BS101: Lecture 4 - Ultrastructure of DNA and Chromatin folding
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
How do Ribosomes make proteins?
Use info from DNA to make proteins via DNA
How is mRNA made?
Transcription uses DNA to make mRNA
Where does Translation occur?
Ribosomes
How does Transaltion happen?
mRNA used to make peptides/proteins
What is the function of the Nucleus relating to separation of DNA?
Separates DNA from cytosol
What is the function of the Nucleus relating to Transcription & Translation?
Separates Transcription & Translation
What is the function of the Nucleus relating to gene storage?
Stores genes on chromosomes
What is the function of the Nucleus relating to gene organisation?
Organises genes into chromosomes, allowing cell division
What is the function of the Nucleus relating to gene replication?
Organises uncoiling of DNA to replicate key genes
What is the function of the Nucleus relating to transport?
Transports regulatory factors & gene products via nuclear pores
What is the function of the Nucleus relating to mRNA production?
Produce mRNA that code for proteins
What is the function of the Nucleus relating to rRNA production?
Produce rRNA in nucleolus?
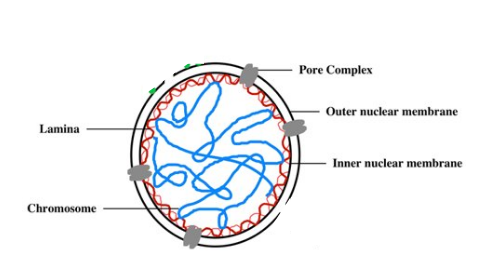
What is the function of the Nuclear Pores?
Regulate entry/exit of molecules from nucleus
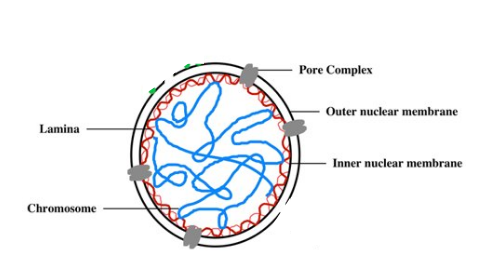
Describe the Nuclear Lamina
Composed of protein filaments to maintain its shape
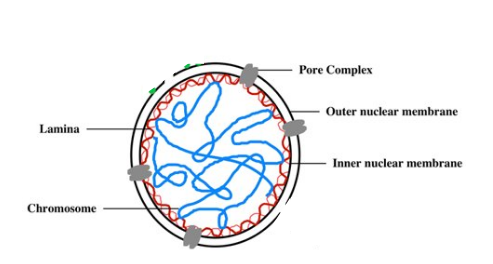
Describe the Nuclear Matrix
Consists of a framework of fibres
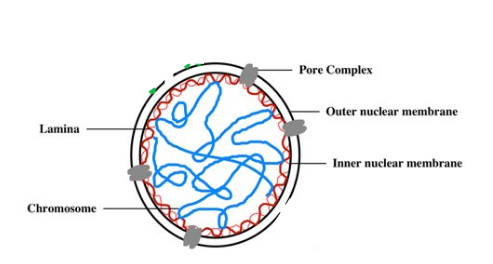
What is the Nuclear Lamina?
Network of intermediate filaments that extend over inner surface of nuclear envelope
What is a function of the Nuclear Lamina relating to chromosomes?
Provides structural support for chromosomes
What is a function of the Nuclear Lamina relating to the structure of the Nucleus?
Required to maintain musle/shape
What is a function of the Nuclear Lamina relating to mitosis?
Essential in disintegration of nuclear envelope during mitosis
What happens to the Lamina when the nuclear envelope disintegrates in mitosis?
Depolymerised
What is LMNA?
Gene that codes for lamina
What happens if there is a mutation in the LMNA gene?
Progeria
What is Progeria?
Premature aging disorder
Describe what happens in LMNA mutation
Changes in the shape of cell nuclei
How can the effects of Progeria worsen?
Gets worse w/ age + affects cell’s ability to divide correctly
What is the Nucleoplasm?
Non-staining liquid/semi-liquid of the interphase nucleus which fills the space around chromosomes + nucleoli
Describe the composition of the Nucleoplasm
Primarily water, dissolved ions + complex mixture of molecules (nucleotides, enzymes)
What is a function of the Nucleoplasm relating to the Nucleus’ Organelles?
Acts as a suspension medium for nucleus’ organelles
What is a function of the Nucleoplasm relating to the Nucleus’ structure?
Maintains nuclear shape/structure
What is a function of the Nucleoplasm relating to transport?
Transports ions, molecules + substances important to cell metabolism & function
What are the Nuclear Pores?
Regulate entry/exit of molecules from the nucleus (eg proteins, RNA)
What can diffuse through Nuclear Pores?
Small proteins & ions
How are Large Proteins transported through the Nuclear Pore Complex?
Actively transported via transporter molecules
How do Transporter Molecules transport large proteins?
Bind to proteins + interact w/ nucleoporins as they pass through
What is the shape of the NPC?
Octagonal made from membrane-embedded proteins
What proteins are on the cytoplasmic surface?
Nucleoporins, extend into cytoplasm
What proteins are on the nuclear surface?
Protein filaments, extend inwards into nucleus forming nuclear basket
What is the Nucleolus?
Region where rRNA is transcribed and processed
What happens to the Nucleoli during Mitosis?
Disappear and reappear in new daughter cells
What are the identifiable compartments in the Nucleolus?
FC
DFC
GC
Fibrillar centre, Dense fibrillar component, Granular component
What happens in the Nucleolus?
FC
DFC
GC
Protein + DNA complexes found in FC
Ribosomal subunits made in DFC
Ribosomes assembled in GC
What is Chromatin?
Complex of DNA and protein, found in nucleus
What are Histones?
Proteins responsible for 1st level of DNA packing in chromatin
Amino Acids in Histones
Lots of positively charged amino acids so bind easily to negatively charged DNA
How does DNA exist in non-dixiding cells?
As chromatin
Describe Chromatin in non-dividing cells
Uncoiled and randomly dispersed
How does DNA prepare for cell division?
S phase
DNA replicates then chromatin condenses into chromsomes
What is the makeup of Chromatin?
50% DNA + 50% Proteins (mainly histones)
What is the Eukaryote Genome packaged into?
Chromatin
Why is the Eukaryote Genome packaged?
Allows long DNA molecules fit into nucleus’ small volume
What is the Nucleosome?
Basic structural unit of chromatin
What is the result of further folding of the chromosome?
Produces visible metaphase chromosomes during cell division
What is the further folding of chromosomes caused by?
Interactions between H1 histone tails and DNA
What is the end product of the further folding of chromosomes?
30nm fibres
What do 30nm fibres form?
Loops
What do the 30nm Loops do when packing DNA?
Looped domains attach to chromosome scaffold proteins to make 300nm fibre
What happens to the 300nm loop domains when packing DNA?
Coil further to result in metaphase chromosomes, width 700nm
How do Chromosomes fold?
Always the same way so specific genes always in same region of chromosome
What is a Chromosome?
Discrete unit of the genome carrying many genes
What is the Chromosome comprised of?
Highly compacted chromatin
When do Chromosomes form?
During cell division to ensure all DNA is divided correctly/completely
What is the Karotype?
Complete set of chromosomes
What is a Chromatid?
Half of a chromatin
What state do Chromatin exist in?
Nucleosome state - histones are bound
What state are Chromosomes in when ready for mitosis?
Fully compacted
Which has a larger diameter, Chromosomes or Chromatin?
Chromosomes
Which has a larger folding magnitude, Chromosomes or Chromatin?
Chromosomes
What are the 2 types of Chromatin?
Heterochromatin and Euchromatin
What state are Chromosomes usually in?
Heterochromatin
What kind of process is the transition between active and inactive chromatin?
Dynamic
What converts chromatin between active and inactive?
Chromatin Remodelling Factors
How do Chromatin Remodelling Factors do their job?
Addition/removal of acetyl/methyl groups
What happens in Histone Acetylation?
Larger acetyl groups attach to positive lysines in histone tails
What is the effect of Histone Acetylation?
Loosens chromatin structure, promoting transcription
What is Methylation?
Addition of CH3 groups
What can methylation do?
Condense chromosomes, found in inactive heterochromatin
Describe Euchromatin
Light colour, active
Less condensed - transcriptionally active
Lightly packed
What is the modification of Histones in Euchromatin?
More acetylated so looser packing
How does Euchromatin relate to interphase (Mitosis)?
Characteristic for interphase chromosomes - not condensed
Describe Heterochromatin
Dark colour, inactive
Highly condensed, tightly packed - transcriptionally inert
Modifications of Heterochromatin Histones
Methylated - tighter packing
Where is DNA usually found in chromosomes?
Centromere
How can Gene Expression be regulated?
Switching between the 2 types of chromatin
What does dense packing of heterochromatin mean for the cell?
Makes it difficult to express genetic info coded

What Nucleotide Base is this?
Cytosine

What Nucleotide Base is this?
Guanine
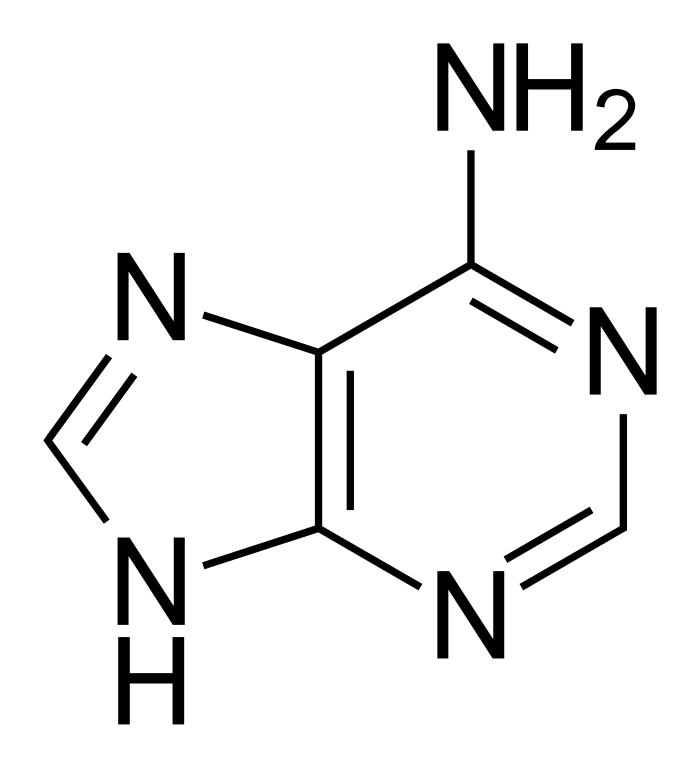
What Nucleotide Base is this?
Adenine
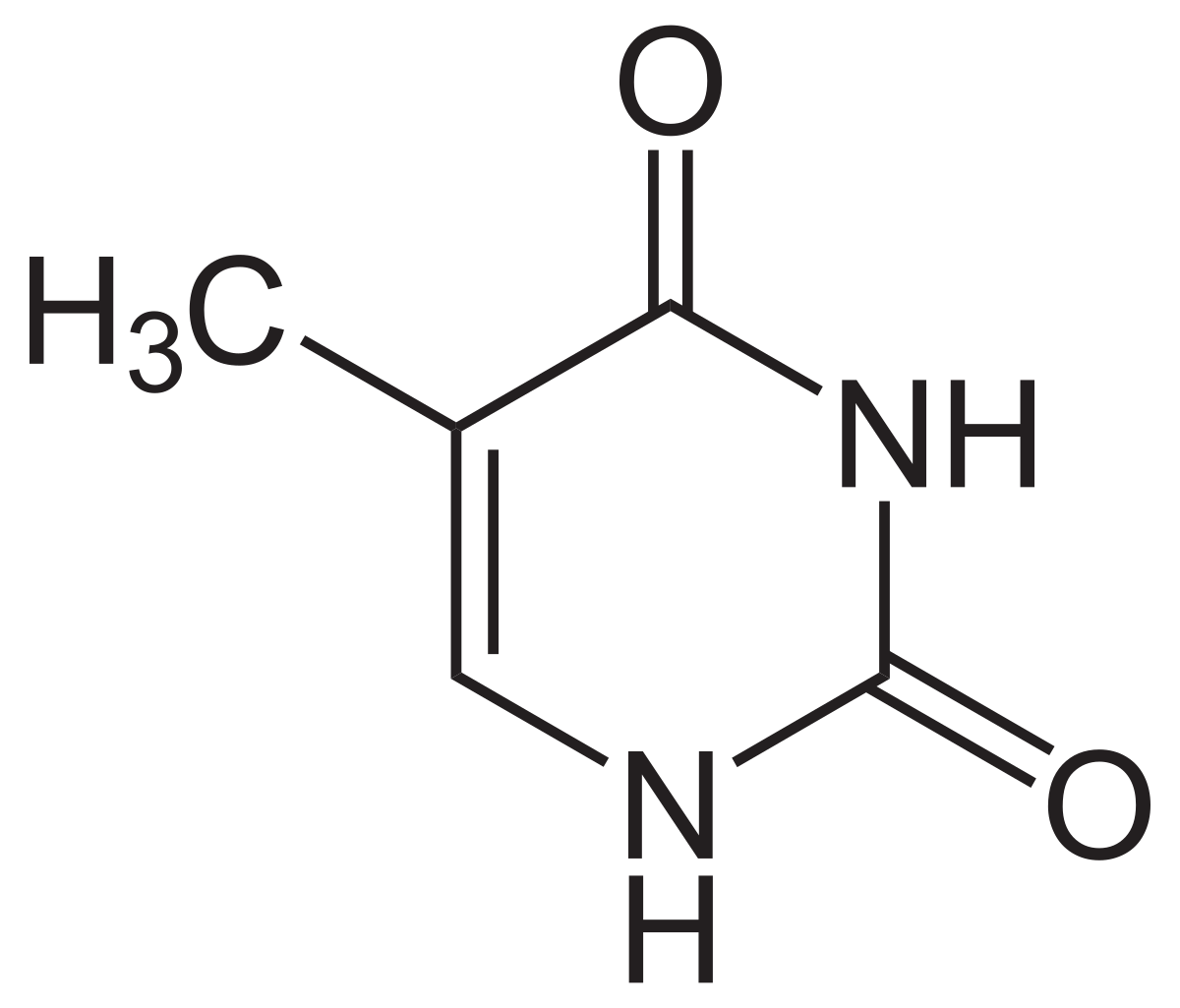
What Nucleotide Base is this?
Thymine

G-C, 3 H Bonds
A-T, 2 H Bonds
G-T Wobble, 2 H Bonds

Termination of translation happens when…
Ribosome hits a stop codon on the mRNA.
Initiation of translation always happens at the…
start codon of the mRNA
Translation
Process by ribosome of reading mRNA and synthesizing a protein
Amino acids are attached to tRNA by enzymes called…
aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
The RNA that has an amino acid attached to it, and that binds to the codon on the mRNA, is called a…
tRNA
If a DNA double helix is 100 nucleotide pairs long and contains 25 adenine bases, how many guanine bases does it contain?
200 total nucleotides
A = T, 25 × 2 = 50
200 - 50 = 150, 150 / 2 = 75
Short segments of newly synthesized DNA are joined into a continuous strand by...
DNA ligase
The action of helicase creates…
Replication forks/bubbles
Why is the new DNA strand complementary to the 3' to 5' strands assembled in short segments?
DNA polymerase can assemble DNA only in the 3' to 5' direction
The synthesis of a new strand begins with the synthesis of a(n)…
RNA primer complementary to a pre-existing DNA strand
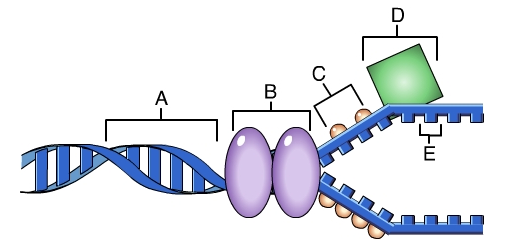
Label
A = DNA ahead of the fork
B = helicase
C = primase
D = DNA polymerase
E = RNA prime