3.4.2 Perfect competition
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Different types of markets
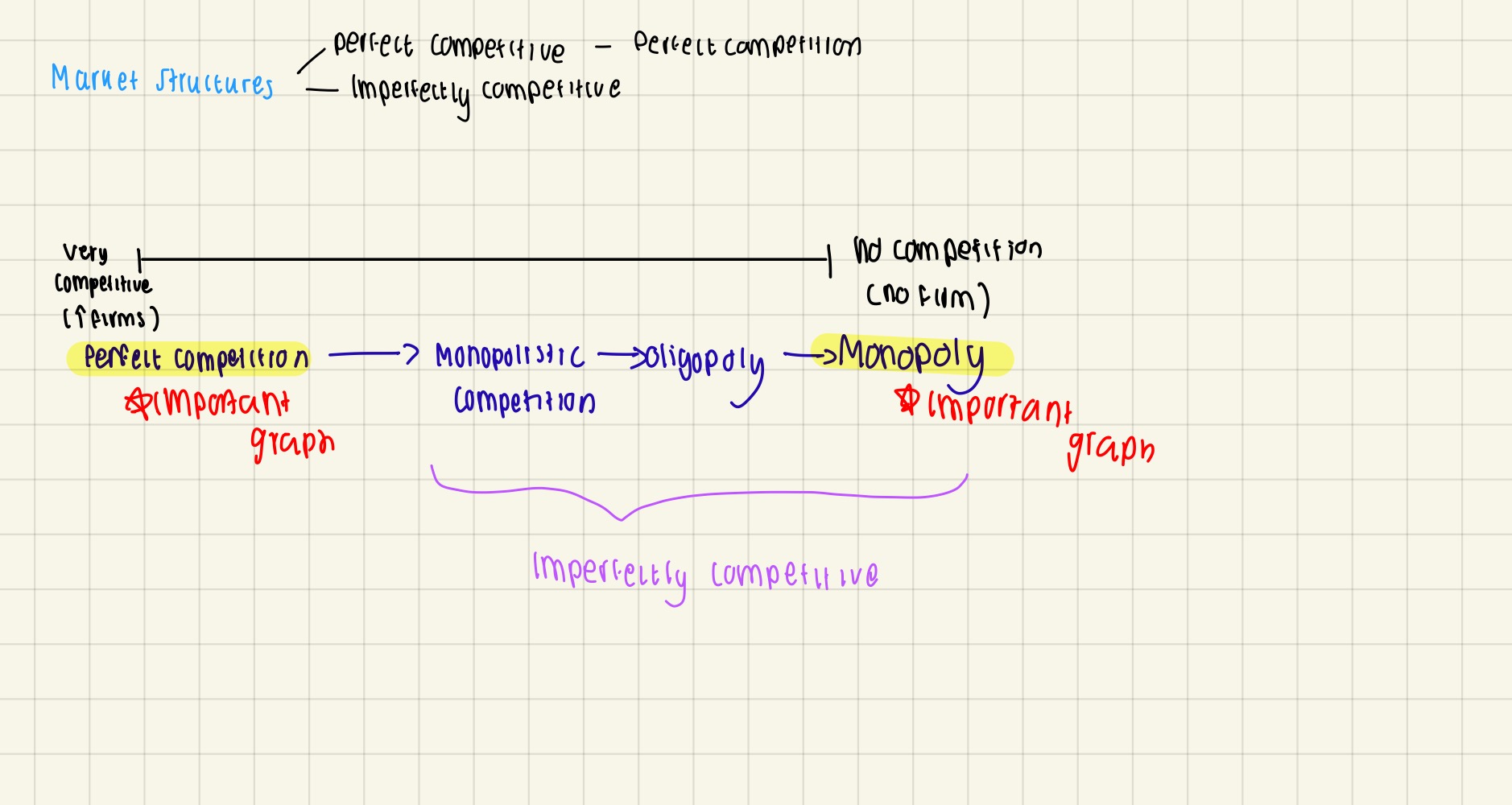
Characteristics of perfect competition (perfect competition is the idealised market model to compare but impossible to happen in real life lol)
Number of firms: many small sellers & buyers (near infinite) (all firms equally small in size)
Type of product: homogenous product (all firms produce the same product - perfect substitutes)
Knowledge: Perfect knowledge (everyone knows everything equally about the market)
Barriers to entry/exit: No, costless
Price-setting ability: None, price taker (this is because all firms sell the exact same good - so can’t determine price of good)
Objective: Profit maximisation

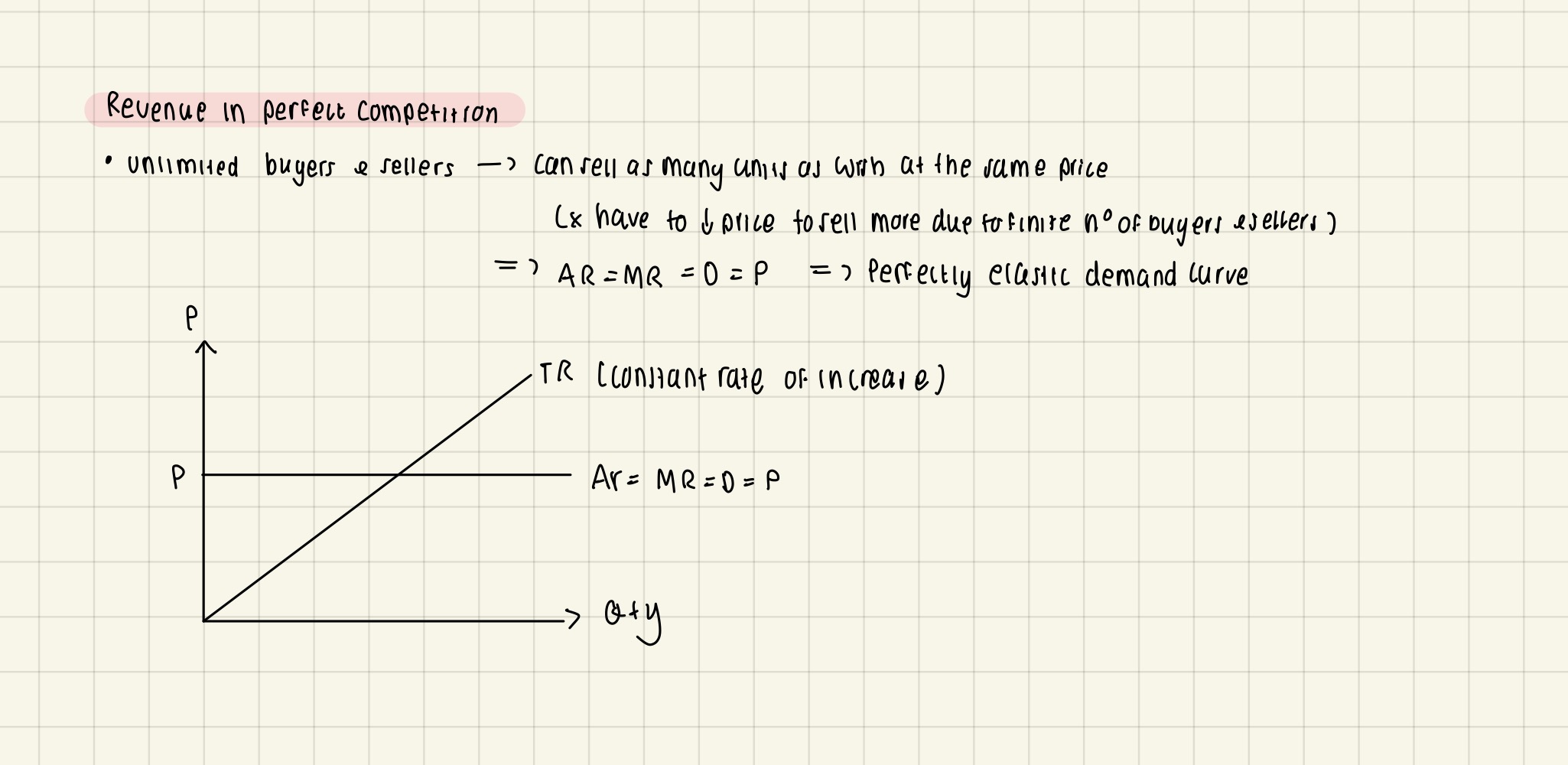
Revenue in perfect competition
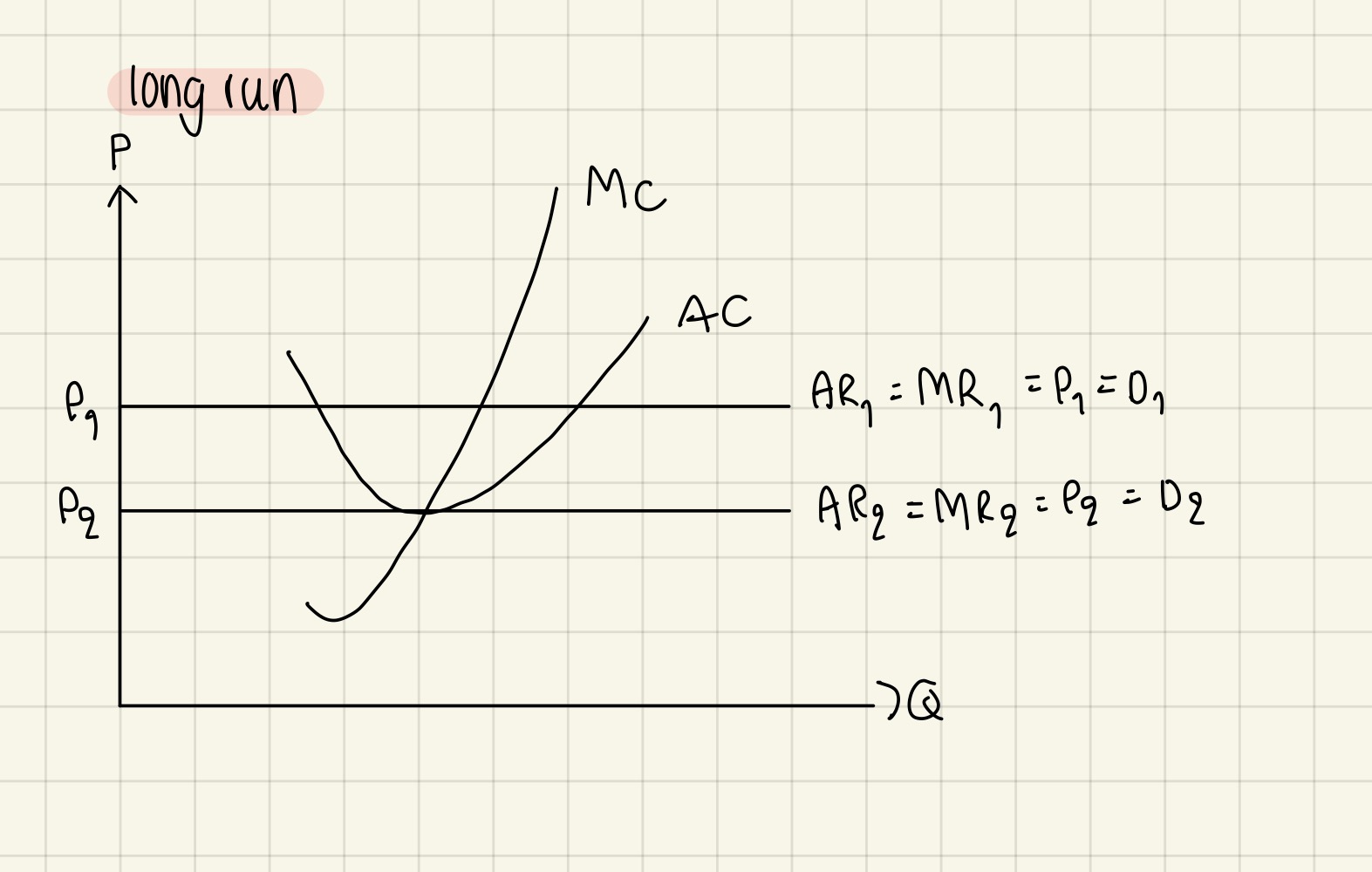
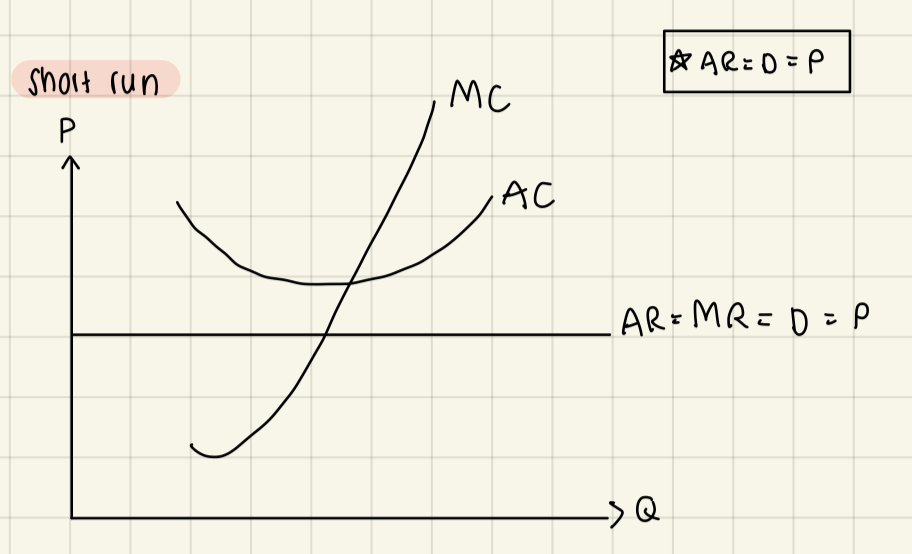
Supernormal profits in short run & long run for perfect competition
Short run:
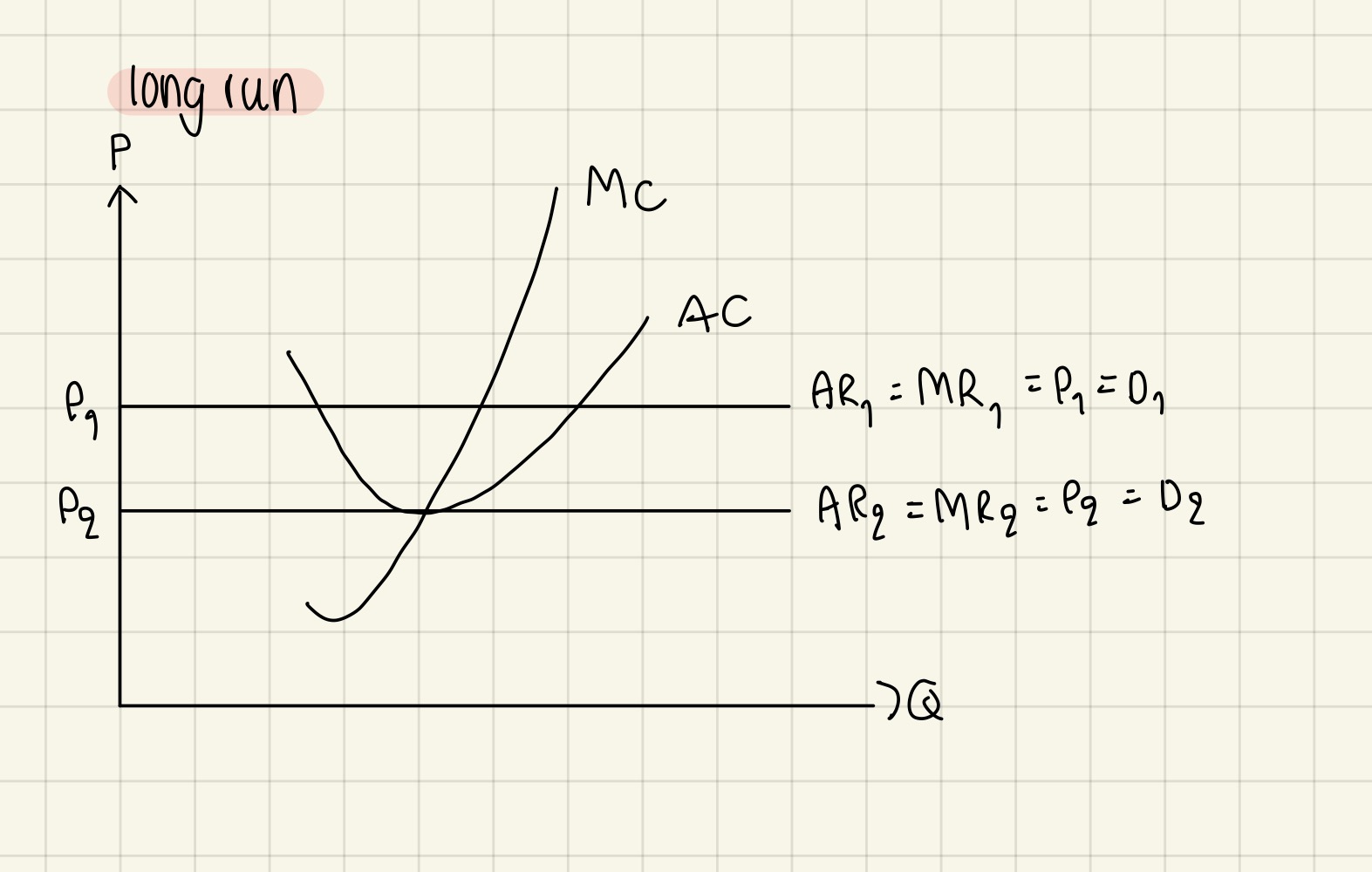
Supernormal profit only happens in short-run, in long run, no supernormal profit only normal profit
This is because:
In short run, supernormal profit attracts new firms to industry → AR decrease (=AR=D=P) → this AR straight line continue to shift down as more firms enter due to no barriers to entry → shift down until land on normal profit so no supernormal profit anymore in long run→ stay there because no firms want to enter industry anymore as they see no profit
In short run, not productively efficient but allocatively efficient & dynamically efficient
Therefore, in long run, firms are productively & allocatively efficient (measure from prof max point) but not dynamically efficient (no supernormal profit)
Profit maximizing equilibrium in the short run & long run

Profit maximizing equilibrium in the long run
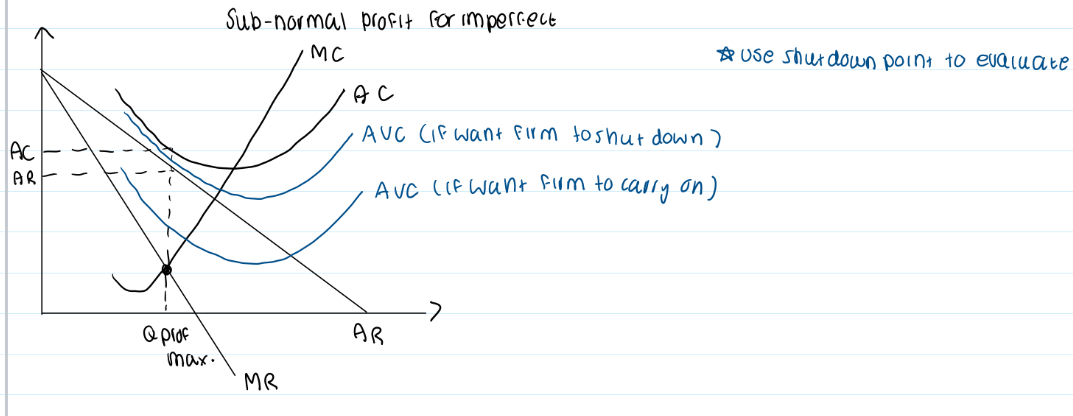
Sub-normal profits in short run
Sub-normal profits in long run
How to calculate (profit) loss per unit from the graph
Profit = Revenue - Cost
Profit loss per unit = Revenue per unit - cost per unit
1) Revenue = p x q
2) Therefore, revenue per unit = price
3) Cost per unit = TC/Q = AC
Therefore, profit loss per unit = AC - P
How to calculate profit per unit from the graph
P - AC
Shutdown point
Long run shutdown condition:
AR less then AC
Short run
AR less than AVC → shutdown
AR more than AVC (but less than AC) → carry on