RCC Final
1/426
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
427 Terms
A complex restoration refers to a restoration that replaces one or more ______
cusps
Provisional (temporary) with questionable prognosis
What is the most important factor when deciding between amalgam and composite?
isolation
If the weakened cusp exceeds more than _____ the distance from the primary groove to the tip of the cusp, cusp coverage is indicated.
2/3
Direct vs Semidirect vs Indirect
Direct: 1 appointment technique sensitive (Restoration)
Semidirect: 1 appointment can be done on benchtop (Cast)
Indirect: 2 appointment best but a lot more expensive (Crown)
Axial Contour should be ______
convex instead of flat
Should the wedge encroach toward the contact area?
No it would deform the matrix leaving a gap
Resistance form qualities
90 degree CSM
Adequate depth (at least 1.5 mm)
Rounded internal angles
Retention form qualities
Convergent walls
Dovetails
Retention features
Which cusp fractures most frequently in Mandibular molars and premolars
Which cusp fractures most frequently in Maxillary molars and premolars
Lingual cusps (twice as often)
Buccal cusps (twice as often)
The functional cusp in maxillary molars and premolars is the ______.
Mandibular?
lingual
facial
The (functional/nonfunctional) cusp is the most likely to fracture.
non-functional
If replacing a functional cusp the reduction should be _____ mm.
If replacing a non-functional cusp the reduction should be _____ mm.
2-2.5
1.5-2
When reducing the cusp, hold bur (parallel/perpendicular) to the cuspal incline.
parallel
When reducing the cusp, Extend reduction just beyond _____ groove, Sloping toward the ______.
F/L
central groove
Boxes are placed _______, _______ or _______ grooves. Great for resistance and retention form.
interproximal, buccal, or lingual
Active lesions appear ______ and usually have _____ present.
dull
plaque
Should tooth surface be observed wet or dry
both
ICDAS is based on _______ examination
visual
ICDAS 0
sound tooth surface, no clinically detectable lesion.
ICDAS 1
First visual change in enamel (seen only after prolonged air drying or restricted to within the confines of a pit/fissure) after air drying
ICDAS 2
lesion visually distinct on wet enamel
ICDAS 3
micro-cavitation
ICDAS 4
underlying dentin shadow
ICDAS 5
distinct cavity with visible dentin
ICDAS 6
More than 50% of dentin involved. Pulp may also be affected
T or F: Forceful use of a sharp explorer for the sole purpose of detecting carious lesions is highly discourage in today's practice of dentistry.
true
The most effective radiographic technique for caries diagnostics is the _______ technique, which is an intraoral, ______ technique.
bitewing
paralleling
Early ______ lesions are difficult to see on radiographs because of the superimposition of the dense B and L enamel cusps. Typically theses lesions can only be seen radiographically once they have passed the _____
occlusal
DEJ
Proximal lesions are most likely detected ________. You may also use an _____ to separate the teeth
radiographically
orthoband
Caries Detection Dye are used primary after _______ is removed
enamel
Mostly work on carious dentin
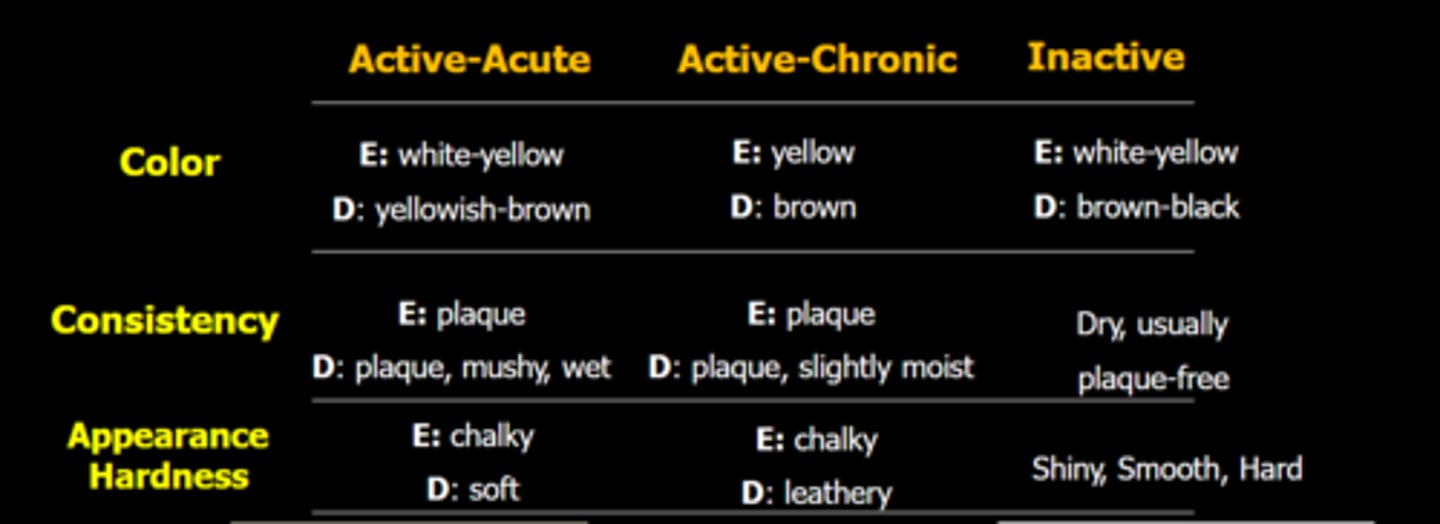
Appearance and Hardness of Active-Acute Lesion, Active-Chronic, Inactive
Active Acute: Soft Chalky (Think that tooth is trying to remineralize)
Active Chronic: Leather chalky
Inactive: Shiny, Smooth, Hard
How to know active or stable lesion
Active is demineralized, soft
Stable is when re-mineralization occurred, shiny, smooth, hard
Color is not solely reliable
What does it mean by cavitated
Enamel demineralized
If an unbalance occurs durign the ______ phase, the enamel defect is called hypoplasia
If it occurs durign the _______ phase, it is called hypomineralization
secretion (less enamel or hole)
maturation (color change)
What is fluorosis
Excessive amount of fluoride during tooth development
Severely fluroised enamel is very porous and prone to fracture and wear
Radiolucency is a resutl of a _______ in the absorption of x-ray photons
decrease
Caries are almost always (more/less) advanced than the radiograph indicates
more
Because the bacterial penetration of the dentinal tubules and early demineralization do not produce significant changes in density to affect the penetration pattern.
Caries appear _______ because the demineralized area of the tooth does not absorb as many x-ray _______ as the unaffected portion
radiolucent
photons
Lesions confined to enamel may not be evident radiographically until ______ demineralization occurs
Typically, it takes _______ for a white spot lesion to progress to cavitation
30-40%
12-18 months
What is the most accurate x-ray to diagnose interproximal caries in posterior and anterior teeth
Periapical for anterior
Bite wings for posterior (do not diagnose on periapical)
Distal of canine should be on what x-ray
Premolar Bitewing
Beam of bitewing x-ray should be _______ to the long axis of the tooth
perpendicular
Where is the most common location for proximal caries
Apical to contact point
Intraoral radiography
Extraoral radiograpy
Bitewings and PA
Pano
What is classified as incipient caries
Less than ½ of enamel
Degree of severity of radiographic lesion
Incipient
Moderate
Advanced
Severe
Incipient: Less ½ of enamel
Moderate: More ½ of enamel
Advanced: Less than ½ of dentin
Severe: More ½ of dentin
E1, E2 and D1 caries are ______. D2 and D3 are ______
microinvasive
invasive
In posterior teeth, teeth may be ________ demineralized before proximal caries appear radiographically.
Approximately ______ of proximally caries do not appear on a radiograph
30-40%
50%
Dentinal lesions are typically (narrower/wider) than enamel lesions
wider
Most proximal caries occur (above/below) the contact.
below
Cavitation is more likely in patients with (high/low) caries risk; however ______ of D1 lesions are not cavitated and can be treated using _____
high
40-60%
fluoride
Occlusal caries are most common in _____
children and adolescents
O1 caries
O2 caries
O3 caries
O4 caries
O5 caries
White or discolored enamel, no cavitation, no radiographic signs of caries
Small cavitation clinically, no radiographic evidence
Moderately sized cavity, radiolucency in outer third of dentin
Large cavity, radiolucency in middle third of dentin
Extensive cavity, radiolucency in inner third of dentin
Is making treatment recommendations based purely on scientific evidence practicing Evidence Based Dentistry
No
Facial/lingual or occlusal caries have more defined border radiographically? Which displays image shift relative to the crown?
facial/lingual
facial/lingual
Root caries are associated with
gingival recession
______ ______ appears as a radiolucent band or notches at the neck of the tooth in the area of the cementoenamel junction (CEJ).
cervical burnout
It is contrasted because the part of the tooth apical to it is covered by bone and hence is more radiopaque, whereas the area of the tooth occlusal to it is covered by enamel and is also radiopaque.
cervical burnout occurs most frequently in ______
mandibular incisor and molar areas
Cervical burnout appears more _____ while root caries are more ______
angular
rounded
Do radiation directly cause caries?
No, it cause loss of salivary gland function which leads to decay
Secondary caries are _____ and typically ____ to the restoration whereas radiolucent restoration materials are more ______
diffuse
gingivally
angular
Image sharpening
An effect applied to digital images to give them a sharper appearance.
Can create generalized, uniform radiolucent bands next to restorations
Increase contrast at edges
Mach bands
Exaggerates the contrast between edges of the slightly differing shades of gray, as soon as they contact one another
Optical illusion
In overlap of x-ray
What class are considered as smooth surface restoration
Class V lesions
T or F: Class V lesions may be carious or non-carious
True
may be caused by erosion, abrasion, or abfraction
Color of active carious lesions
Color of inactive carious lesions
Yellow/brown
Dark brown or black
Do inactive lesion have plauq
No only active lesion have plaque
The CEJ is ______ making it ______ retentive to bacteris
irregular, more
Cementum is (more/less) susceptible to drops in pH than Enamel.
more
caries process begins at pH below 6.2-6.7
Abfraction vs Abrasion
Abfraction is loss of tooth surface in the cervical area, caused by tooth grinding compression forces
Enamel rod fracture and dislodge
Abrasion is excessive mechanical or frictional forces
Non-carious Cervical Lesions are most likely on _______ side. Why
Facial
Stress, Toothbrushing, Erosion (from acidic food not GERD)
Loss of tooth structure due to aggressive brushing is an example of
abrasion
Chemical loss of tooth structure without bacteria
Erosion
Abrasion causes smooth, concave ______ shaped lesions along the gum line
V or U
Abfraction lesions tend to occur on the _____ surface
facial
lingual surface is compressed while the lingual surface is flexed
How can you differentiate between abfraction and abrasion
Check occlusion
abfraction is typically localized (Certain point have most stress) while abrasion will affect many/all of the teeth (brush all surface)
Wear is typically caused by the (toothpaste/toothbrush)
toothpaste
Abrasion alone do not cause damage, combining with acid cause more damage
It is unlikely, that toothbrushing alone causes abrasion. Presence of _____ greatly increases the risk of abrasion.
acid
Extrinsic causes of erosion
Intrinsic causes of erosion
soda, coffee, citrus fruit
GERD, bulimia, regurgitation
Extrinsic erosion affects the _____ surfaces
Intrinsic erosion affects the ____ surfaces of _____ teeth
Occlusal and labial
Occlusal and lingual of maxillary and facial of mandibular anterior teeth.
Cervical enamel is (more/less) brittle
more
Why NCCL at cervical
What is usually the problem of NCCL
occlusion issue
Direct thermal shock to the pulp via temperature changes transferred from the oral cavity through the _______ _______, especially when remaining dentin is thin.
restorative material
Use of insulating base is indicated in composite or amalgam
How thick should the base be
amalgam
0.50 to 0.75 mm no more than 0.75 mm
The theory of hydrodynamics of the pulp states that there is a gap between the tooth and the restoration which allows fluid to enter the space. _____ fluids can cause a sudden contraction of the tubule which causes an _____ in the flow of dentinal fluid which is perceived as pain
Cold
increase
As dentin nears the pulp, tubule density and diameter _______
increase
Explain why deeper restorations with more problem of sensitivity
Rubber Dam Clamp for Class V lesion
212 clamp
Shade selection should be with dry or wet teeth
Wet
Dry have different shade
What is the first step in managing the disease process?
Is caries risk assessment for diagnosis or prognosis
caries risk assessment
prognosis
Disease indicator (WREC)
Risk factors (BAD)
Protective factors (SAFE)
White spots, Restorations (<3 years), Enamel lesions, Caries/dentin
Bad bacteria, Absence of saliva, Dietary habits (poor)
Saliva and sealants, Antibacterials, Fluoride, Effective diet
Patients with no active disease but 2 or more high-risk factors are _____ risk.
High
If patients are between risk groups, place them in the _____ risk group
higher
CAMBRA
Caries Management by Risk Assessment
Caries risk is ultimately up to ______
the clinical judgment of the physician
The presence of active lesions and fillings (caries prevalence) show the balance between caries _______ and _______ factors have been in the past or may be at present
pathological
protective
DMFT score
caries prevalence index
Decayed, Missing, and Filled Teeth
What is the most important indicator of caries risk?
past and current caries experience
How does medical history contribute to caries risk?
-medications that cause xerostomia
-conditions that make dental hygiene difficult or require carbohydrate-enriched diets
-medications containing fermentable carbohydrates such as glucose
Reassessment of a patient's caries risk should occur every ______ months depending on _____
3-12
the caries risk of the patient
For high caries risk patients, recall should be every ___ months and BW should be taken every ____ months
For moderate risk patients, recall should be every ____ months and BW should be taken every ____ months
For low risk patients, recall should be every ____ months and BW should be taken every ____ months
3, 3-6
3-6, 12-18
12-24, 24