Heme cumulative
1/265
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
266 Terms
What is included in a CBC w/ differential?
WBC count
Hgb/Hct
RBC count
RBC indices
WBC differential
platelet count
What does a differential measure?
percent of each type of leukocyte
what is a normal Hgb value for males?
14-18 g/dl
what is a normal Hgb value for females?
12-16 g/dl
what is a normal Hct value for males?
42-52 %
what is a normal Hct value for females?
37-47%
what is a normal MCV value?
80 - 100 um
What measure is best to classify anemias?
MCV
what is normal range of MCH?
30-34 pg/cell
what is normal range for MCHC?
31-37 g/dl
What does an increased retic count reflect?
ongoing or recent RBC production activity
ex: post bleeding, post hemolysis (hemolytic anemia), response to therapy
what does a decreased retic count reflect?
decreased RBC production
ex: anemia, aplastic anemia, decreased EPO, post XRT, bone marrow replacement by benign or malignant process
What is IPF?
method to quantify reticulated platelets
(increased in conditions w/ inc plt production)
what is the most abundant cell type?
erythrocytes / RBCs
What is HgF?
normal Hgb product in the RBCs of a fetus and im small amounts in infants
What are the granulocytes?
neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
What are the agranulocytes?
lymphocytes, monocytes
where does hematopoiesis occur in adults?
red bone marrow of long bones and axial skeleton
precursors cells
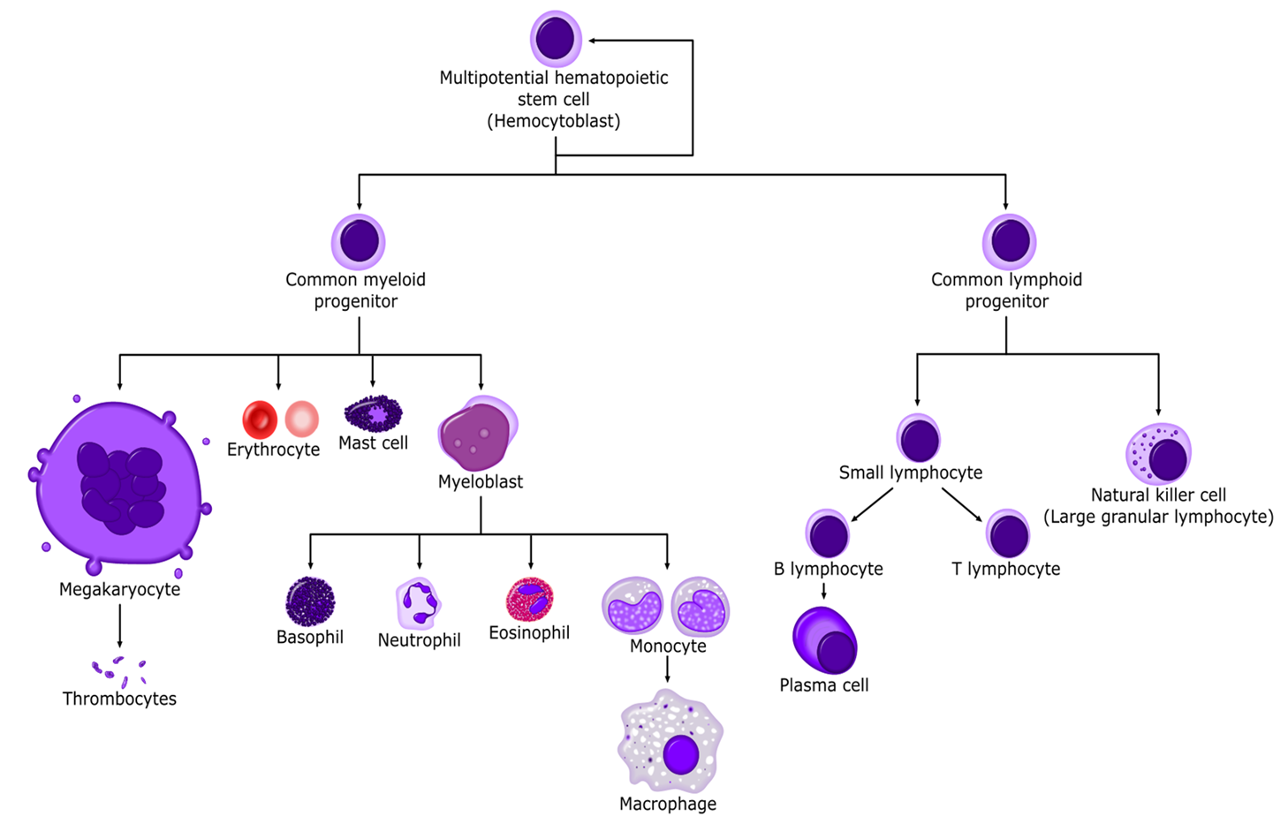
Where is EPO produced?
in the kidneys by cells that sense the adequacy of tissue oxygenation
What is anisocytosis?
abnormal variation in size
what is microcytosis?
cell size < 6 um or MCV < 80
what is macrocytosis?
cell size > 8 um or MCV > 100
what is hypochromia?
cells w/ dec concentration of Hgb
what is poikilocytosis?
abnormal cell shape
what is spherocytosis?
spherical, w/o pale centers
What is a crescent shaped cell known as?
sickle cell
what are target cells?
dark center and periphery w/ clear ring in the center (bullseye)
what are schistocytes?
fragmented irregularly contracted cells
What is the definition of anemia?
condition in which there are decreased number of circulating erythrocytes or decrease in total amount of hgb resulting in decreased oxygen transport
What are generic sx of anemia?
fatigue, weakness, malaise, pallor, SOB, dizzy/lightheaded
What is pica?
abnormal craving ice or other non food items (sign of anemia)
What are PE findings you might see in an anemic patient?
pale skin, conjunctiva, mucosa
check tongue and mouth for lesions
nail defects
tachycardia, murmurs
dyspnea, esp w/ exertion
What workup would you order for anemia?
CBC w/ diff (dec H&H)
RBC indices → MCV, MCH, MCHC
reticulocyte count
fecal hem occult looking for occult GI bleeding
urinalysis (hematuria)
MCV ≤ 80 fL is considered …
microcytic
MCV 81-99 fL is considered …
normocytic
MCV ≥ 100 is considered …
macrocytic
If reticulocytes are low, where is the problem?
in the marrow (marrow failure or lack of substrate); reflects dec RBC production
if reticulocytes are high, where is the problem?
not in the marrow (appropriate response is to compensate); reflects ongoing or recent RBC production activity
What is the pathophysiology of iron deficiency anemia (IDA)?
depletion of iron stores (common in children and menstruating/pregnant individuals)
iron becomes limiting factor in heme biosynthesis
heme deficiency then limits Hgb assembly
Hgb deficiency limits RBC production
RBC cells become (microcytic, low MCV) and deficient in hgb (hypochromic, low MCH)
Where is iron primarily absorbed?
in the duodenum
What are possible causes of iron deficiency?
occult/overt GI losses, traumatic, or surgical losses
failure to meet inc requirements (rapid growth in infancy/adolescence, menstruation, pregnancy, delivery)
inadequate dietary source (vegan diets, impoverished)
malabsorption (GI dz/surgery, duodenal/small bowel malabsorptive dz)
chronic hemolysis (paroxysmal nocturnal hgb (PNH), mechanical hemolysis)
what is ferritin?
protein created to store iron in the cells;
also an acute phase reactant and rises in high inflammatory states
when would ferritin decrease?
in the presence of iron deficiency in an effort to free up iron to become heme
what is the most useful test for iron deficiency?
ferritin → no other causes of low ferritin
What does serum Fe measure?
amount of free iron in the serum
what is transferrin?
holds iron in the serum
what is total iron binding capacity (TBIC)?
indirect measure of transferrinw
when is transferrin elevated?
in the presence of iron deficiency as a futile attempt to gather more iron
what is the most common cause of anemia?
iron deficiency
what is the most common cause of iron deficiency anemia?
GI bleeding or dysfunctional uterine bleeding
what is the definition of iron deficiency anemia (IDA)?
hypochromic, microcytic anemia resulting from under production of RBCs due to lack of adequate amount of iron
etiologies of IDA
abnormal blood loss (cancer, menstruation, PUD, IBD)
malnutrition
dec absorption (celiac sprue, gastrectomy/gastric bypass)
inc demand (pregnancy, lactation, rapid growth)
kidney dz (CRF, dialysis)
What is the clinical presentation of IDA?
can be asx; insidious onset
fatigue, weak, WOB
pallor
palpitations
HA, dizzy, tinnitus
sx of underlying dz → ulcer, gastritis, melon, menorrhagia
what are unique manifestations of IDA?
glossitis- red smooth waxy tongue w/ atrophy of papillae
angular cheilitis- ulcerations or fissures at corners of mouth
koilonychias- thin, friable, brittle spoon shaped nails
pica- cravings for non food
what would iron studies look like in IDA?
low serum iron
high TBIC (empty seats on the bus)
low ferritin (best test)
dec percent transferrin saturation
what is the treatment for IDA?
correct underlying problem
oral iron supplementation (preferred)
ferrous sulfate
IV iron supplementation
INFeD, Venofer, Injectafer
for patient’s unable to absorb or no improvement w/ oral
blood transfusion, packed RBCs
reserved for prodounf anima (Hgb < 7), significant acute bleeding, hypoxia, or coronary insufficiency
What are possible SE from ferrous sulfate?
constipation, change in stool color, heartburn
What patient education should you give to an IDA patient?
avoid tea and coffee- blocks absorption of iron
take vit C 500mg+ to enhance iron absorption
beware of s/sx of bleeding
if severe, limit activities until corrected
what is thalassemia?
genetically heterogenous spectrum of dz characterized by mutations that result in reduction or absence of 1 or more globin chains
disrupts ⍺ / β chain ratio, stability of hgb, and leads to hemolysis
what are classic findings of thalassemia?
microcytosis out of proportion to the degree of anemia; normal iron studies
Patho of thalassemia?
deficiencies of globin chain synthesis produce inadequate hgb → microcytic RBCs
deficiency if alpha globin synthesis results in unused beta globin chains accumulating in RBC injuring cell membrane
these abnormal RBCs are removed from circulation early by spleen, further worsening the anemia
similar results w/ alpha globin chain accumulation in beta thalassemia
Where is thalassemia most common?
mediterranean, asian, and African regions where malaria is endemic
What happens if you inherit only one abnormal β allele (β/β+ or β/βo)?
thalassemia trait / silent carrier
mild anemia / no transfusions
what happens if you inherit 2 abnormal β alleles (βo/βo)?
thalassemia major
marked hemolysis, profound anemia, and transfusion dependency
how many β globin genes are located on chromosome 11?
2
how many ⍺ globin genes are there on chromosome 16?
4
What does a deletion of 1 ⍺ gene (-⍺/⍺⍺) result in?
silent carrier
no clinical manifestations
what does a deletion of 2 ⍺ genes (-⍺/-⍺ or --/⍺⍺) result in?
thalassemia trait or talassemia minor
mild anemia
what does a deletion of 3 ⍺ genes (- -/-⍺) result in?
Hgb H dz (hgb precipitates → hemolysis → splenomegaly)
mod-severe microcytic anemia (smear w/ striking hypochromia, target cells, basophilic stippling)
what does a deletion of all 4 ⍺ genes result in?
thalassemia major or hydrops fetalis
almost total hemolysis of RBCS, fetus usually dies in utero
what is the clinical presentation of thalassemia?
varies; asx or sx of anemia, hepatosplenomegaly, jaundice
what is the gold standard for evaluation of thalassemia?
hemoglobin electrophoresis
what would a lab evaluation of thalassemia show?
microcytosis, hypochromia
stippled cell
target cell
elliptical cell
What would hemoglobin electrophoresis show in thalassemia?
beta: increased Hgb F and A2
alpha: may be normal, difficult to dx
what is the treatment for thalassemia major?
only required if sx severe
chronic transfusion therapy
iron chelation
splenectomy- to stop excessive destruction of RBCs
allogenic stem cell transplant only curative measure
Thalassemia trait (minima) manifestation
manifests as mild-mod microcytic hypochromic anemia
most often asx
asian, mediterranean, and African populations
required no tx other than genetic counseling
Why is thalassemia trait often confused w/ IDA and why is this a problem?
low MCV
places pt at risk for inappropriate/toxic treatment w/ iron
When should you always suspect thalassemia?
low MCV is Fe deficiency has been r/o
pt fails to respond to Fe replacement therapy
What would labs show in thalassemia trait?
MCV < 70
RBC count > 5.0
normal RDW
normal or increased iron studies
What patient education should you provide for thalassemia?
genetic counseling
supplements- folic acid, vit C, vit E
drink tea and coffee (decreases iron absorption)
do NOT give iron and avoid iron rich foods
normal activity is tolerated
what is microcytic hypochromic anemia w/ basophilic stippling?
lead poisoning anemia
what is the pathophysiology of lead poisoning anemia?
chronic repeated lead exposure → iron is displaced by lead and zinc protoporphyrin is formed
what is the clinical presentation of lead poisoning anemia?
often vague and non specific sx; often unrecognized
(dx usually made via screening program or elevated blood/urine levels)
early: loss of appetite, vomiting, irritability etc
late or acute: CN paralysis, encephalopathy, seizures, coma
Lead values
above 10 = toxicity
above 45 = chelation therapy
above 70 = medical emergency
What is the treatment for lead poisoning anemia?
prevent further exposure
chelation- mobilize lead from bone and encourage urinary excretion (succimer PO or Dimercaprol IM)
supportive care- anticonvulsants, vitamin D, high calcium/phosphorous diet
chronic blood loss leads to _____ anemia ; acute blood loss leads to _____ anemia
microcytic; normocytic
what is the accelerated destruction of erythrocytes resulting in anemia?
hemolytic anemia
Types of hemolytic anemia
extravascular: through reticuloendothelial system (spleen)
intravascular: w/in circulation itself (prosthetic heart valve, G6PD, TTP)
what would a laboratory evaluation of hemolytic anemia show?
CBC: normocytic anemia
total bili: elevated (d/t intravascular release of hgb)
LDH: increased
Haptoglobin: decreased (consumed by binding to free hgb, rapidly removed by liver)
reticulocyte count: marked increase (marrow attempting to compensate)
what is the most common RBC defect?
G6PD deficiency
Who is G6PD deficiency more common in?
males
What do Heinz bodies and bite cells indicate?
G6PD deficiency
What is the clinical presentation of G6PD deficiency?
asymptomatic in steady state
hemolysis occurs under oxidative stress
acute infx (COVID)
drugs- dapsone, pyridium, etc
diet- fava beans
metabolic acidosis
How is G6PD deficiency diagnosed?
quantitative enzyme assays
what is the treatment for G6PD deficiency?
avoid triggers
blood transfusions in acute hemolysis or blood exchange
splenectomy (controversial)
What condition has antibodies that develop against RBCs, resulting in their destruction?
autoimmune hemolytic anemia (warm and cold)
Which AIHA is more common and typically IgG and signals macrophages in spleen to target IgG/Fc?
warm
which AIHA is typically IgM and activates complement cascade?
cold
Warm AIHA clinical presentation?
could be asx
anemia sx
jaundice
splenomegaly