L3 Chemical Reactions and Equations Overview
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
CHEMICAL REACTION
A process in which one or more substances, called reactants, are converted to one or more different substances, called products.
CHEMICAL CHANGE
A change of materials into another, new materials with different properties and one or more than one new substances are formed.
CHEMICAL EQUATION
A written representation of a chemical reaction that uses chemical symbols to show what happens during a chemical reaction.
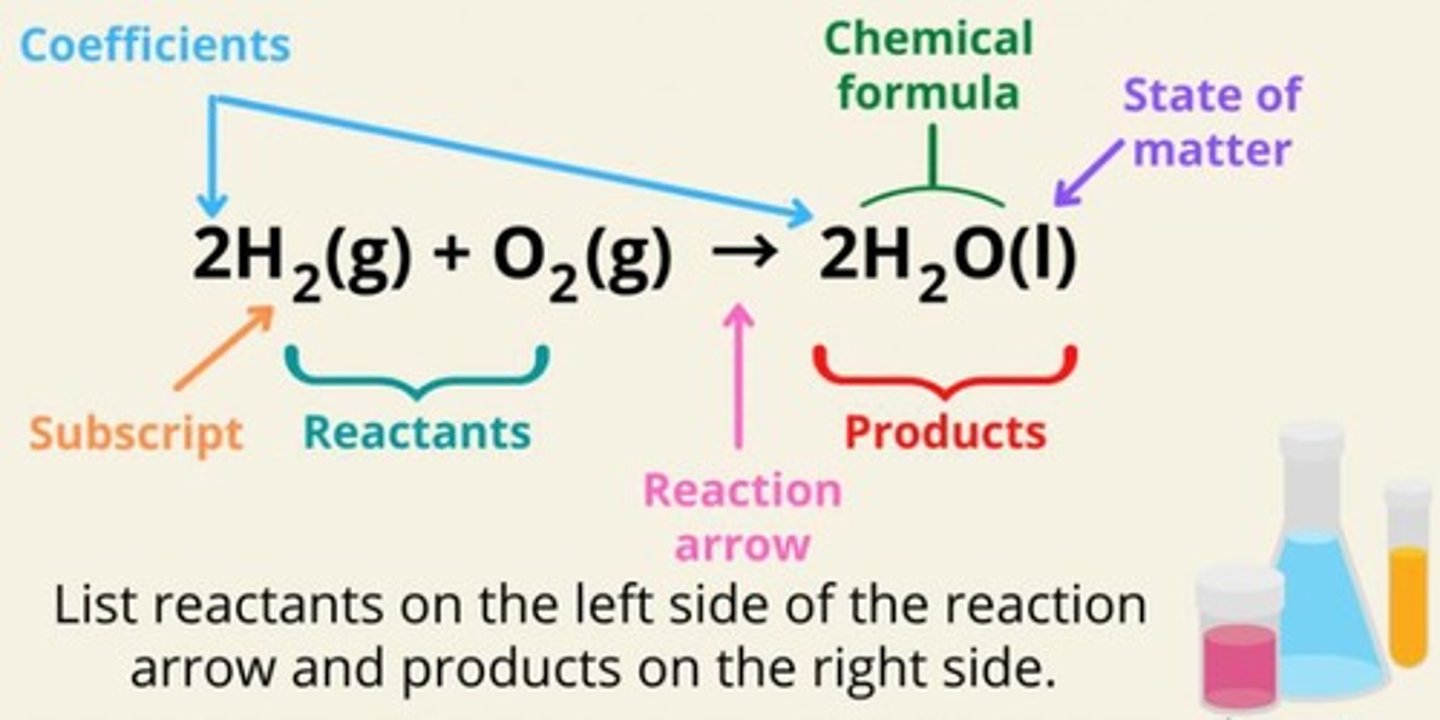
Reactants
The substances that react in a chemical reaction.
Products
The substances that are formed as a result of a chemical reaction.
Coefficients (or Stoichiometric Coefficients)
Numbers that are placed before the chemical formulas of the reactants and products, indicating how many molecules or moles of each substance are involved in the reaction.
Subscripts
Numbers that are written after the symbols of the elements in a chemical formula, indicating how many atoms of each element are present in one molecule or mole of the substance.
Combination Reaction (or Synthesis Reaction)
A reaction where two or more substances combine to form a single new substance.
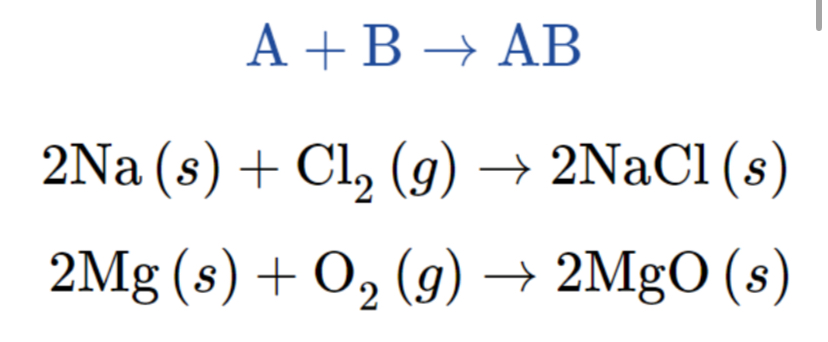
Decomposition Reaction
A reaction where a compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances.
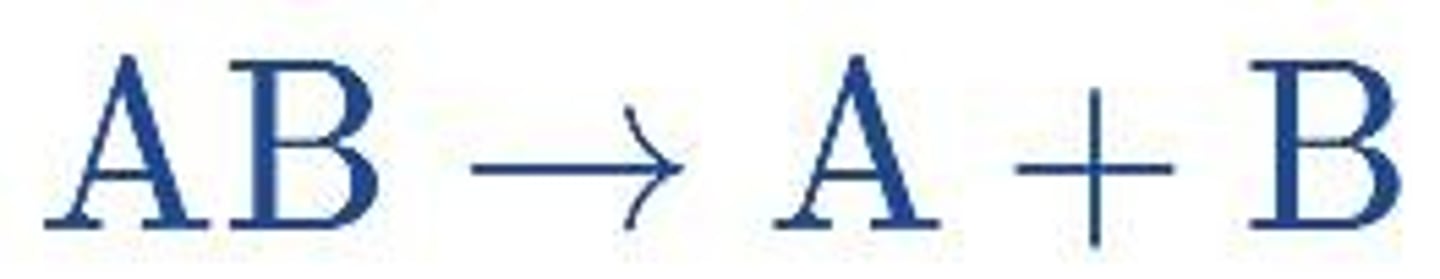
Single Replacement Reaction (or Single Displacement Reaction)
A reaction where one element replaces another in a compound.
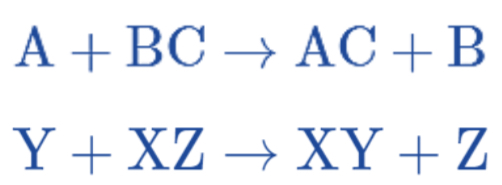
Double Replacement Reaction (or Double Displacement Reaction)
A reaction where the positive and negative ions of two ionic compounds exchange places to form two new compounds.
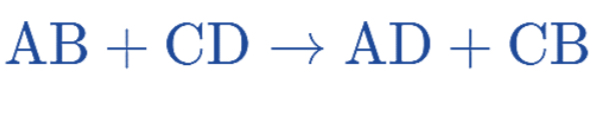
Combustion Reaction
A reaction where a substance reacts with oxygen gas (O2), releasing energy in the form of light and heat.
Neutralization Reaction (or Acid-Base Reaction)
Acids and bases of equal strengths react to form a neutral solution. The neutral solution that is formed consists of salt and water.
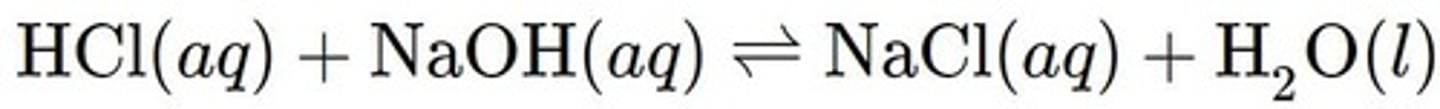
Balanced Chemical Equation
An equation for a chemical reaction in which the number of atoms for each element in the reaction are the same for both the reactants and the products.
Law of Conservation of Mass
In a chemical process, atoms cannot be created, destroyed, nor changed, only rearranged into different combinations.
Unbalanced Chemical Equation
An equation that does not have the same number of atoms for each element on both sides.
Balanced Chemical Equation Example
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
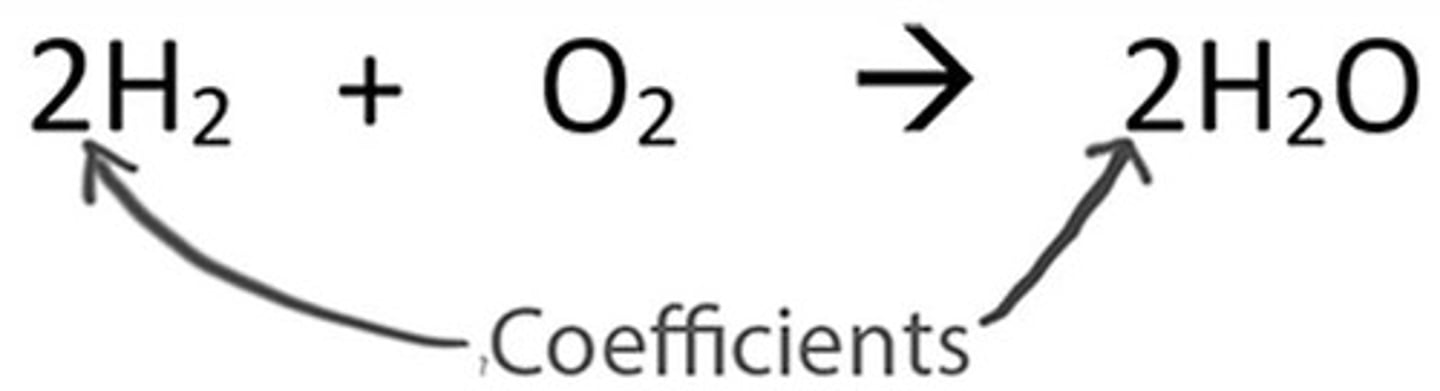
Coefficients in Balancing
We can change the coefficients (the numbers preceding the formulas) but not the subscripts (the numbers within formulas).
Smallest Possible Set of Whole Numbers
The coefficients used in balancing the last equation are the smallest possible set of whole numbers.
Chemical Reactions
Processes that involve the rearrangement of the molecular or ionic structure of a substance.
Chemical Reaction Types
Different categories of reactions such as synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, double replacement, and combustion.
Synthesis Reaction
A reaction where two or more substances combine to form a new compound.
Single Replacement Reaction
A reaction where one element replaces another in a compound.
Double Replacement Reaction
A reaction where the anions and cations of two different compounds swap places to form two new compounds.