Vision
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/38
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
1
New cards
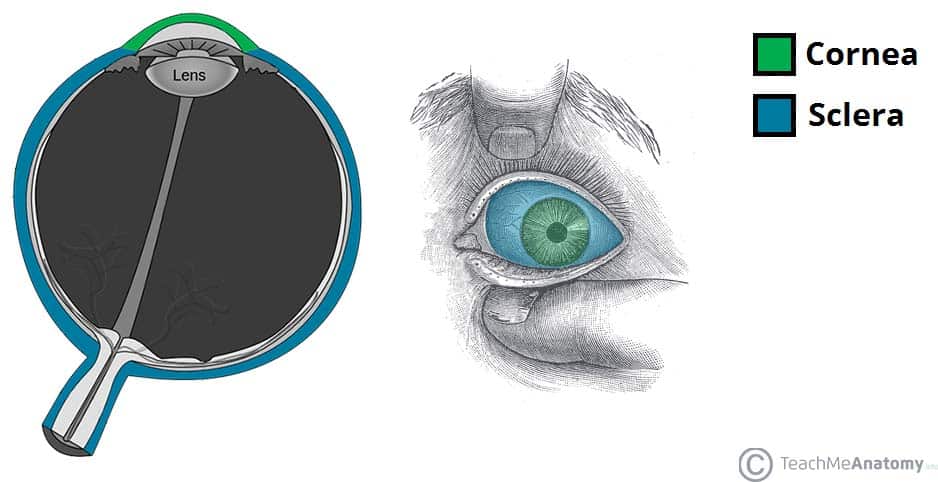
fibrous layer
outside layer of eye ball
contains cornea + sclera
contains cornea + sclera
2
New cards
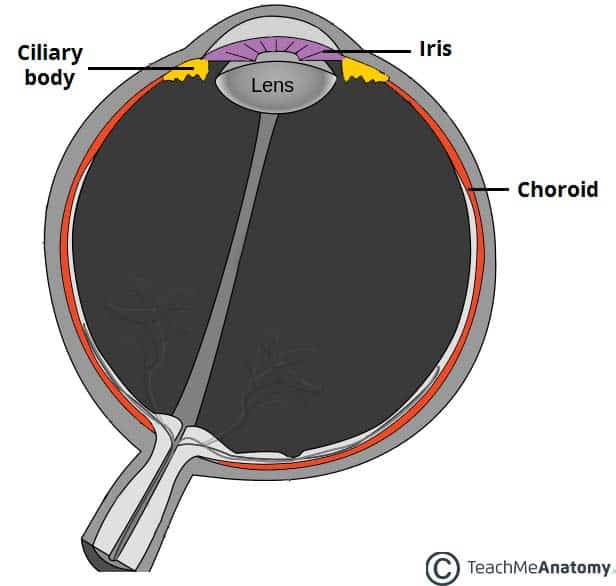
vascular/choroid layer
middle layer of eye ball
contains blood vessels, melanin, iris, pupil, ciliary muscles
contains blood vessels, melanin, iris, pupil, ciliary muscles
3
New cards
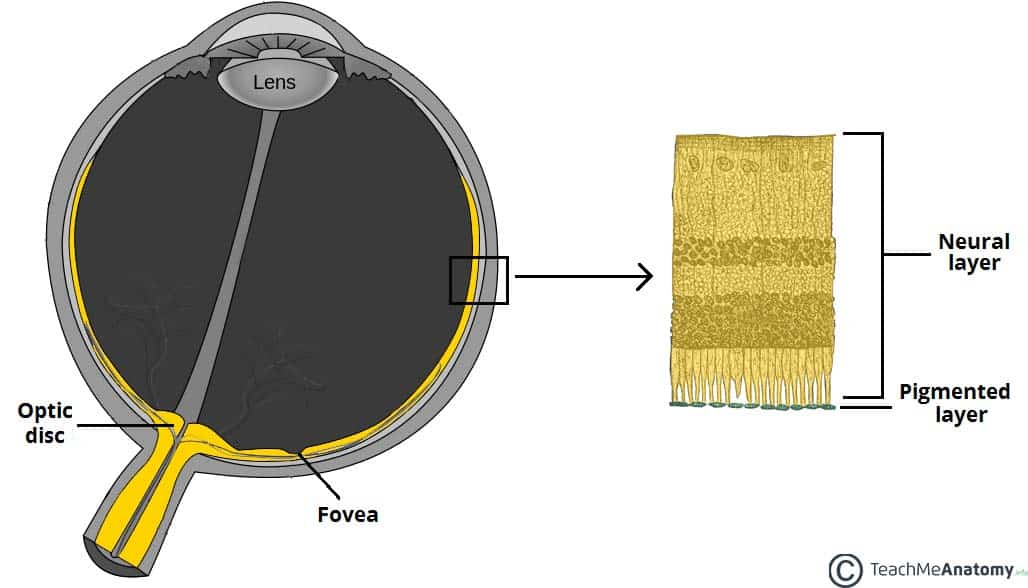
sensory/neural layer
inside layer of eye ball
contains retina, rods, cones
contains retina, rods, cones
4
New cards
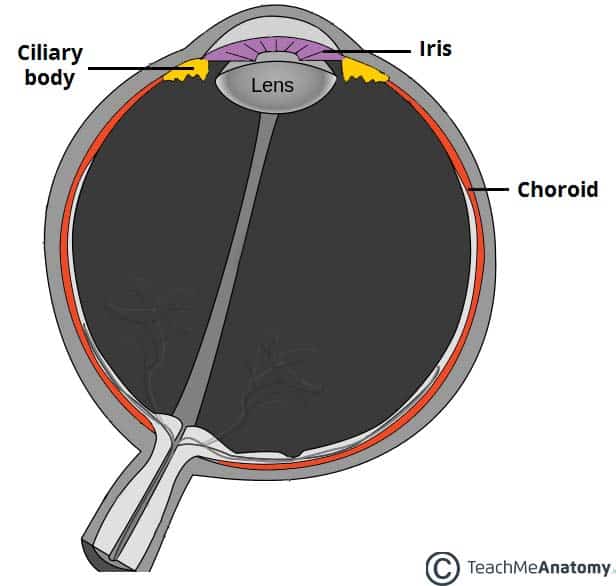
vascular layer (choroid, iris, pupil, melanin, muscles)
what part of the eye contains blood vessels?
5
New cards
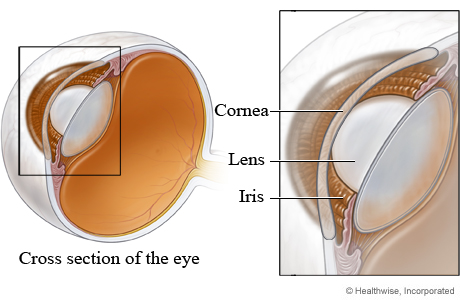
would block vision, made of tissue that doesn’t contain/need blood supply?
Why are there not blood vessels in the cornea or lens?
6
New cards
sphincter pupillae muscle, bright light, distance of focus cause lens to change shape
What factors into pupil dilation/constriction?
7
New cards
Photopupillary reflex
pupils constrict because of bright light
8
New cards
ciliary muscles relax, lens is elongated (tall + thin) and flattened (dilation)
Fight or flight effect on vision: set up for distant vision
9
New cards
ciliary muscles contract (lens is short and thick), pupil constriction, convergence (medial rotation)
Rest and digest effect on vision: set up for close vision
10
New cards
crystalline protein
what the lens is made of
11
New cards
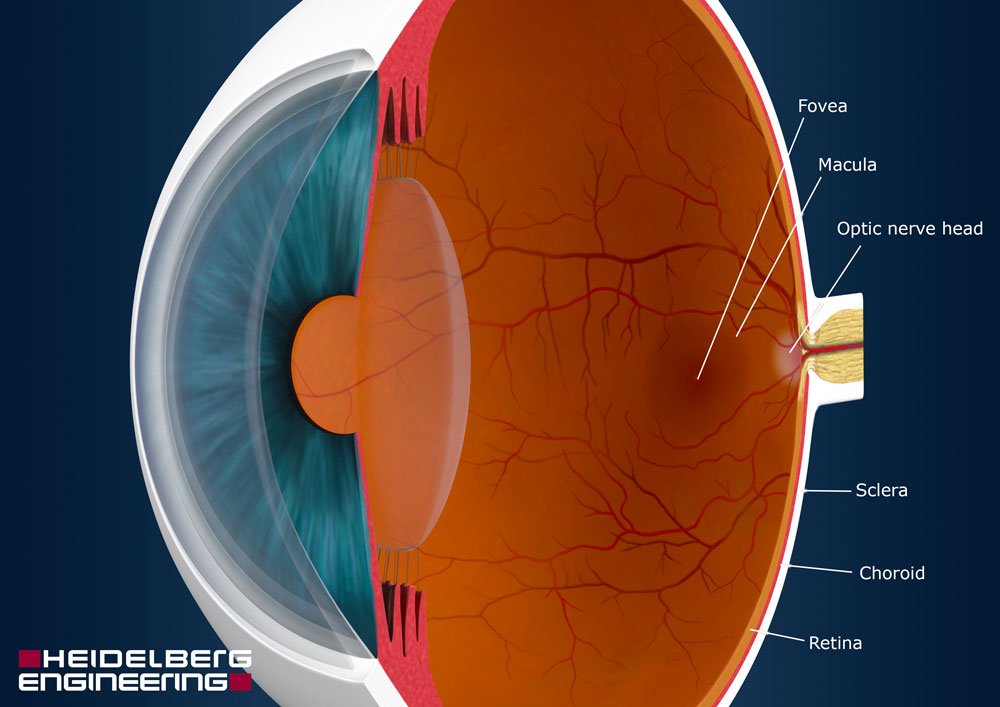
very tough but crystalline proteins and ciliary muscles allows it to be elongated or shorted
how is the lens “flexed?”
12
New cards
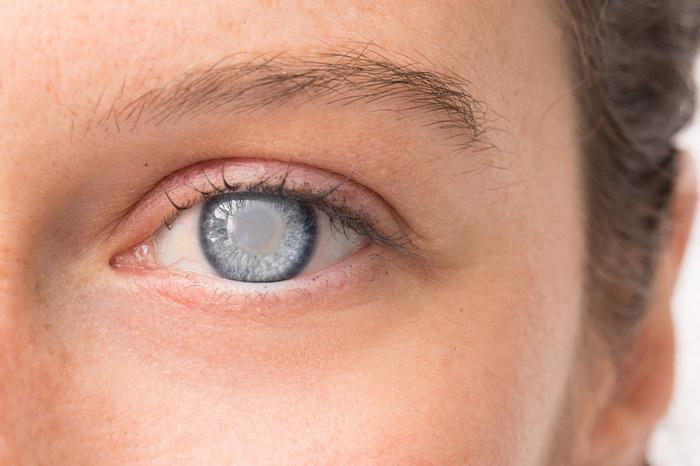
cataracts
clouding of lens; oxidation of crystallin proteins--blocks light from coming through
caused by age, diabetes, smoking, intense light, ionizing radiation
caused by age, diabetes, smoking, intense light, ionizing radiation
13
New cards
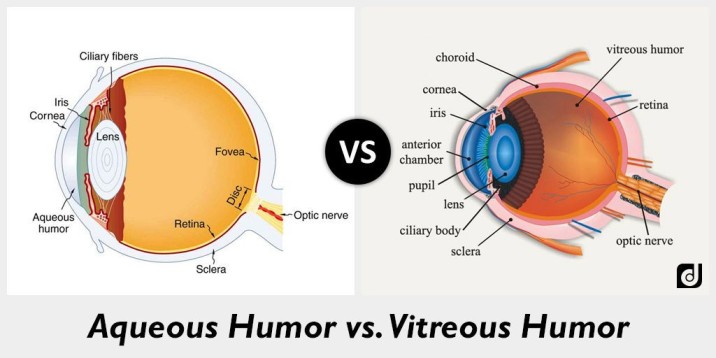
aqueous: watery, anterior chamber
vitreous: thick, posterior chamber
(divide at lens)
vitreous: thick, posterior chamber
(divide at lens)
aqueous humor vs vitreous humor?
14
New cards
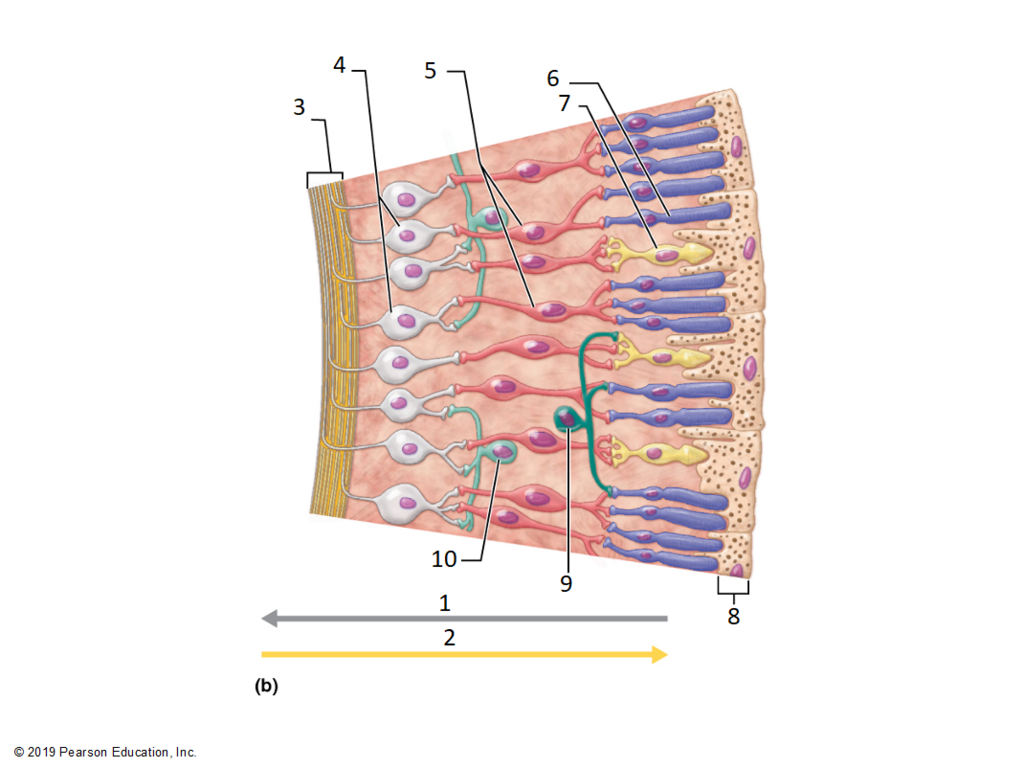
most numerous photoreceptor
Dim light
More sensitive to light- peripheral and night vision (more rods at edges)
NOT color- gray scale
NOT sharp images- many rods on one optic nerve
Dim light
More sensitive to light- peripheral and night vision (more rods at edges)
NOT color- gray scale
NOT sharp images- many rods on one optic nerve
tell me everything know know about rods
15
New cards
MANY rods connect to one optic nerve
Why do rods produce fuzzy images?
16
New cards
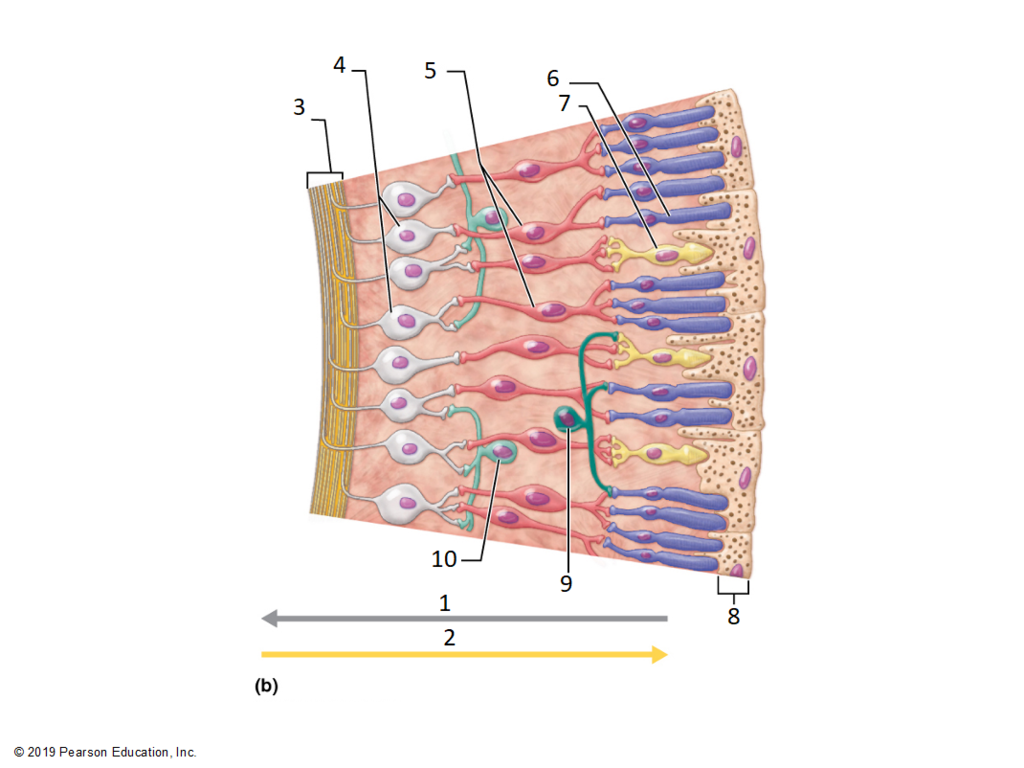
poor sensitivity- require bright light
faster reaction
COLOR- red green blue
crisp images- each cone/option nerve
every person perceived different shades
faster reaction
COLOR- red green blue
crisp images- each cone/option nerve
every person perceived different shades
tell me everything you know about cones
17
New cards
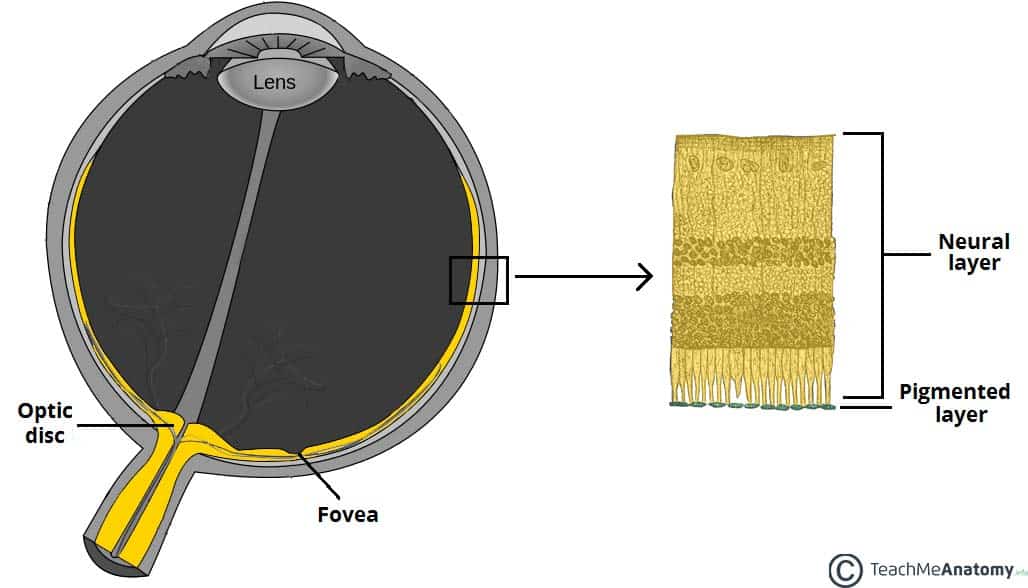
retina of neural layer
where are rods and cones?
18
New cards
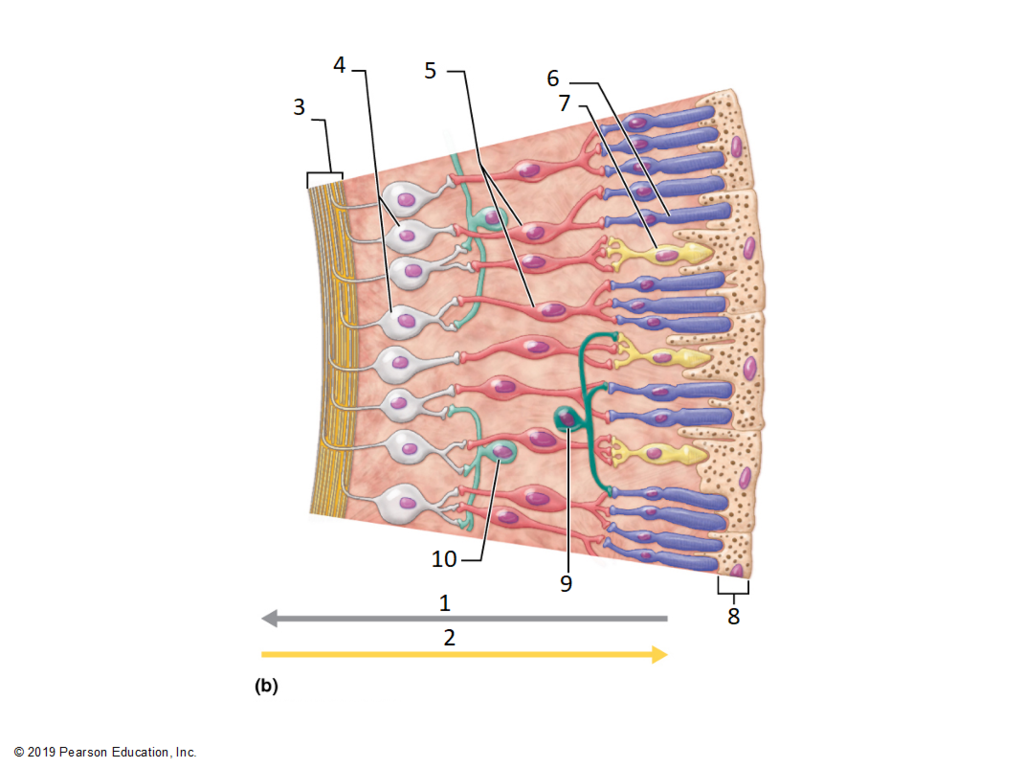
photoreceptors
light absorbing cells; special sensory receptors
rods and cones
rods and cones
19
New cards
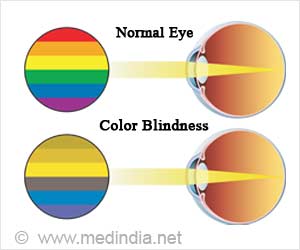
color blindness
lack of one or more cone pigments (red, green, or blue)
most common: red-green
most common: red-green
20
New cards
hereditarily linked to the X-chromosome
why is color blindness more common in males?
21
New cards
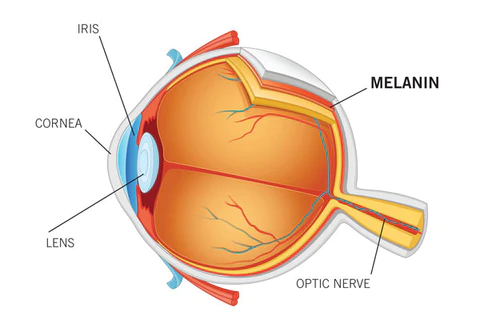
absorbs light and colors the iris
purpose of melanin?
22
New cards
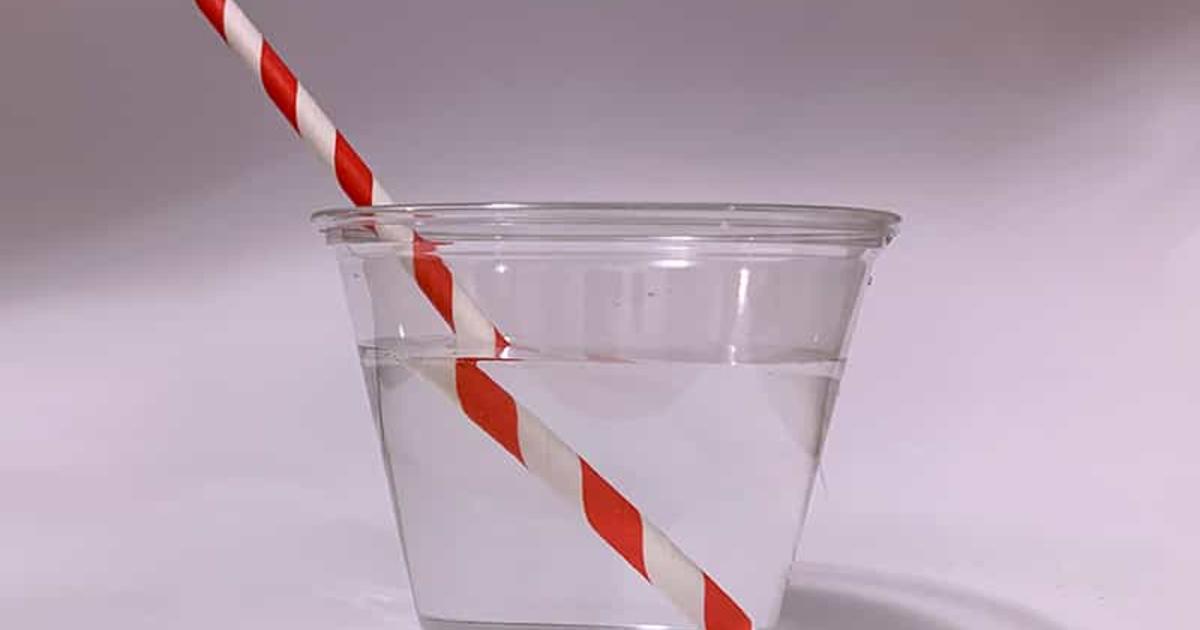
refraction
bending of light as light passes from one medium to another

23
New cards
1) into cornea (air→liquid)
2) into lens (aq humor→lens)
3) leaving lens (lens→vitreous humor)
2) into lens (aq humor→lens)
3) leaving lens (lens→vitreous humor)
In what locations does refraction occur in the eye?
24
New cards
cornea (air→liquid)
Where is the greatest amount of refraction?
25
New cards
lens + cornea direct light onto the fovea
How does our eye focus light onto the fovea?
26
New cards
improper refraction (everyone)
What causes an astigmatism?
27
New cards
upside down and backwards
How does the image formed on the retina differ from the image in front of us in reality?
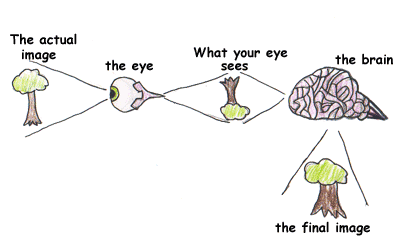
28
New cards
wavelength
What aspect of light determines its color?
29
New cards
shorten front to back
How does the shape of the eyeball change with aging?
30
New cards
emmetropia
even normal eye focus
focal point is on retina
20/20 vision
focal point is on retina
20/20 vision
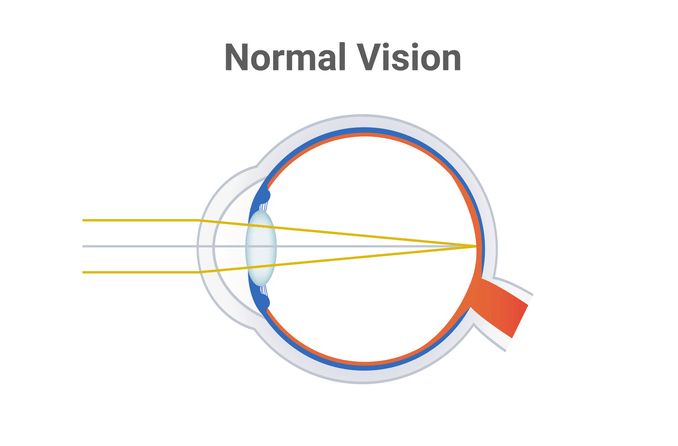
31
New cards
myopia
nearsighted
eyeball too long
focal point is in front of retina
eyeball too long
focal point is in front of retina
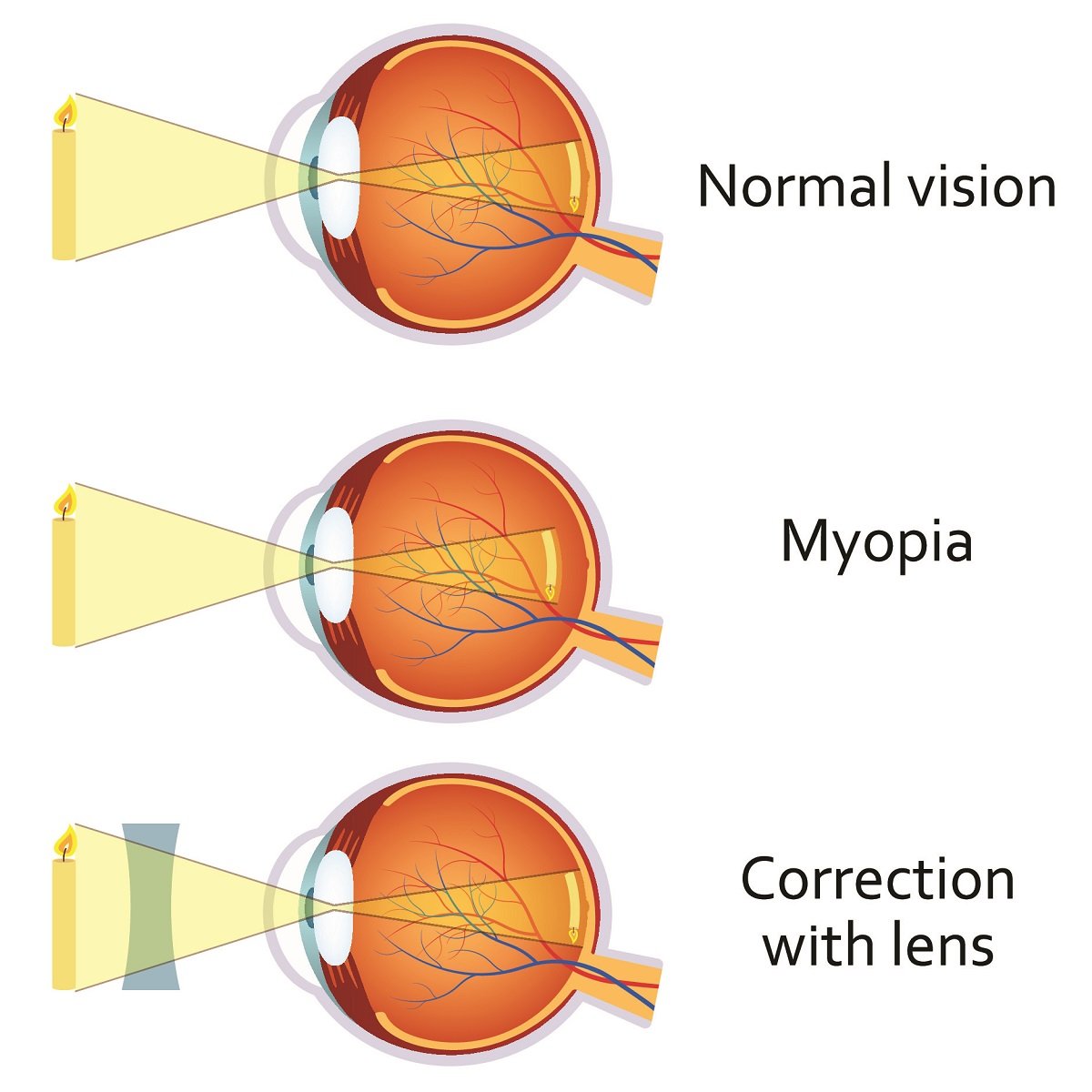
32
New cards
hyperopia/presbyopia
farsighted
eyeball too short
focal point behind retina
eyeball too short
focal point behind retina
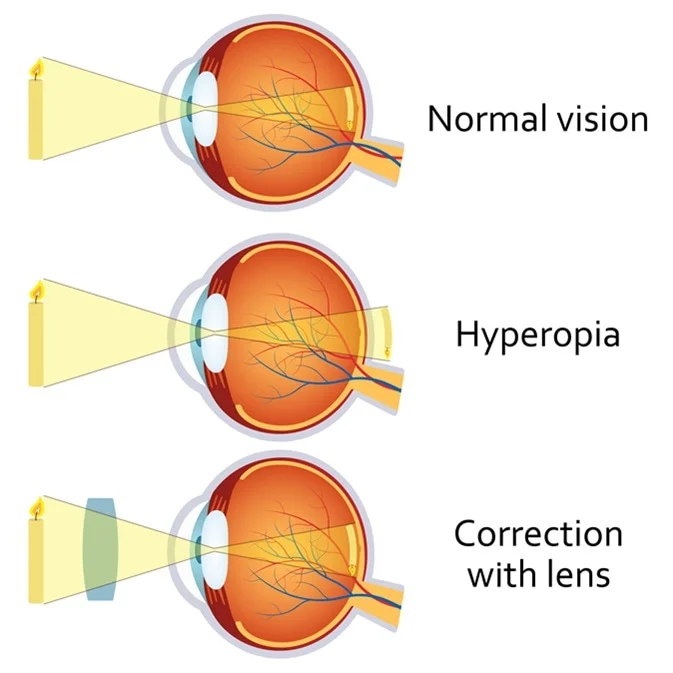
33
New cards
binocular vision
Each eye “sees” a slightly different view
Field of view overlaps for each eye
Field of view overlaps for each eye
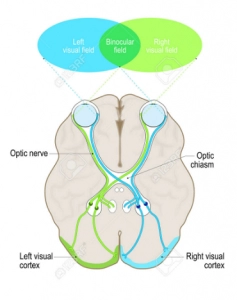
34
New cards
depth perception/3-d vision
what does binocular vision allow for?
35
New cards
glaucoma
too much aqueous humor
36
New cards
chalazion
infected tarsal gland with cyst formation
big and rare
big and rare
37
New cards
sty
inflamed/infected sebaceous gland
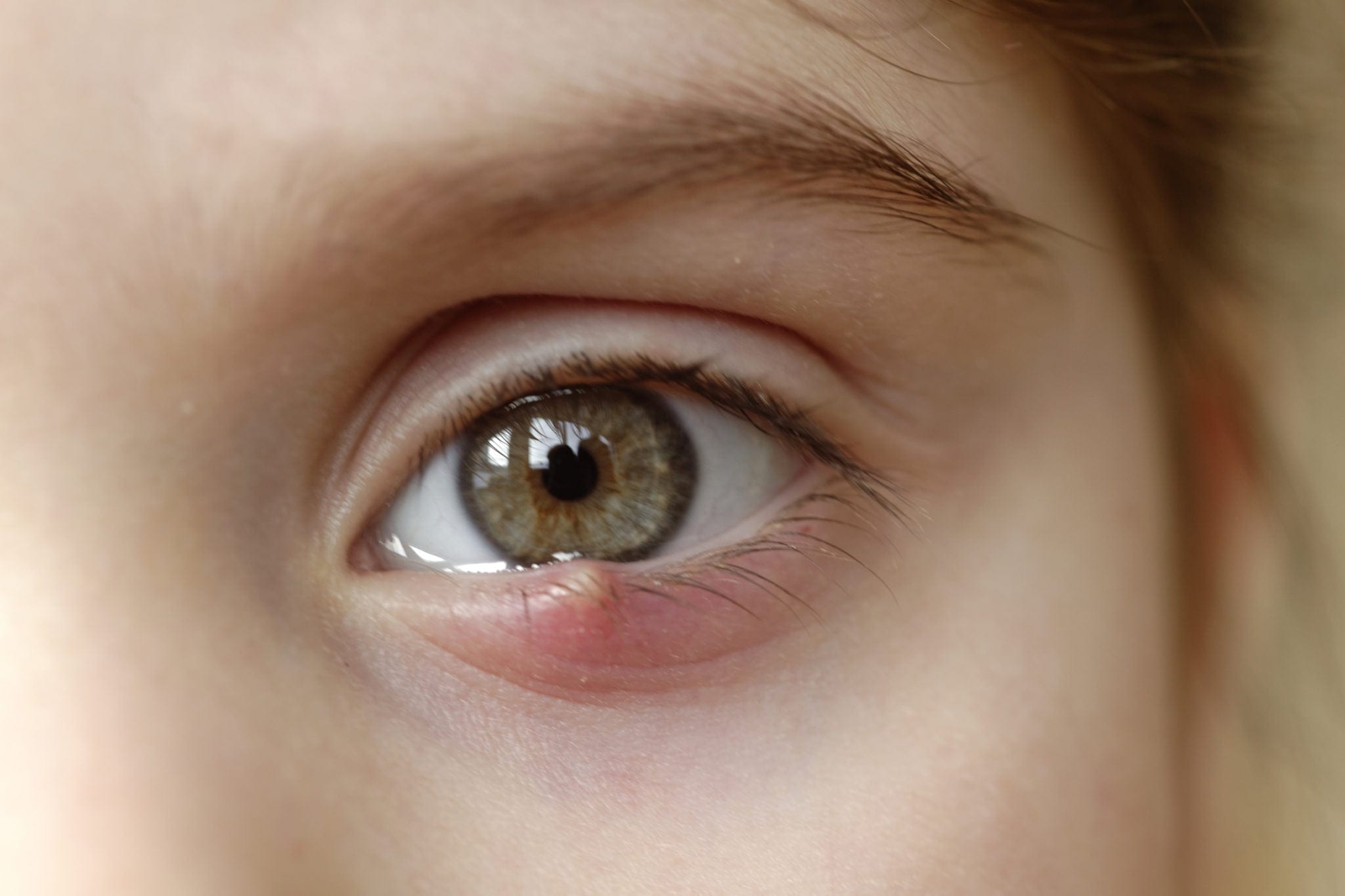
38
New cards
conjunctivitis/pink eye
either viral or bacteria infection that inflames the conjunctiva (membranes around the eyelids and eyeball)
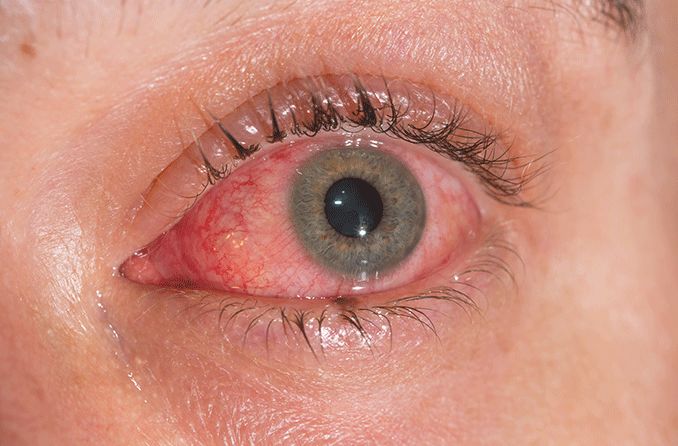
39
New cards
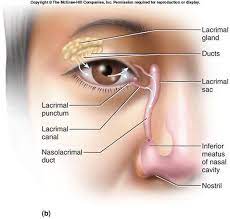
your lacrimal sack that contains your tears connects to the nasolacrimal duct which empties into the nasal cavity
why does your nose run when you cry?