Apologia Biology Module 14
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Botany
The study of plants.

Perennial plants
Plants that grow year after year.

Annual plants
Plants that live for only one year.

Biennial plants
Plants that live for two years.

Vegetative organs
The parts of a plant (such as stems, roots and leaves) that are not involved in reproduction
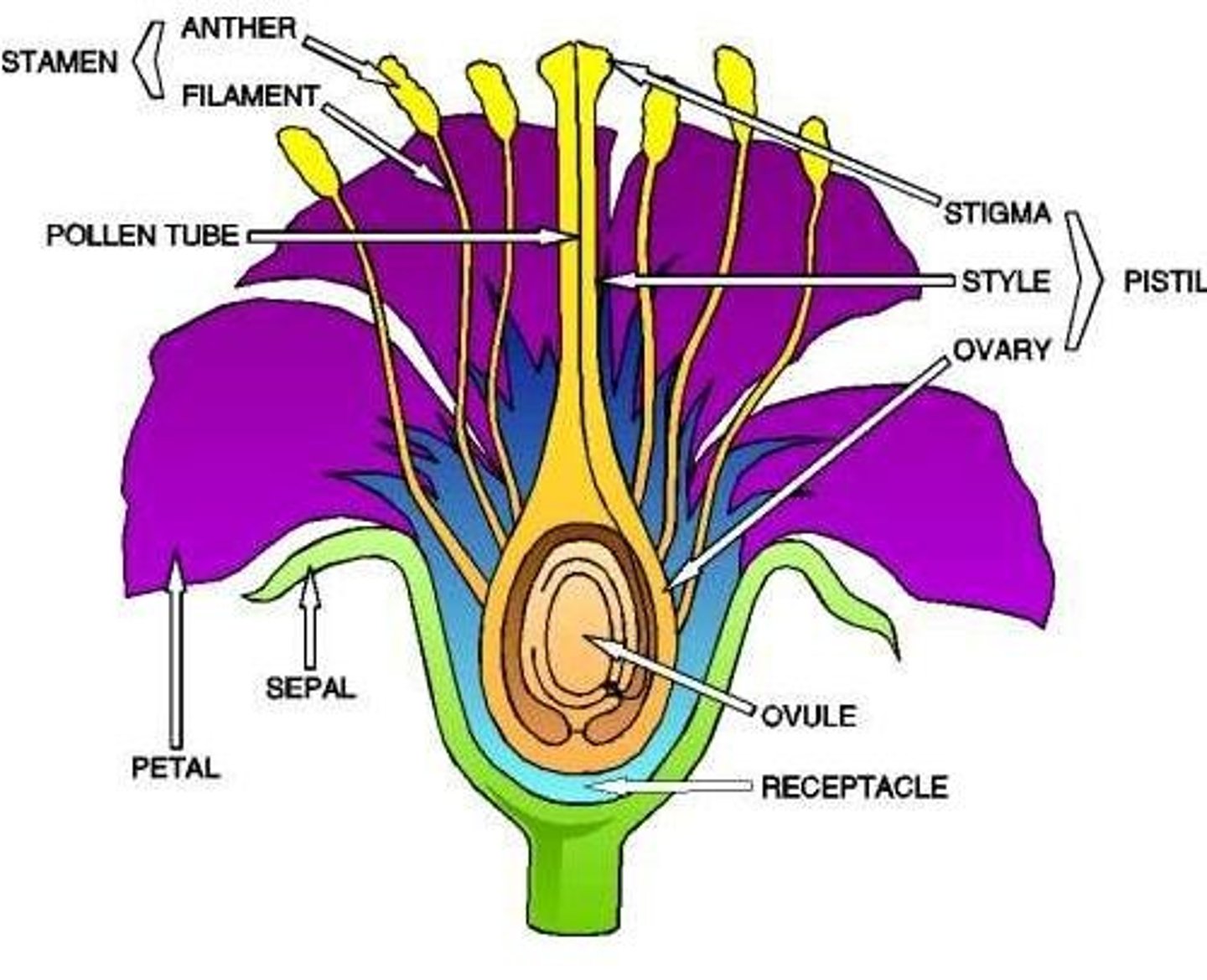
Reproductive plant organs
The parts of a plant (such as flowers, fruits and seeds) involved in reproduction.
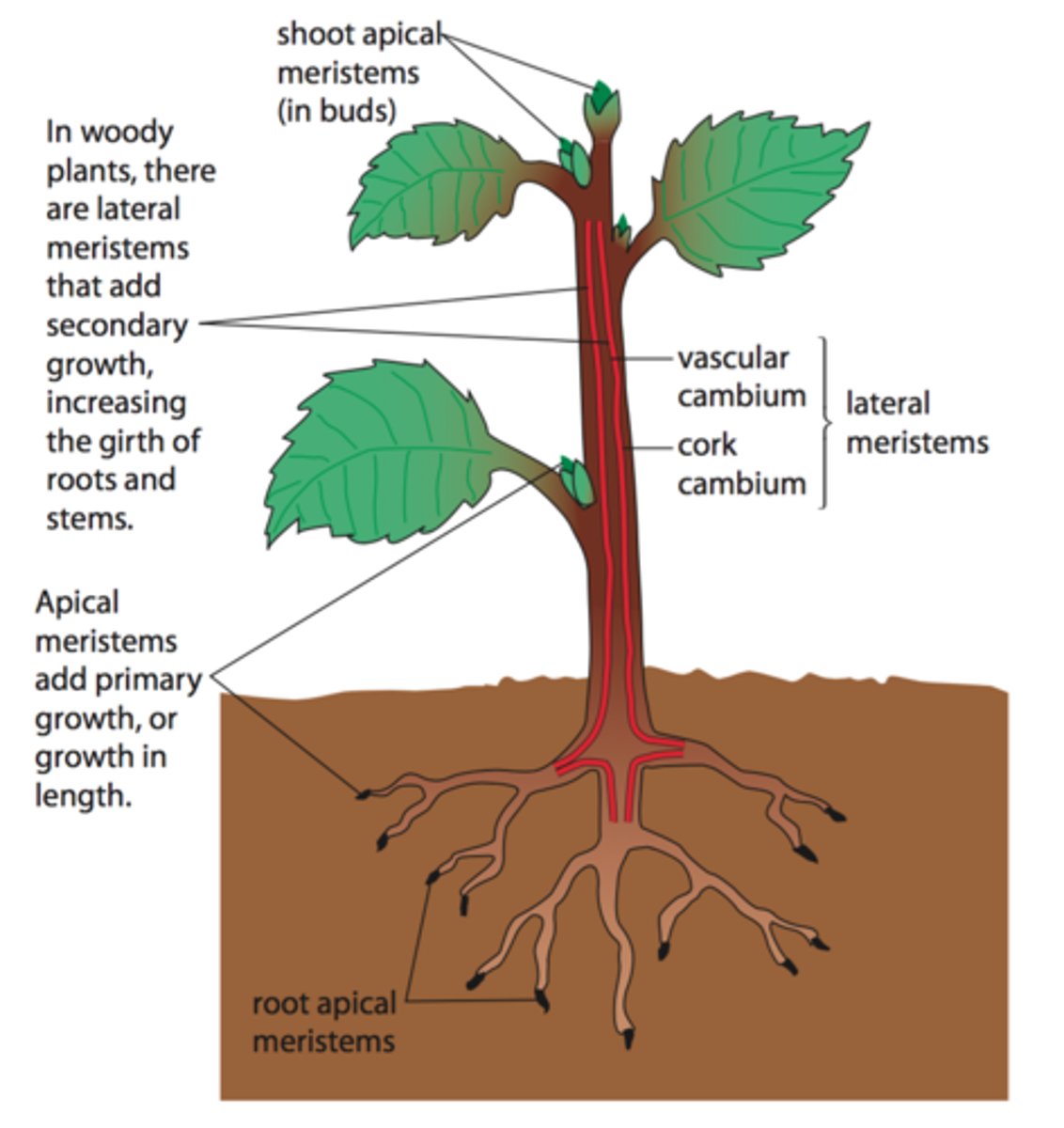
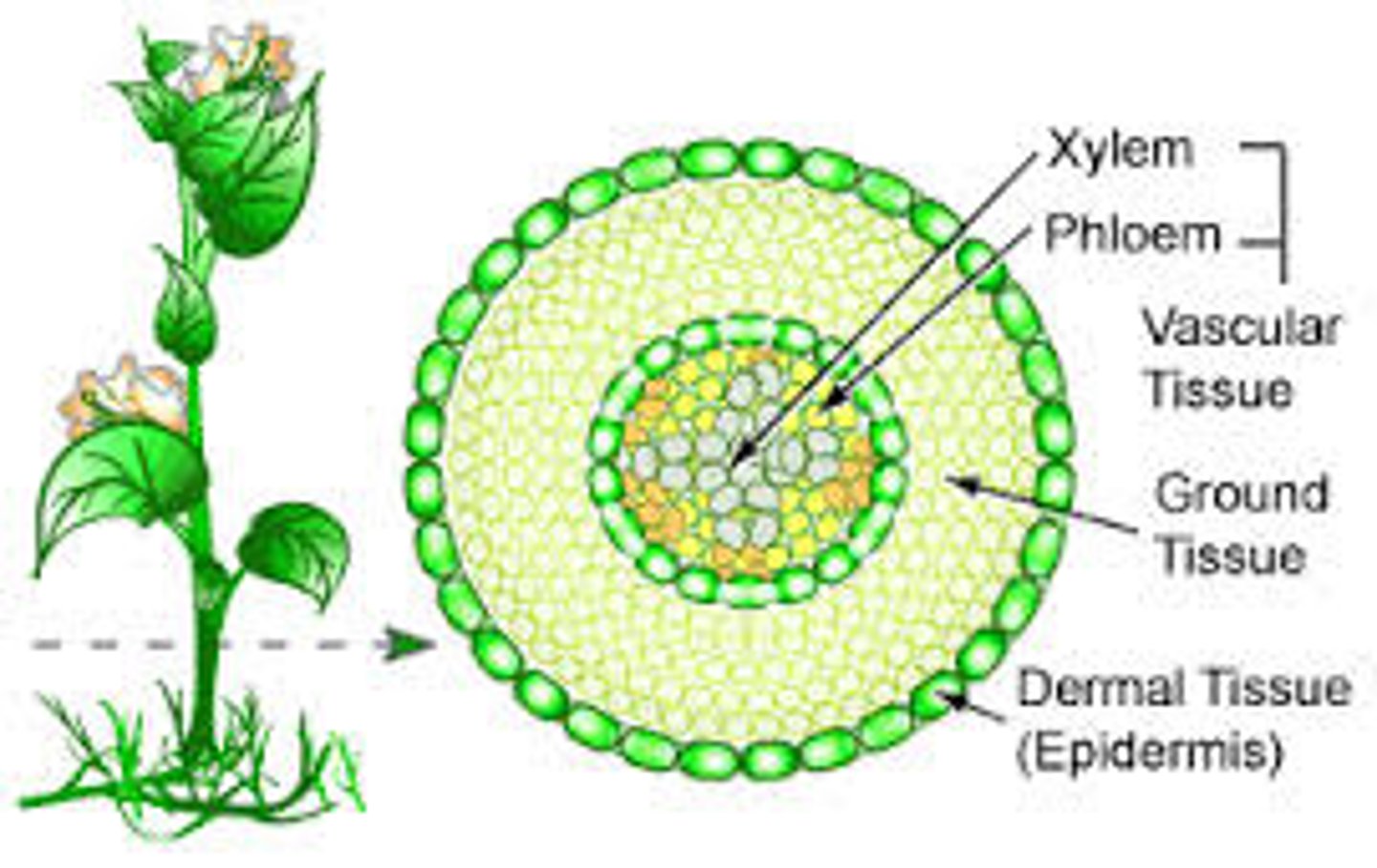
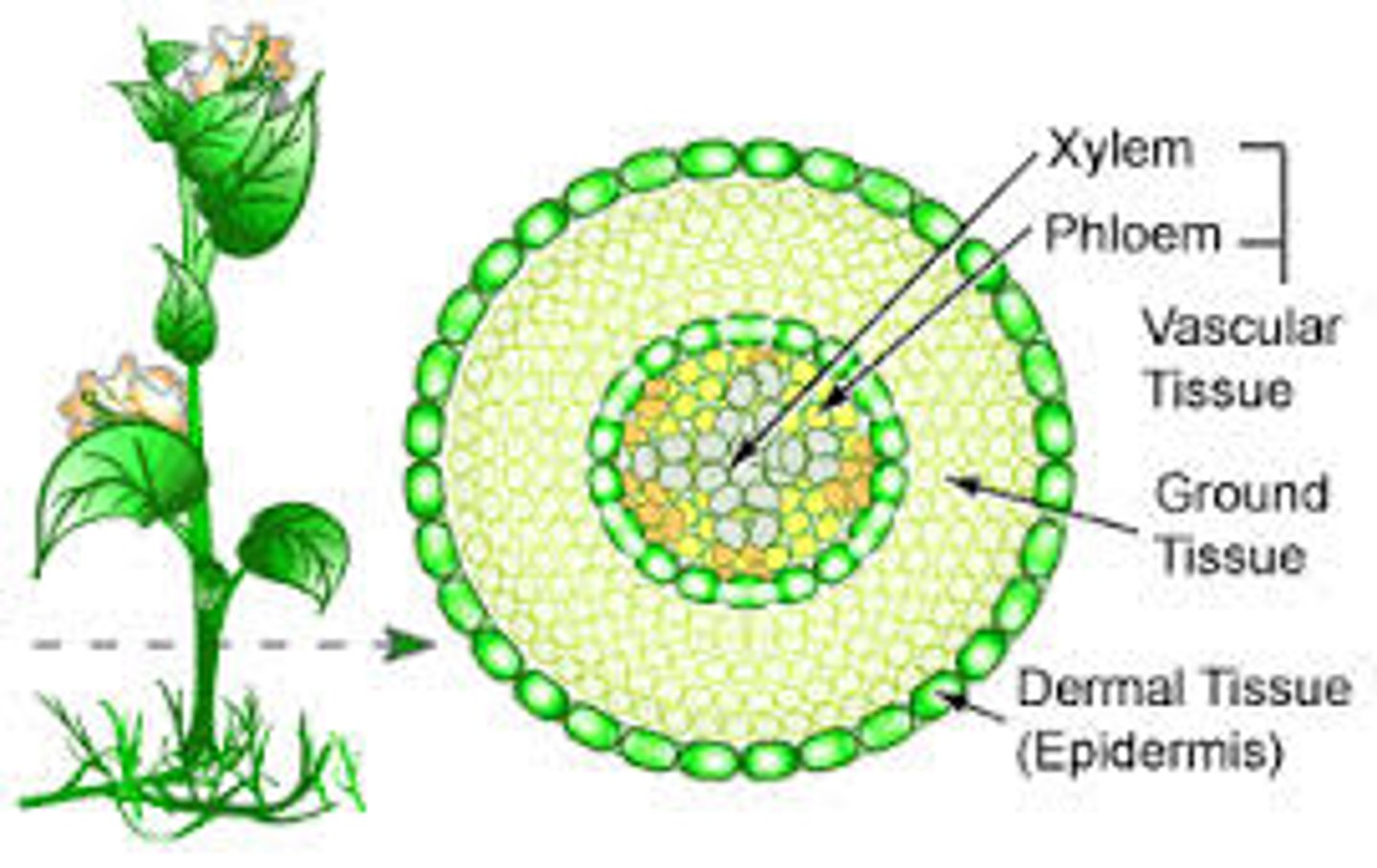
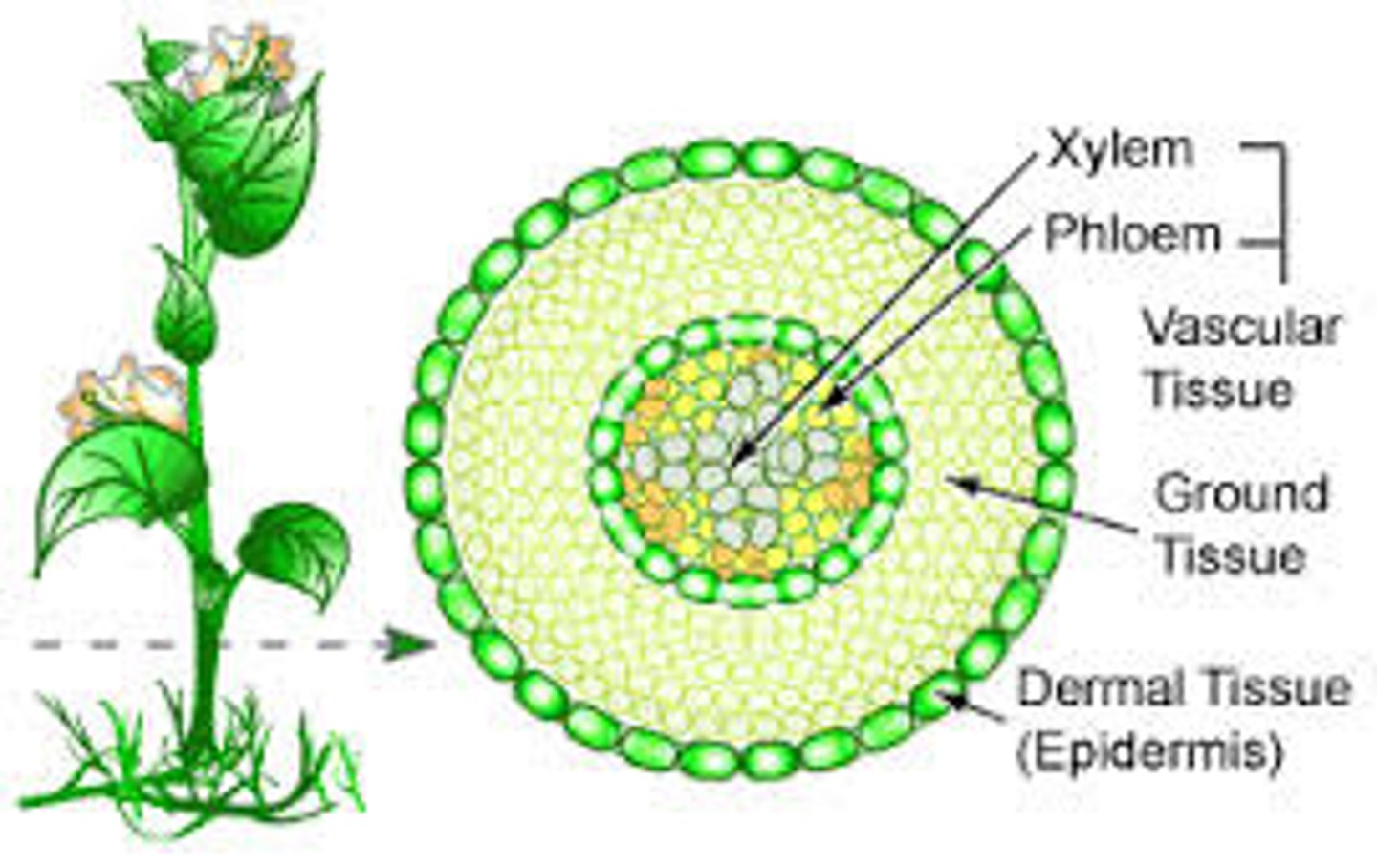
4 kinds of plant tissues
Dermal tissue
Meristematic tissue
Vascular tissue
Ground tissue
(DMVG)
Dermal Tissue of a plant
made out of a single layer of cells on outside of plant
protects plant from environment by being a "shield"
Undifferentiated cells
Cells that have not specialized in any particular function.
vascular tissue
specialized tissue in plants that carries water and nutrients (xylem and phloem)
Meristematic tissue
contains cells that are undifferentiated
mitosis (cell division and growth) takes place here
It's where GROWTH takes place
Ground tissue
most common type of plant tissue
tissue between the dermal tissue and vascular tissue of a non-woody plant that functions in photosynthesis, storage, and support
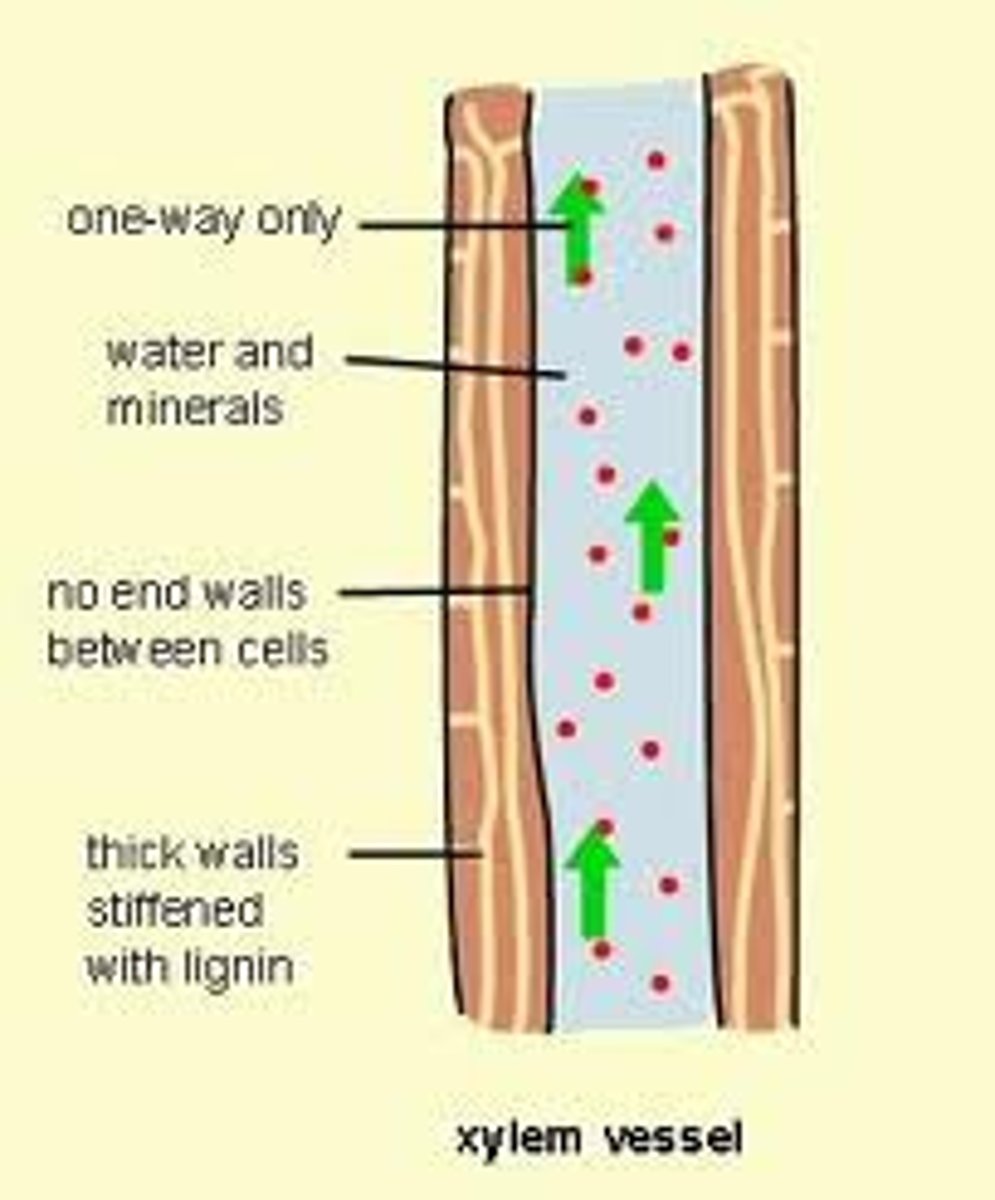
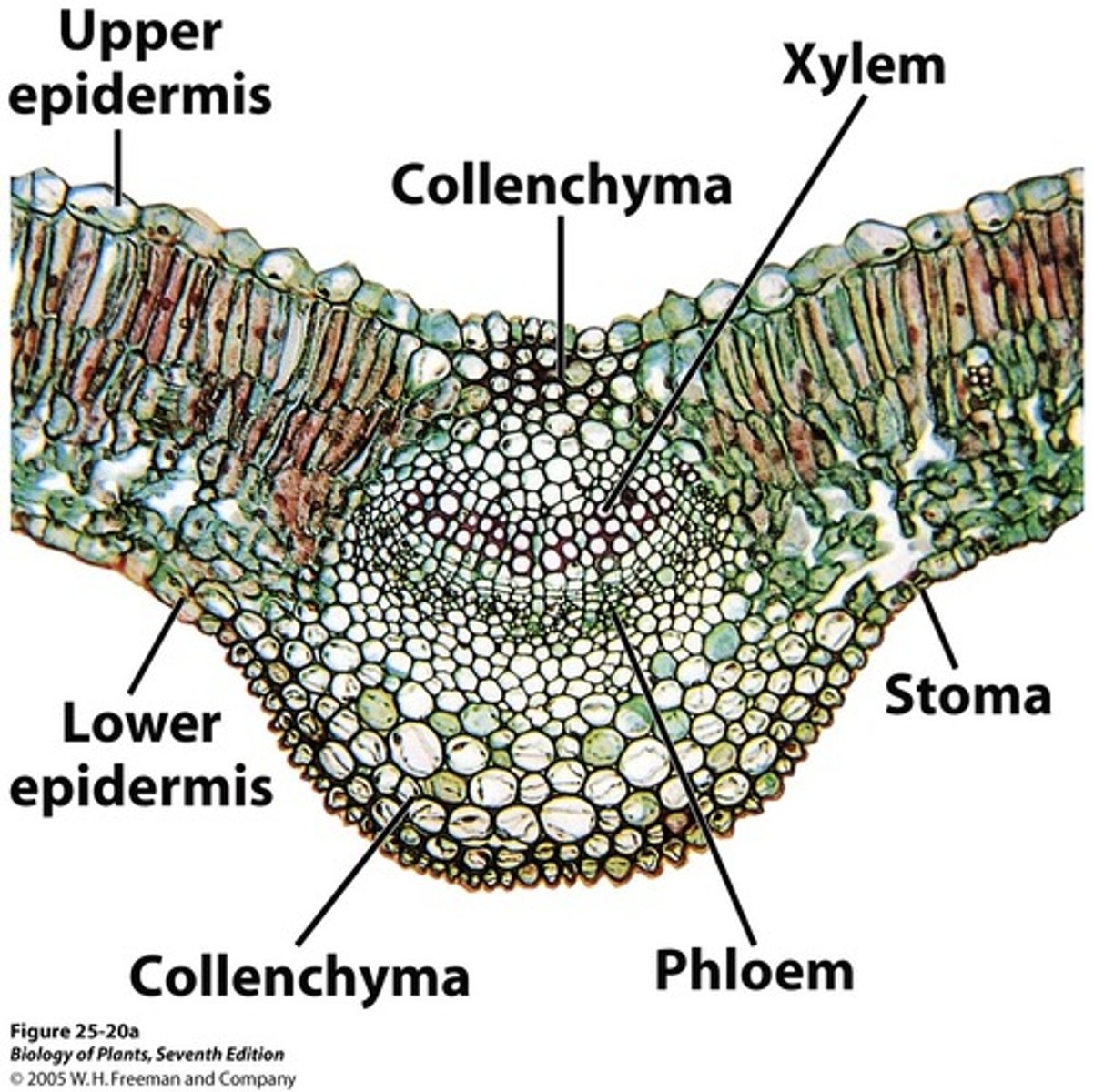
Xylem
Nonliving vascular tissue that carries water and dissolved minerals from the roots of a plant to it's leaves.
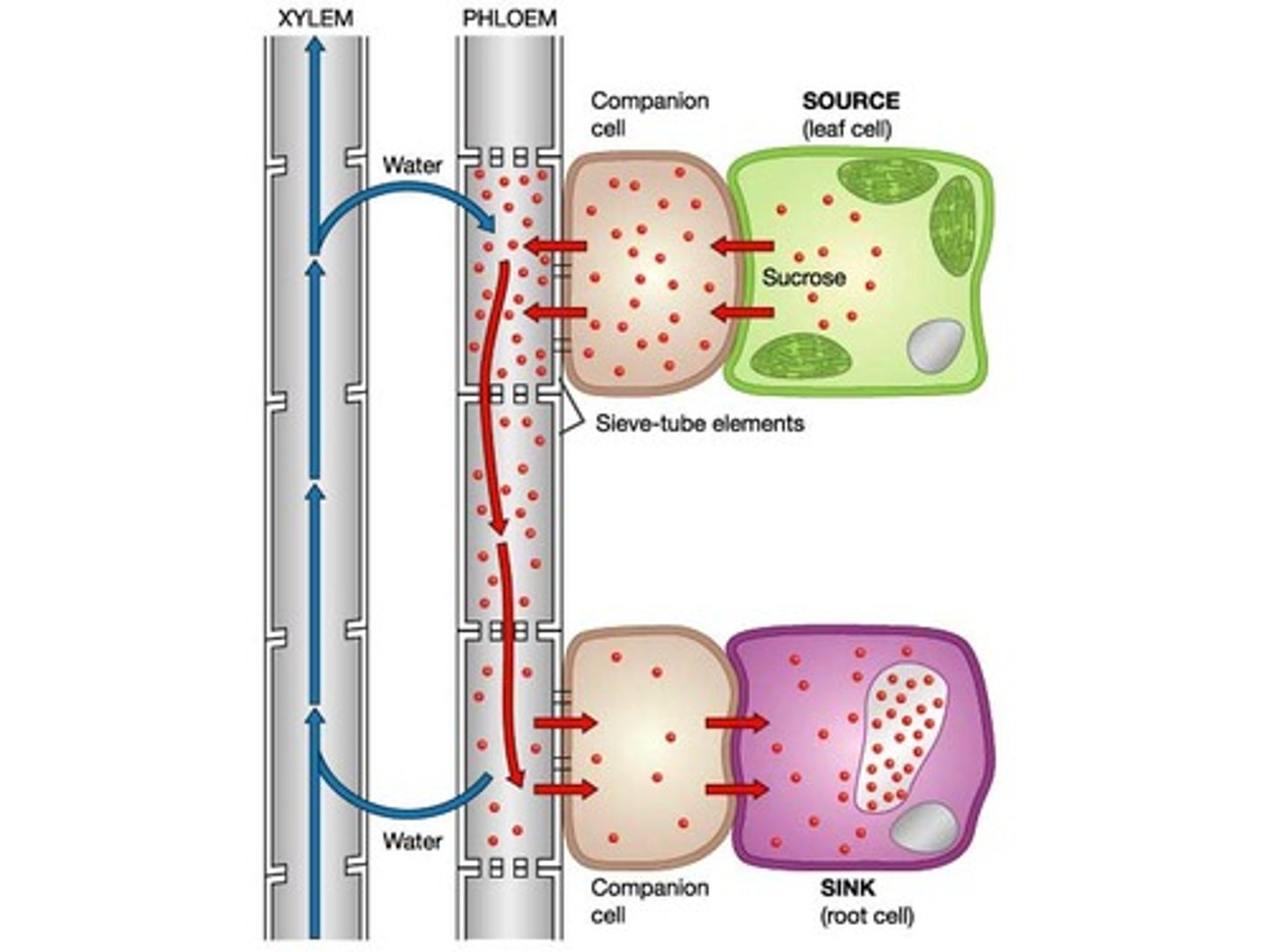
Phloem
Living vascular tissue that carries sugar and organic substances throughout a plant.
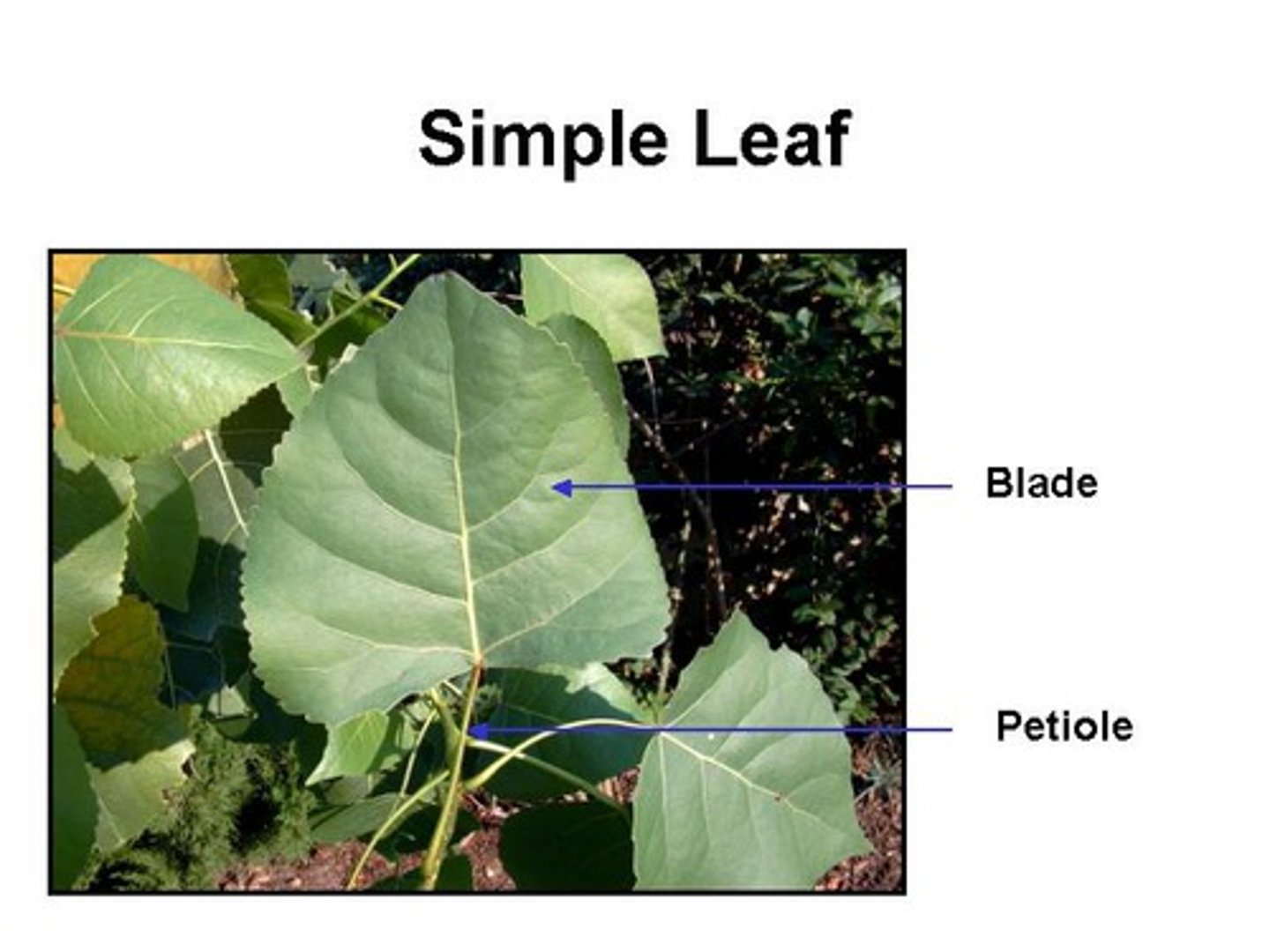
Major parts of a leaf
Blade
Apex
Petiole
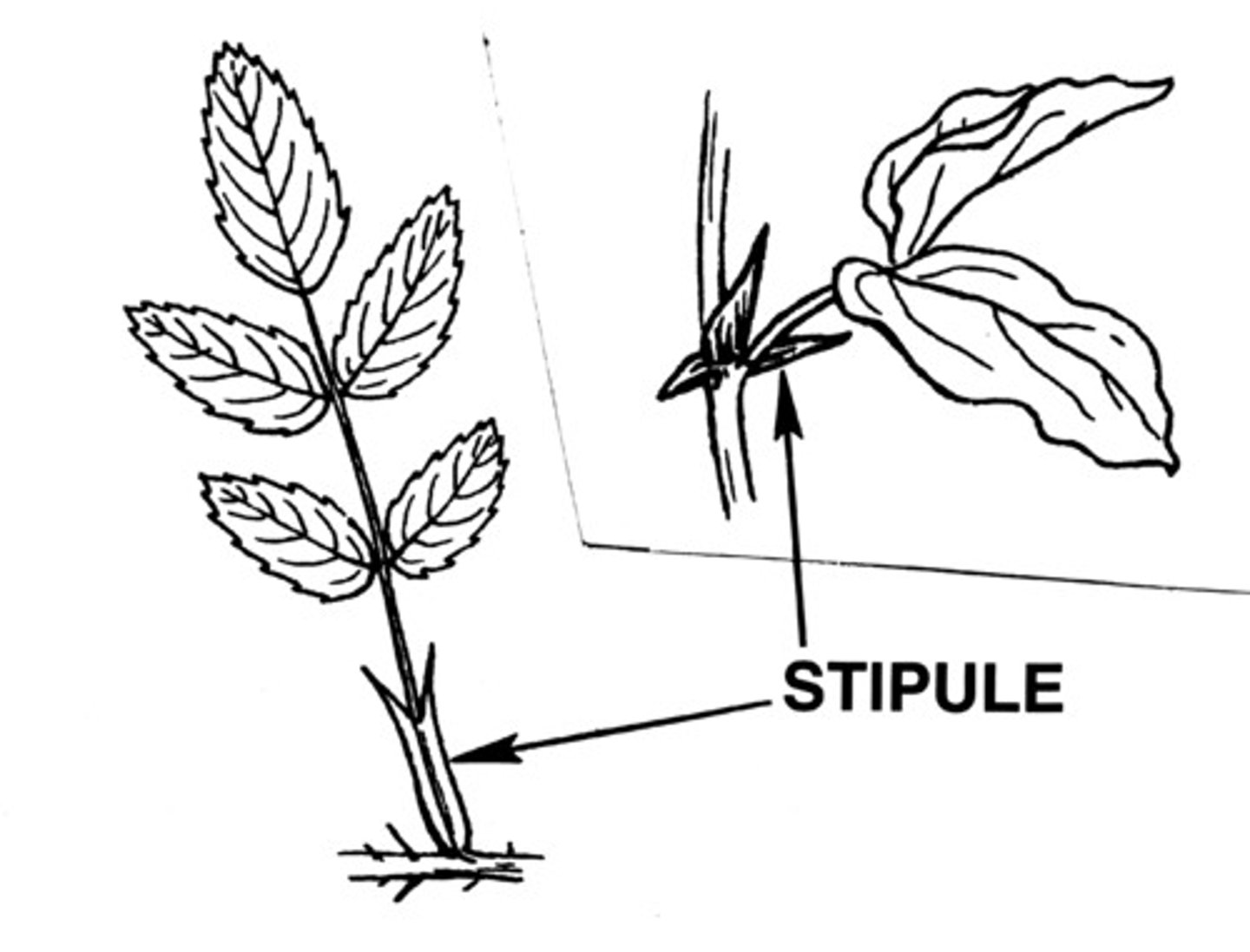
Stipules
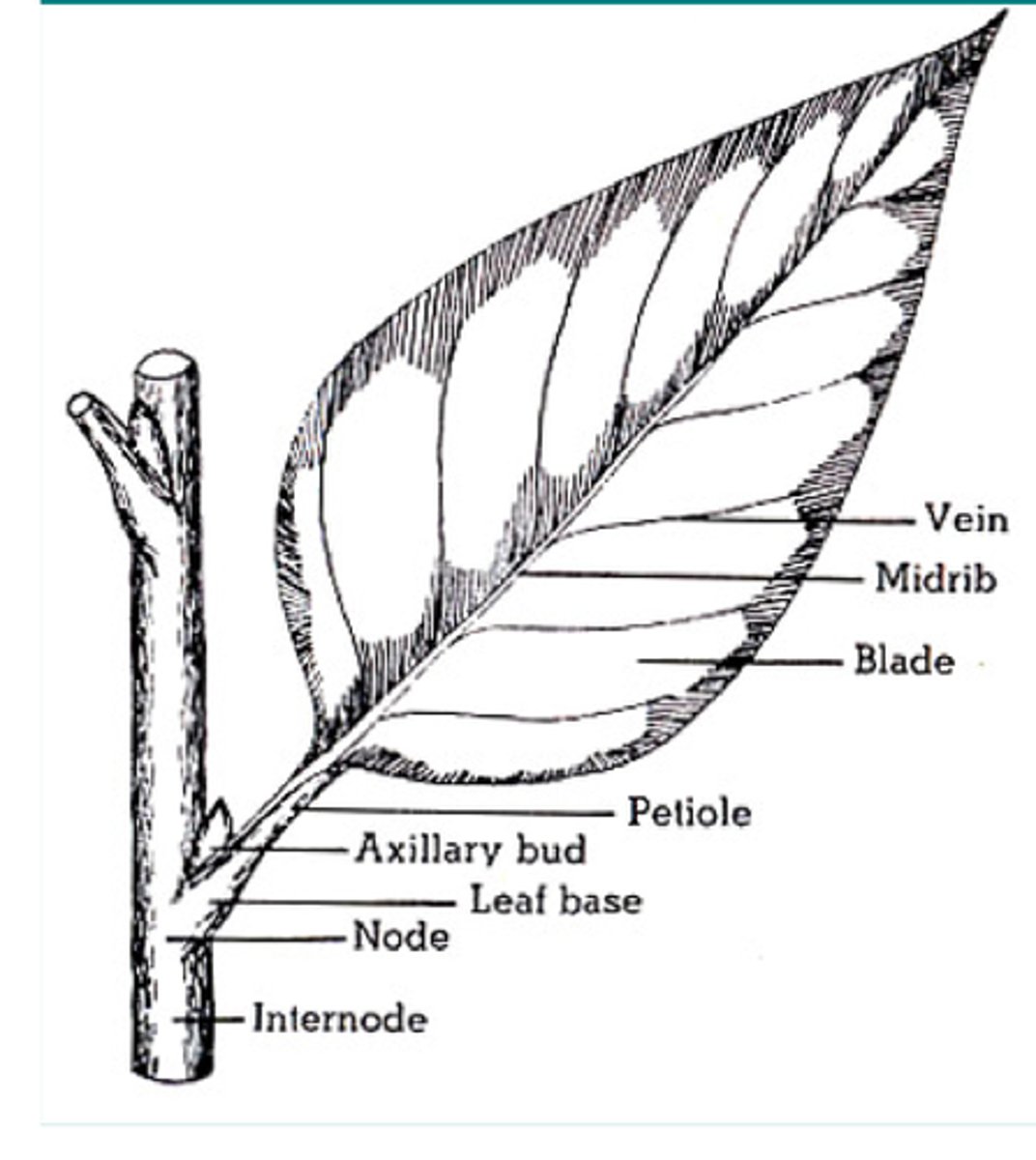
blade
primary portion of leaf
apex of a leaf
tip of the blade of the leaf (top)

petiole
blade is attached to the stem with a small stalk
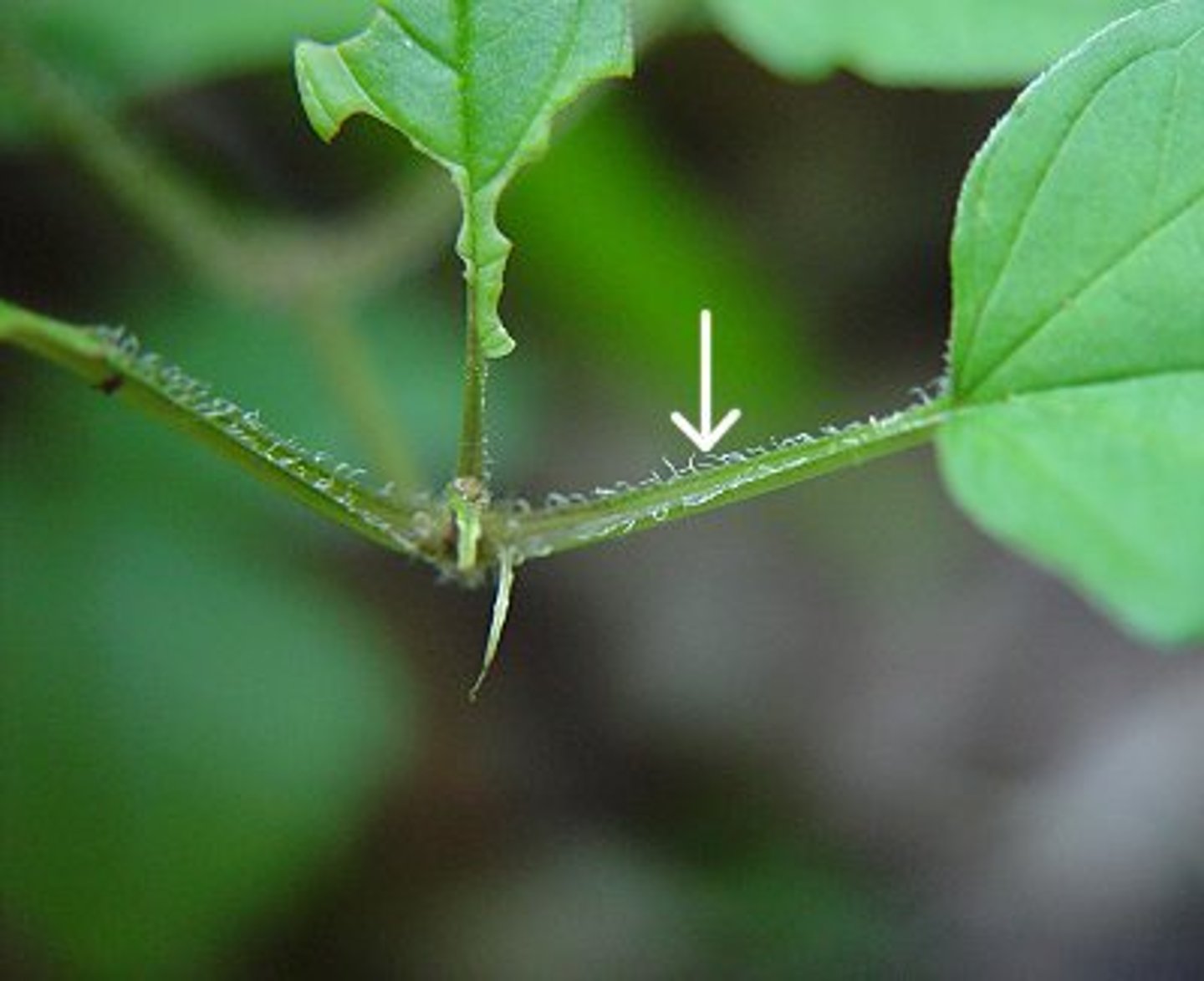

stipules
base of the petiole
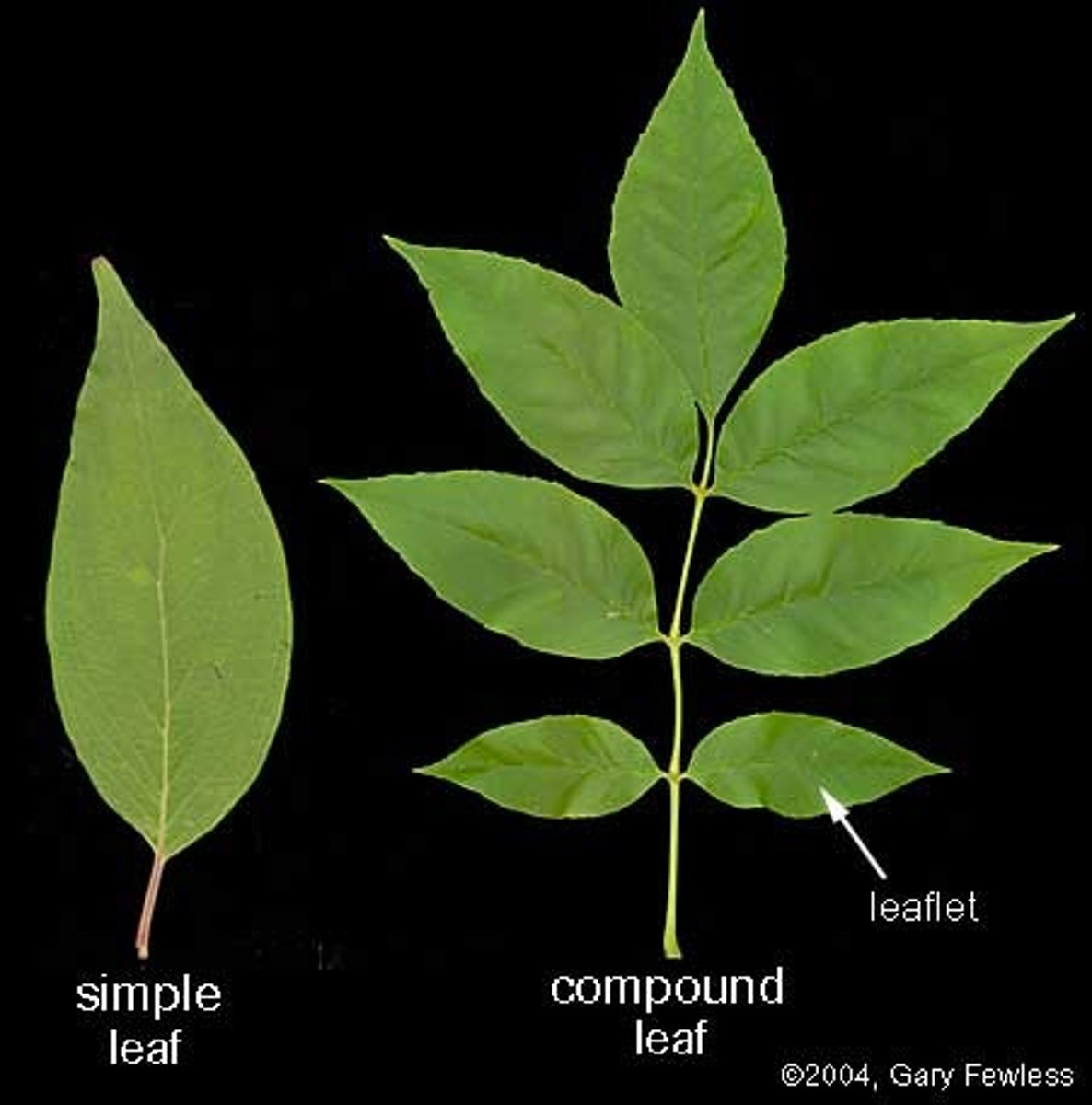
simple leaf
a single leaf that is attached to the stem of the plant by a single petiole.

compound leaf
a leaf of a plant consisting of several or many distinct parts (leaflets) joined to a single stem.
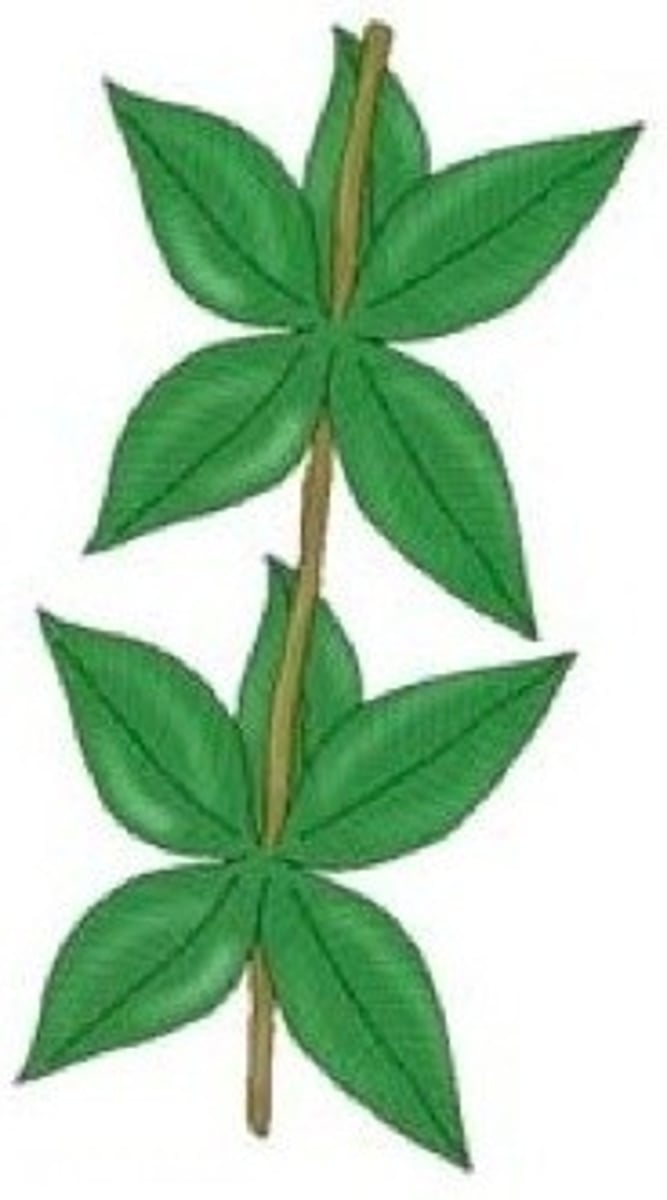
leaf mosaic
the arrangement of leaves on the stem of a plant
Alternate Leaf Mosaic
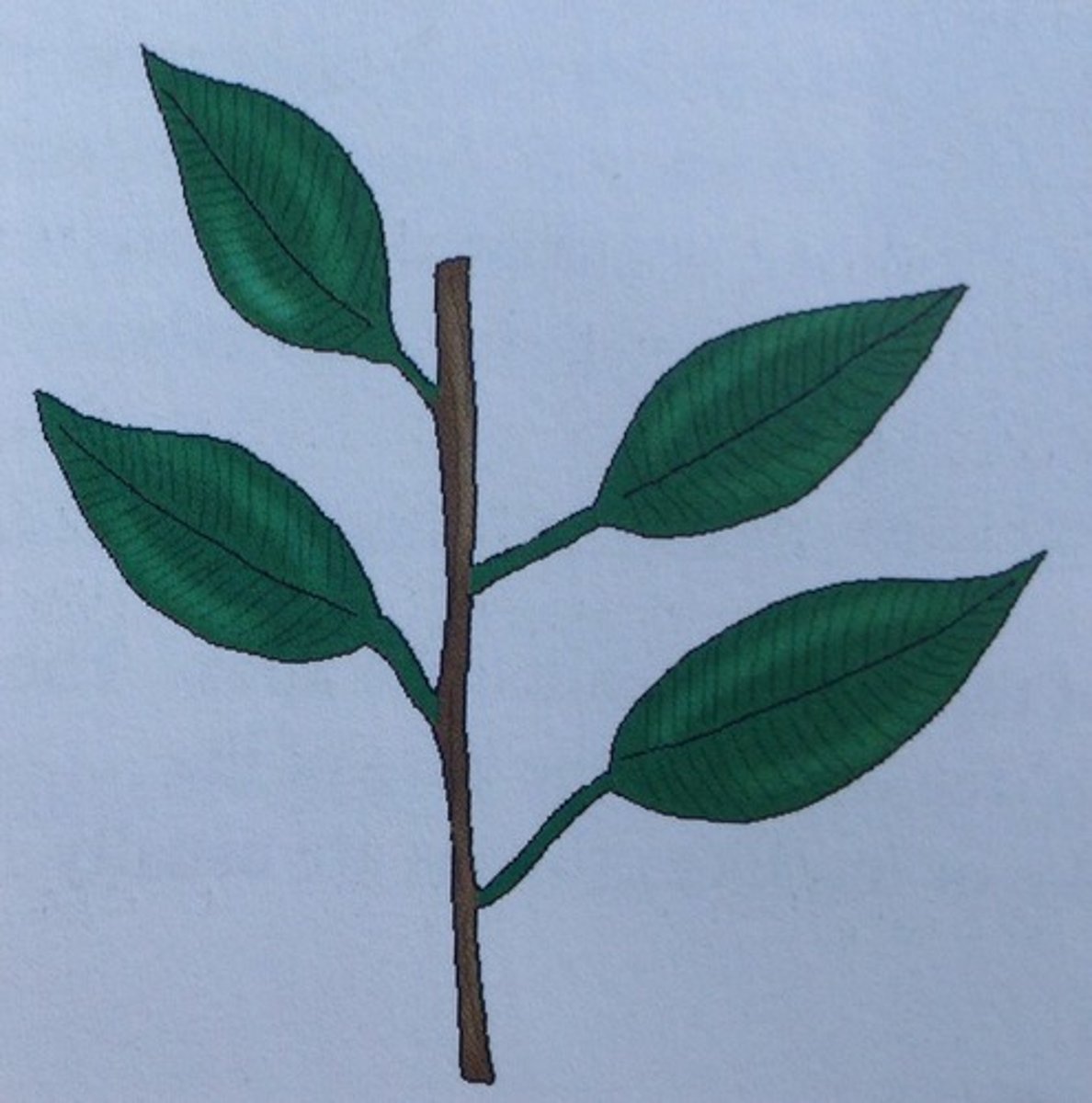

Opposite Leaf Mosaic
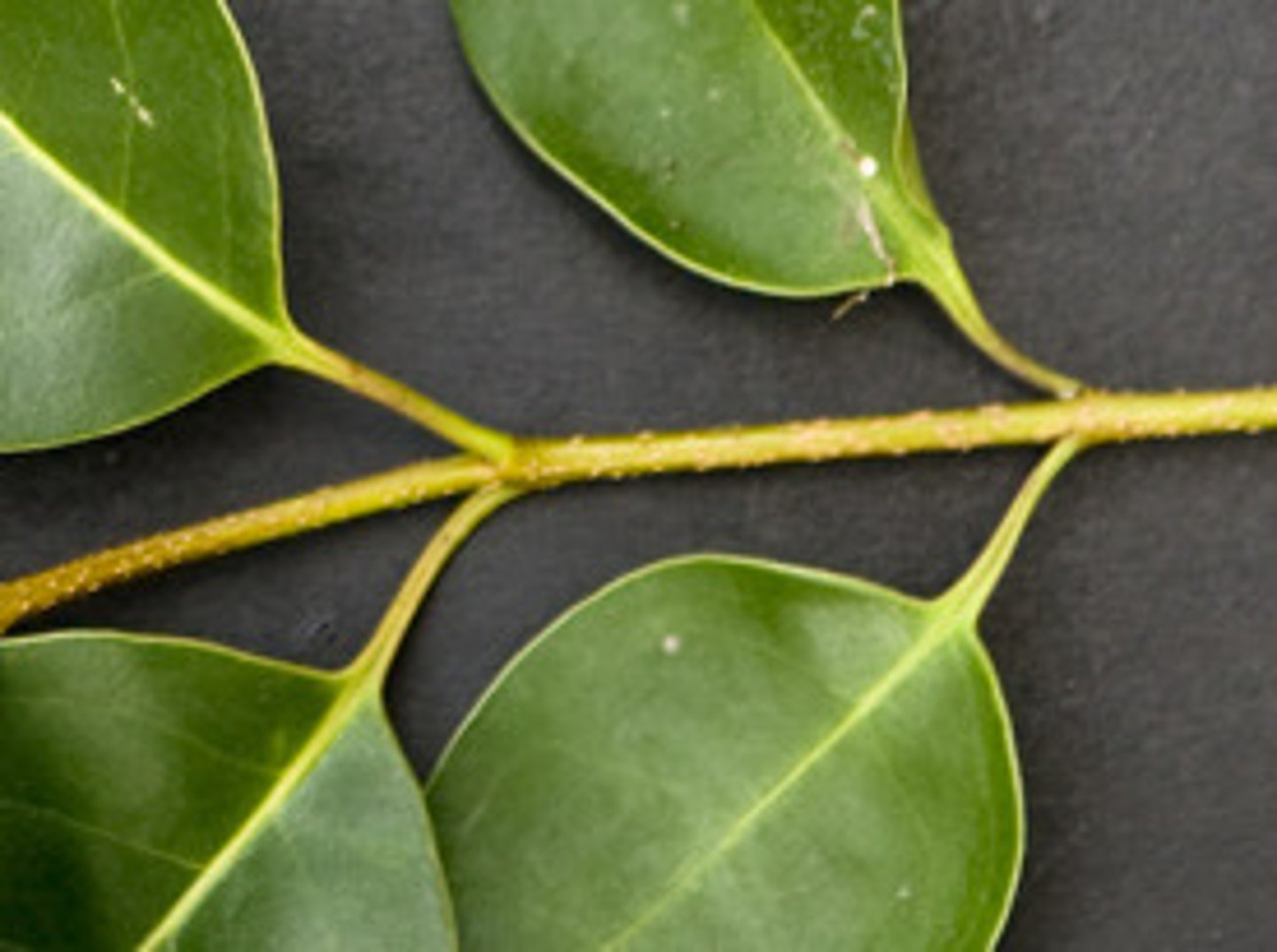

Whorled Leaf Mosaic

Characterizing a Leaf
Botanists use the leaf shape, margin and venation to help classify a plant.

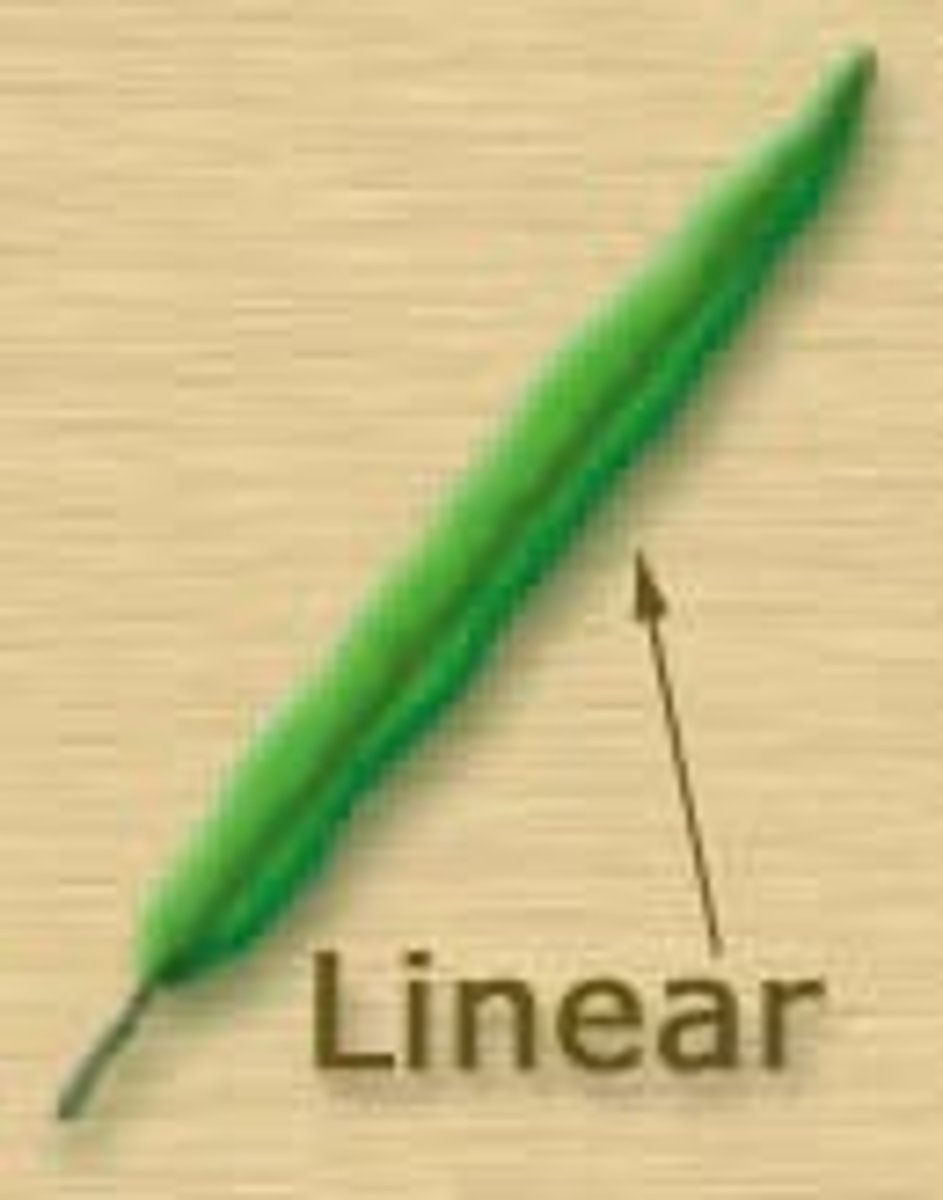
Linear Leaf
about the same width from the top of the leaf to the bottom

Elliptical Leaf
Tapers at both ends but is still longer than wide

Oval leaf Shape
egg shaped

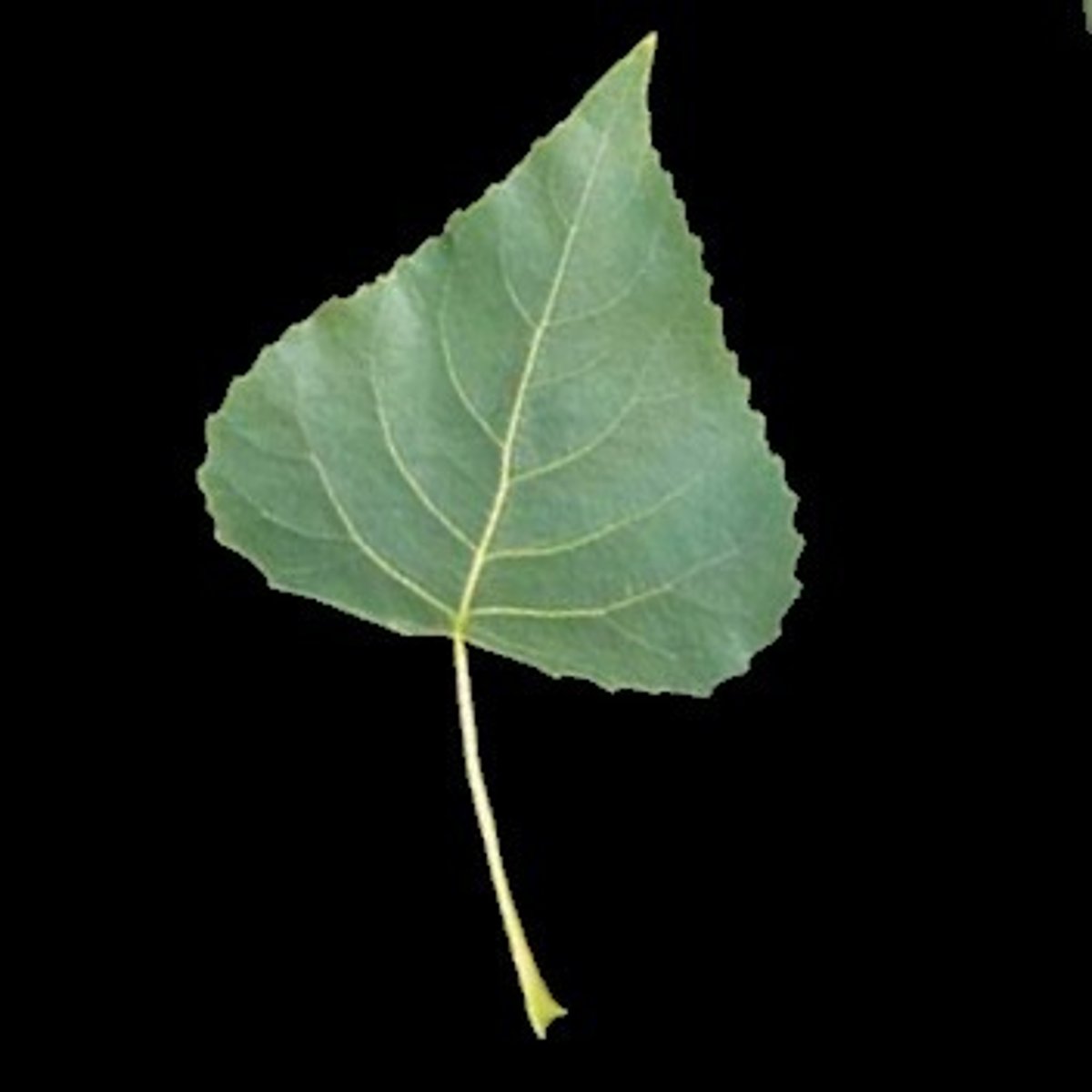
Deltoid Leaf Shape
triangular shape

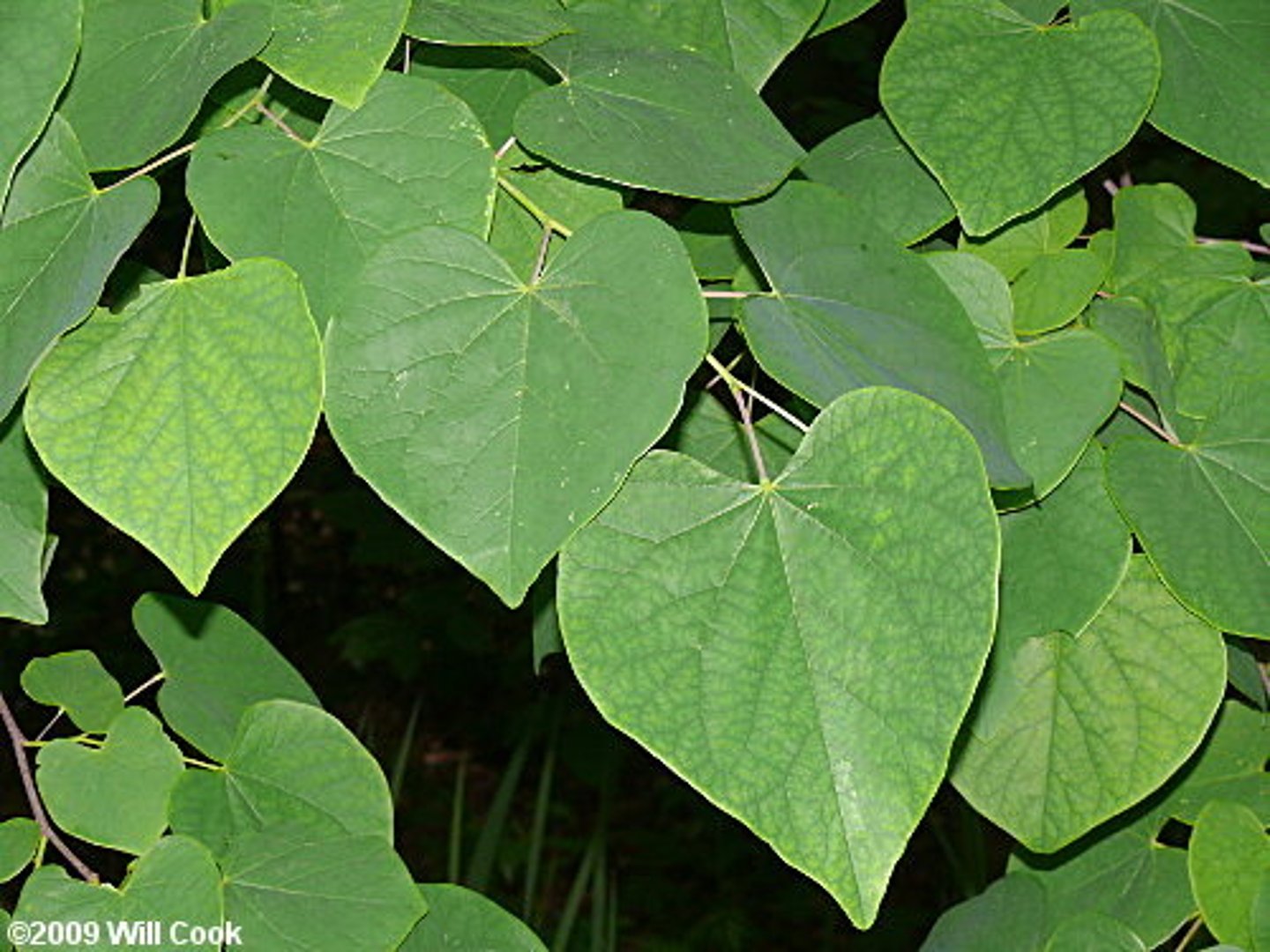
Cordate Leaf Shape
Like an upside down heart

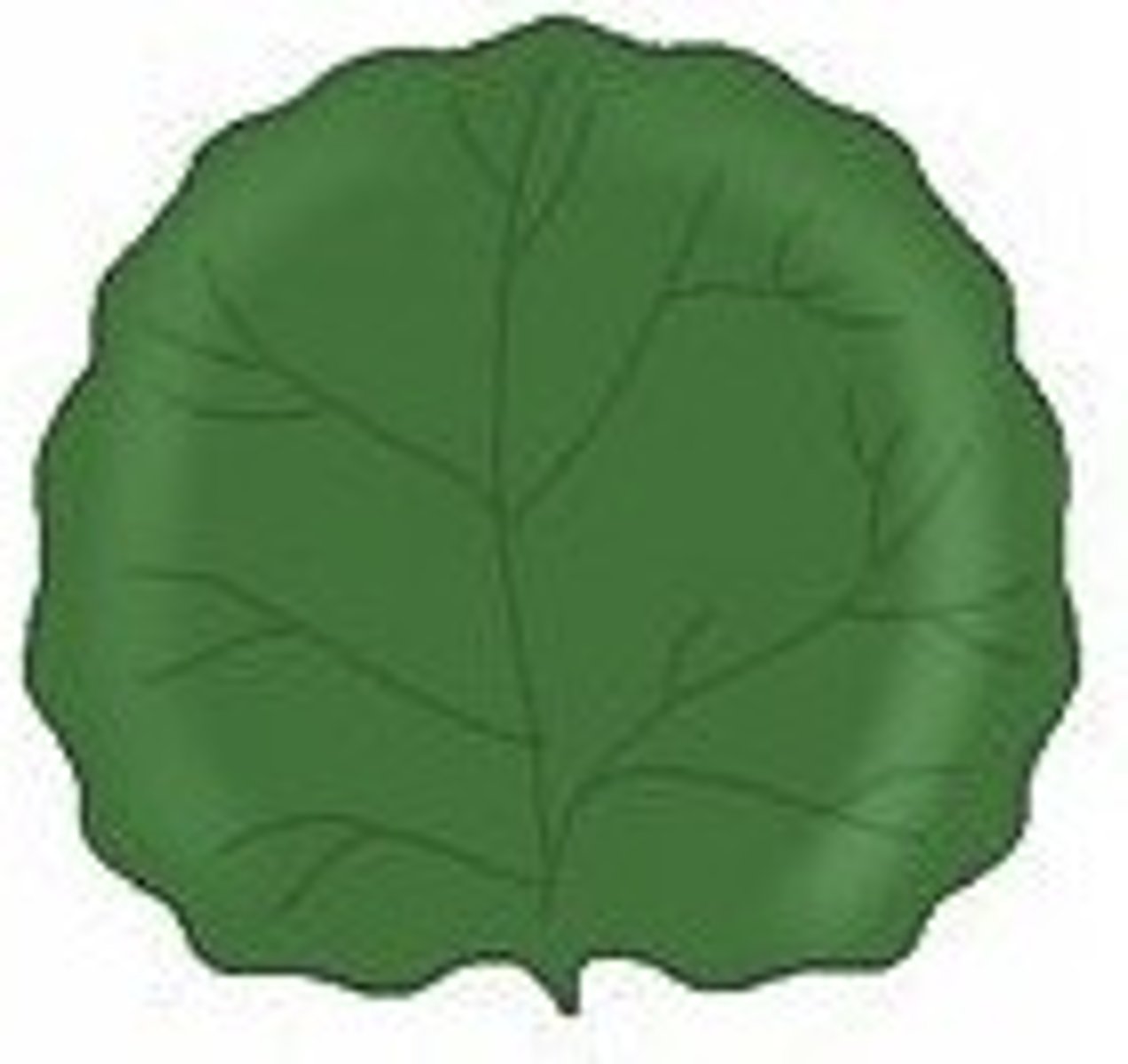
Orbicular Leaf Shape
ciruclar

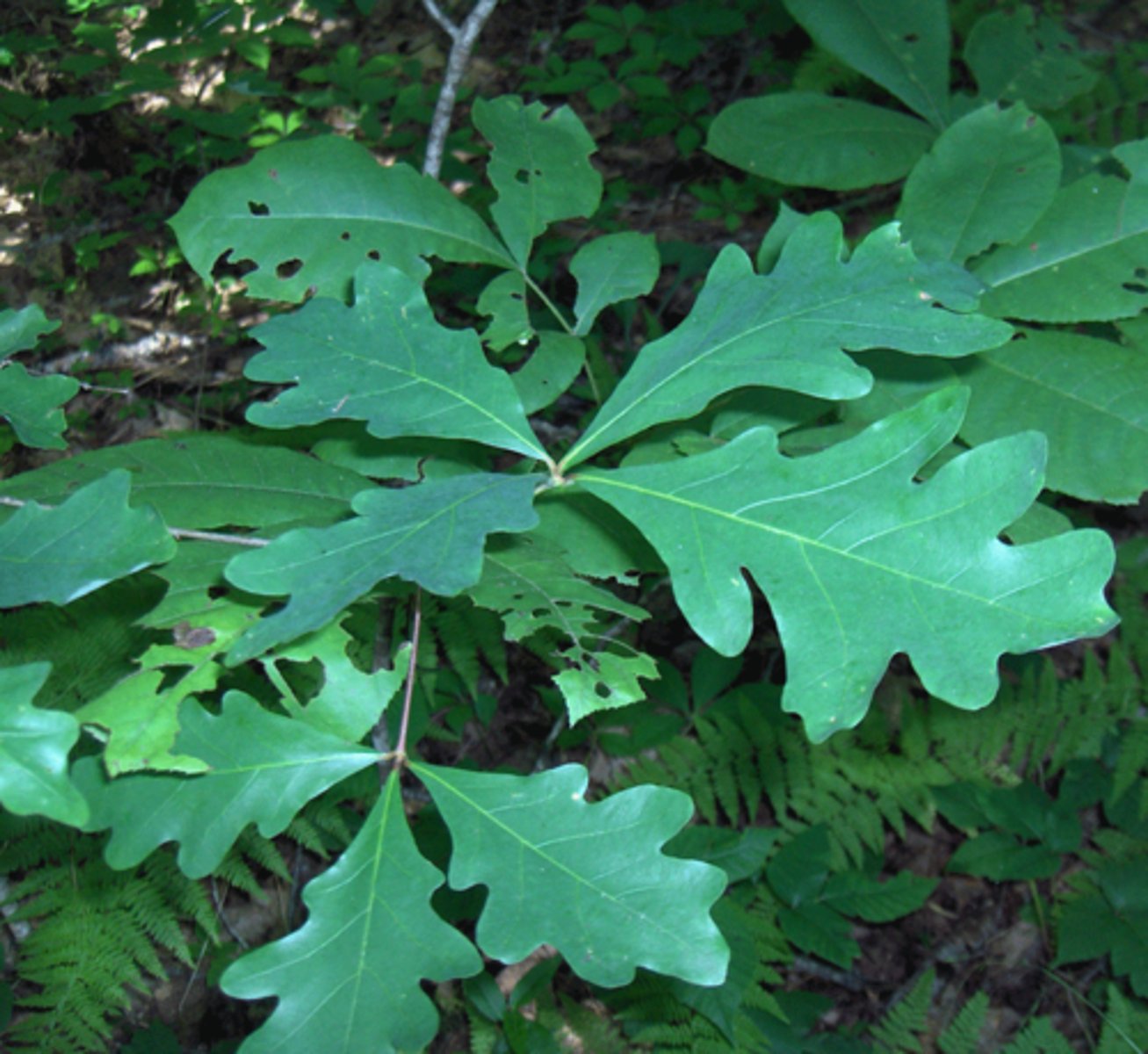
Lobed leaf shape
deep indentations in the leaf

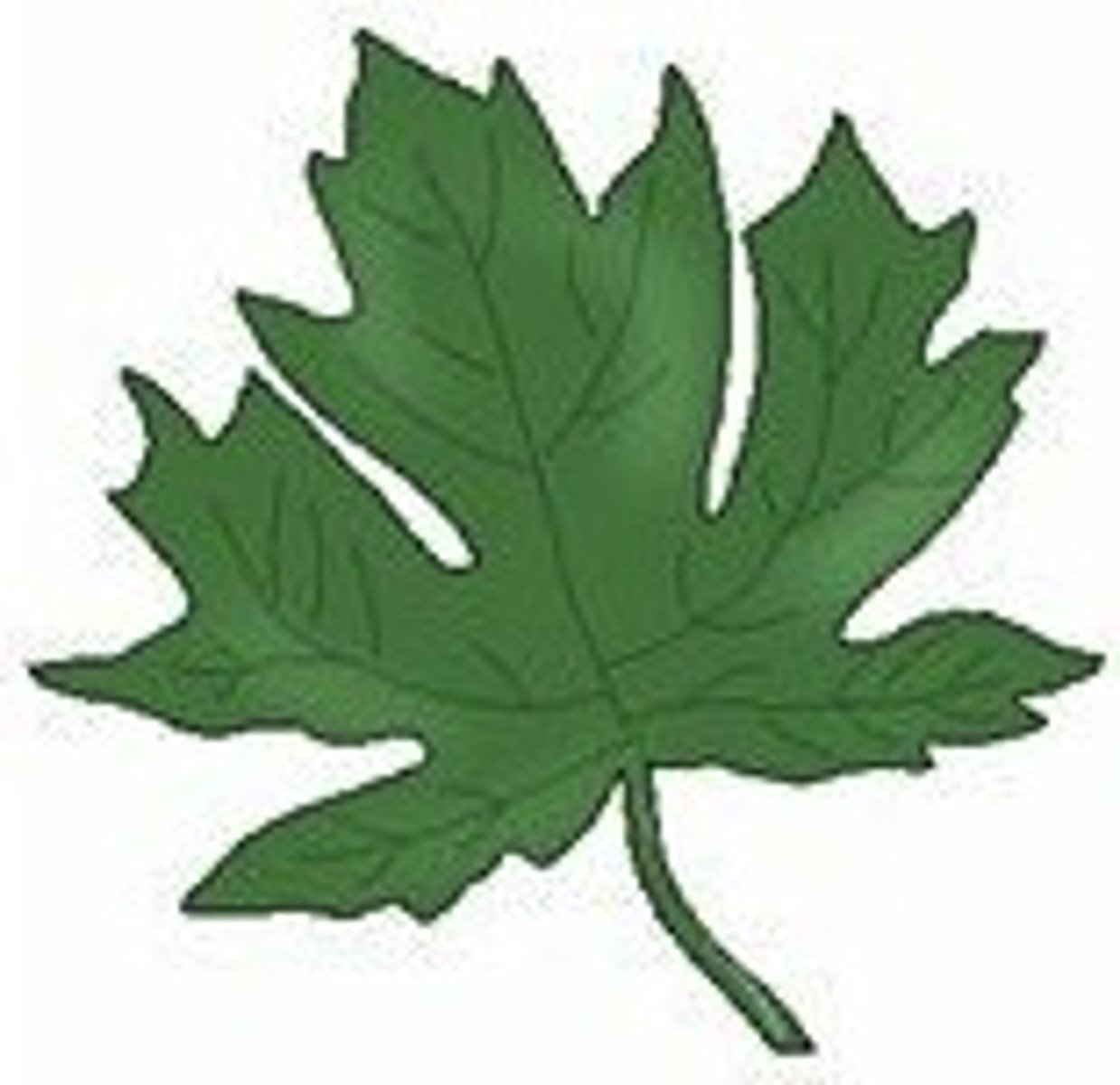
Cleft Leaf Shape
deep indentations that tend to be sharp

Needlelike Leaf Shape
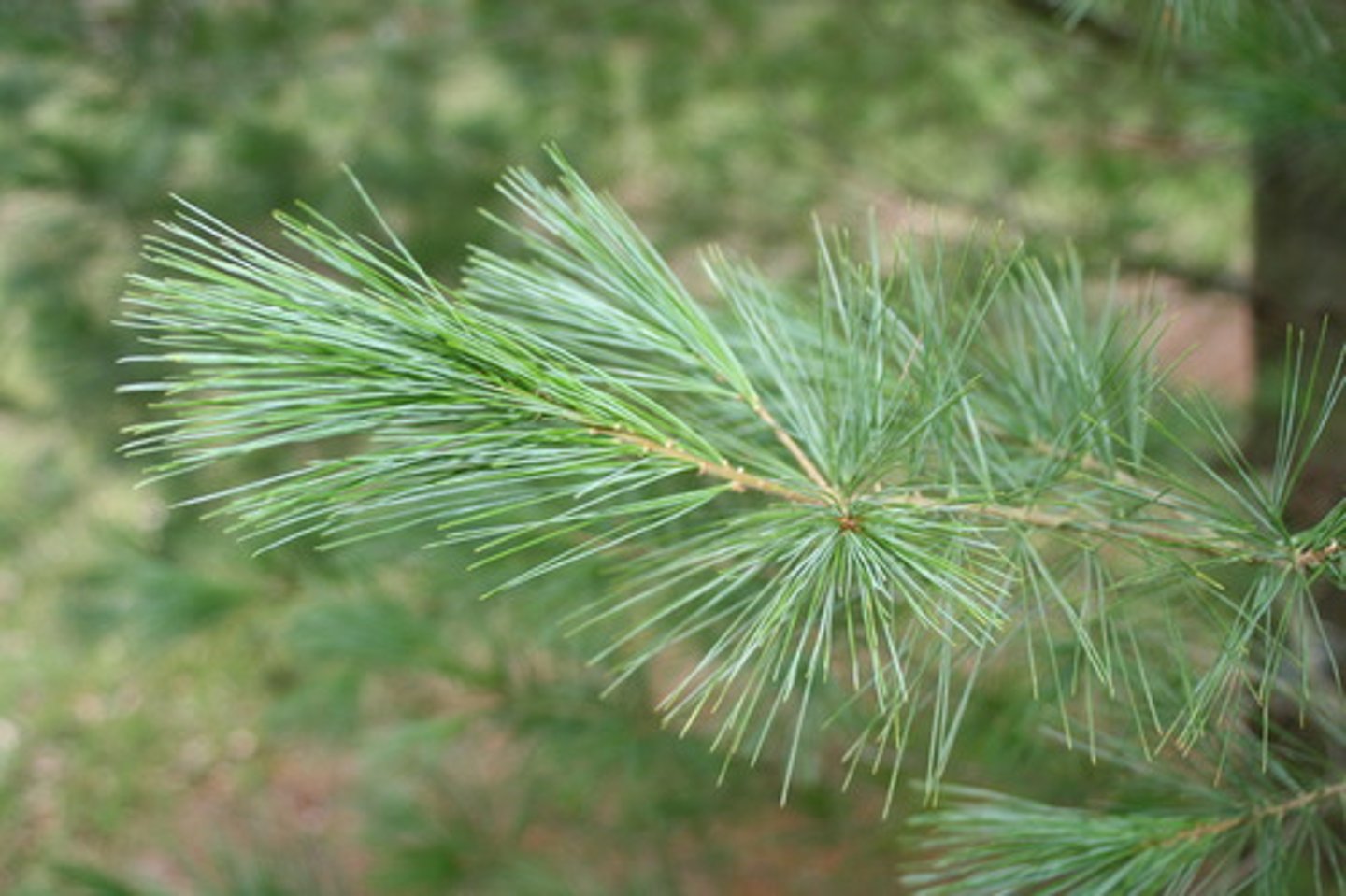

Scalelike Leaf Shape
almost like the scales of a fish
Leaf Margin
The characteristics of the leaf edge
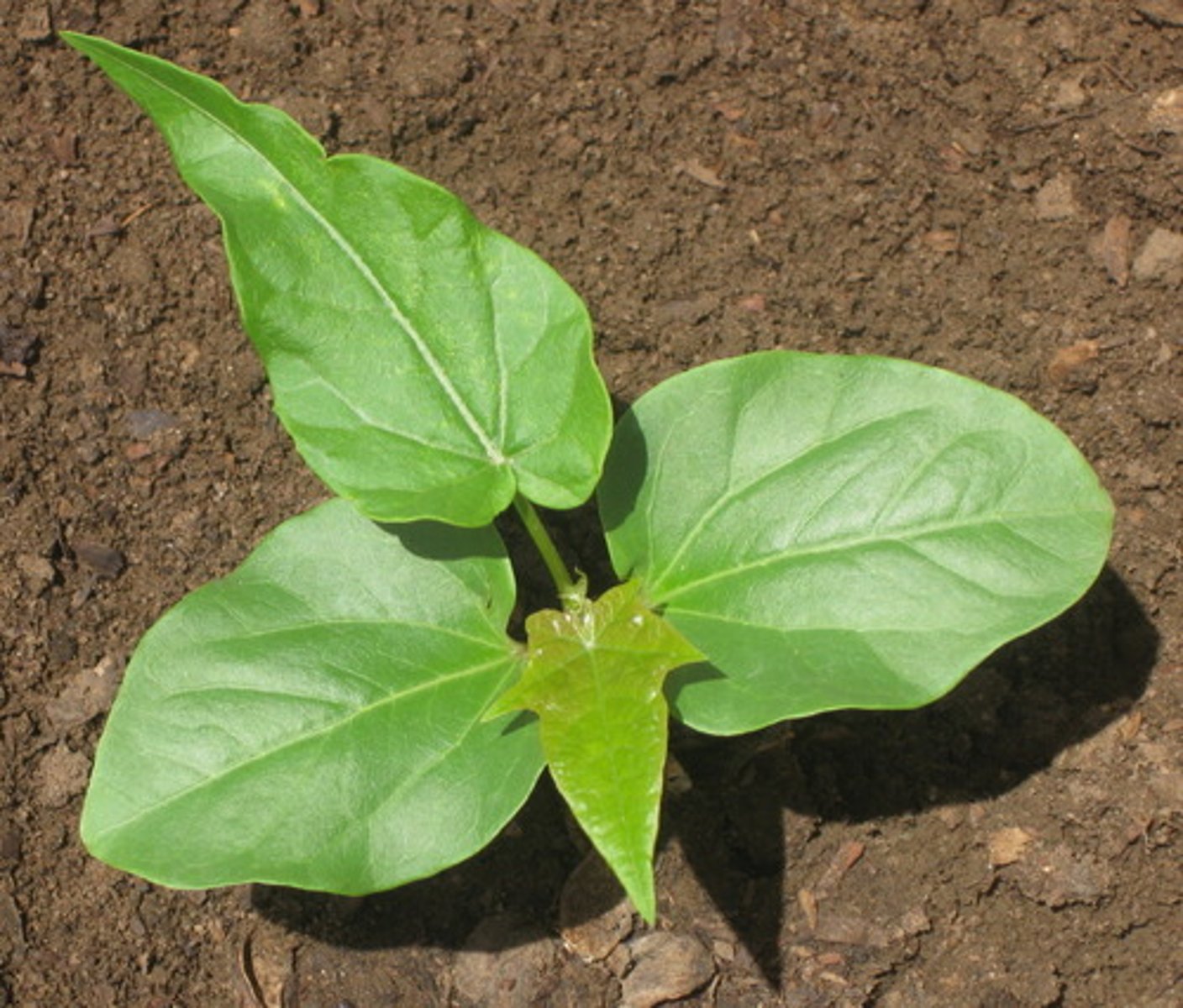
Entire leaf margin
not toothed, notched, or divided. but smooth

Serrate leaf margin
tiny sharp teeth on it's outer edge, which usually point upwards towards the apex
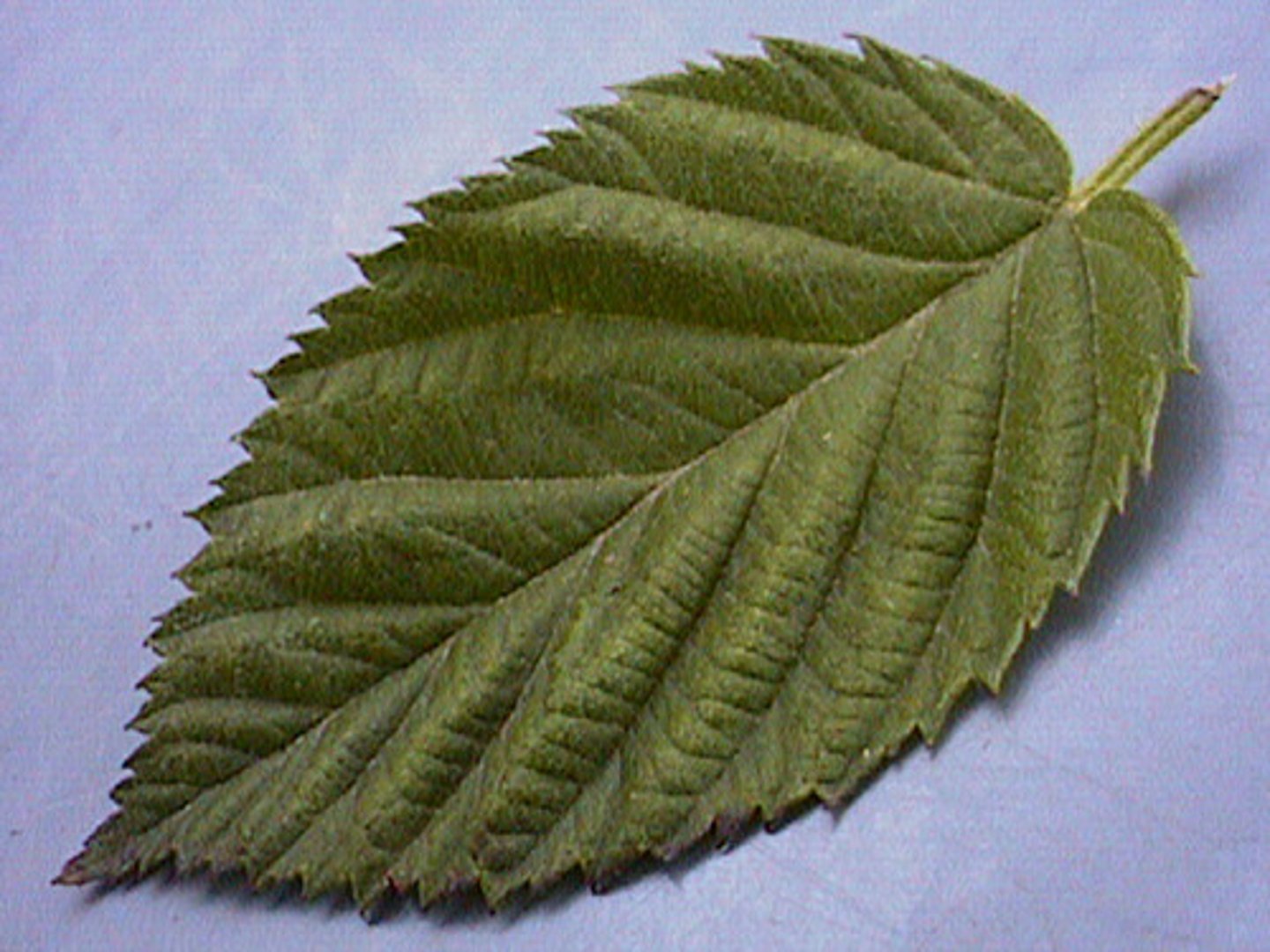

Dentate Leaf margin
More pronounced teeth that usually point outward
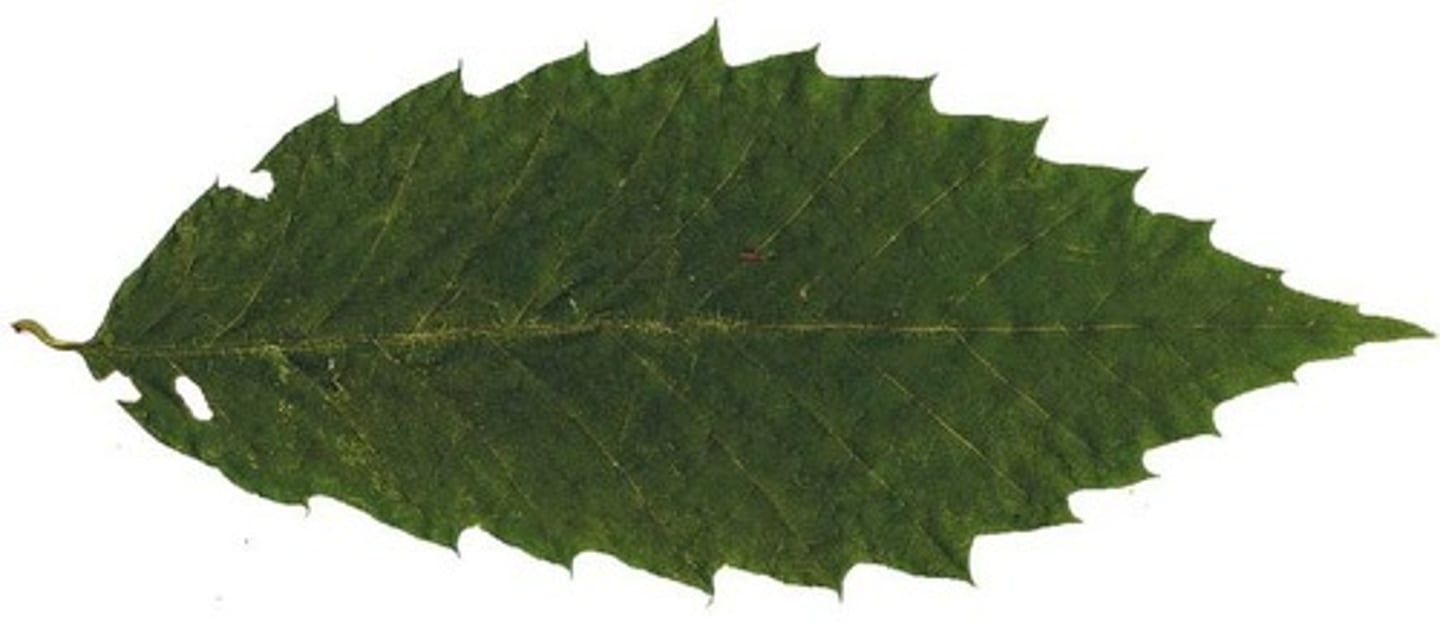

Crenate Leaf margin
teeth are more rounded than pointed
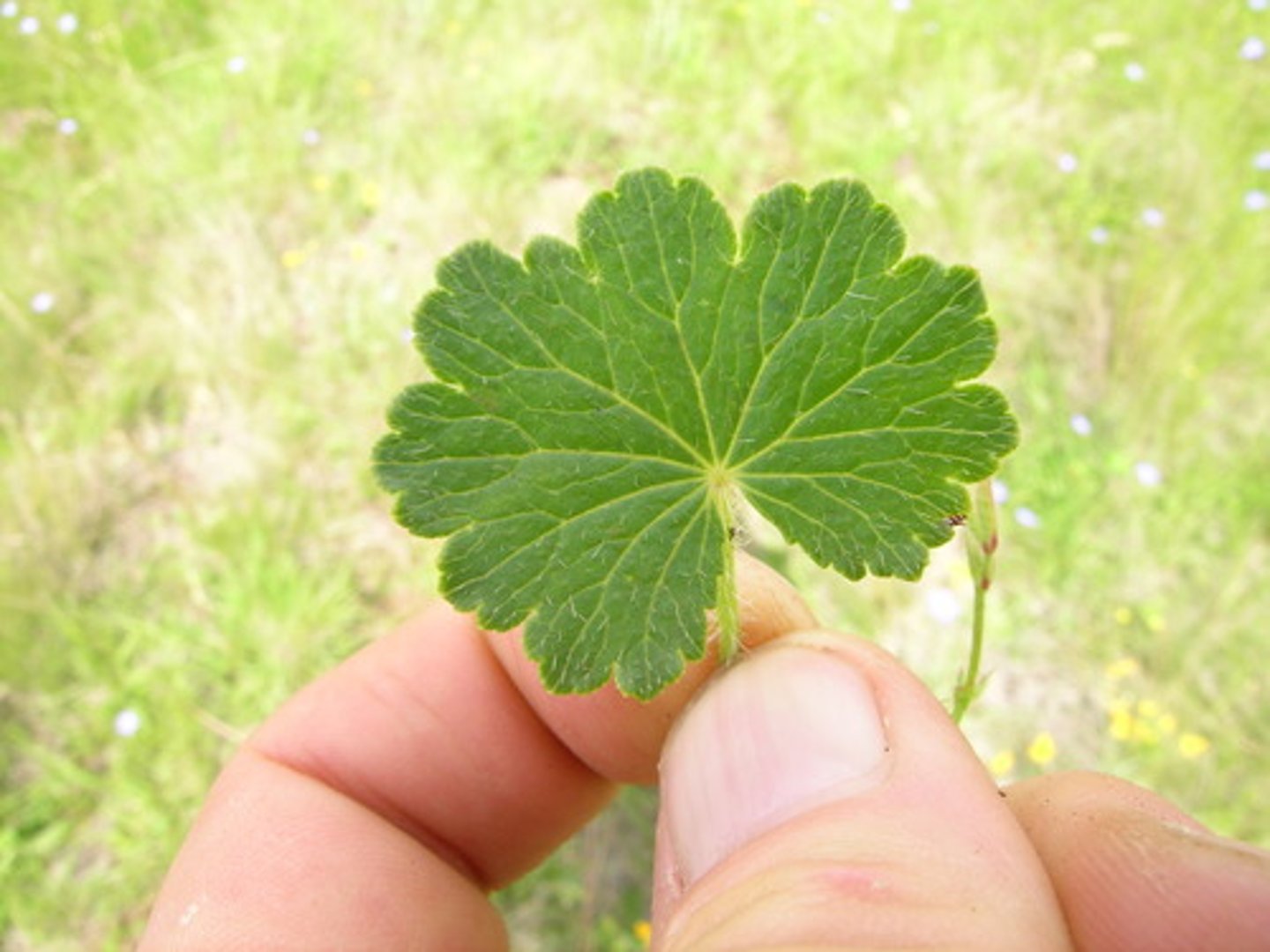

Undulate Leaf Margin
tends to be wavy instead of with teeth

Leaf Venation
the pattern of veins in leaves
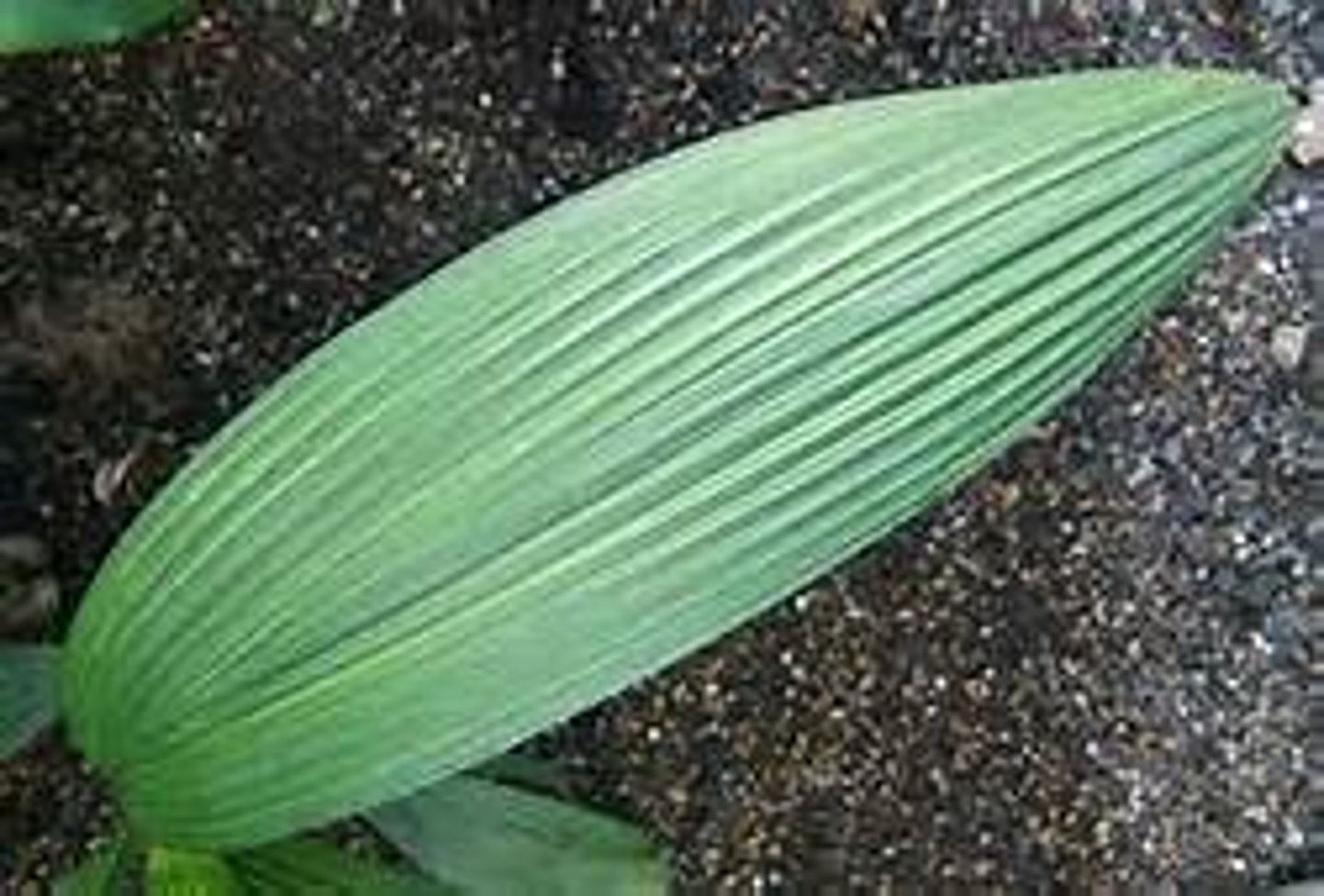
Parallel Leaf Venation
a type of broad leaf that has long veins that do not intersect (monocots) e.g. grass

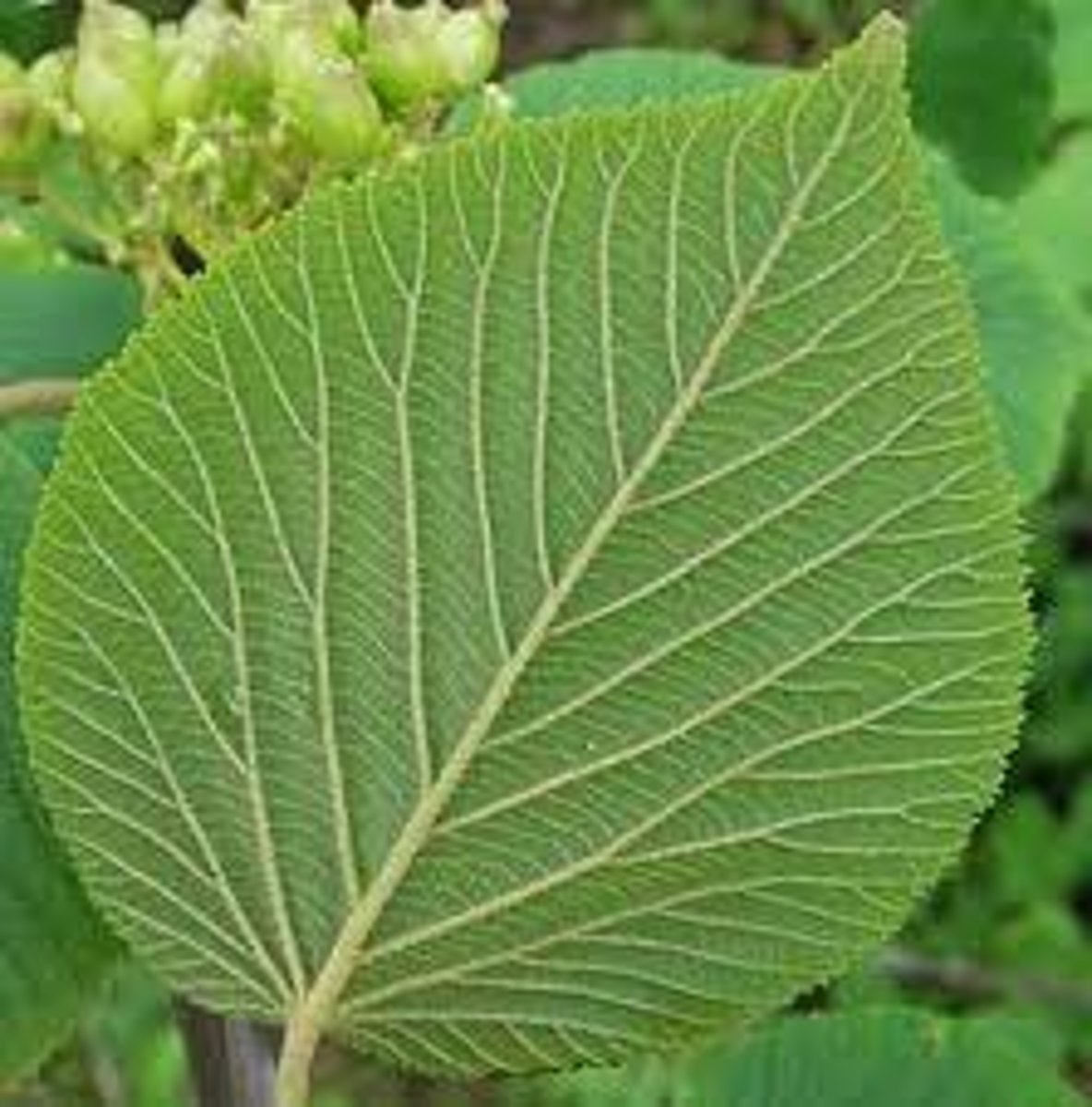
Pinnate Leaf Venation
Many veins of a leaf that branch out from the midrib

Palmate Leaf Venation
the leaf's veins brand out from the midrib and those branches also have branches.

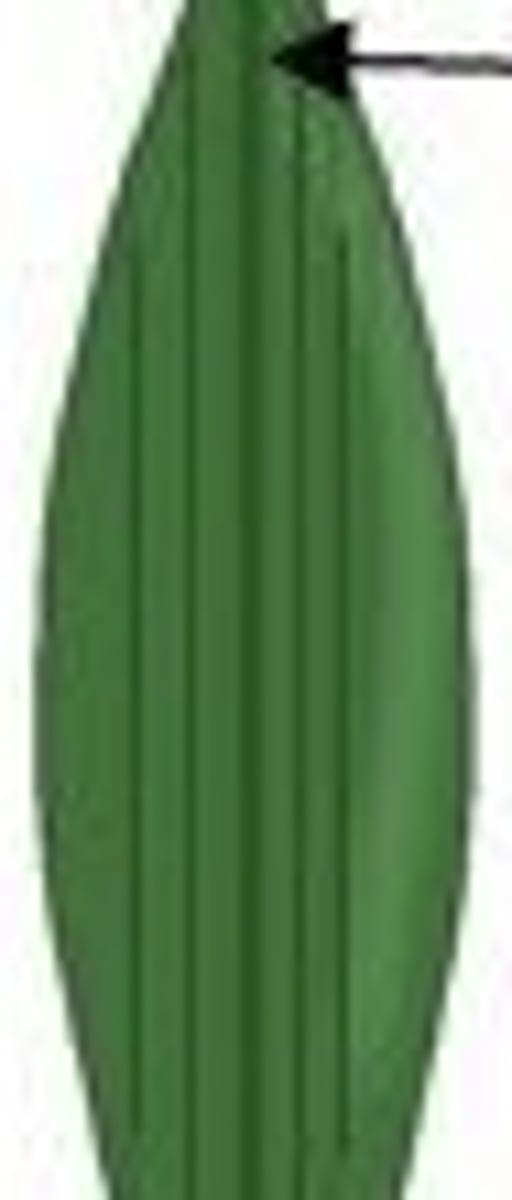
Monocot
a plant whose leaf's venation is parallel

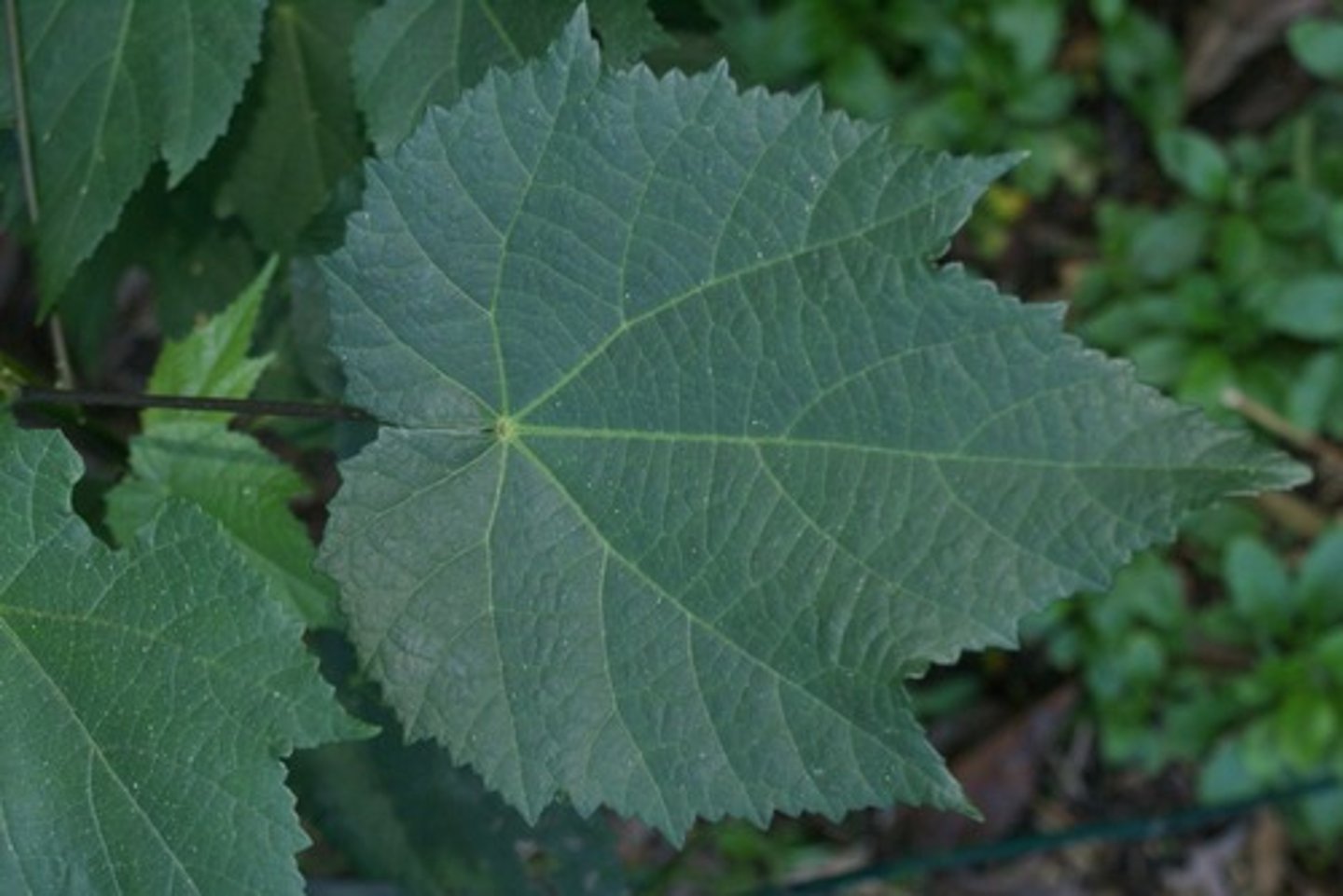
Dicot
a plant whose leaf's venation is netted
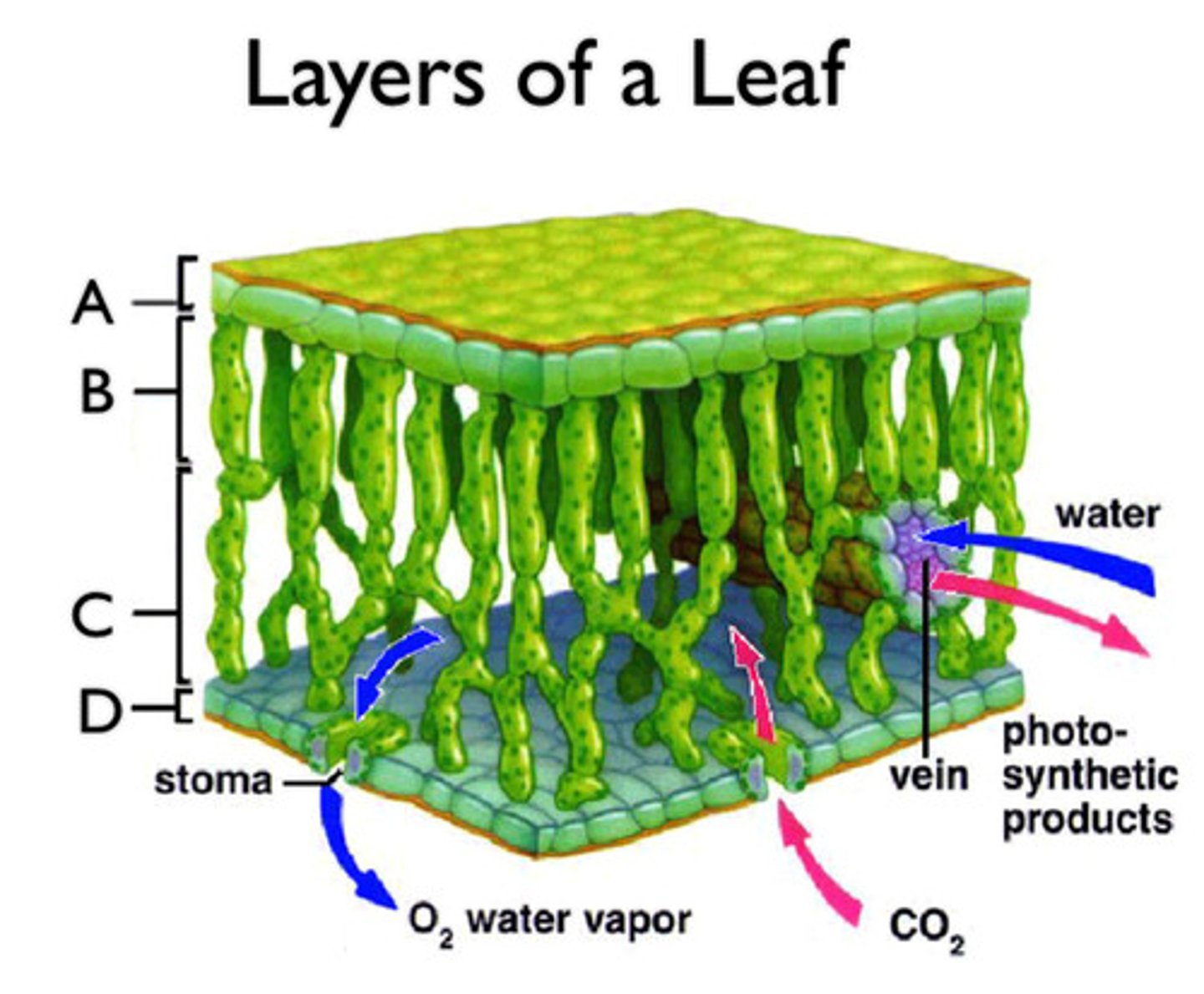
leaf epidermis
a single layer that covers the top and bottom of a leaf
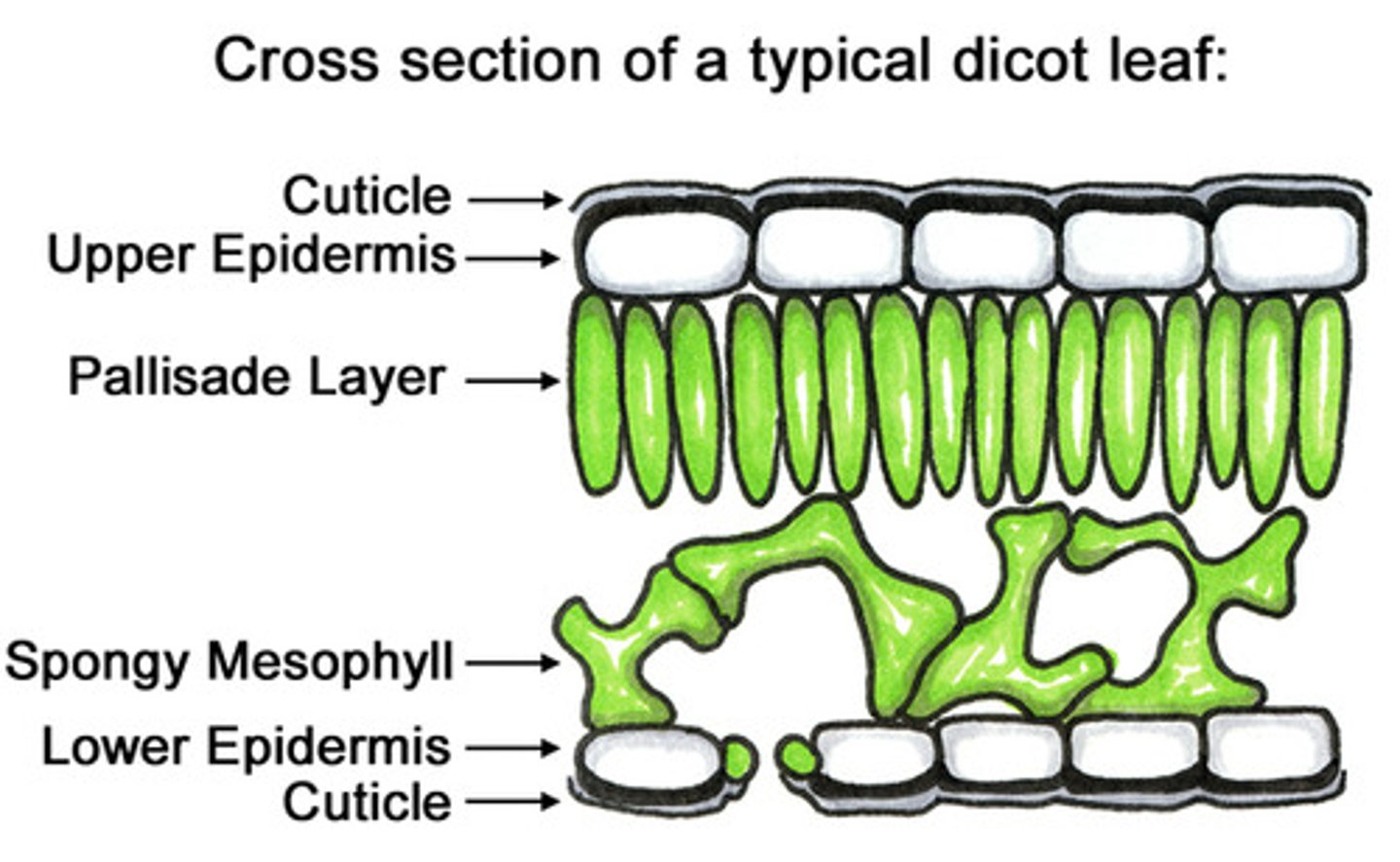
leaf cuticle
waxy protective layer that covers leaves.
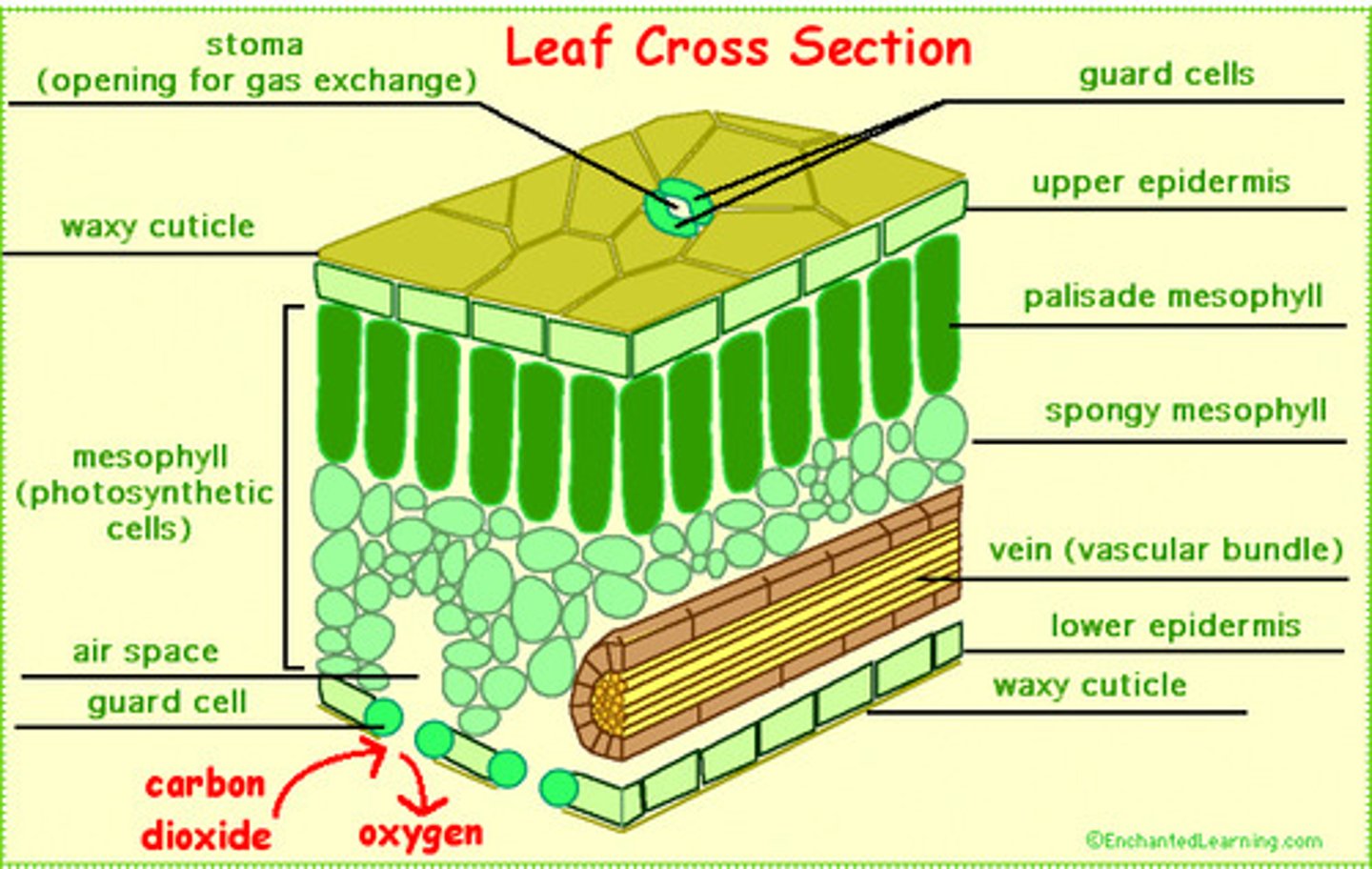
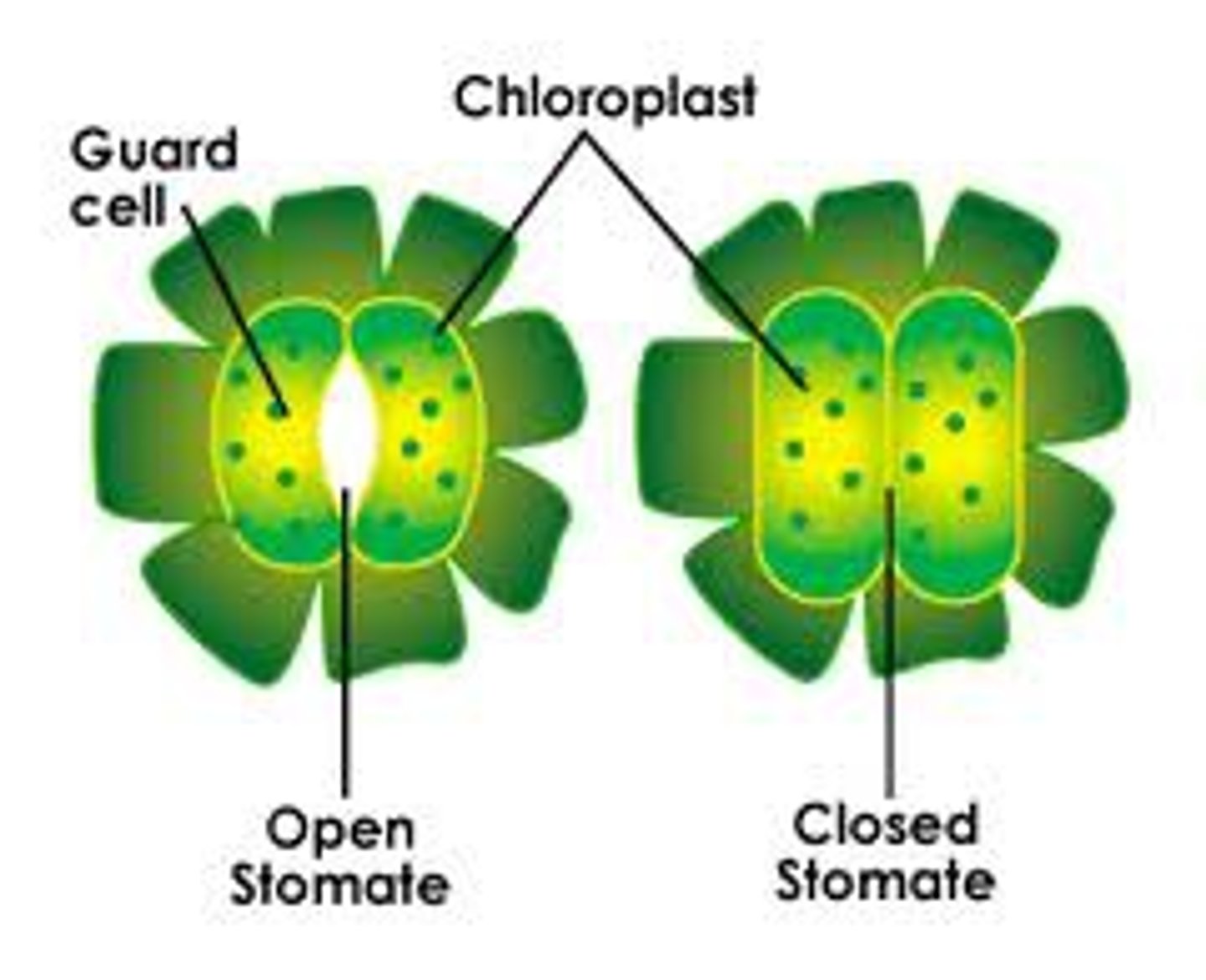
Stomata
the small openings on the undersides of most leaves through which oxygen and carbon dioxide can move
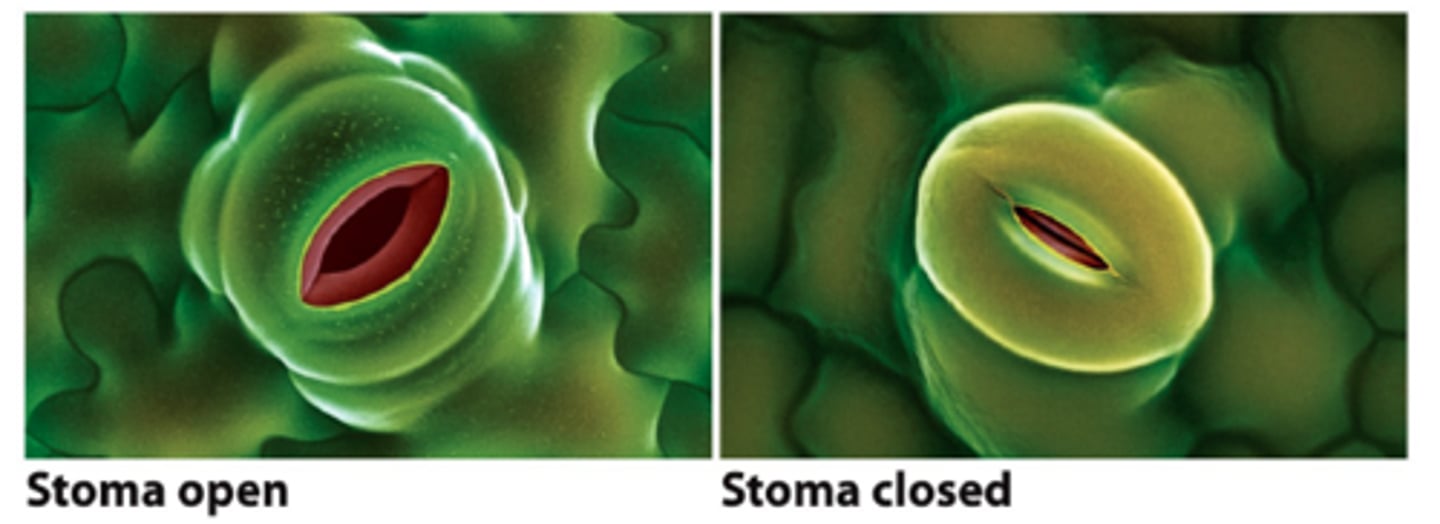
Guard Cells
The two cells that flank the stomatal pore and regulate the opening and closing of the pore.
Parenchyma Tissues
under the epidermis on both sides of the plant that do the photosynthesis
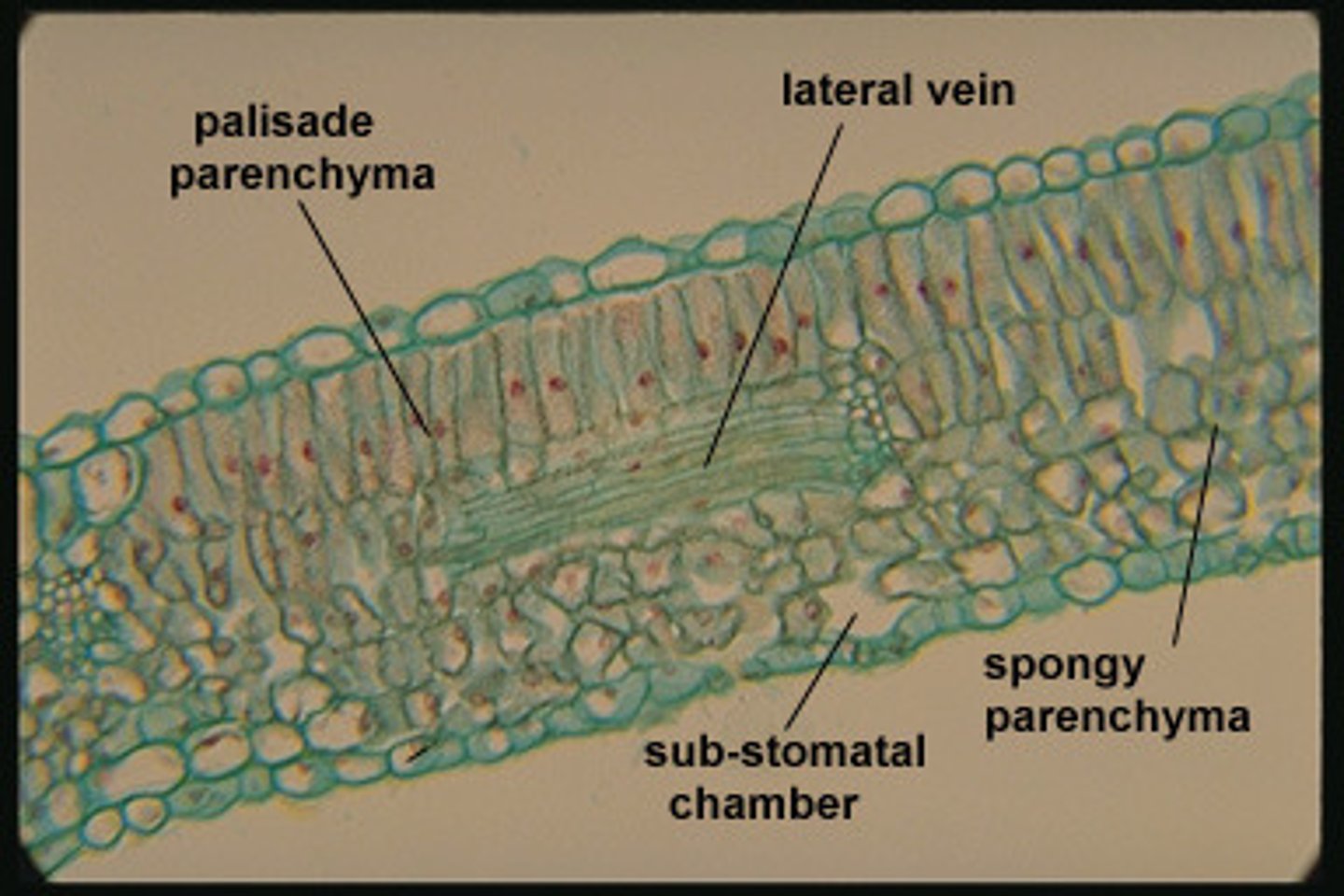
Palisade Mesophyll
layer of closely packed mesophyll cells under the epidermis that absorb light that enters the leaf
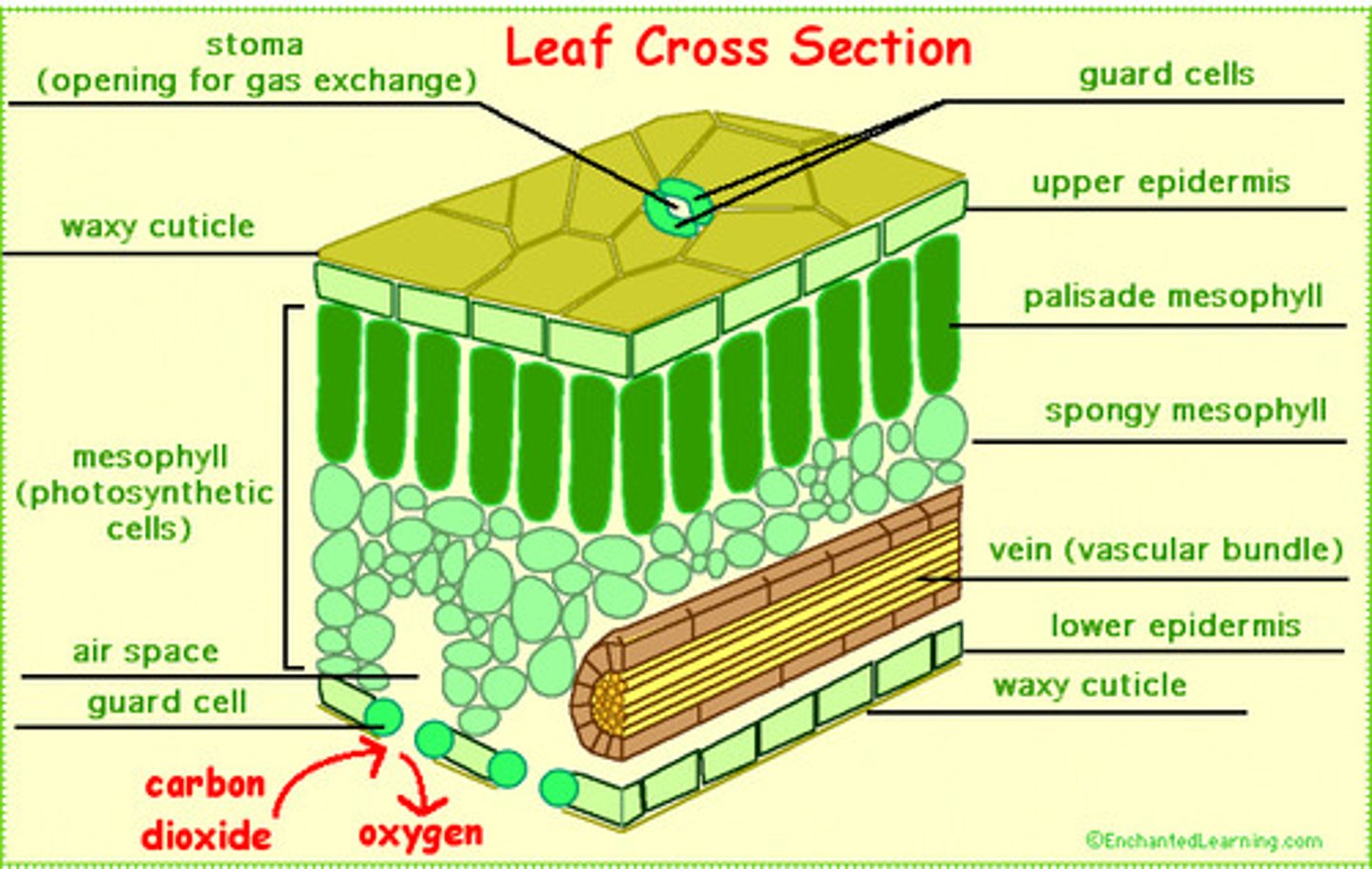
Spongy Mesophyll
Loose tissue beneath the palisade layer of a leaf; has many air spaces between its cells
Collenchyma
Cells with thicker walls to support the vein in the leaf
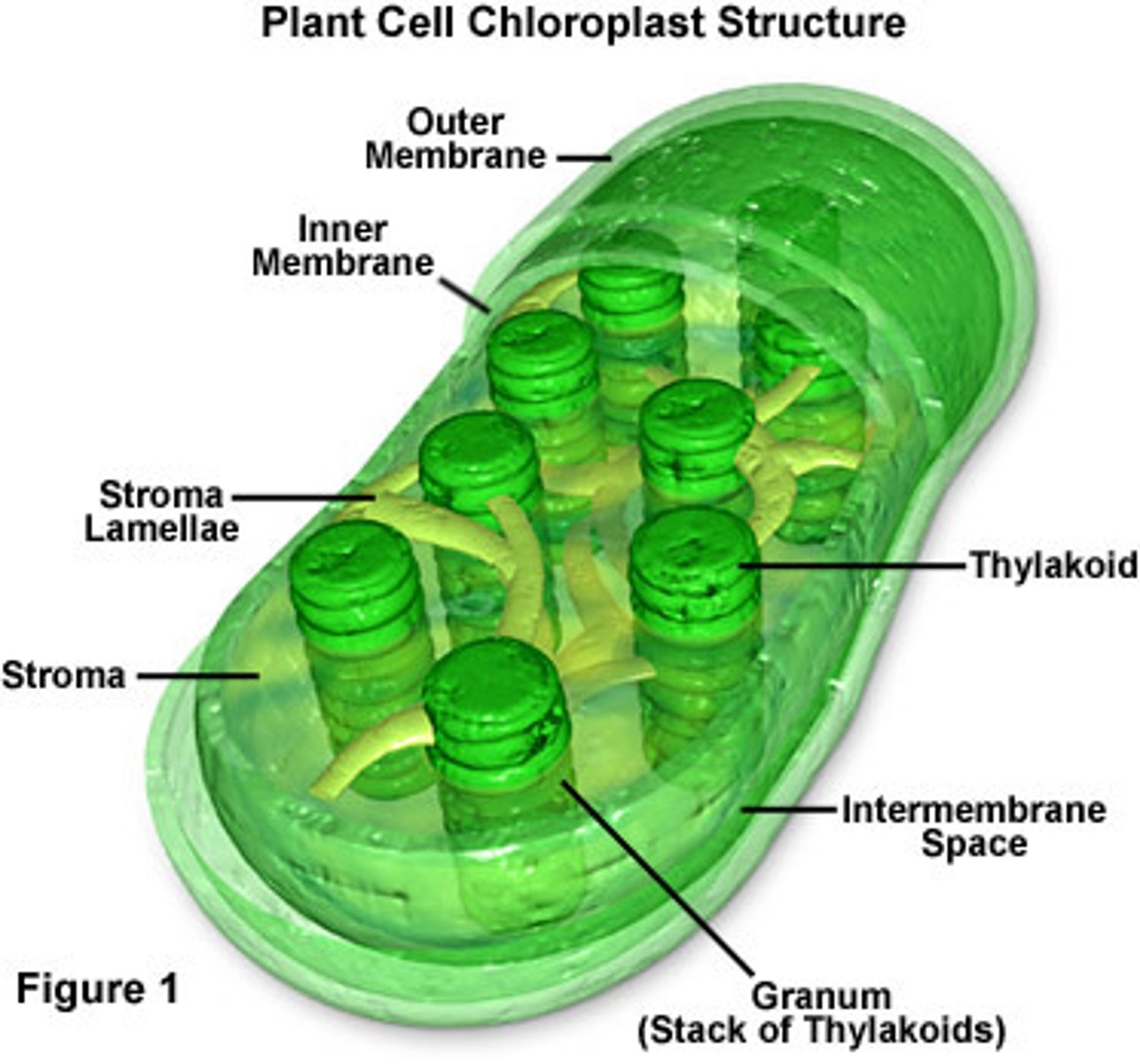
Plastids
hold pigments, starches and oils
Carotenoids
Accessory pigments that broaden the spectrum of colors that can drive photosynthesis.

Anthocyanins
red, purple, or blue pigments; responsible for those colors in some parts of trees and other plants

Deciduous plant
A plant that loses its leaves for winter.

abscission layer
layer of cells at the petiole that seals off a leaf from the vascular system
involved in the loss of leaves of deciduous trees
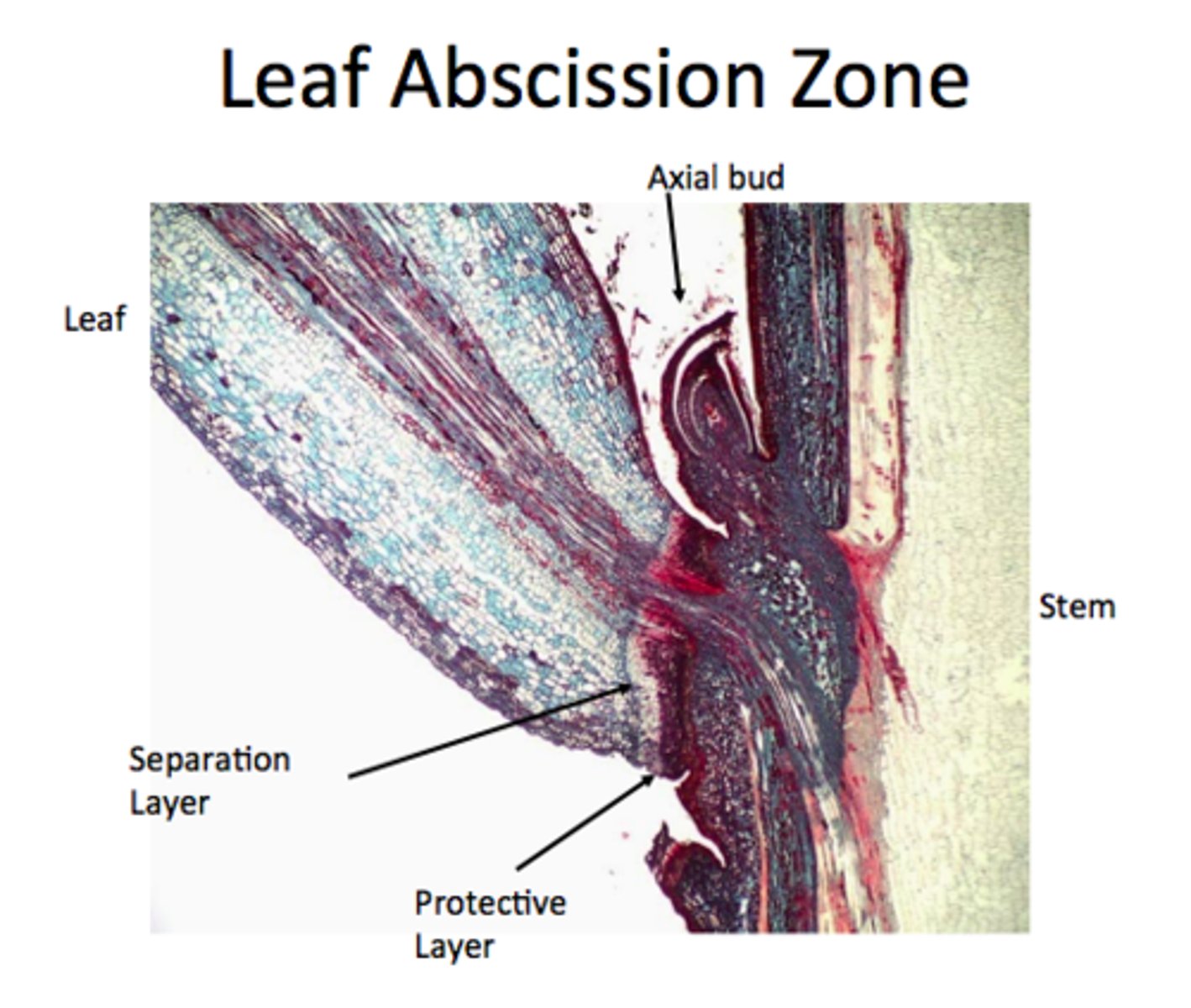
Tannic Acid
product of the breakdown of plant cell contents

roots
Absorbs water and minerals from the ground. Anchors plant in ground. Used as a place for food storage.
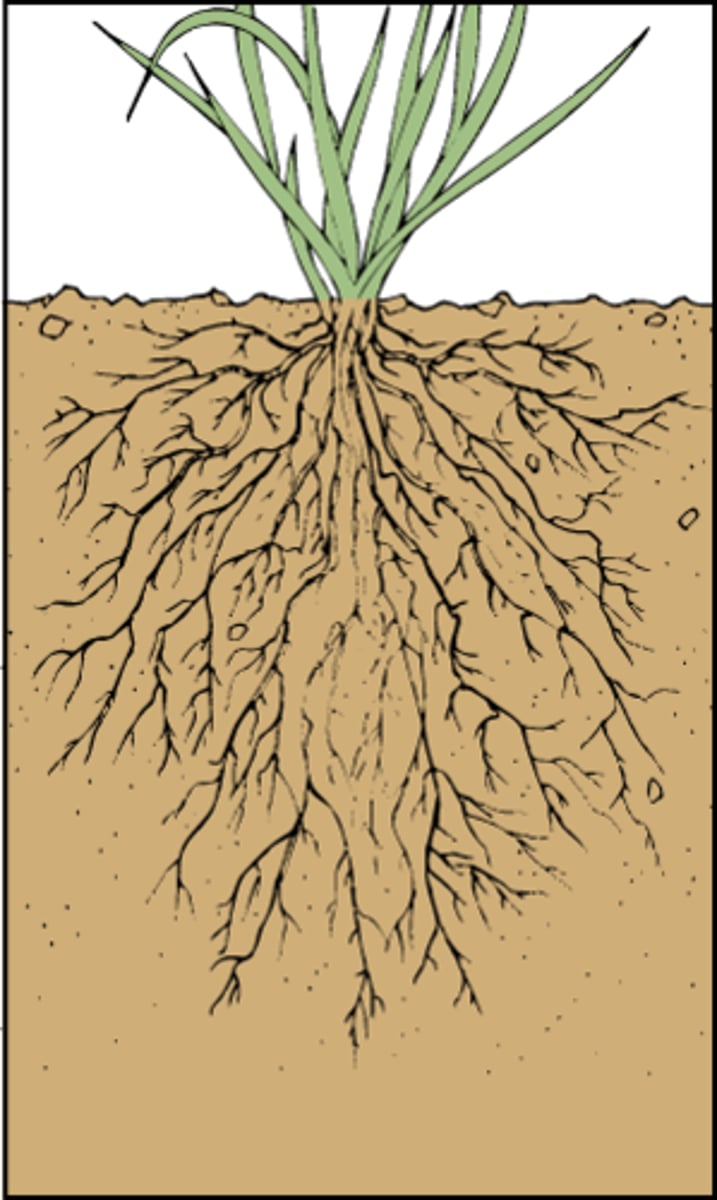
Fibrous root systems
Have fine branches
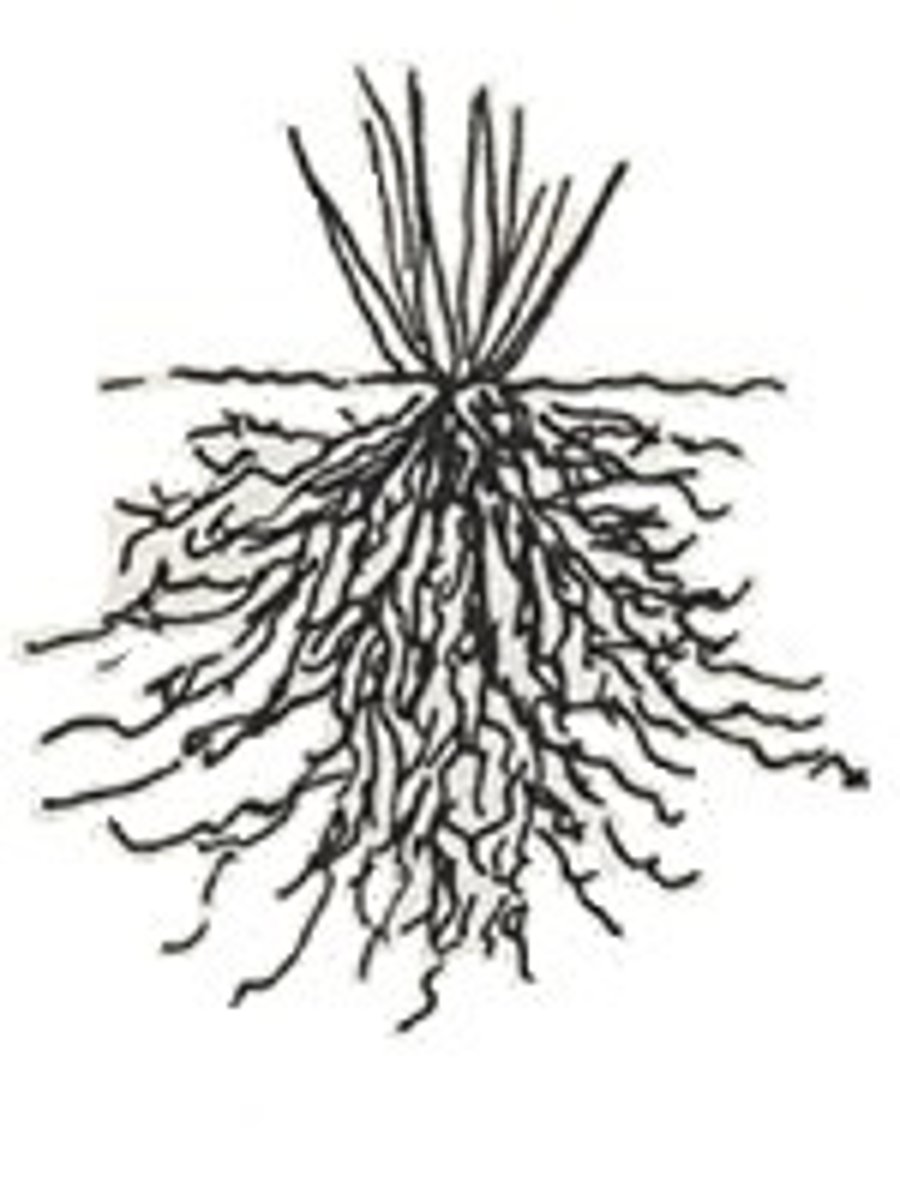
Taproot System
A root system consisting of one prominent main root with smaller lateral roots branching from it
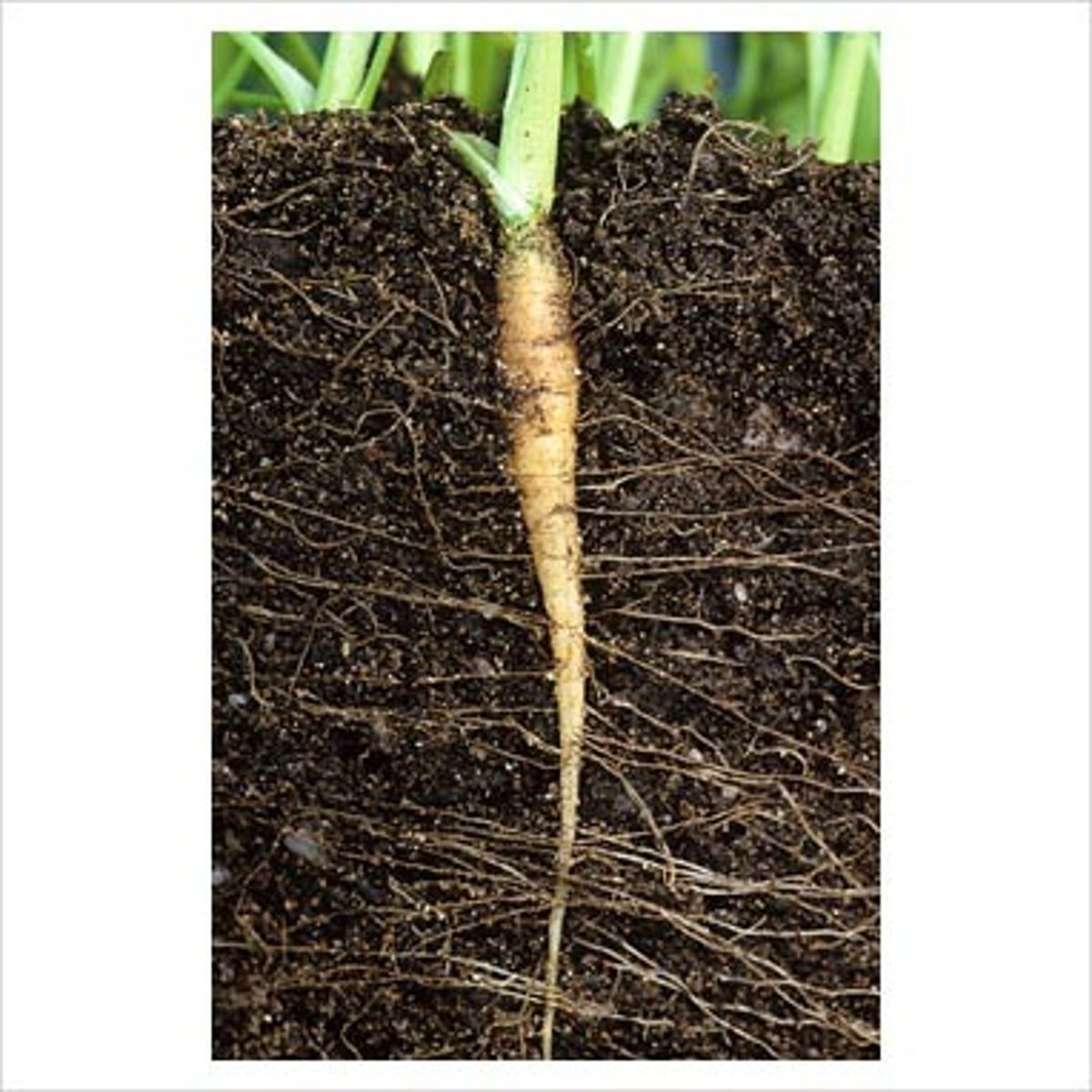

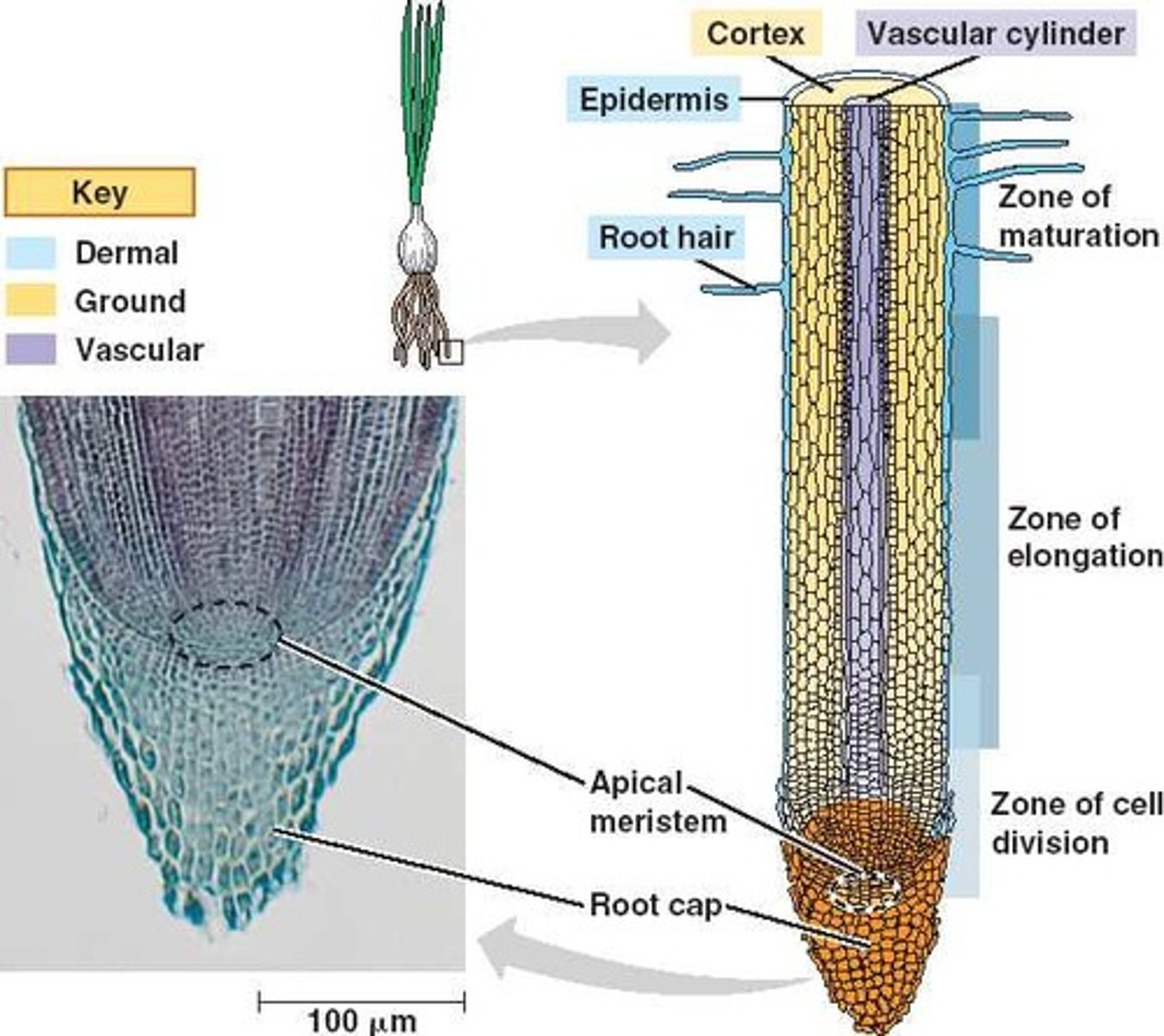
Primary Root
Main root. has 4 main regions
Root Cap
Meristematic Region
Elongation Region
Maturation Regoin
Root Cap
Protective layer of dead thick walled cells that cover the tip of the root.
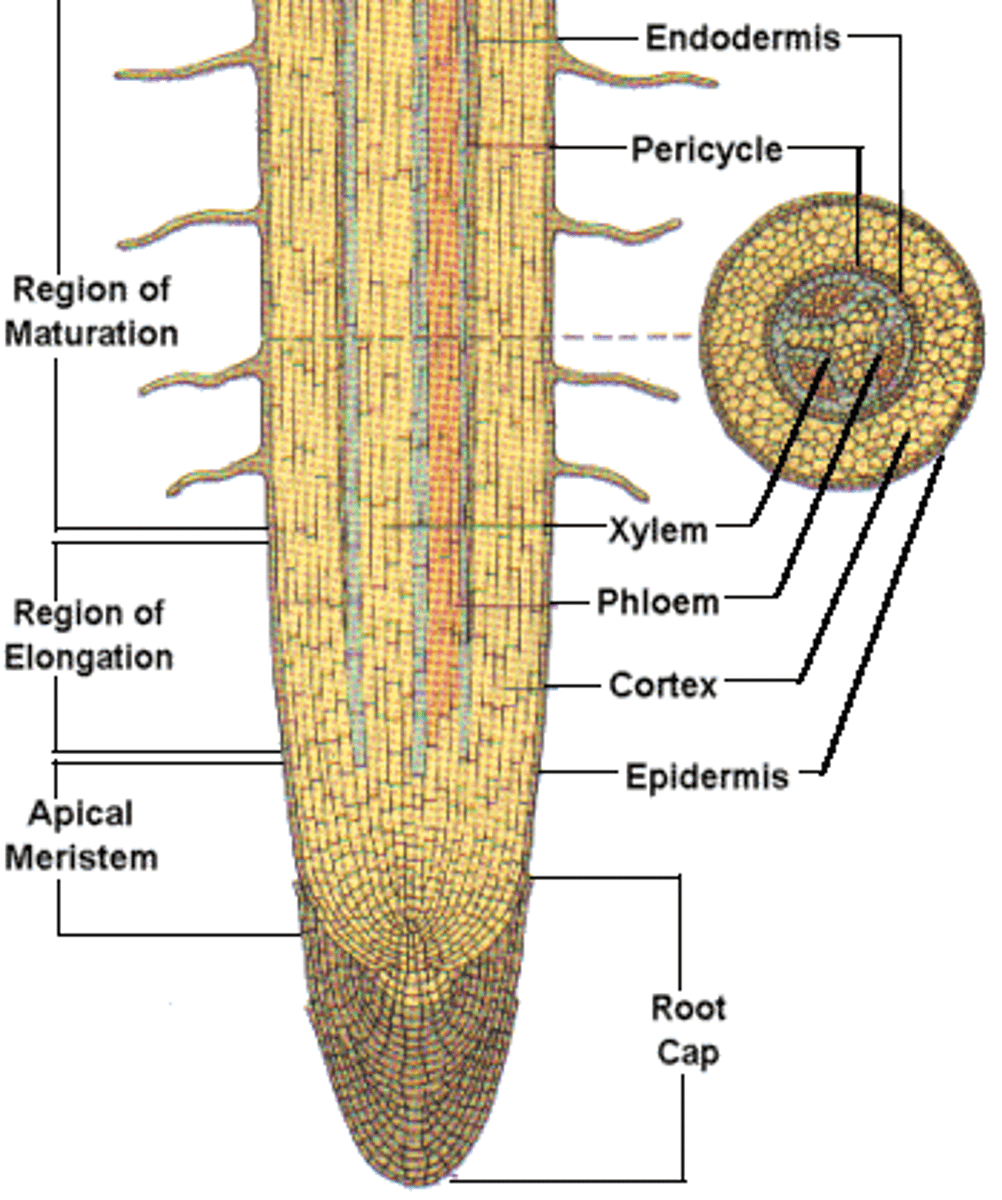
Meristematic Region
Where the tiny undifferentiated cells carry on mitosis.
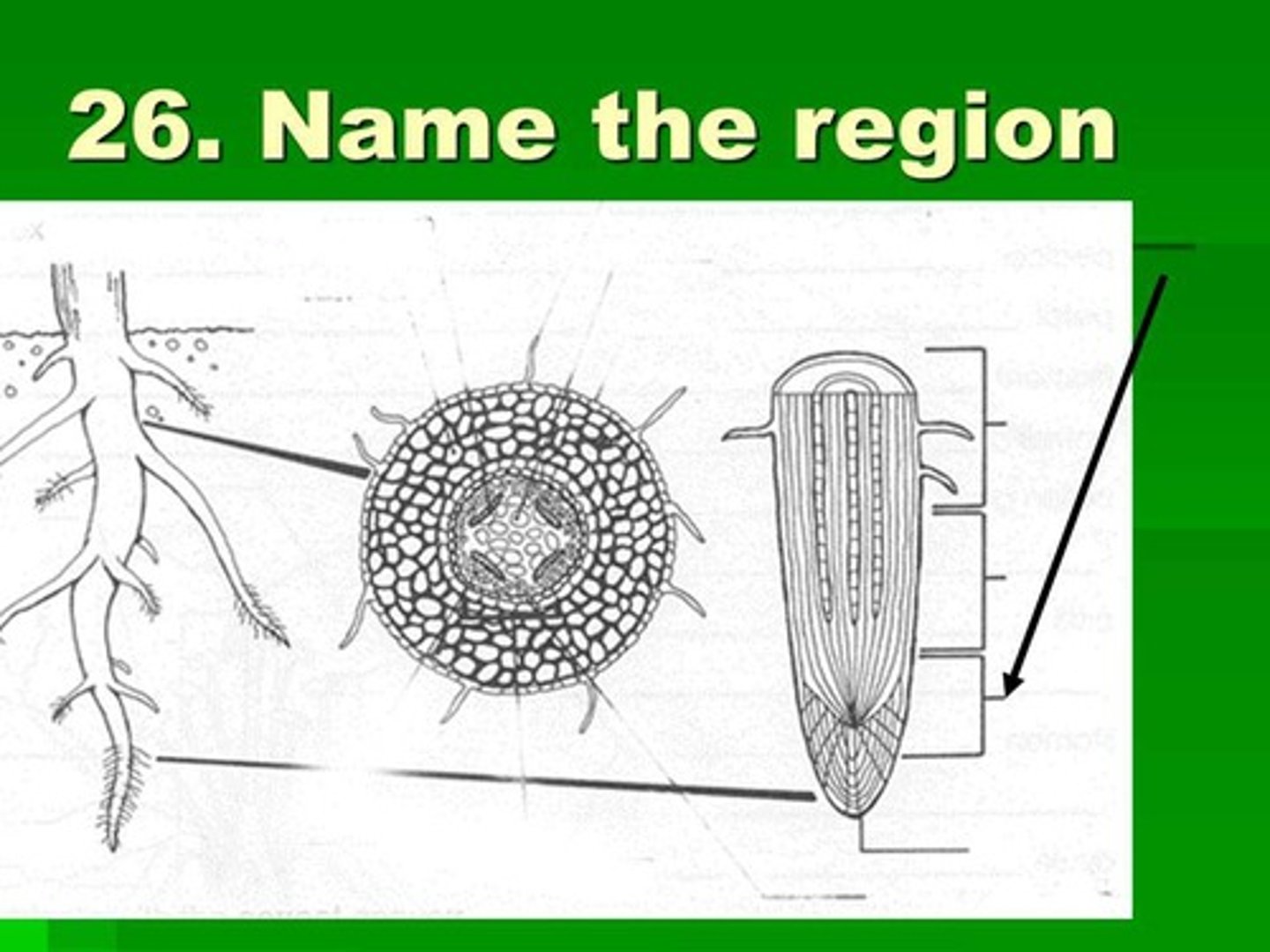
Elongation region
region in root where cells elongate, grow in size and increase root length
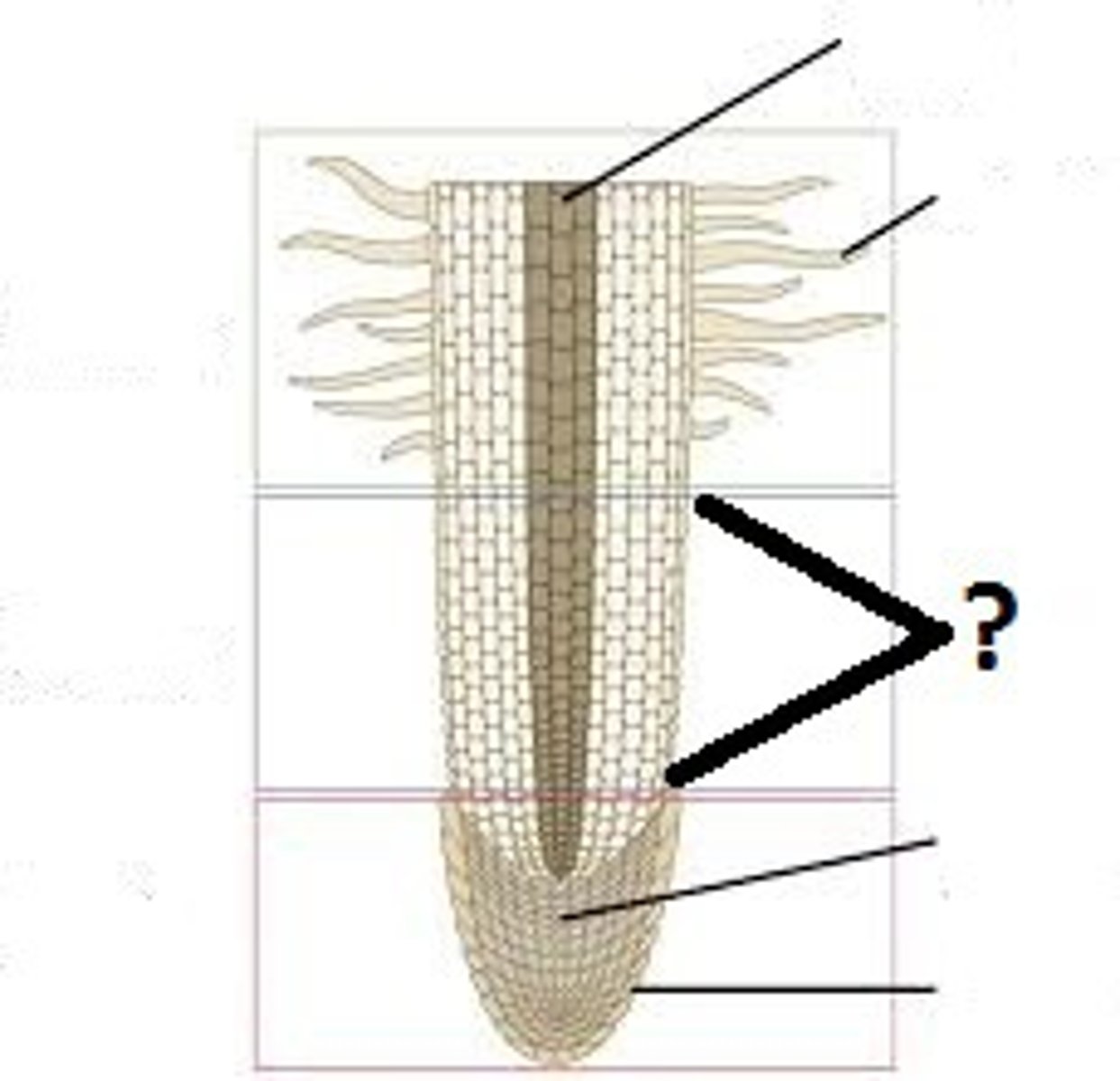
maturation Region
Where the cells are becoming fully differentiated
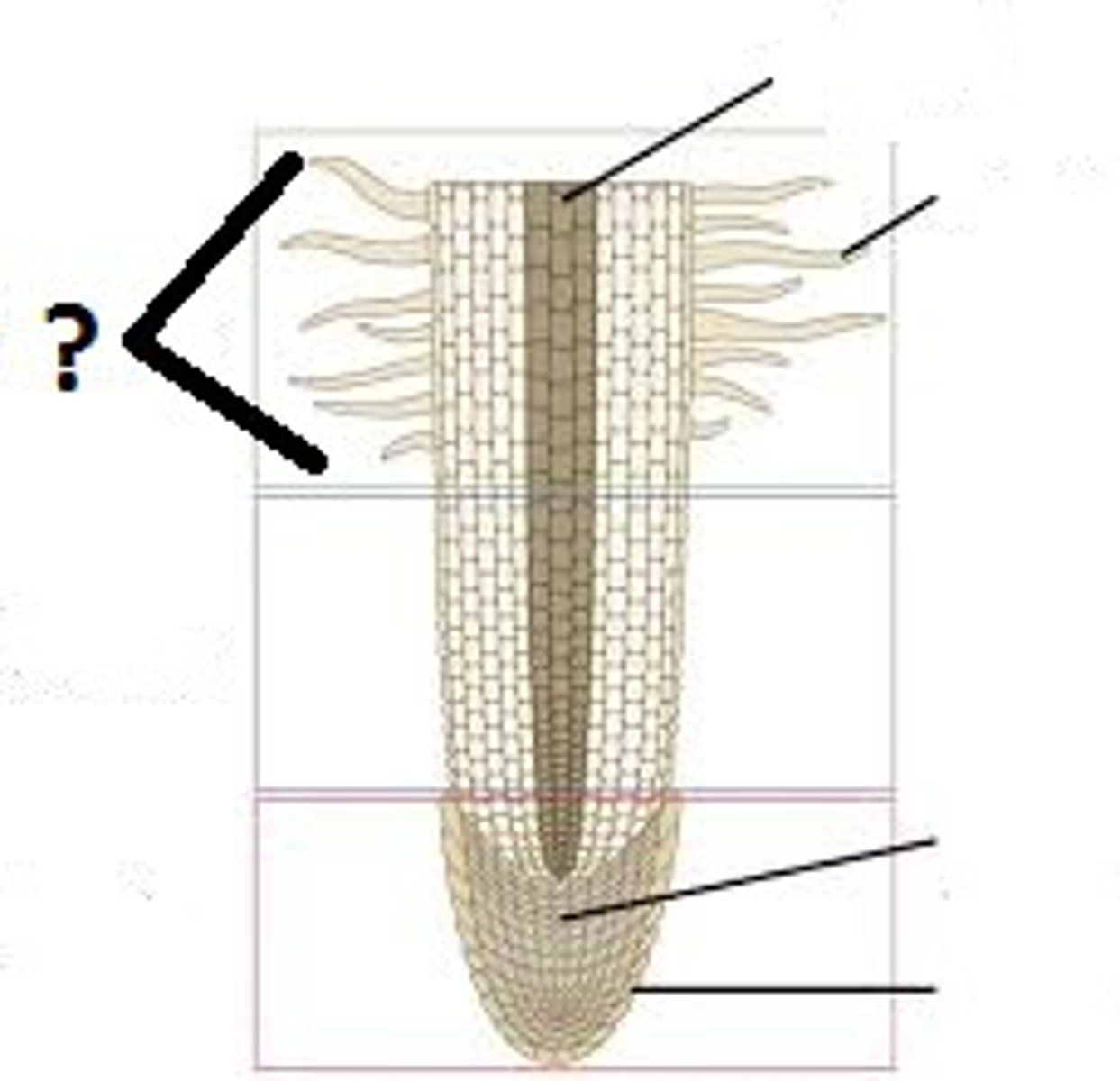
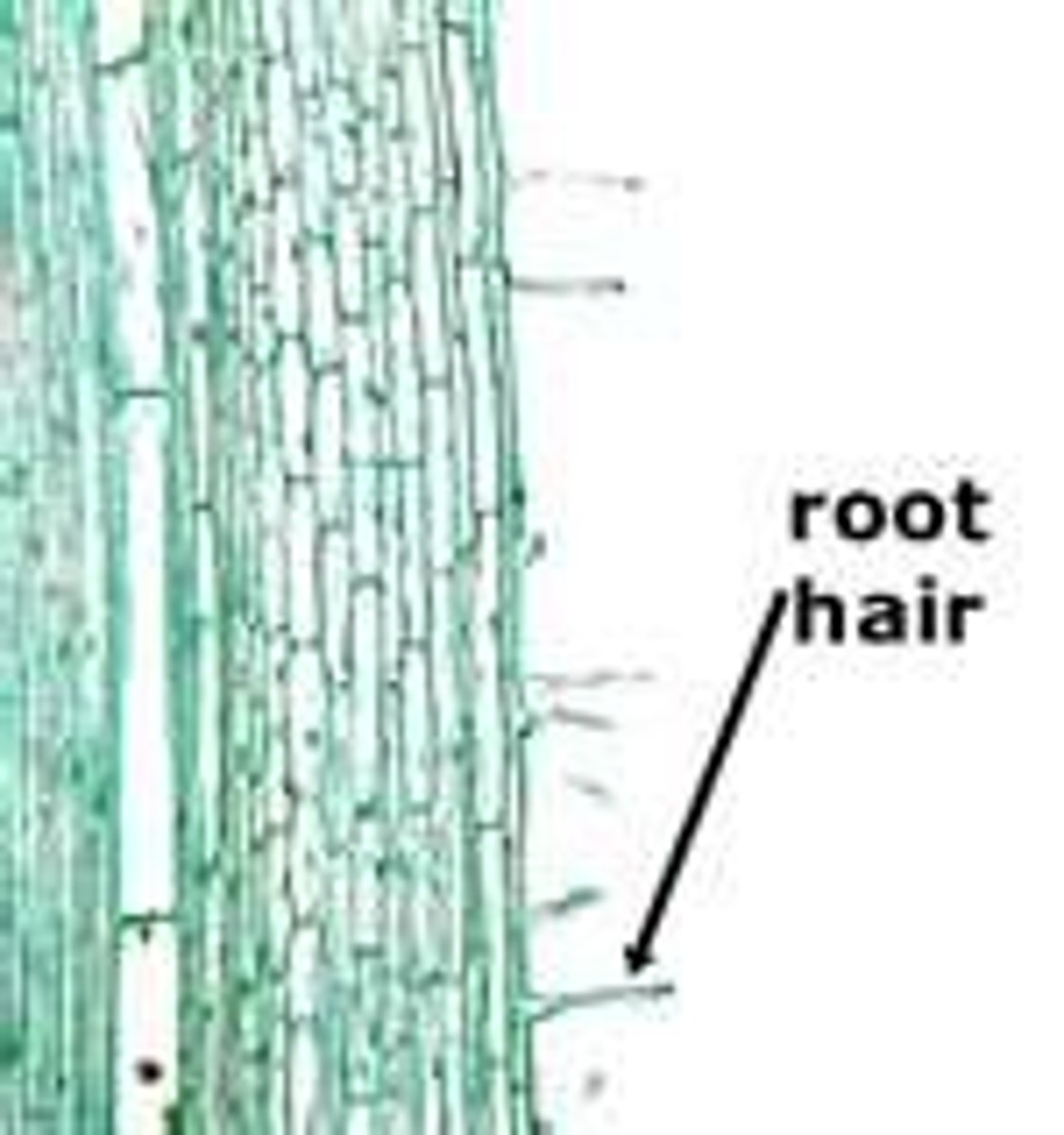
Root Hairs
Root hairs are tiny hair- like things the root grows to drink up water.
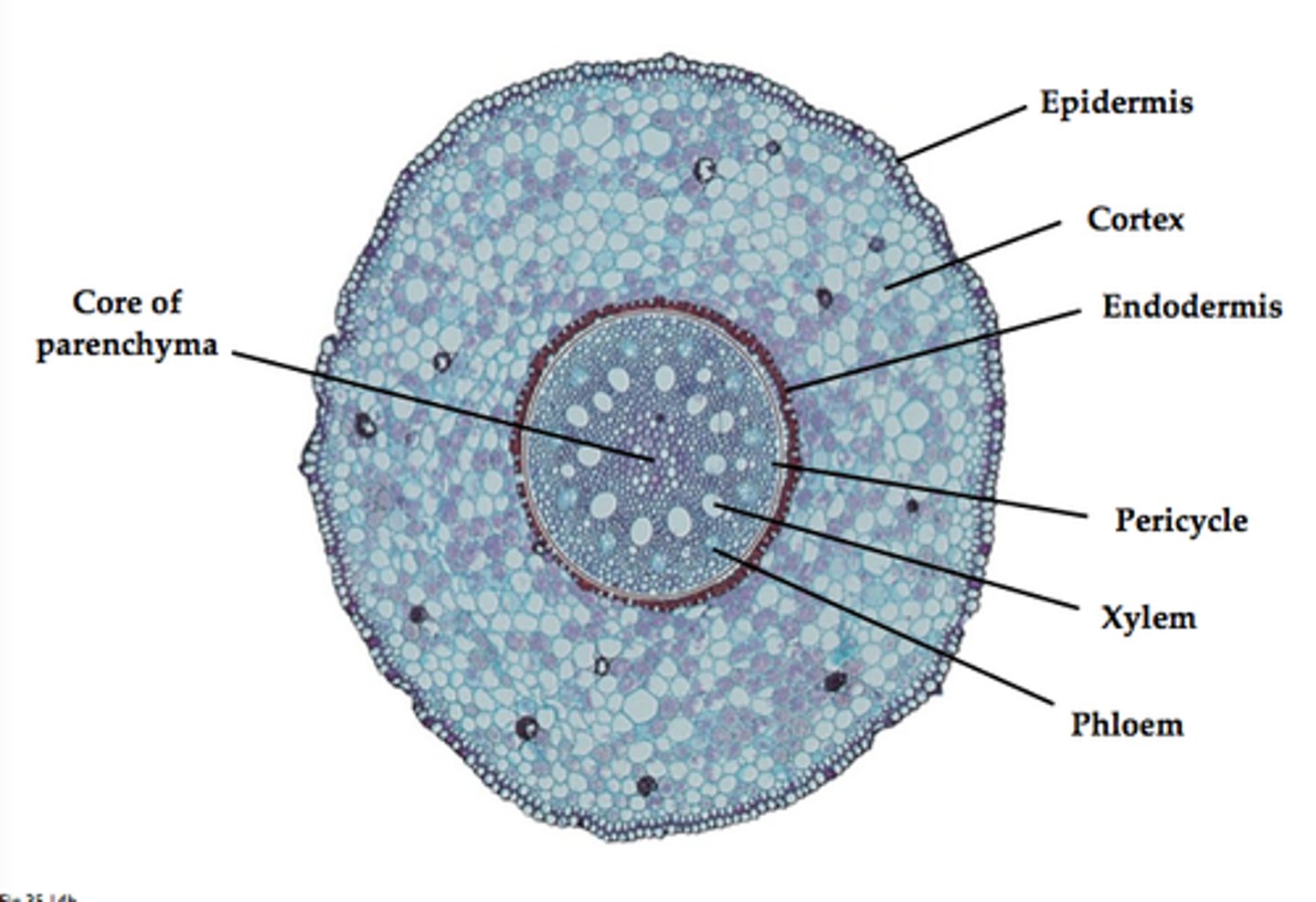
Cortex
Cells inside the epidermis where substances are stored for later use
Stems
Can be woody or herbaceous. Perform three basic functions
Support
conduct water and nutrients
photosynthesis
Herbaceous stems
In dicots and monocots, does not have bark,
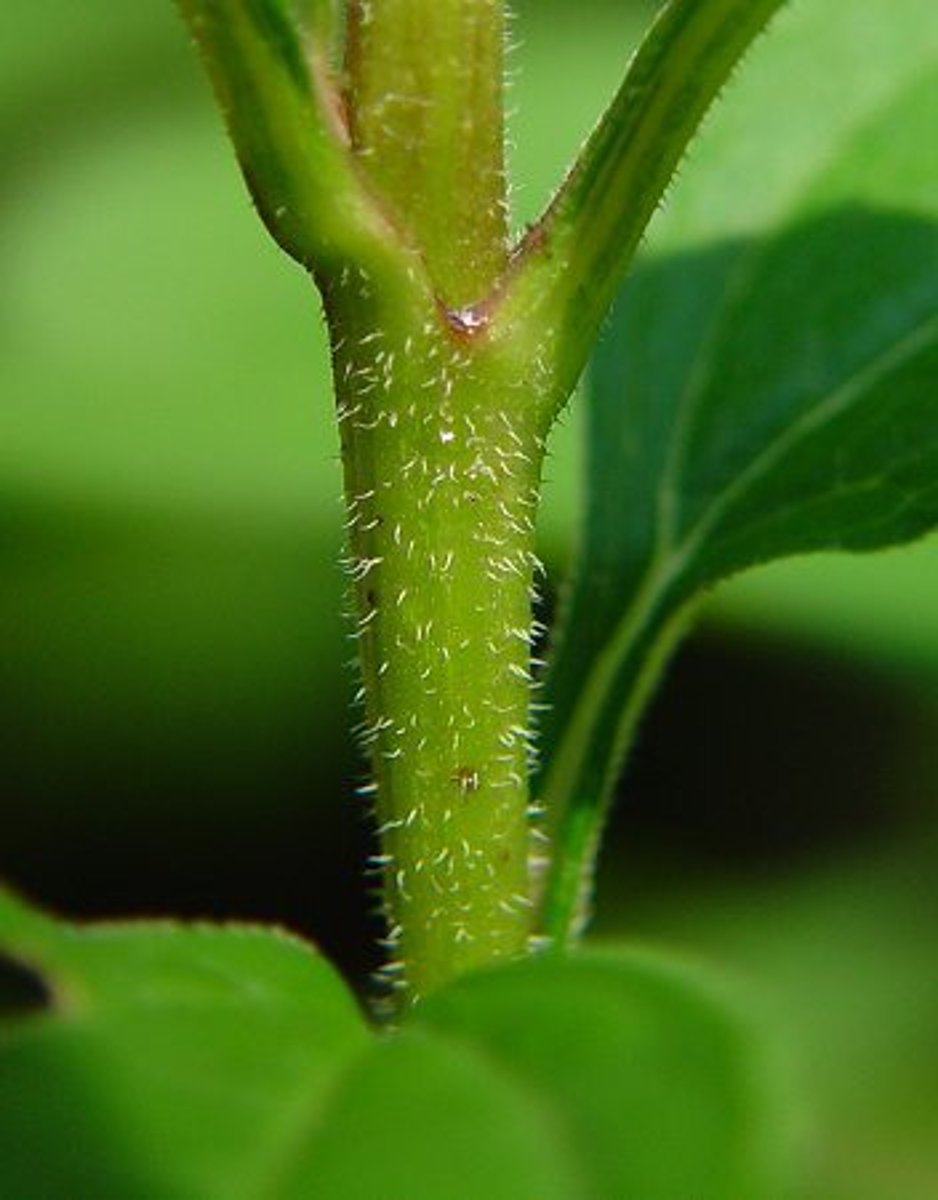

Woody stems
Rigid stems made of wood and bark found on trees and shrubs, composed of two layers, the inner bark and the outer bark.

Inner bark
Contains phloem and cortex tissue.
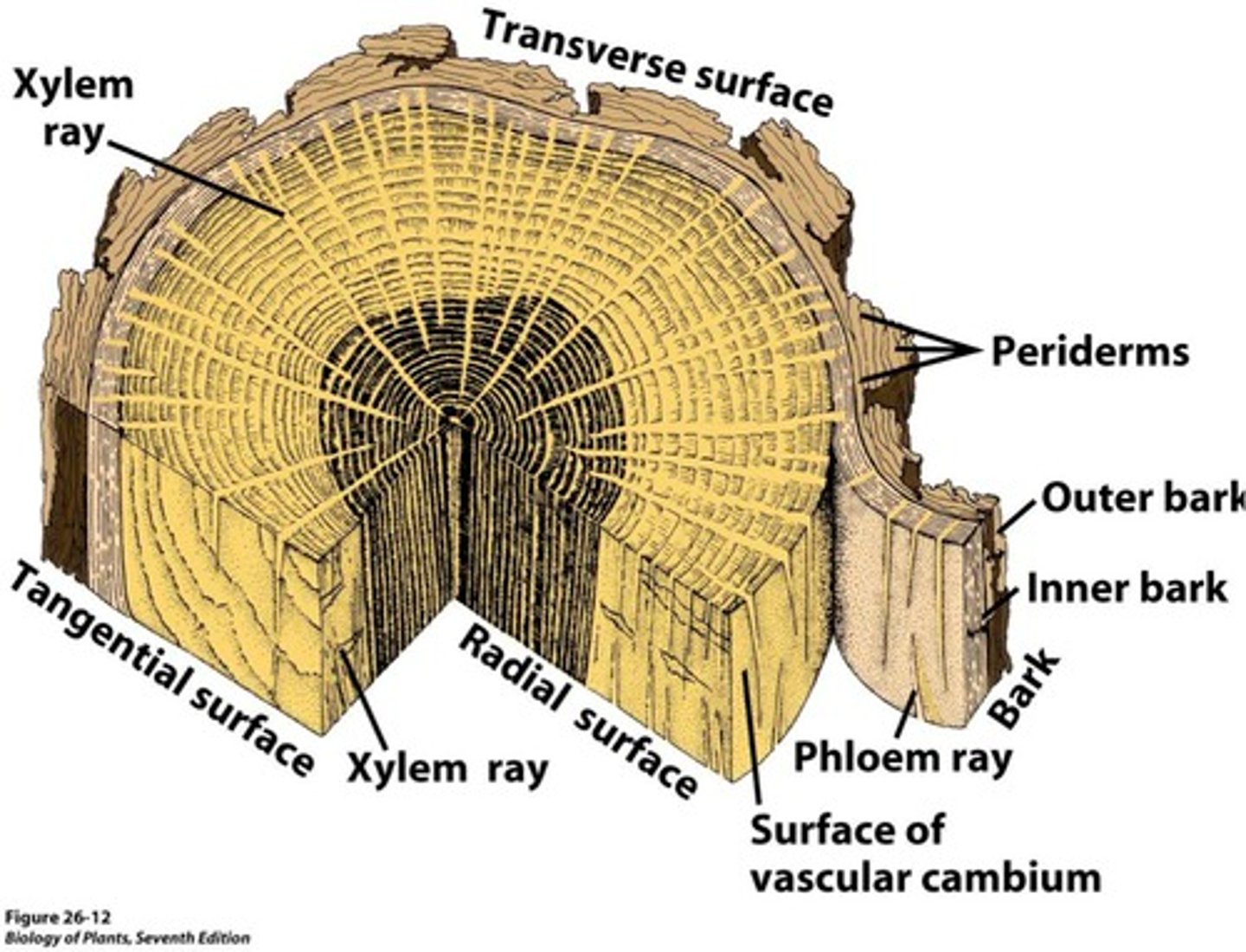
Cork Cambium
Produces outer bark, a layer in between the inner and outer bark that continually produces cork cells which die and become the outer bark.
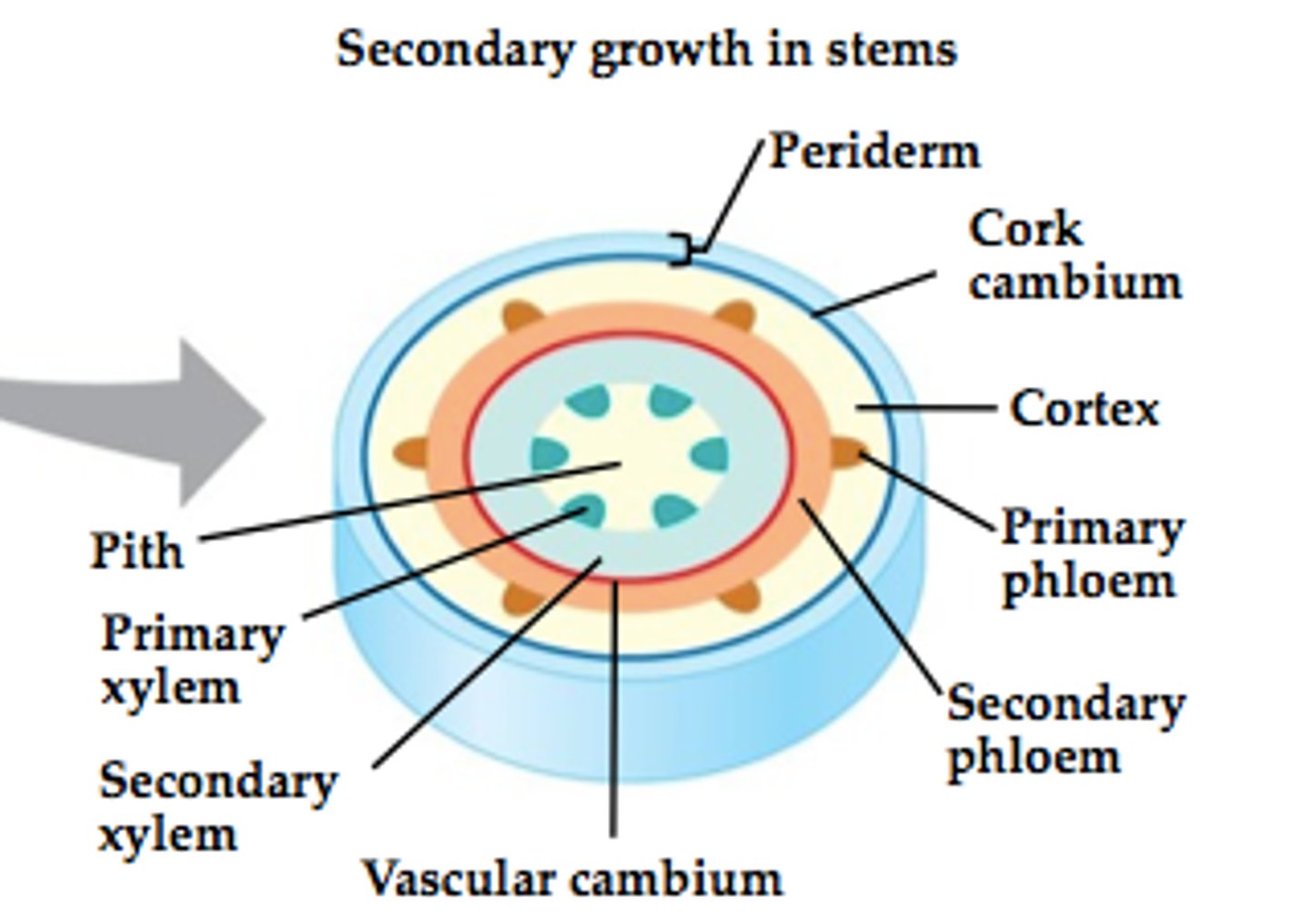
Outer Bark
Inactive cells that form protection for inner bark.

Vascular Cambium
adds layers of vascular tissue called secondary xylem (wood) and secondary phloem
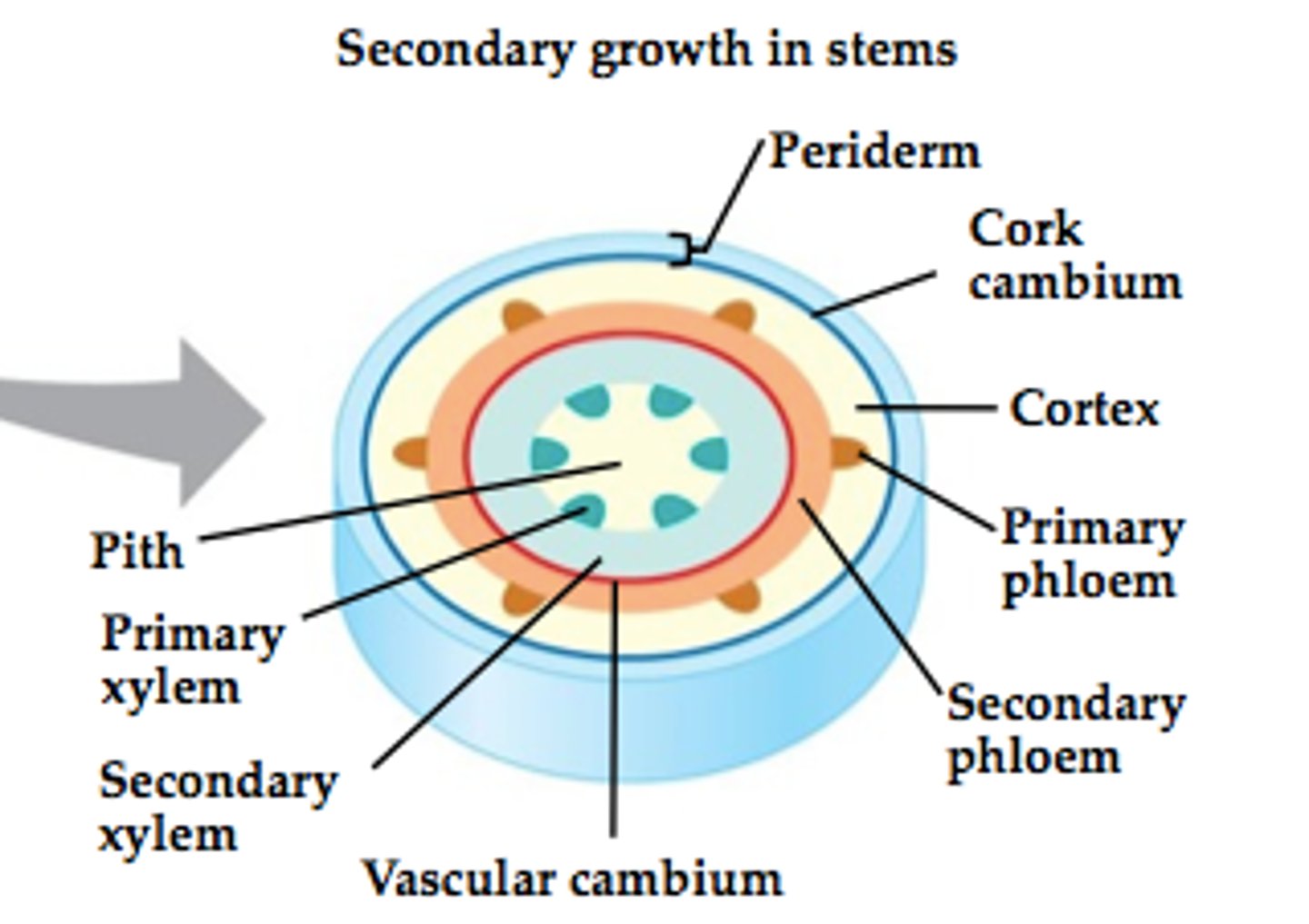
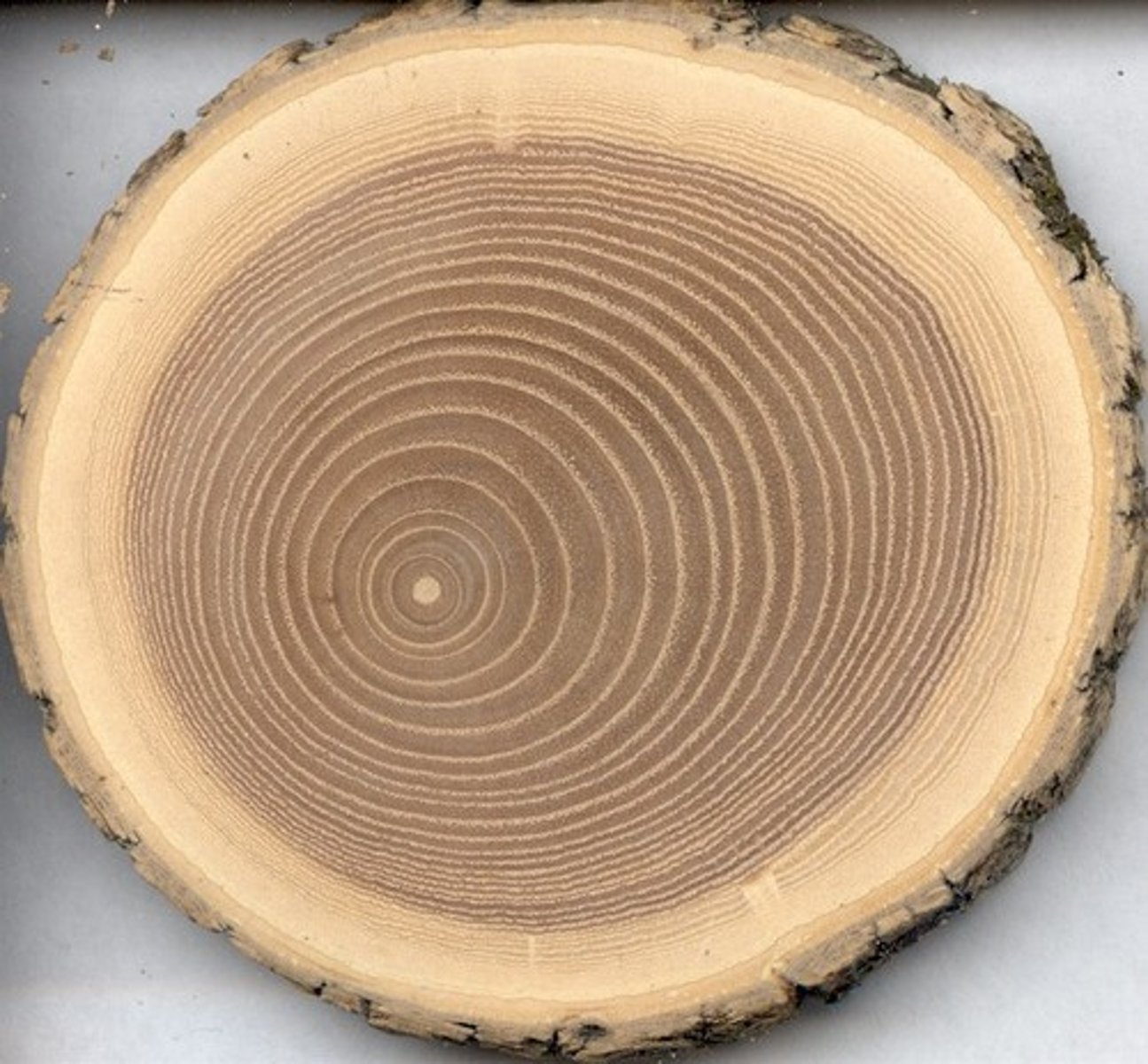
Annual Growth Rings
Periods of faster/slower growth result in distinct layers of xylem.

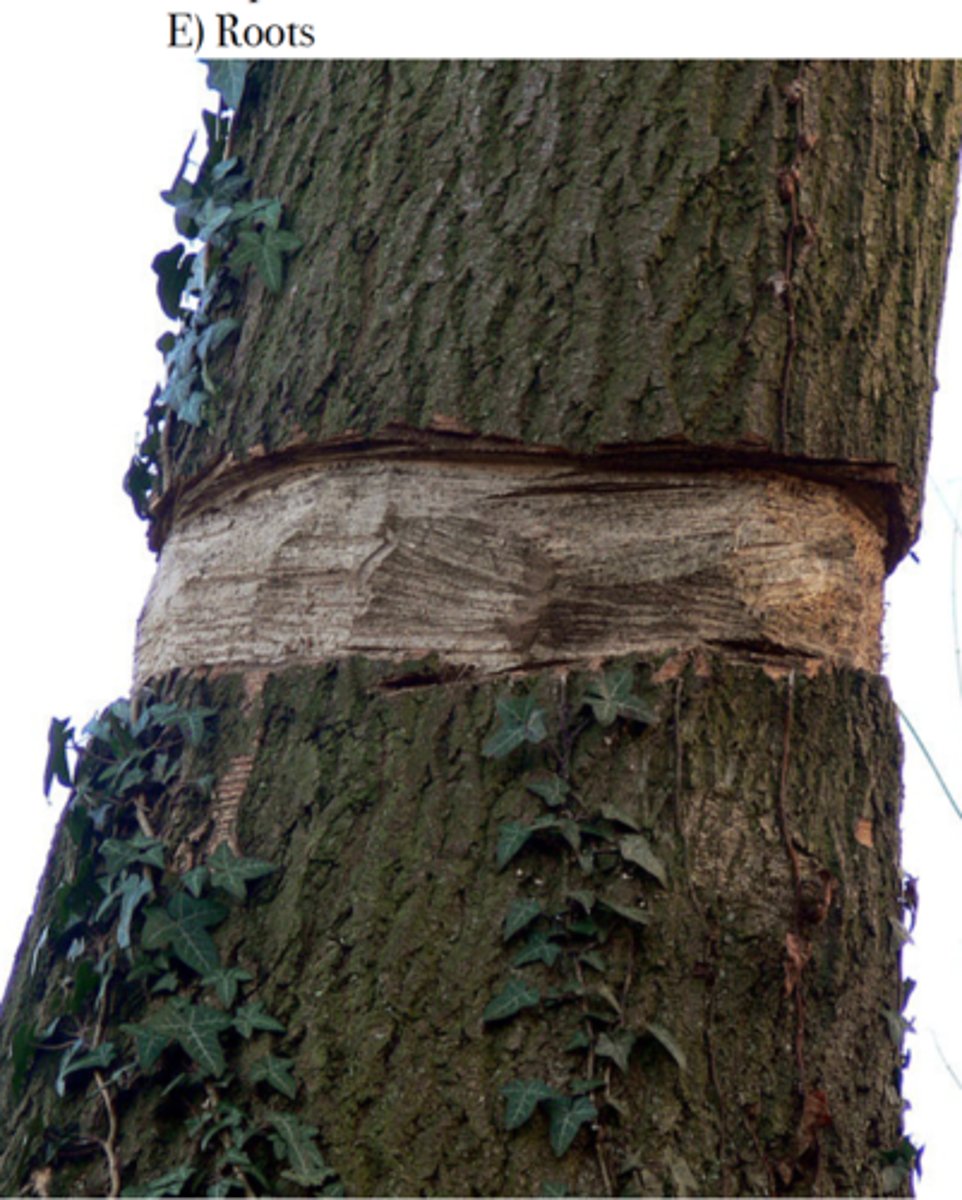
Girdling
The process of cutting away a ring of inner and outer bark all the way around a tree trunk.

bryophytes
nonvascular plants
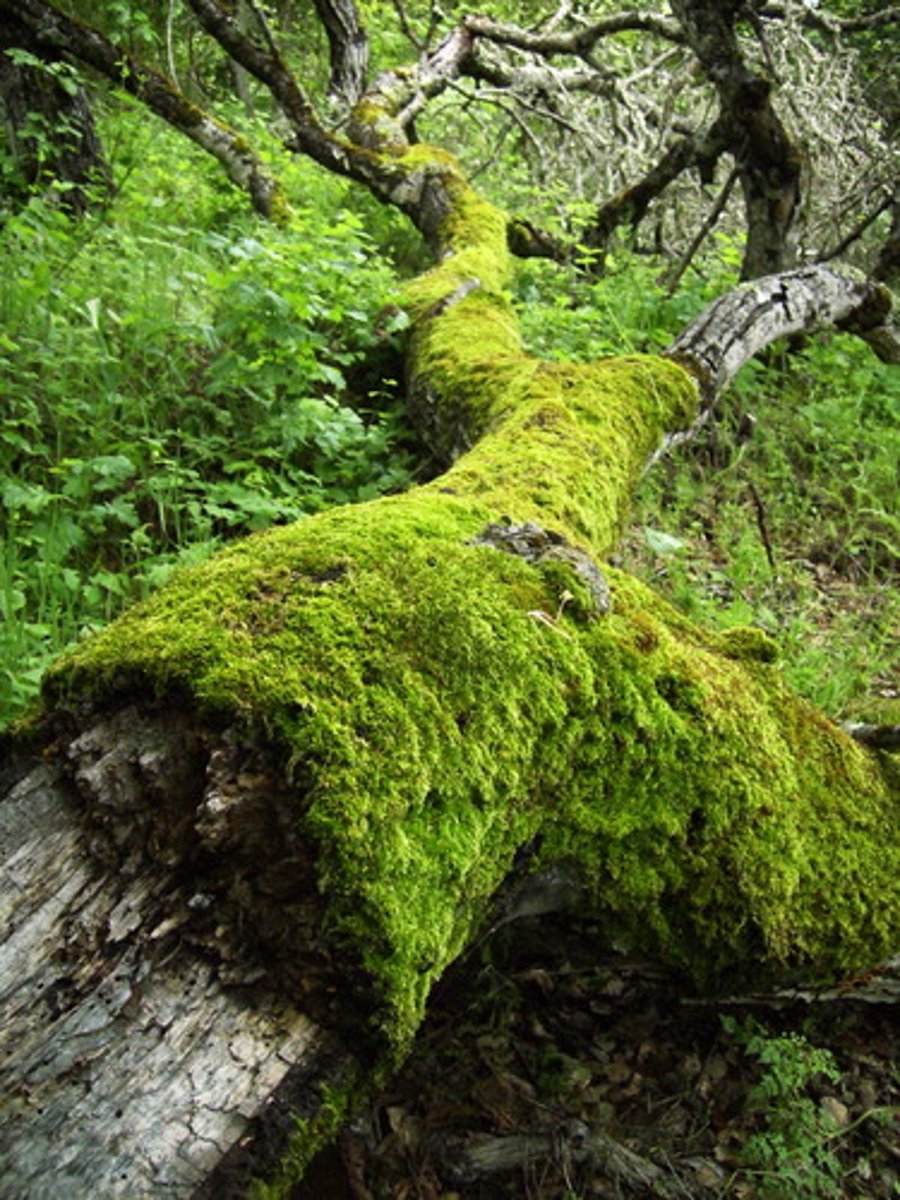

Moss
soft, small, green and nonvascular and are found on the ground near water tightly packed tiny plants composed of leafy shoots and rhizoids

Tracheophytes
Vascular plants

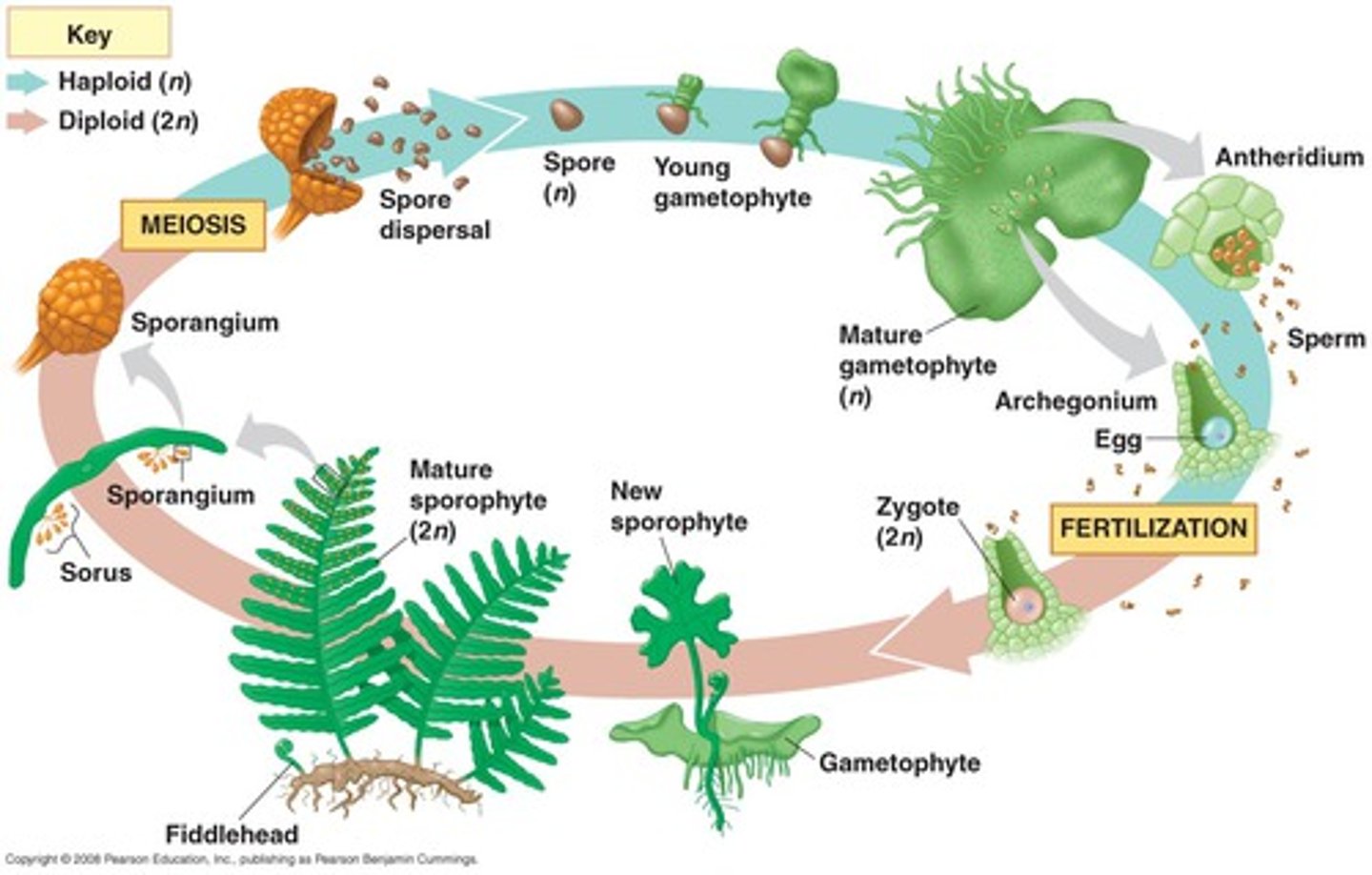
Alternation of generations
A life cycle in which there is both a multicellular diploid form and a multicellular haploid form.
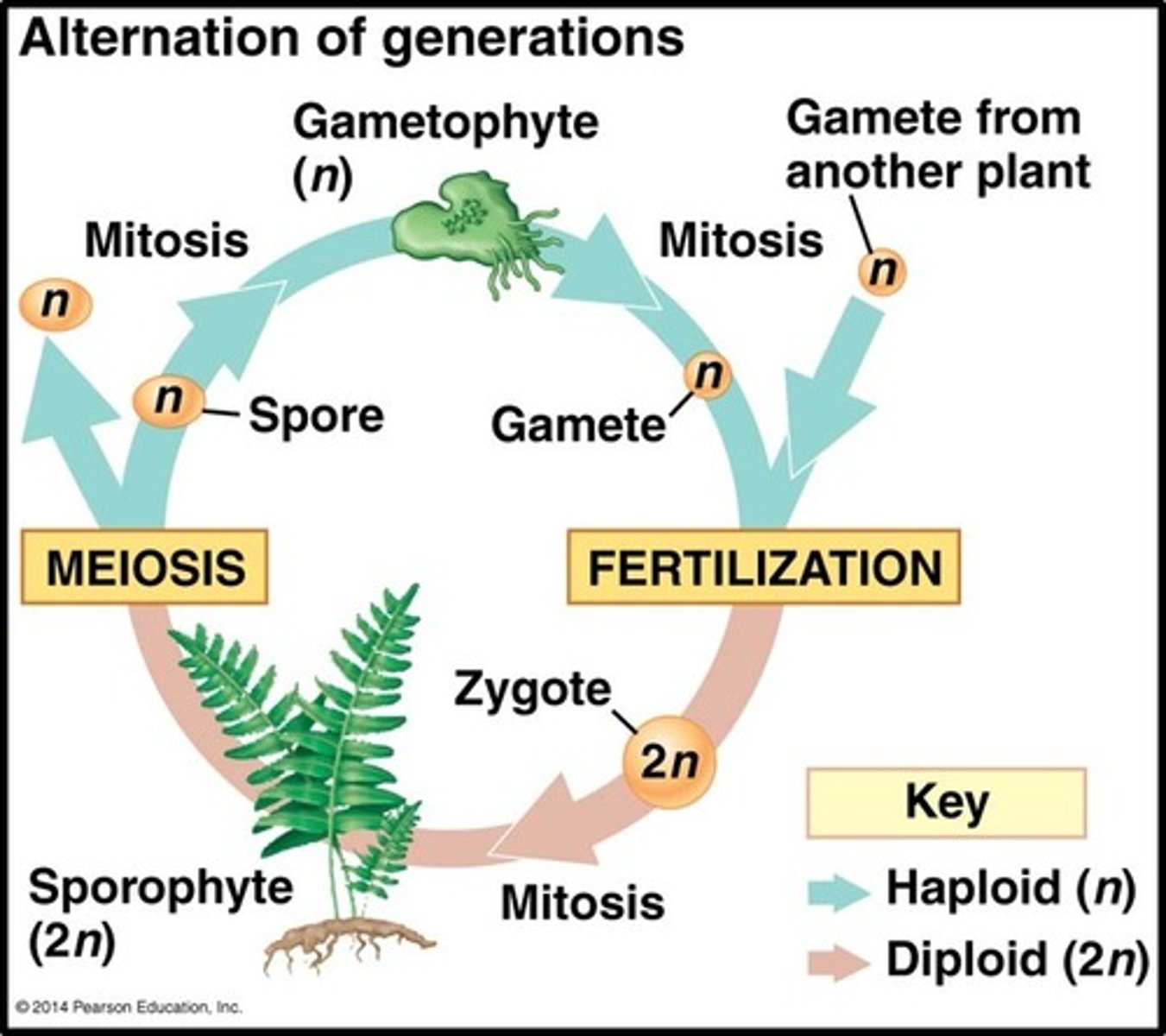
gametophyte generation
a life cycle stage in plants in which a haploid sex cell is produced by mitosis
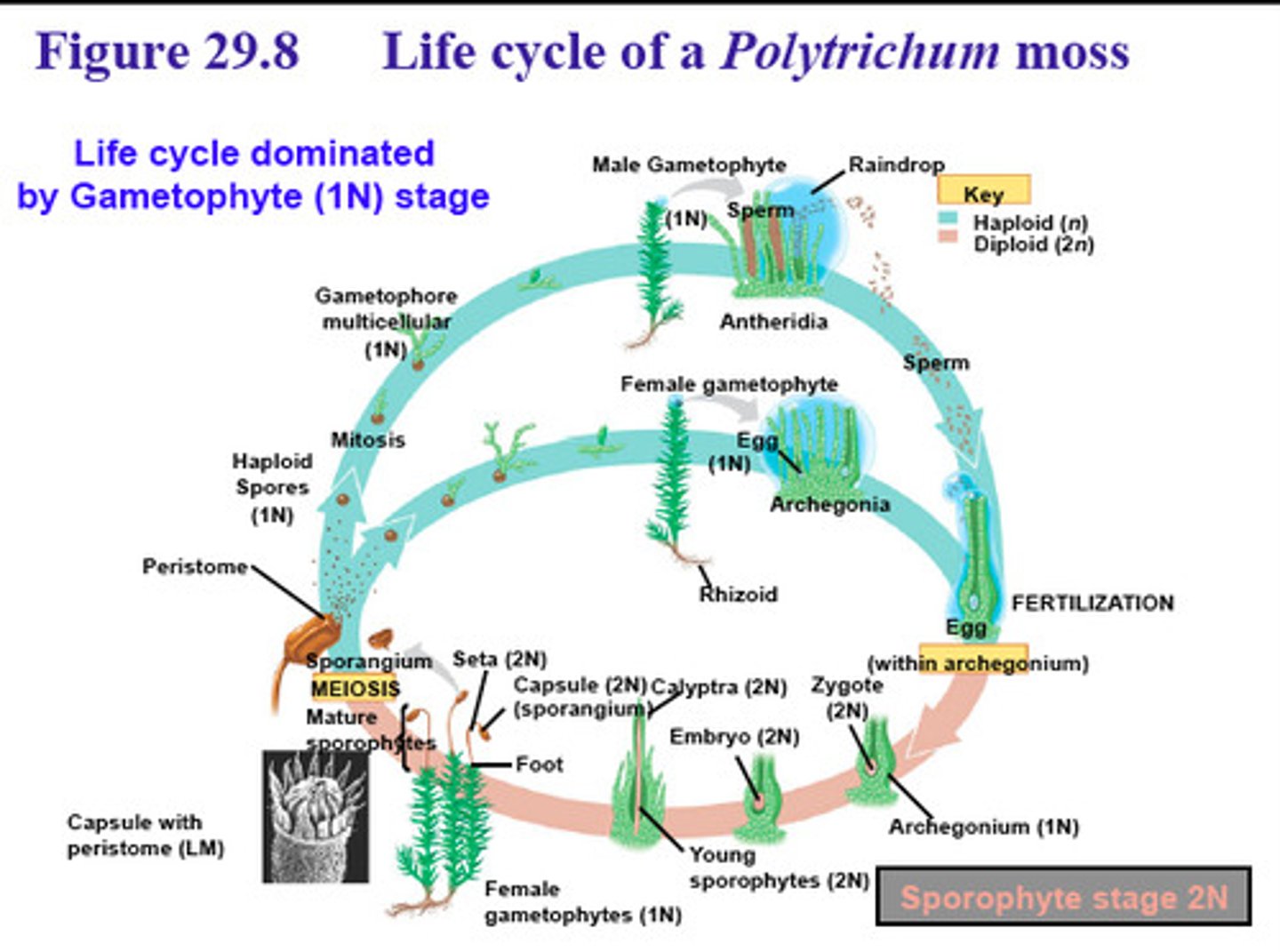
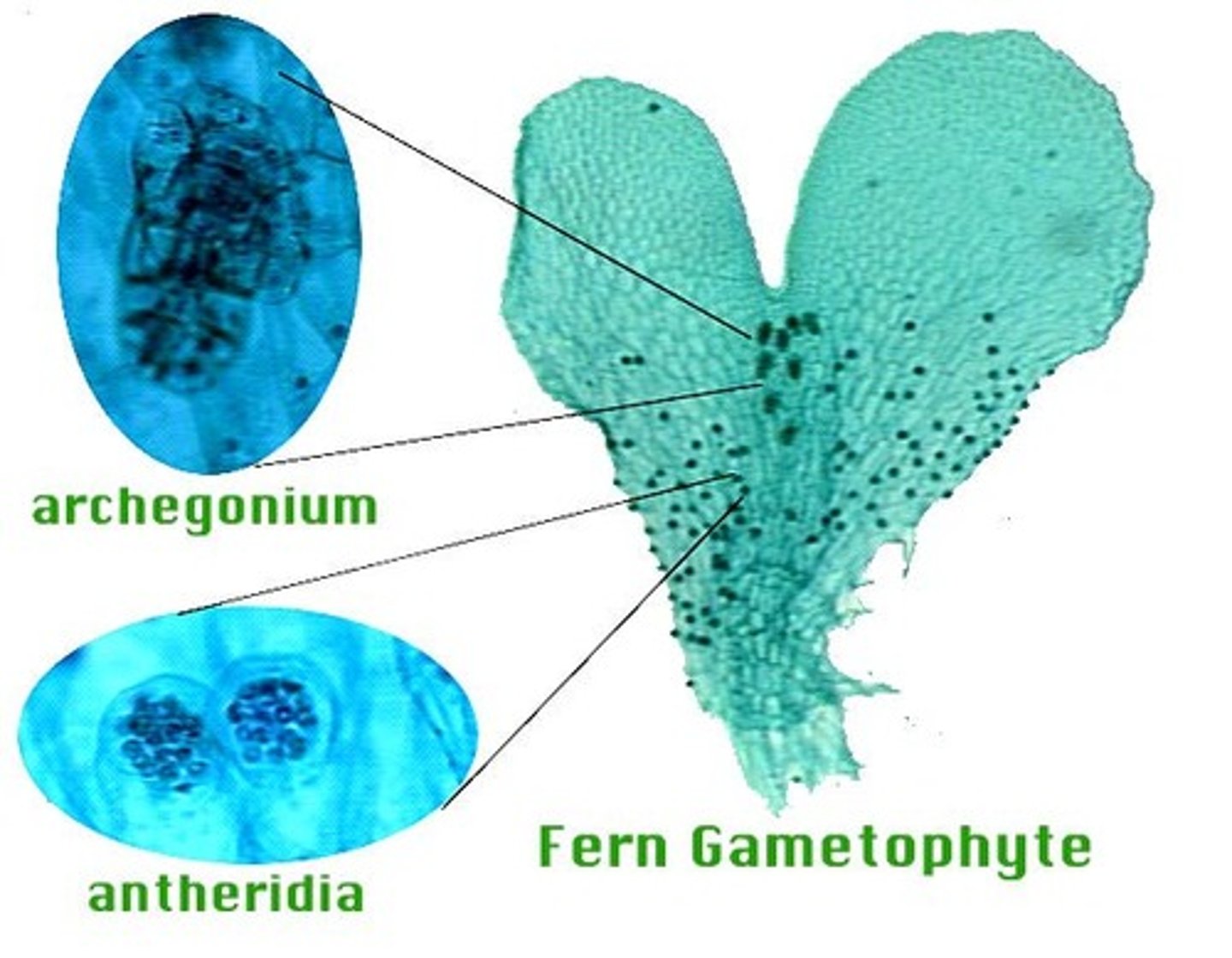
antheridia
in plants, the male gametangium, a moist chamber in which gametes develop.
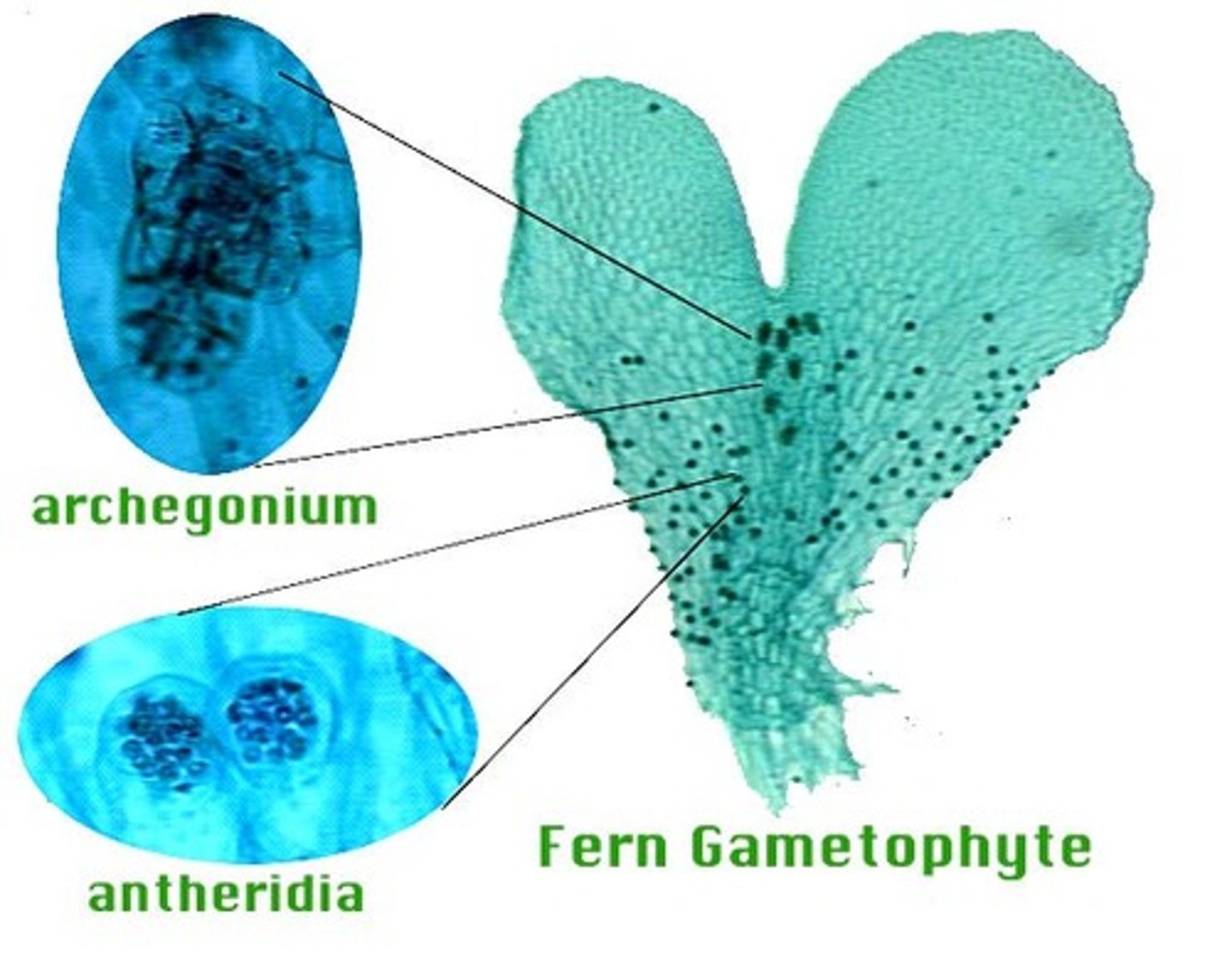
archegonia
Female reproductive part of a nonvascular plant
sporophyte generation
after fertilization a diploid zygote develops into this generation of moss life cycle
Dominant generation
In alternation of generations, the generation that occupies the largest portion of the life cycle.
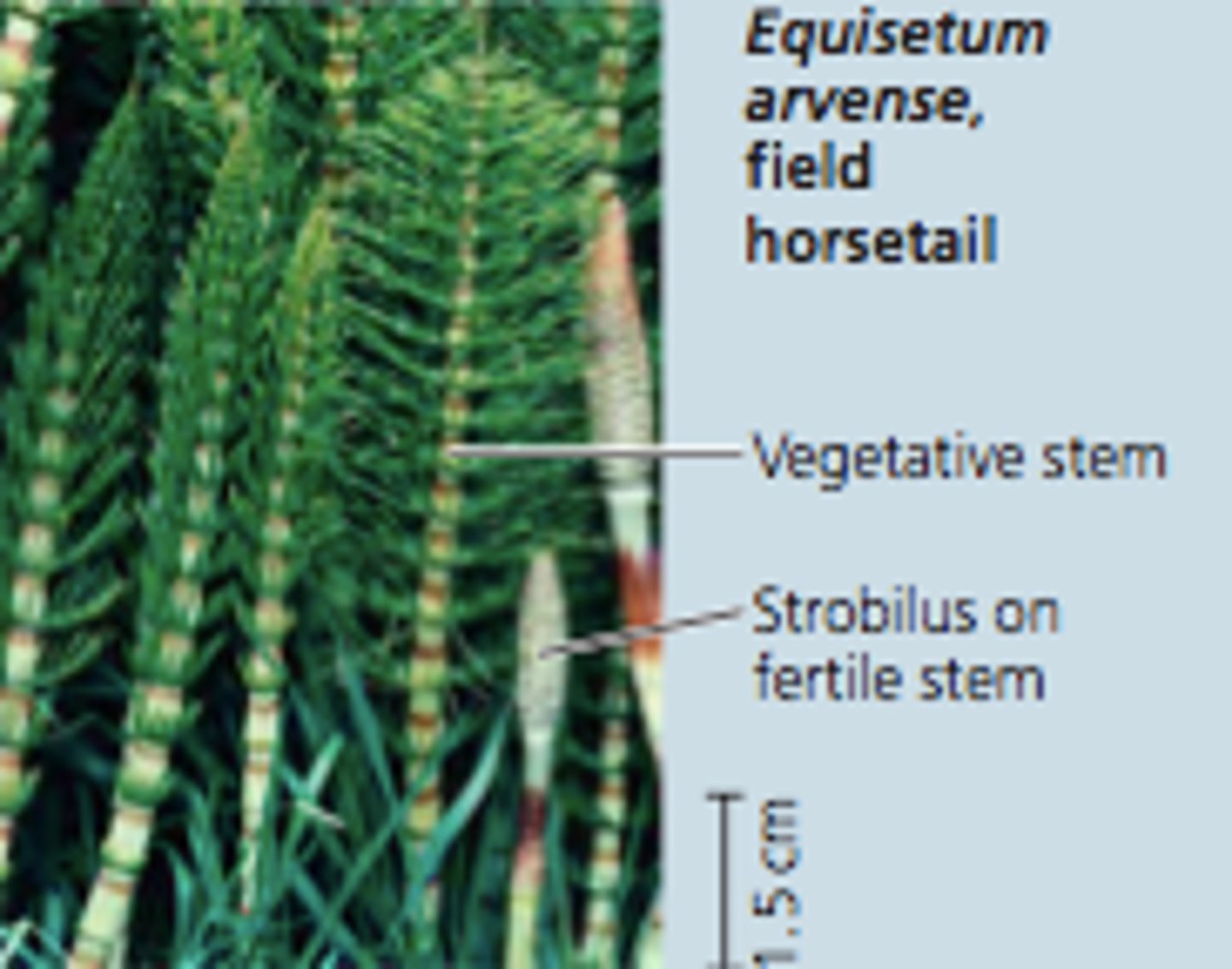
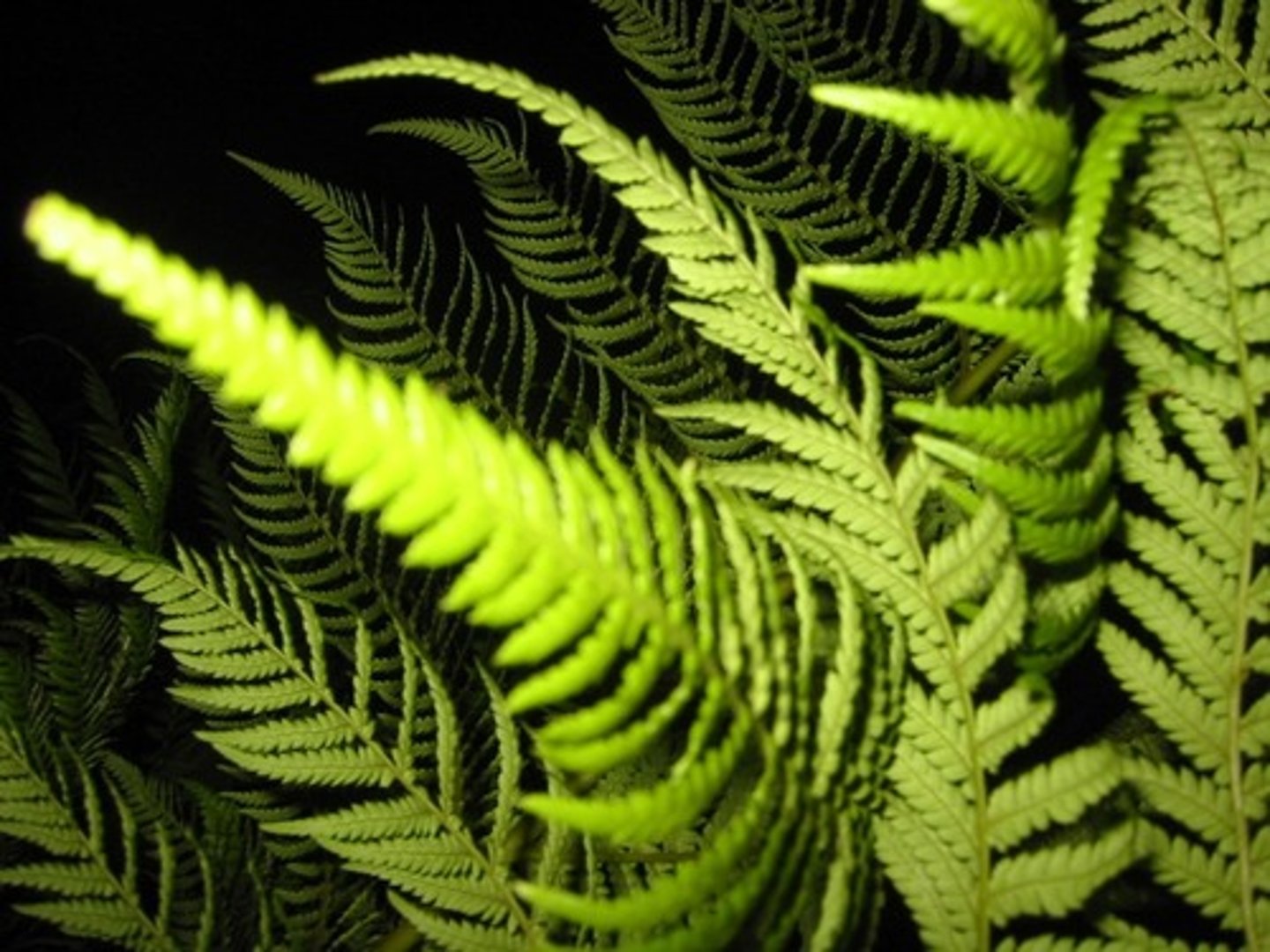
seedless vascular plant
Plant with vascular tissue, but no seeds; the most common plants of this type are ferns .
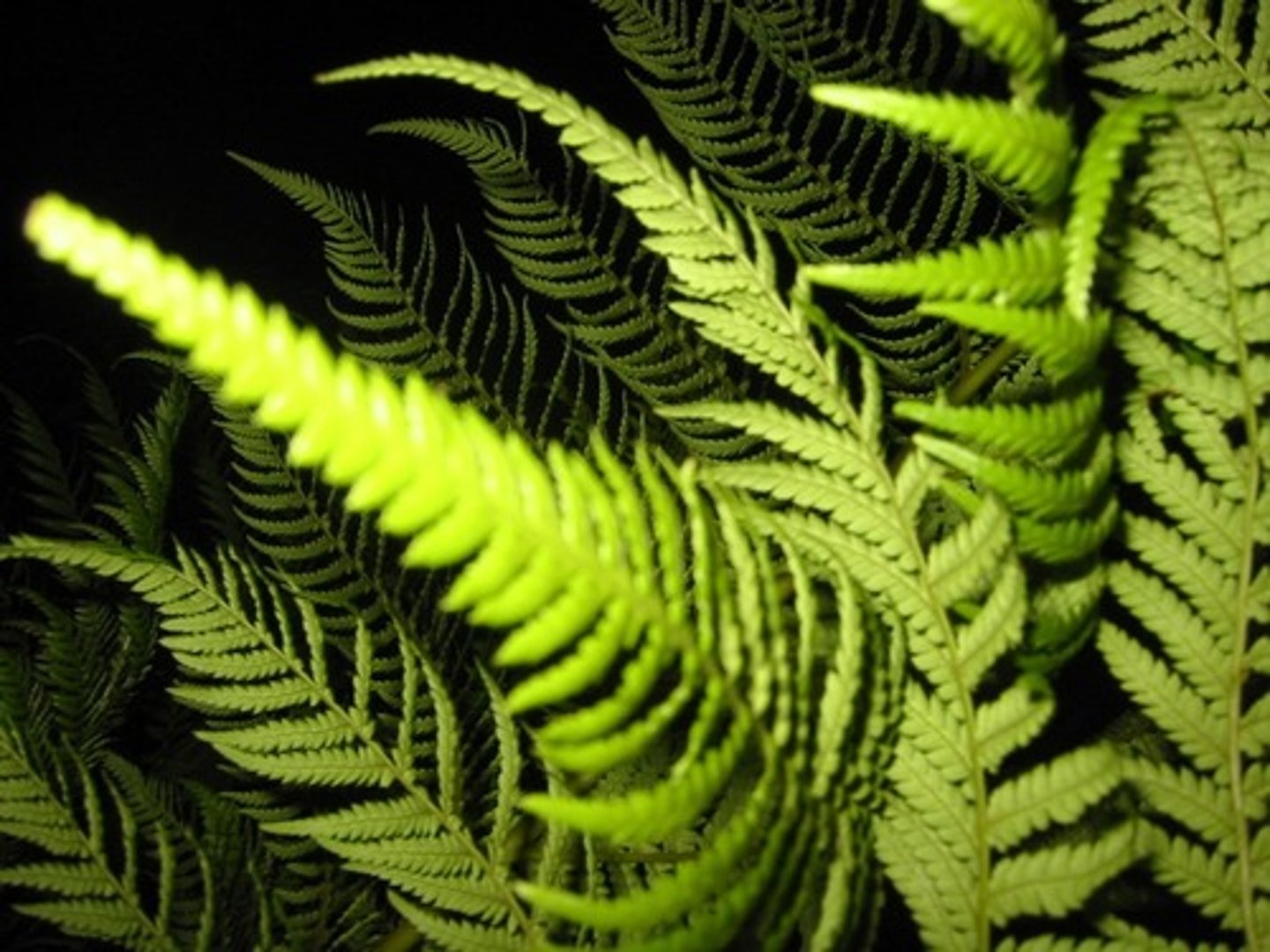

pterophyta
ferns

Fern Life Cycle
Coniferophyta
Cone-bearing plant. "Conifer" is Latin for cone bearer and "phyta" means plant.

Seed Cones
Usually found in other branches of the same tree. Ova are on the scales of these.

Pollen Cones
cone in gymnosperms that produces male gametophytes in the form of pollen grains

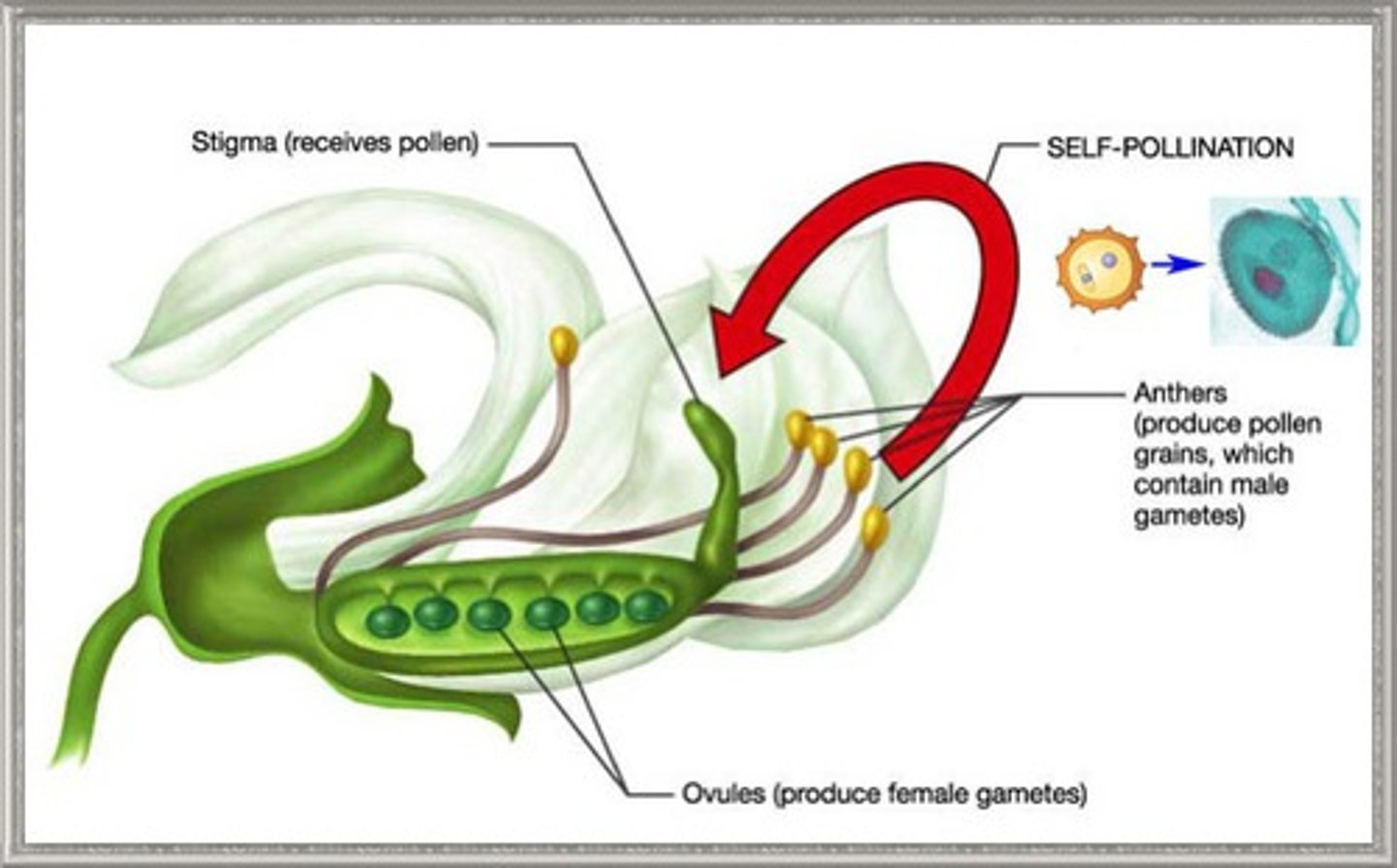
self fertilization
fertilization in which both egg and pollen come from the same plant
Anthophyta
Flowering plants

Pollen
A fine dust that contains the sperm of seed-producing plants.

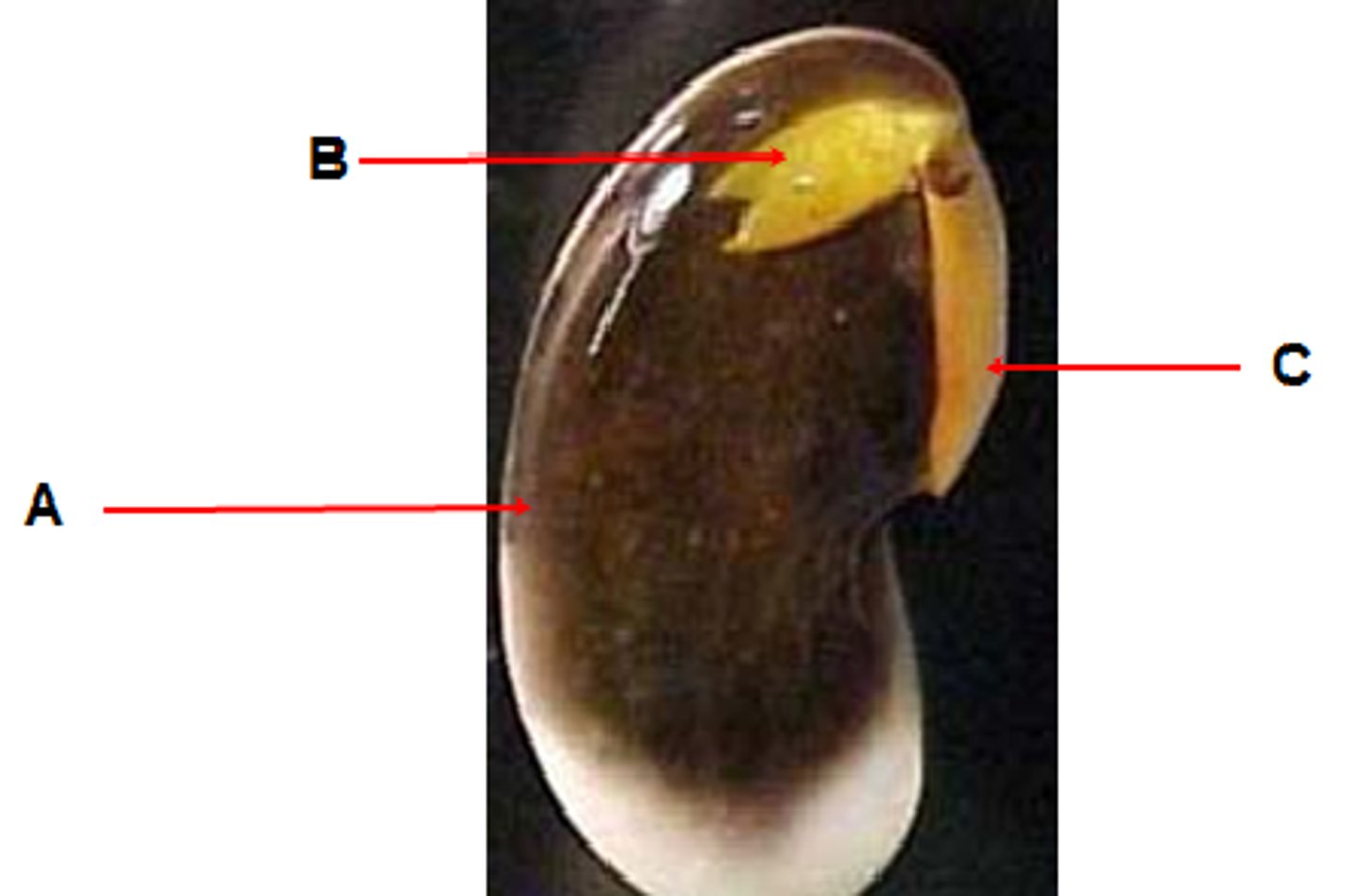
Cotyledon
A "seed leaf" which develops as a part of the seed. It provides nutrients to the developing seedling and eventually becomes the first leaf of the plant.