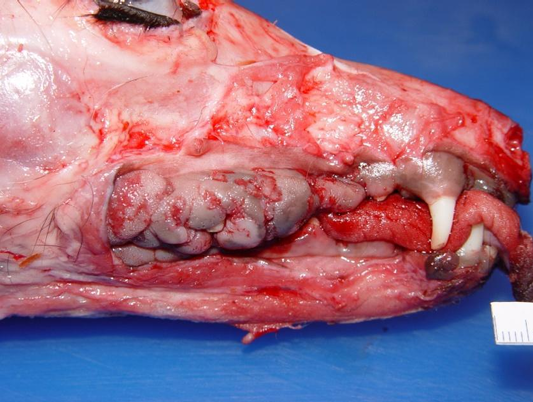
Gingival hyperplasia
Gum tissue
Adult Brachycephalic Dogs
Benign
Disease
Simple overgrowth of the ___
Common in ___ dogs
Malignant/Benign?
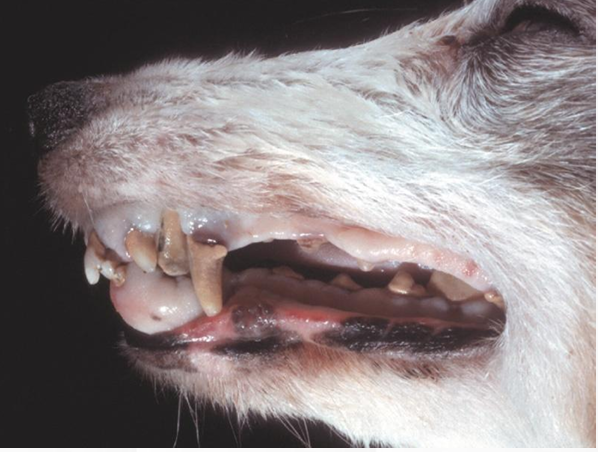
Epulis
Periodontal ligament
“Gingival growth”
Benign
Disease
Neoplasia of the ____
“___ growth”
Malignant/Benign?
Papilloma
Papovirus-induced
Benign
F. MAY regress
Disease
____-induced tumor
Malignant/Benign
T or F. CANNOT regress
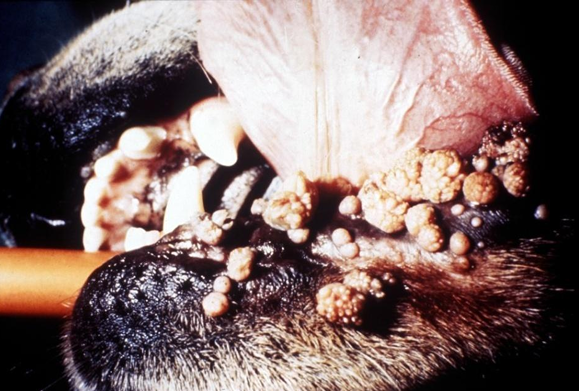
Papilloma
Papovirus-induced
Benign
F. MAY regress
Disease
____-induced tumor
Malignant/Benign
T or F. CANNOT regress
Papilloma
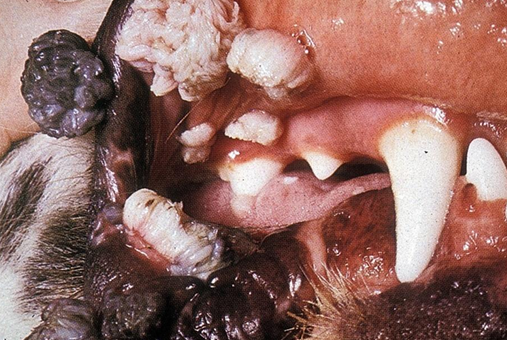
Bovine
Disease
Spp.
Note the finger-like projection from the surface
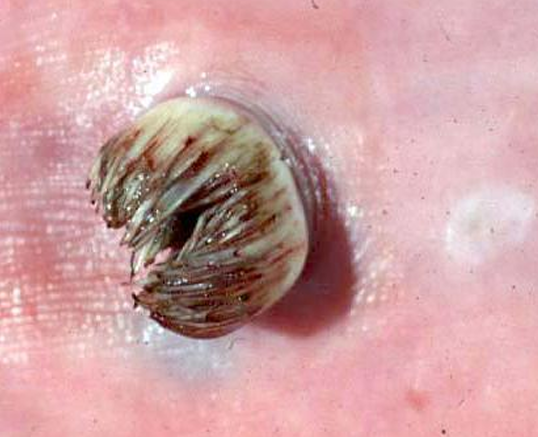
Papilloma
Papillary projections called Fronds
Hyperkeratotic epidermis covering a collagenous core
Disease
Arrow
#2 is composed of?
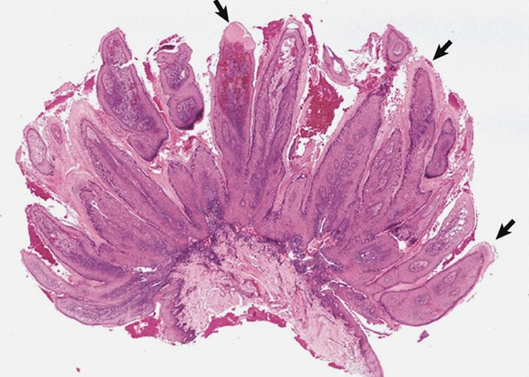
Papilloma
Nuclear pallor & Prominent Keratohyaline Granules
Disease
Cite the cytopathic alterations associated with viral infections
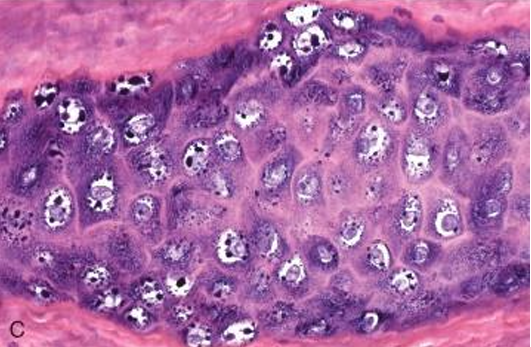
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Cats
Poor
Poor
Disease
Most common oral tumor in this animal
Prognosis in Cats
Prognosis in Dogs if tonsillar
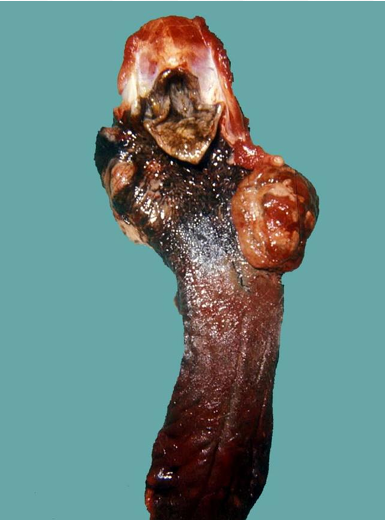
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
Disease
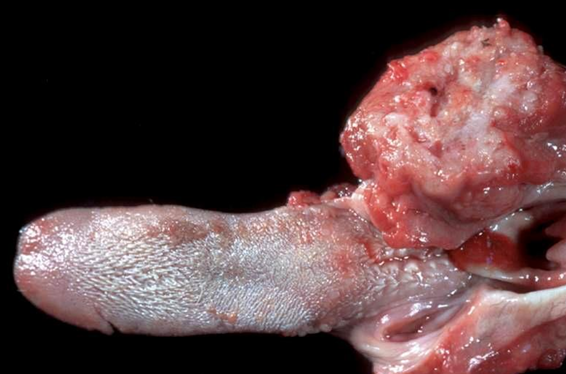
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Proliferating trabeculae of squamous epithelium
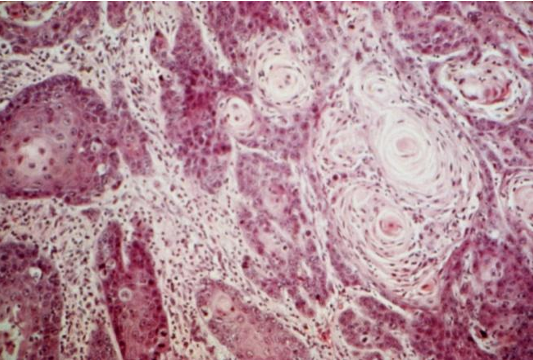
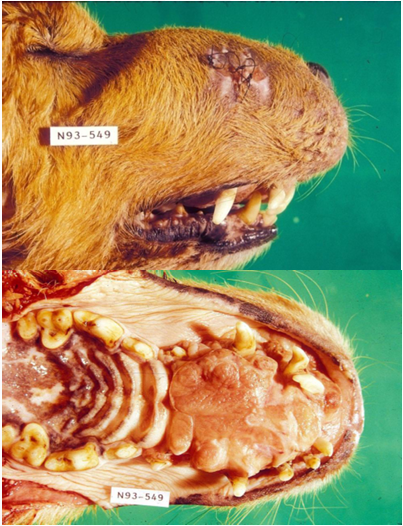
Malignant Melanoma
Dogs
Small breed, Oral pigmentation
Poor
Amelanotic melanoma in mandibular symphysis
Disease
Most common oral tumor in what spp
Risk factors (2)
Prognosis
Lesion Description
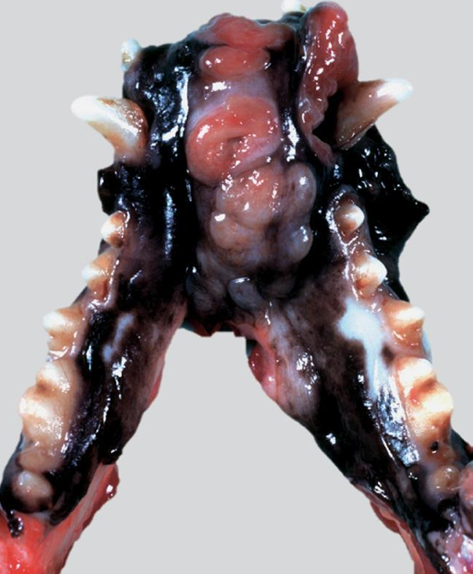
Malignant melanoma
Canine
Nucleus to Cytoplasm ratio
Disease
Spp
Increased ___ - ___ ratio
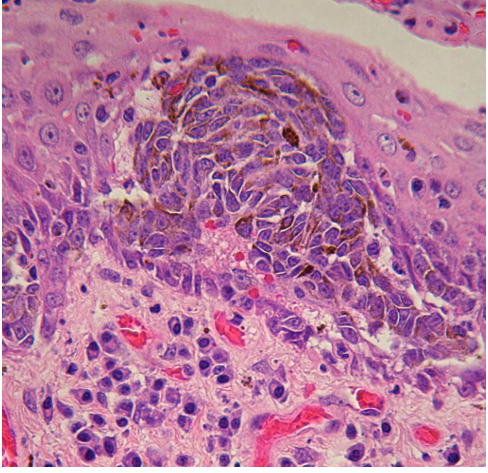
Fibrosarcoma
False. LESS COMMON
True.
Disease
T or F. More common than SCC & Melanoma
T or F. Has a Better prognosis
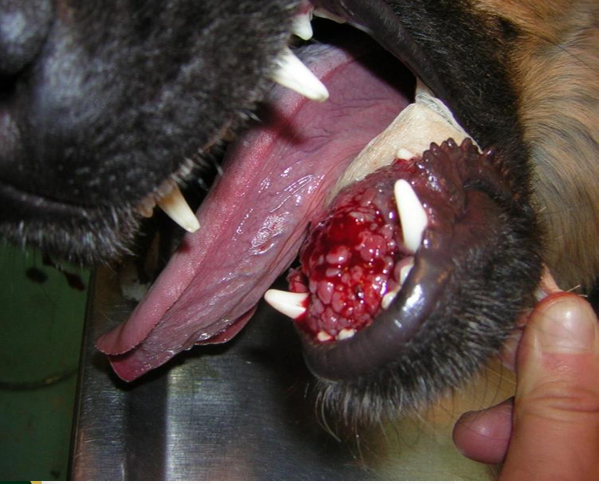
Fibrosarcoma
False. LESS COMMON
True.
Disease
T or F. More common than SCC & Melanoma
T or F. Has a Better prognosis