10. Branding Decisions
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Three brand P’s
Brand Promise: Does it fulfill consumer values?
Brand Positioning: Perception of our brand?
Brand performance: Are the expectations met?
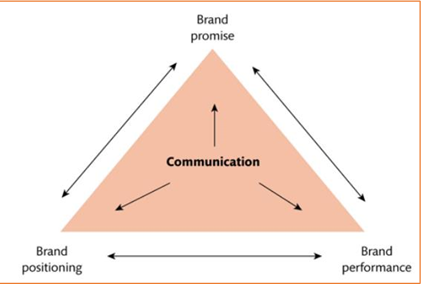
Brand positioning
Try to get into the winning zone
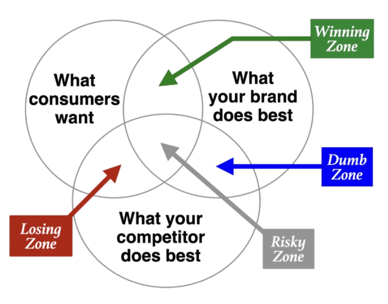
Brand promise
= A statement that businesses write to describe the value they deliver to customers
Sets expectations for brand experience
Brand promise = Positioning + Vision + Value proposition
Brand performance
= The measure of a brand’s results against the business and marketing goals
Brand performance is accomplished when the expectations & experiences match the promise
Brand
= Name, symbol, words, or mark that identifies and distinguishes a proposition/company from its competitors
Functional (Appearance, taste, functionality)
Emotional (Self-expression, social benefits)
Dimensions of brand
Brand awareness
→ Top-of-mind awareness = First brand that comes to mind when you think about something
→ Recall = Spontaneous or unaided awareness
→ Recognition = Aided awareness
Brand associations (Strong, favorable, unique)
→ Distinguishing yourself from competitors
Types of brands
Manufacturer brands (National brand)
Distributor brands (Private label)
Generic brands
Non-commercial brands
Manufacturer brands
= National brands
Sold by manufacturers under their own brand name
Distributor brands
= Private label
Identities and images developed by the wholesalers, distributors, dealers and retailers
NOT by the manufacturers
Types of Private Labels
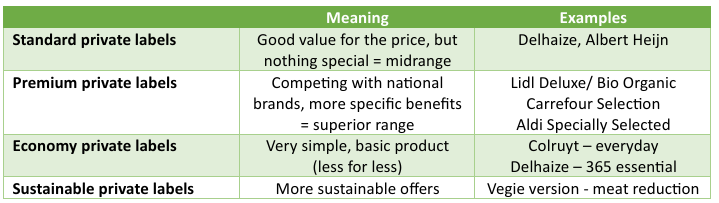
Generic brands
= Sold without any promotional materials or identifyable information
→ Non-branded products
Ex. Medicine
Non-commercial brands
Idea brands: Ideologies, initiatives…
Beliefs and values within society
Person brands: Real people
Ex. Calvin Klein
Place brands: Based on a specific place (geographical)
Why use a brand?
To help consumers make decisions
Consumers like brands because
Helps people identify their preferred products
Reduce perceived risk and psychological reassurance (cognitive dissonance)
Symbolic meaning & value (express yourself)
Assess quality
Efficient shopping
Trust
Informs customers about the source of an object
Brands as a means of self-expression
Desired self (who you want to be)
Ideal self (who you strive to be)
Ought self (who you think you should be)
Why do marketers and retailers use brands?
Financial benefits
Strategic benefits
Relationship benefits

Financial benefits
Premium pricing
Cross-selling
Opportunities for brand extensions
Premium pricing
Can ask higher prices for loyal clients
Cross-selling
Same customer buys other products from the same manufacturer
Opportunities for brand extensions
Introduce new products with the same brand name → Easier with familiar clients
Strategic benefits
Differentiate products
Strengthen image
Integrated marketing communication
Legal protection (against imitation from competitors)
How to build a brand
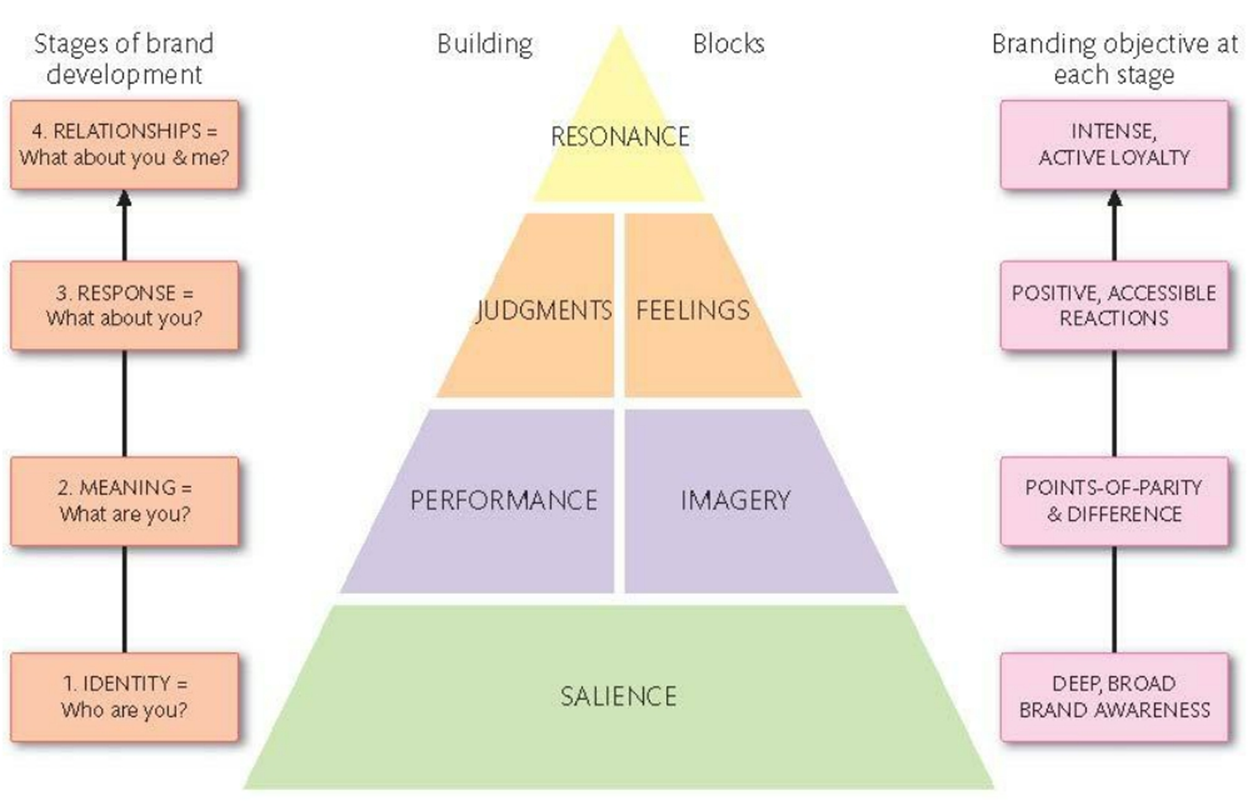
Identity → Meaning → Response → Relationship
Salience = Brand awareness
Performance: How well does it work?
Imagery = External cues that are evaluated by customers (everything that surrounds your brand (slogan, packaging…)
Judgements: Customers’ evaluations & concerns
Feelings: Emotional responses & reactions
Resonance: Connection customer and brand → Loyalty

Good brand names
Easy to recall, spell, and speak
Indicative of the offering’s major benefits and characteristics
Distinctive: No similarity with competitors
Meaningful to the customer
Capable of registration and protection
Consistent with the organization’s branding policies
Criteria for choosing brand names
For technological products: Numerical brand names work better (Ex. Iphone 17)
Make it transferable → No weird translations
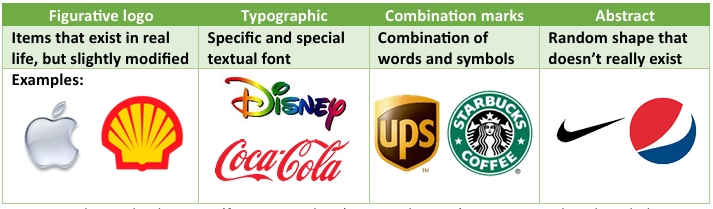
Different types of logos
Figurative (shape that does exist in real life)
Typographic (font)
Combination marks (combination of words and symbols)
Abstract (shape that doesn’t exist in real life)
Brand personality with their traits
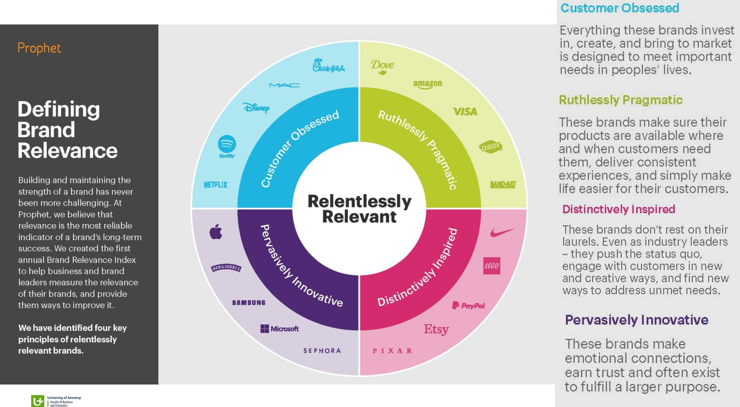
Defining Brand Relevance
(Just know the meaning of those 4)
Customer obsessed (Very customer-centric)
Ruthlessly pragmatic (Make sure they’re trustworthy & credible)
Distinctively inspired (Try to be industry leader, challenge market leaders)
Pervasively innovative (Focus on being most innovative)
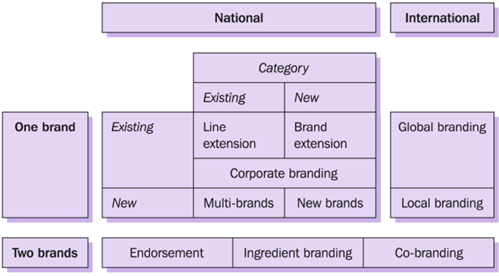
Branding strategies
Individual branding
Family branding
Corporate branding
Line extensions
Brand extensions
Endorsement branding
Co-branding
Ingredient branding
Glocal branding
Individual branding
Each brand has a separate, unique identity
Family branding
= Umbrella branding
Brand name is used for all products in similar categories
Advantage: Positive brand associations
Ex. Sonic headphones & Sonic phones
Corporate branding
Same brand name for completely different products
Line extensions
Extending your offering, add additional items under the same name
Small adaptation
Ex. Coca cola invents a new flavor
Brand extensions
Launching new product in a completely new market
Using the same brand name
Ex. Mr Clean (Carwash)
Endorsement branding
Parent brand supports the branding of another sub-brand
Adding the name of the parent brand to show its support, and show that it can be trusted (reputation)
Risks of line and brand extensions
Brand dilution (Confused about what your brand value really is)
Cannibalization (People buy the new product (New cola flavor) more than the regular version)
Has to fit the parent brand → Could create a bad reputation
Co-branding
Collab with other brands to create value together
Product-based
Communications-based
Ingredient branding
One brand is an ingredient of the other
Ex Milka and Oreo
Product-based co-branding: Benefits and risks
Benefits
Added value & differentiation
Better positioning
Reduction of cost
Risks
Loss of control
Loss of brand equity
Brand equity
What the brand stands for
Brand scope
Domestic: Operate in a single country
International: Active in different countries, focus on extending to multiple countries with limited localization (no focus on local needs)
Multi-domestic: Present in multiple countries, but adapt to local needs (=glocalization)
Global brands: Present around the globe, unified and standardized brand
Global branding
Consumer preference for global brands: more trustworthy
Organizational benefits: you don’t need to adapt your processes
Marketing benefits: a standardized marketing strategy without adaptations
Economic benefits: buy it in other countries too
Transnational innovation: brands across borders, where they innovate to meet different needs
Semiotics perspective
= Importance of using signs in a crowded marketplace
Adopting semiotics into brand architecture builds layers of meaning
Ex. University logos
Ex. Perception that gamers are lazy
Customer-based brand equity vs Financial brand equity
Customer-based
Brand awareness
Brand associations
Perceived quality
Brand loyalty
Price sensitivity
Financial
Discounted future income streams
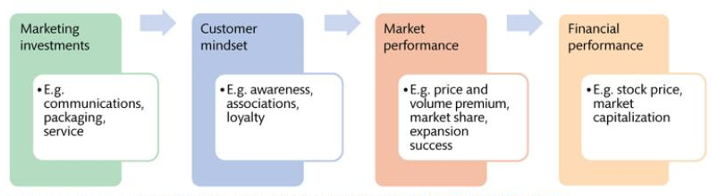
The brand-value chain (!!!)
= Process where a brand creates value
Marketing investments
Customer mindset: Associations, loyalty, awareness
Market performance: Tangible outcomes of customer attitudes
Financial performance: Reflects economic values
Power branding
Brands with strong customer perceptions → Deliver much better returns for shareholders
High degree of resilience when times get tough
Recover their value much quicker