MCQ 14 - Determination of irradiation during and/or monitoring units in radiation therapy with high energy ionizing radiation
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
384. In order to reduce the energy of the electrons produced through a photoelectric effect, one needs to:
a. Increase the intensity of the incident light beam
b. Increase the wavelength of the incident light beam
c. Increase the frequency of the incident light beam
b. Increase the wavelength of the incident light beam
385. During cancer radiation therapy, the malignant tissue is affected by:
a. Generation of excess heat
b. Ionization of tissues
c. Generation of (non-native) toxins
b. Ionization of tissues
386. Which of the following conditions is associated with radioactivity?
a. Accelerated electron beams
b. X-rays beams
c. Unstable nuclides
c. Unstable nuclides
387. Indirect ionizing radiation:
a. Have positive charge
b. Have negative charge
c. Have no electric charge
c. Have no electric charge
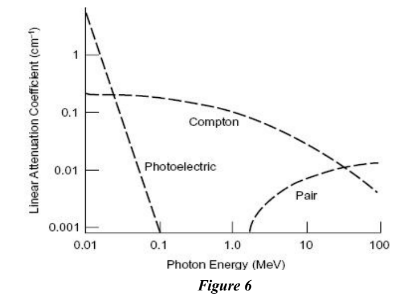
388. Which of the three basic interaction modes, between radiation and matter, dominates during medical treatment with 60Co gamma rays (refer to Fig. 6)?
a. Photoelectric absorption
b. Compton effect (scattering)
c. Pair production (electron-positron)
b. Compton effect (scattering)
The Compton effect is the dominant interaction mode between radiation and matter during medical treatment with 60Co gamma rays
389. Compton effect (scattering) is the predominant mode of interaction between radiation and tissue (mostly water) for the following energy range:
a. 60 keV – 10 MeV
b. 0.5 MeV – 5 MeV
c. Up to 460 keV
a. 60 keV – 10 MeV
Compton effect-
a photon collides with an electron, and the photon loses some of its energy to the electron.
The scattered photon has a longer wavelength than the incident photon,
and the electron recoils with some kinetic energy.
390. The unit Absorbed Dose of ionizing radiation is called “Gray” (Gy), and measures the amount of energy absorbed per unit mass. Choose the correct units:
a. Gy = C/kg
b. Gy = J/Kg·s
c. Gy = J/Kg
c. Gy = J/Kg
391. What property of Gamma-rays makes them more appropriate for treatment of deep- seated tumors?
a. The maximum dose is not near the surface but deep within the body
b. The absorbed dose decreases gradually within the body
c. The absorbed dose falls rapidly within the body
b. The absorbed dose decreases gradually within the body
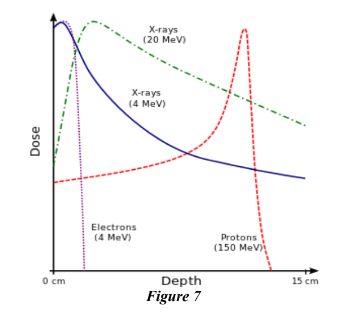
392. What property of Electron beams, produced in medical accelerators, make them better suited for treatment of surface and skin tumors (see Fig. 7)?
a. The maximum electron energy is lower than the maximum photon energy
b. The absorbed dose drops gradually with penetration depth
c. The absorbed dose drops rapidly with penetration depth
c. The absorbed dose drops rapidly with penetration depth
393. The unit Gray (Gy) measures:
a. Absorbed dose
b. Exposure
c. Activity
a. Absorbed dose
394. The unit Sievert (Sv) is the product of absorbed dose and radiation weighting factor (wR), specific for different types of tissue. It measures a quantity called:
a. Equivalent dose
b. Absorbed dose
c. Dose rate
a. Equivalent dose
395. In medical radiology the unit of Exposure (X) measures how much electric charge is
produced by ionization per unit mass. Choose the correct units:
a. J/Kg
b. C/kg
c. C/s
b. C/kg
396. Directly ionizing radiation is composed of:
a. Charged particles
b. Electromagnetic waves
c. Neutrinos
a. Charged particles
Directly ionizing radiation - charged particles that can ionize atoms directly by fundamental interaction (via Coulomb force) if carrying sufficient kinetic energy. eg alpha particles, beta particles, and neutrons.
Indirectly ionizing radiation, on the other hand, does not ionize atoms directly. Instead, it interacts with water molecules in the body, creating free radicals that can then go on to ionize atoms . eg gamma rays, X-rays, and the higher energy ultraviolet part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
397. Which of the following processes produces scattered photons?
a. Electron –Positron pair production
b. Compton effect
c. Piezoelectric effect
b. Compton effect
(The Compton Effect is the scattering of a high-energy photon (such as an X-ray or gamma-ray photon) by a free, loosely bound electron)
398. Probability for Compton scattering (linear attenuation coefficient) depends strongly on:
a. Atomic number
b. Electron density per unit mass
c. Atomic mass number
b. Electron density per unit mass
The linear attenuation coefficient is a measure of how easily a material can be penetrated by a beam of light, sound, particles, or other energy or matter.
But probability of compton scattering:
It decreases as the photon energy increases.
The probability of Compton scattering per one interaction with an atom increases linearly with atomic number Z because it depends on the number of electrons available for scattering in the target atom
399. In a photoelectric event, the incident photon:
a. Loses all of its energy
b. Loses fraction of its energy
c. Does not lose energy
a. Loses all of its energy
400. Coherent scattering (Rayleigh scattering) is when after the collision the incident photon:
a. Changes its energy
b. Changes its direction and frequency
c. Changes direction
c. Changes direction
Coherent scattering - form of photon interaction, occurs when energy of x-ray or gamma photon is small in relation to ionization energy of the atom.
in medical imaging (but doesnt usually occur in diagnostic range) - not impt in diagnost. radiol.
The whole atom acts as a unit
Atom recoils when bombarded by a low-energy photon.
Upon interacting with the attenuating (reduce the effect of) medium, the photon does not have enough energy to liberate the electron from its bound state,
so no energy transfer occurs.
There is no energy deposition and thus no dose resulting from coherent scattering.
401. The Absorbed Dose (D) as well as the Equivalent Dose (H) received during radiotherapy are measured in units of:
a. Energy absorbed per unit mass
b. Ionization events per unit volume
c. Total number of alpha and beta particles imparted on unit surface
a. Energy absorbed per unit mass
402. Absorbed and Equivalent doses will have the same numerical values for this type of ionizing radiation:
a. Gamma rays
b. Neutrons
c. Protons
a. Gamma rays
(Dose equivalent is greater than absorbed dose for alpha and neutron radiation, because these types of radiation are more damaging to the human body)
403. What particles are emitted in a photoelectric effect?
a. No particles are emitted, only photons are absorbed
b. Electrons
c. Photons
b. Electrons
404. The Nobel Price for the explanation of the photoelectric effect, was awarded to:
a. Isaak Newton
b. Michal Faraday
c. Albert Einstein
c. Albert Einstein
405. Solar panels (photovoltaic cells) are based on this effect:
a. Electron-positron pair production
b. Photoelectric effect
c. Coherent scattering
b. Photoelectric effect
The photoelectric effect is the release of electrons from a material when light hits it, creating an electric current.
406. Gas (such as air) can be ionized by:
a. Microwaves
b. Ultraviolet rays
c. Infrared rays
b. Ultraviolet rays
407. For external radiotherapy, medical accelerators, and cobalt-60 units are used. With respect to radiation safety, what is the most significant difference between the two?
a. Accelerators generate higher energy radiation;
b. Cobalt-60 emits higher energy photons;
c. Accelerators produce radiation only when powered on, and cobalt-60 sources are always on (produce radiation continuously).
c. Accelerators produce radiation only when powered on, and cobalt-60 sources are always on (produce radiation continuously).