women and mens health
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
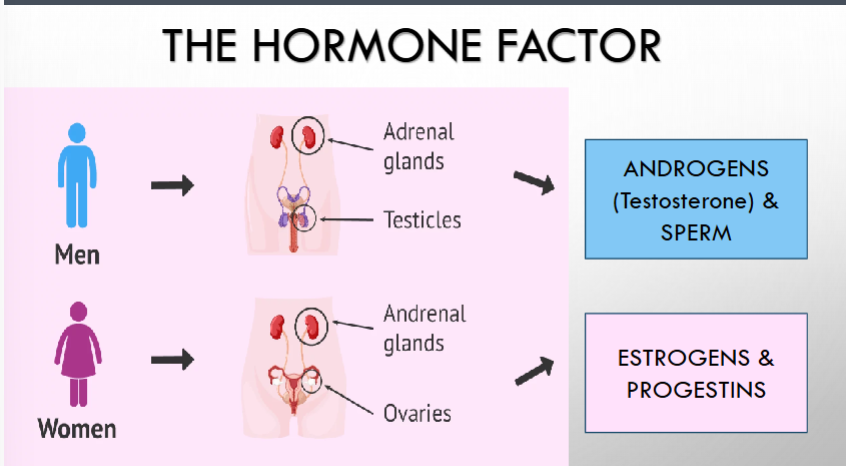
what do the adrenal glands and testicles produce in men?
what do the adrenal glands and ovaries produce in women?
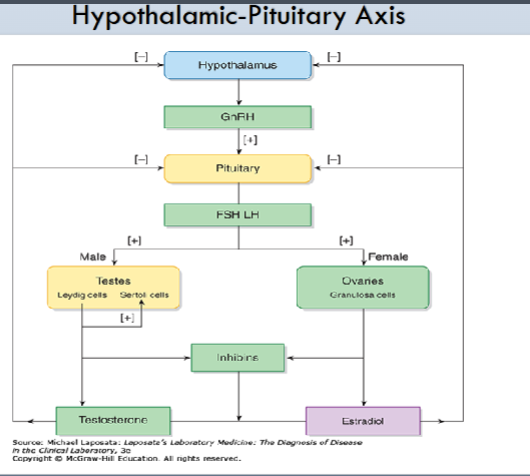
In regards to reproductive hormones, what does the hypothalamus produce?
What does the pituitary gland produce?
what do the ovaries and testes produce?
what effect does Testosterone, estradiol and inhibin have on the HPA?
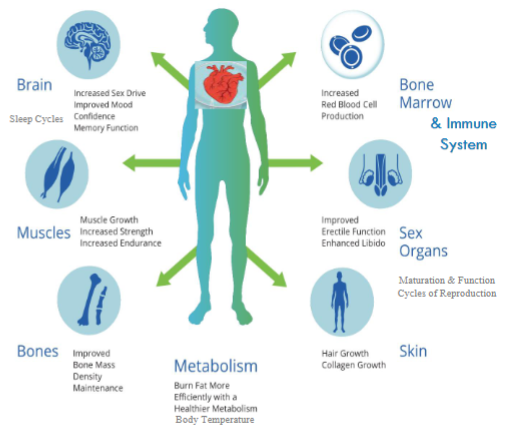
remember they can help increase ___ cell production, snd help with memory
remember reproductive hormones can help increase ___ cell production, and help with _____
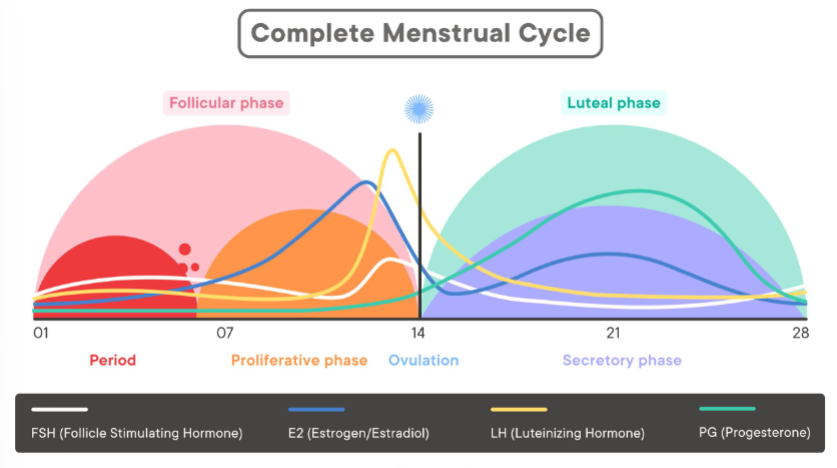
what two main parts does the menstrual cycle occur in?
During days 1-14 what two phases do you expect?
On day 14 what occurs?
right before day 14 what two hormones surge?
what hormone is more lucrative during the luteal phase?
what are the 4 main phases of the menstrual cycle?
Aging & Development
what is a big factor in the changes of hormones levels over time?
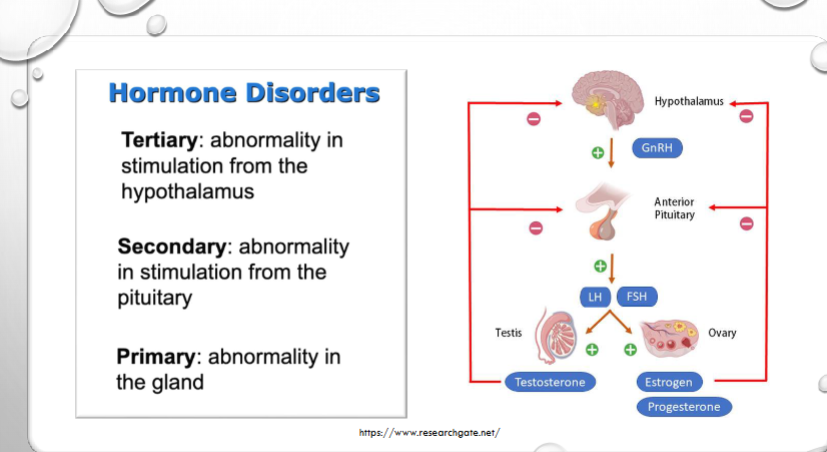
what is the difference in hormone disorders between primary, secondary and tertiary?
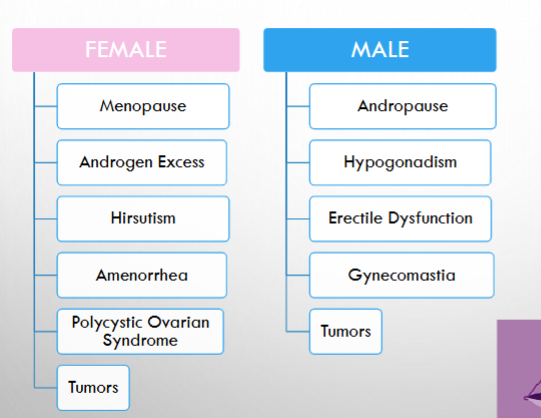
what are 6 common disorders women can get?
what are 5 common disorders men can get?

men: can become more prone to diabetes / infections
women: changes in breast
what are signs and symptoms of a hormone imbalance in men?
what are signs and symptoms of a hormone imbalance in women?
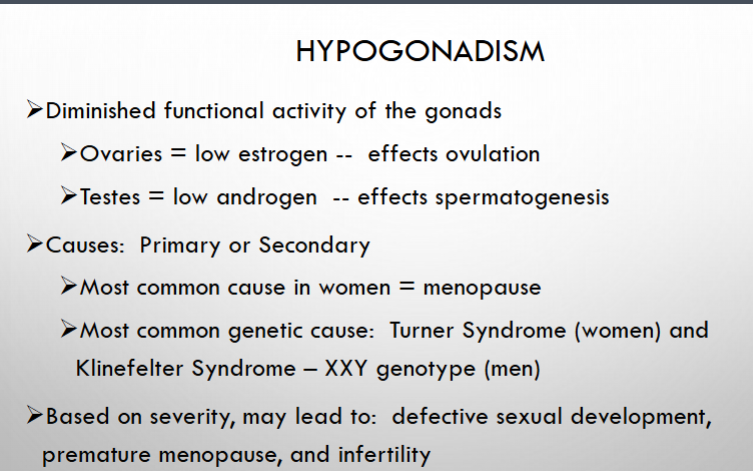
what is hypogonadism defined as?
what would be low in the ovaries and what would it affect?
what would be low in the testosterone and what would it affect?
what is the most common cause of hypogonadism in women?
what is the most common genetics causes of hypogonadism?
Depending on the severity what can it lead?
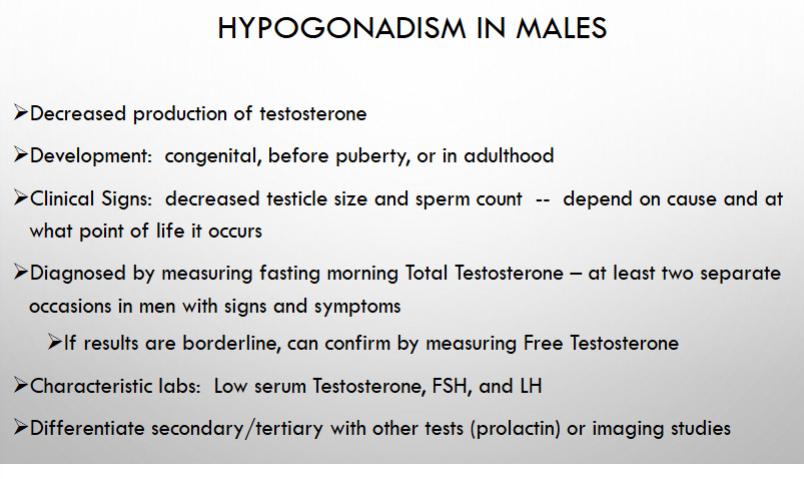
how could hypogonadism (testosterone deficit) affect development in males?
what are the clinical signs?
What labs can you run and expect? If those results are borderline?
what can you use differentiate secondary and tertiary hypogonadism ?
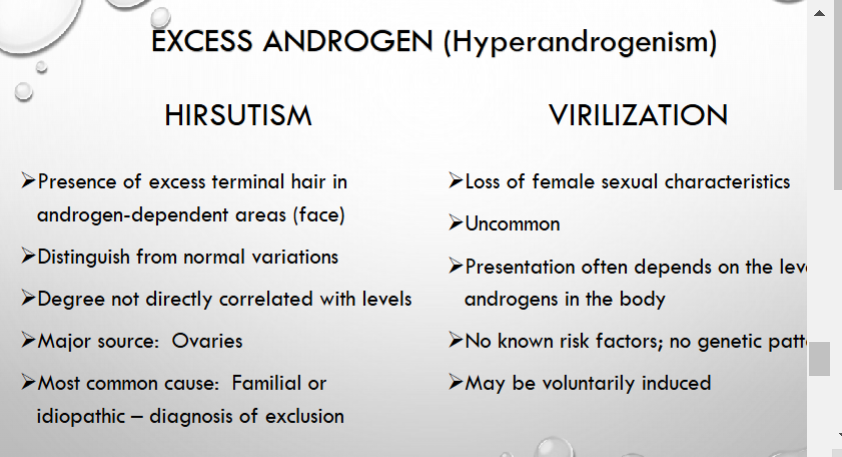
what are two main side effects of EXCESS androgen in women?
what is this also known as?
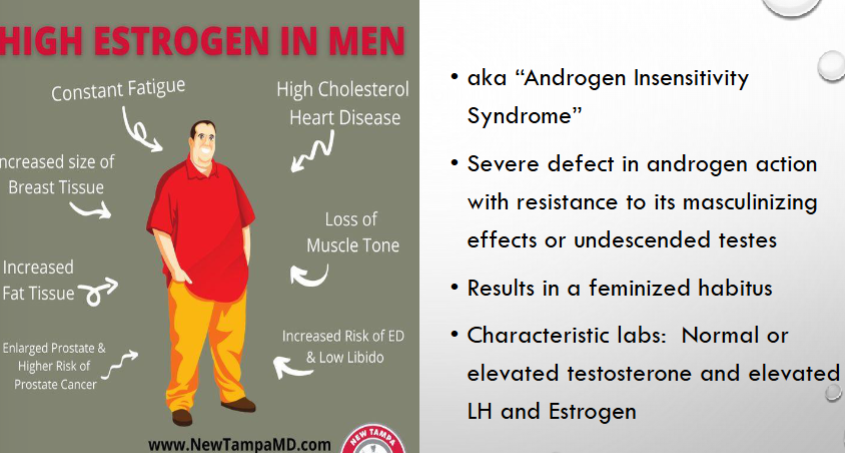
what are the side effects of high ESTROGEN in men? what is this also known as?
what can cause this and what can it result in?
what three labs would be high?

what is the absence of normal menses called?
what is the difference between primary and secondary?
what can cause secondary amenorrhea?

what type of labs can you run for both primary vs secondary amenorrhea?

what is the most common hormonal disorder among women of reproductive age?
what hormone is this caused by?
what do most women who suffer from this have?
what are common symptoms?
what are complications of PCOS?
what kind of cancer can PCOS cause?
How can this be managed?
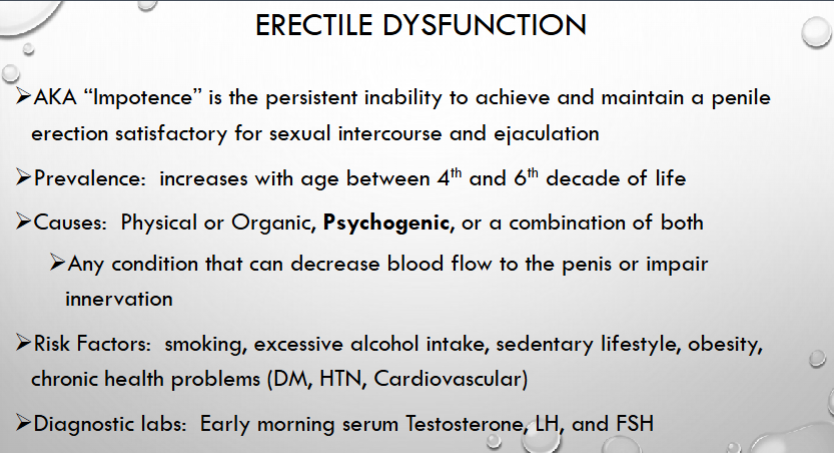
What is male impotence known as?
when is it most prevalent?
What can cause this impotence?
What are risk factors that can lead to impotnce?
what labs can be run for impotence?
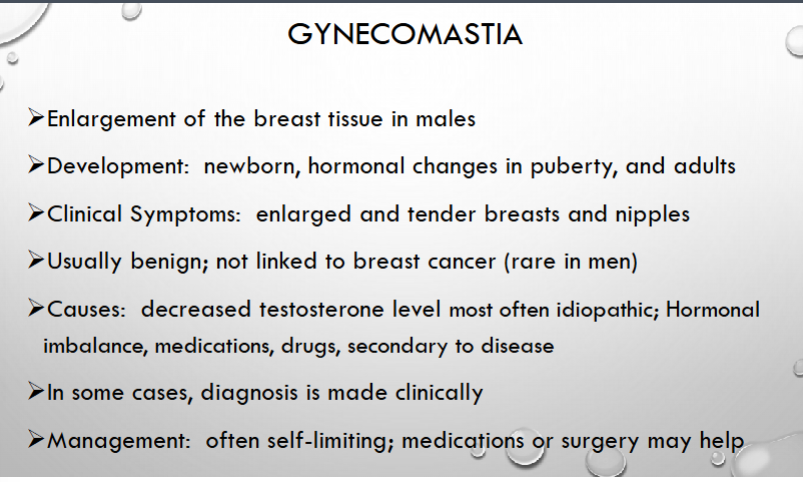
what is gynecomastia?
when can this occur?
what are the symptoms?
is this benign?
what are common causes>
how can this be managed?
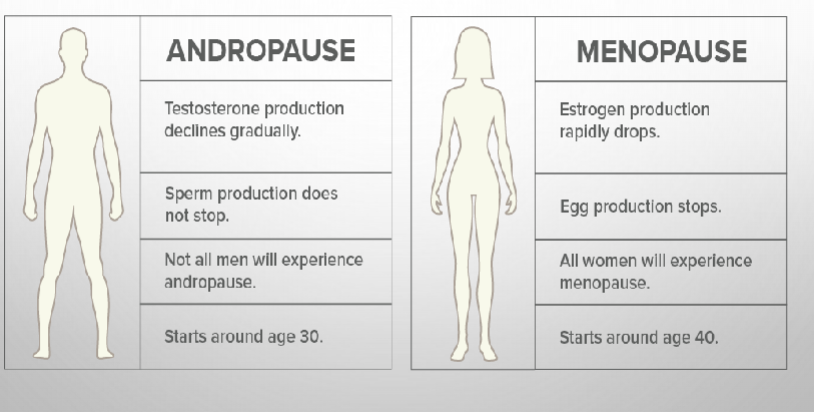
what is andropause vs menopause?
andropause causes what to decline?
what remains the same in andropause?
Do all men experience andropause?
At what age do men begin andropause ?
what drops in menopause?
what stops in menopause?
do all women experience menopause?
at what age do women begin menopause?
highest = ovulation (want to draw at this time)
lowest = menstruation
Note: radioisotopes and oral contraceptives can interfere with levels
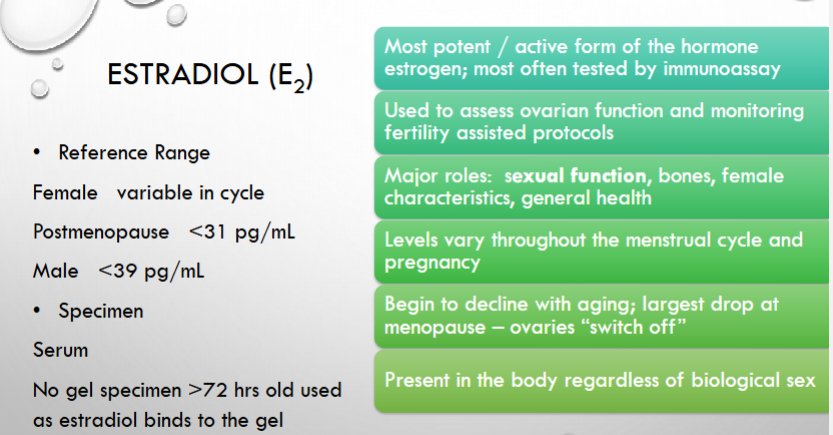
what is the most potent/active form of the hormone estrogen
what is it used to assess and monitor?
what are major roles?
when does it begin to decline?
When do the levels fluctuate?
Do only women have this?
How can you test for this and what levels indicate post-menopause in women?
what levels can you expect in men?

what is the FSH produced and stored by?
what is the major role in females for fsh?
what is the major role in males for fsh and what is it used to count?
when does it rise and incease?
what day should FSH hormone be measured in the cycle?
what can it be used to asses and differentiate?
what is a good reference range?
What specimen should be given to test from it?
increase, menopause
where is the LH produced?
what does it trigger in women?
what major role does LH play in men?
what is LH measured by? when does it peak?
what two things is it used to determine?
what specimen should be run and does it have a reference range?
Levels of LH ______ with age and therefore may indicate____

what is progesterone normally produced by?
At how many weeks of pregnancy will the progesterone level be elevated?
what does it help women prepare for ? what does it promote?
what major role does progesterone play in males? what does it promote?
what day does progesterone peak in a woman’s cycle and how can it be tested?
what is progesterone used to confirm, evaluate, and asses in terms of fertility?
what is a reference range for men?
what type of test specimen should be run?

what is prolactin normally produced by?
what major role does it play in females?
what big role does prolactin play in puberty in both men & women?
How do they levels of prolactin change?
What is prolactin also used for?
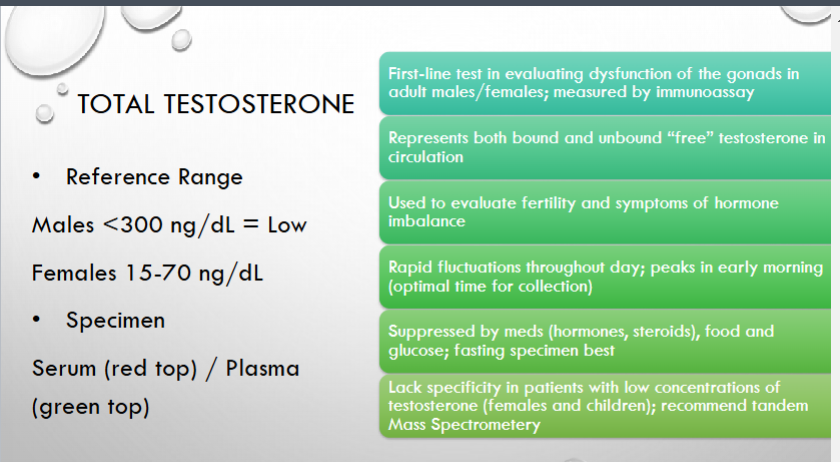
what is the first line test in evaluating dysfunction of the gonads in adult males? what is it measured by?
what does total testosterone represent/
what can it be used to evaluate?
when does testosterone peak?
what is testosterone suppressed by and should therefore be avoided during collection?
in what population does testosterone lack specificity? therefore what should it also be checked with>?
what is a ABnormal reference range for male?
FEMALES?
WHAT TUES SHOULD BE USED TO COLLECT THIS SPECImen?

total testosterone, SHBG (sex hormone binding globulin), albumin
what does free testosterone measure?
what is used to diagnose in males or females?
what situations is more helpful with?
what is it free testosterone calculated by?
what does free testosterone correlate well with?
what is the only exception?
the range of free testosterone is based on ____.

NOT a red tube>
where is DHEA (DEHYDROEPIANDROSTERONE) produced in?
what does it help produce?
what is DHEA a preferred test to check for? (3 things)
how is it tested?
what is a reference range for men?
what should it be used to evaluate?
what tubes should it be run in?
should patient fast?
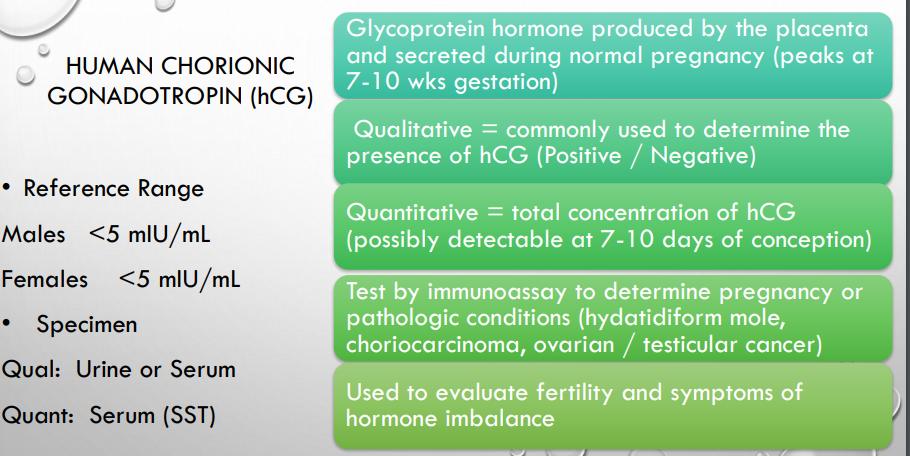
what is hcg produced by? what weeks does it peak in pregnancy?
what is the difference between qualitative and quantitative? and what days can this be detectable?
what is it tested by and what could be a bad indicator?
what is it used to evaluate?
what is a normal ref range for male and female?
what does the qualitative test sample require (2 things)
vs quantitative test requires …..
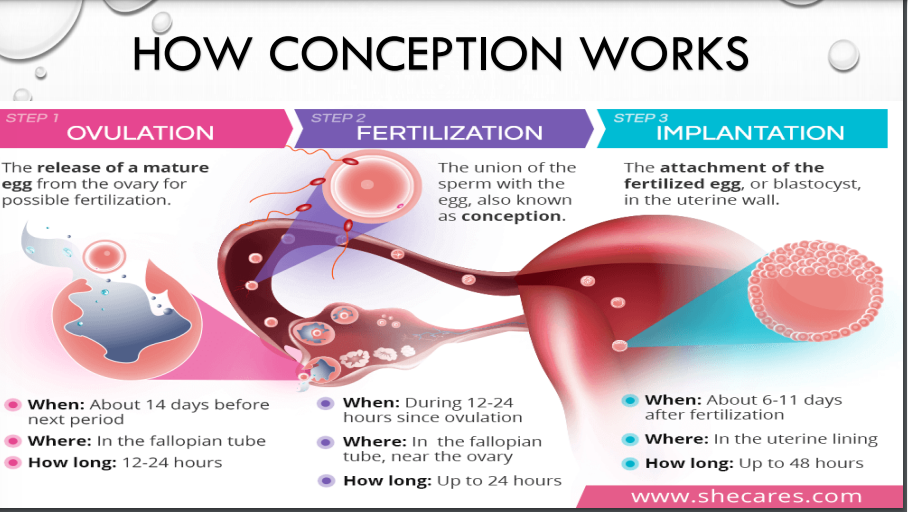
what are the three steps of conception?
when and where and how long does ovulation occur?
when and where does and how long does fertilization occur?
when and where does and how long implantation occur?

what 6 factors affect fertility?
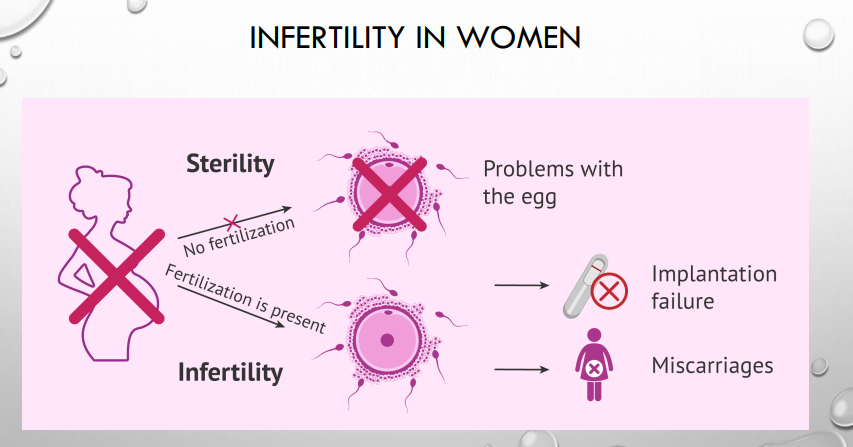
woman’s Sterility: no fertilization --> problems with the egg
Infertility: fertilization is present --> implantation failure or miscarriages basically the baby never makes it birf
what is the difference between woman’s sterility and infertility?

Concentration, motility and morphology
can be tested through blood or urine
what do fertility studies look at?
what 3 things can sperm be graded on?