Finals Prep - im on my 2nd cup of coffee. it is not my last for the night
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/155
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:44 PM on 12/20/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
156 Terms
1
New cards
Psychology
The study of mental processes and behavior
2
New cards
Gestalt Psychology
An approach to psychology that focuses on the organization of perception and thinking in a "whole" sense rather than on the individual elements of perception.
3
New cards
What was the Gestalt figure drawn in in class
Linked rings
4
New cards
Psychodynamic theory
Freud’s perspective. Believes behavior is motivated by inner, unconscious forces over which a person has little control
5
New cards
Behavioral theory
Focuses on observable behavior
6
New cards
Humanistic theory
Contends that people can control their behavior and that they naturally try to reach their full potential
7
New cards
Cognitive theory
Examines how people understand and think about the world
8
New cards
Evolutionary theory
Behavior is influenced by our genetic inheritance from our ancestors.
9
New cards
Scientific method
1. identifying questions of interest
2. formulating an explanation
3. conducting an experiment/research
4. communicating findings
10
New cards
Experimental manipulation
Is the change that a researcher deliberately makes in an experiment
11
New cards
Experimental group
Any group that receives a treatment
12
New cards
Control group
A group that receives no treatment
13
New cards
Independent variable
The condition that is manipulated by an experimenter.
14
New cards
Dependent variable
The condition that is manipulated by an experimenter.
15
New cards
Theory; Hypothesis
Remember that a ______ is a broad explanation, whereas a ________ is a more narrow prediction.
16
New cards
Significant outcome
Indicates that the findings of a research study are statistically meaningful.
17
New cards
Neuron
Nerve cells, the basic elements of the nervous system. They are the fundamental unit of the central nervous system.
18
New cards
Dendrites
The part of the neuron that receives messages from other neurons
19
New cards
Axon
Carries messages received by dendrites to the other neurons
20
New cards
Terminal buttons
The small bulges at the end of an axon that send messages to other neurons.
21
New cards
Myelin sheath
A protective coating of fat and protein that wraps around the axon
22
New cards
Autonomic division
Part of the peripheral nervous system. controls the parts of the body that automatically function to keep us alive
23
New cards
Somatic division
Part of the peripheral nervous system specializes in the control of voluntary movements
24
New cards
Sympathetic division
Our body's fight or flight
25
New cards
Parasympathetic division (autonomic division)
Calms down the body after an emergency has ended
26
New cards
What is the central nervous system (CNS) composed of
Brain and spinal cord
27
New cards
Heritability
The degree to which a characteristic is related to inherited genetic factors.
28
New cards
Twin studies
Studies conducted on identical/fraternal twins to study the influence of genetic vs environmental factors.
29
New cards
Sensation
Refers to the activation of the sense organs (a physical response)
30
New cards
Perception
Refers to how stimuli are interpreted (a psychological response)
31
New cards
Absolute threshold
The lowest intensity of stimulus that an organism can detect
32
New cards
Difference threshold (aka. Just noticeable difference)
The smallest level of added or reduced stimulation required to sense that a change in stimulation has occurred
33
New cards
Weber's law
Our perception of change in a stimulus is based on what the stimulus is
34
New cards
Rods
Thin, cylindrical receptor cells in the retina that are sensitive to light
35
New cards
Cones
Receptor cells in the retina that are responsible for sharp focus and color perception in bright light
36
New cards
Gestalt laws of organization
A series of principles that describe how we organize bits and pieces of information into meaningful wholes.
37
New cards
Learning
A relatively permanent change in behavior that is brought about by experience.
38
New cards
Habituation
The decrease in response to a stimulus that occurs after repeated presentations of the same stimulus.
39
New cards
Classical conditioning
A type of learning in which a neutral stimulus comes to elicit a response after being paired with a stimulus that naturally brings about that response.
40
New cards
Neutral stimulus
A stimulus that, before conditioning, does not naturally bring about the response in which we are interested.
41
New cards
Unconditioned stimulus (UCS)
A stimulus that naturally brings about a particular response without having been learned. (ex: meat is the UCS b/c it made the dogs salivate instinctually)
42
New cards
Unconditioned response (UCR)
A natural, innate response that occurs automatically and needs no training. Instinct
43
New cards
Conditioned stimulus (CS)
Classical conditioning transforms the neutral stimulus into this after it is paired with an unconditioned stimulus. The transformed NS now brings about a response formerly caused by the UCS. (ex: the dogs salivate at the bell now instead of the meat)
44
New cards
Conditioned response (CR).
A response that, after conditioning, follows a previously neutral stimulus (e.g., salivation at the ringing of a bell).
45
New cards
Extinction
Occurs when a previously conditioned response decreases in frequency and eventually disappears.
46
New cards
Stimulus generalization
A process in which after a stimulus has been conditioned to produce a particular response, other stimuli that are similar to the original stimulus produce the same response.
\
Ex: Little Albert who was conditioned to fear white rats also began to fear other furry white creatures.
\
Ex: Little Albert who was conditioned to fear white rats also began to fear other furry white creatures.
47
New cards
Stimulus discrimination
Occurs if two stimuli are sufficiently distinct from each other such that one evokes a conditioned response but the other does not.
48
New cards
Operant conditioning
Learning in which a voluntary response is strengthened or weakened, depending on the response's favorable or unfavorable consequences.
49
New cards
Negative reinforcement
The more I do something, the more something I don't care for goes away.
50
New cards
Positive punishment
Adding something to suppress behavior (Yelling at someone for hitting you)
51
New cards
Negative punishment
Taking something you like away to suppress a behavior. (Silent treatment in a relationship.
52
New cards
Positive reinforcement
Giving you something you like to reinforce a behavior.
53
New cards
B.F Skinner & Thorndike's Law of Effect
Responses that lead to satisfying consequences are more likely to be repeated
54
New cards
Albert Bandura
Theorized that observation and modeling play a crucial role in how we learn.
55
New cards
Memory
The process by which we encode, store, and retrieve information
56
New cards
**Sensory memory**
Refers to the initial, momentary storage of information that lasts only for an instant.
57
New cards
Iconic memory
Reflects information from the visual system.
58
New cards
Echoic memory
Stores auditory information coming from the ears. Fades in 2 or 3 seconds
59
New cards
Chunk
A group of separate pieces of information stored as a single unit in short-term memory
60
New cards
Rehersal
The repetition of info that has entered short-term memory. It allows material to be transferred from short-term to long-term.
61
New cards
Central executive processor
Part of the working memory, it determines what we pay attention to and what we ignore.
62
New cards
Episodic buffer
Part of the working memory, it contains info that represents events and occurrences, the things that happen to us.
63
New cards
Heuristic
A thinking strategy that may lead us to a solution or a decision but sometimes leads to errors. They are essentially shortcuts that might provide a solution.
64
New cards
Availability heuristic
We judge the likelihood of an event occurring on the basis of how easily we can bring to mind examples of the event.
65
New cards
Familiarity heuristic
Leads us to prefer familiar objects, people, and things over those that are unfamiliar or strange to us
66
New cards
Intelligence
The capacity to understand the world, think rationally, and use resources effectively when faced with challenges.
67
New cards
G-factor
The single, general factor that produced intelligence. Believed that there was an underlying form of intelligence
68
New cards
Fluid intelligence
Reflects the ability to think logically, reason abstractly, solve problems, and find patterns.
69
New cards
Crystalized Intelligence
Accumulation of information, knowledge, and skills that people have learned through experience and education. Stored in long-term memory.
70
New cards
Practical intelligence
Intelligence related to overall success in living, learned mainly through observation of others' behavior.
71
New cards
Emotional intelligence
The set of skills that underlie the accurate assessment, evaluation, expression, and regulation of emotions.
72
New cards
Analytical intelligence
Focuses on abstract, but traditional types of problems measured on IQ tests
73
New cards
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-IV (WAIS-IV) / Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children-V (WISC-V)
IQ test made by David Wechsler that measured verbal comprehension, perceptual reasoning, working memory, and processing speed.
74
New cards
Reliability
Refers to the consistency of a test in measuring what it is trying to measure. Every time we administer a test, the test-taker will achieve the same or nearly similar results.
75
New cards
Validity
Occurs when a test actually measures what it's intended to measure. Accuracy of the test.
76
New cards
5 solutions to the 6+4 = 4 puzzle
0 + 4 = 4
8 - 4 = 4
5 + 4 = 9
6-4 ≠ 2
6 + 4 > 4
8 - 4 = 4
5 + 4 = 9
6-4 ≠ 2
6 + 4 > 4
77
New cards
**What is the single most preventable form of mental handicap?**
Fetal alcohol syndrome
78
New cards
What does Dr. Hinitz say is at the core of every relational experience?
An awareness of acceptance or rejection.
79
New cards
What are Dr. Hinitiz's thoughts on: If a tree falls in a forest, if nobody hears it, does it ever really make a sound?
it doesn't make a sound, rather it makes a vibration
80
New cards
Emotions
Feelings that generally have both physiological and cognitive elements that influence behavior.
81
New cards
3 Functions of emotions
1. Preparing us for action
2. Shaping our future behavior
3. Helping us interact more effectively with others
82
New cards
Maslow's Hierarchy
Suggested that before more sophisticated, higher-order needs can be met, certain primary needs must be satisfied.
(SELSP)
(SELSP)
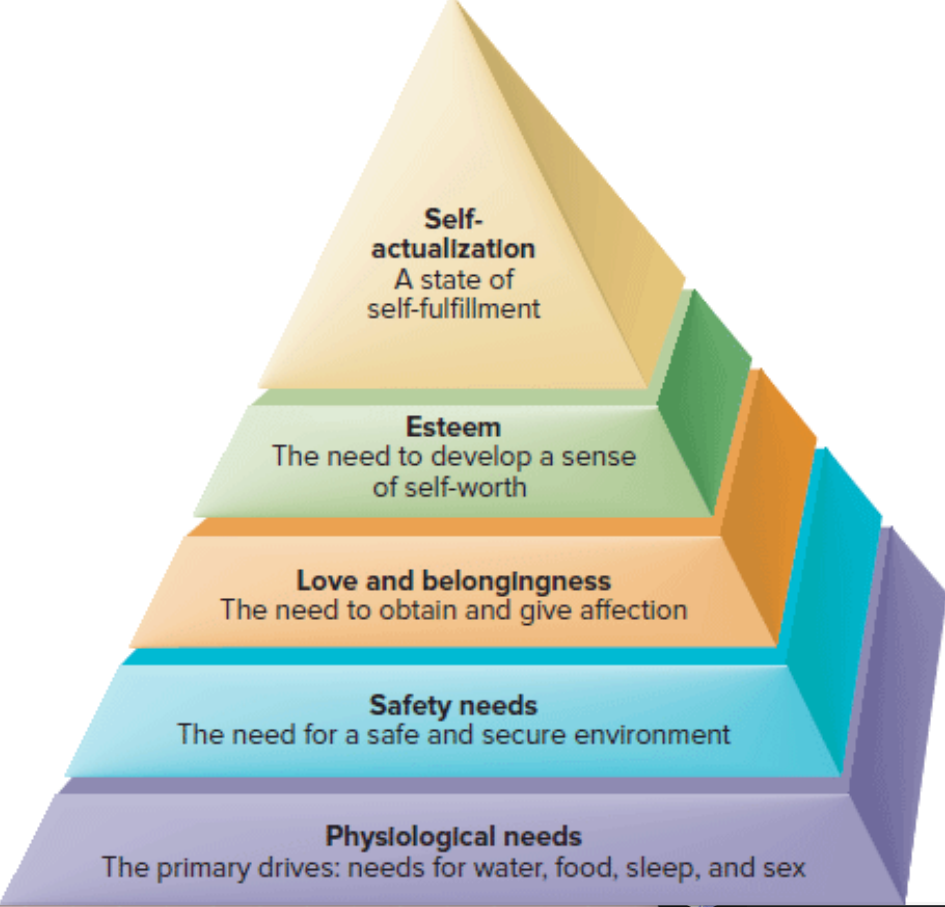
83
New cards
Learned helplessness
Occurs when people conclude that unpleasant or aversive stimuli cannot be controlled.
\
ex: Someone believes they’re not good at math so they might not try anymore in the subject.
\
ex: Someone believes they’re not good at math so they might not try anymore in the subject.
84
New cards
What example did Dr. Hinitz use to describe empathy?
Salad forks and tuning forks. Empathy is people being attuned to you.
85
New cards
Masters and Johnson and sexual response cycle
Sexual responses follow a regular pattern consisting of four phases:
Excitement, plateau, orgasm, resolution
Excitement, plateau, orgasm, resolution
86
New cards
Excitement phase
An arousing stimulus begins a sequence that prepares the genitals for sexual intercourse. Can last for a few minutes to over an hour.
87
New cards
Plateau phase
The body's preparation for orgasm.
88
New cards
Orgasm
An intense, highly pleasurable experience wherein breathing and heart rates reach their maximum.
89
New cards
Resolution stage
The body returns to its resting state, reversing the changes brought by arousal.
90
New cards
Androgen
Male hormone
91
New cards
Estrogen
Female hormone
92
New cards
Determinism
The notion that behavior is largely produced by factors beyond people’s willful control
93
New cards
Id
The instinctual and unorganized part of personality
94
New cards
Ego
The rational and logical part of personality. Attempts to balance the desires of the id and the realities of the objective, outside world.
95
New cards
Superego
The part of the personality that harshly judges the morality of our behavior. It represents the rights and wrongs of society and includes the conscious.
96
New cards
Personality
Is the pattern of enduring characteristics that produce consistency and individuality in a given person.
97
New cards
What does Dr. Hinitz say is the groundwork of all psychology?
Attachment
98
New cards
When does attachment begin?
When the baby is still in the uterus
99
New cards
Teratogen
An environmental agent that can hurt the child
100
New cards
Rates of depression go up when
Sunlight contact isn’t met