Regulation of Genetic Expression
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
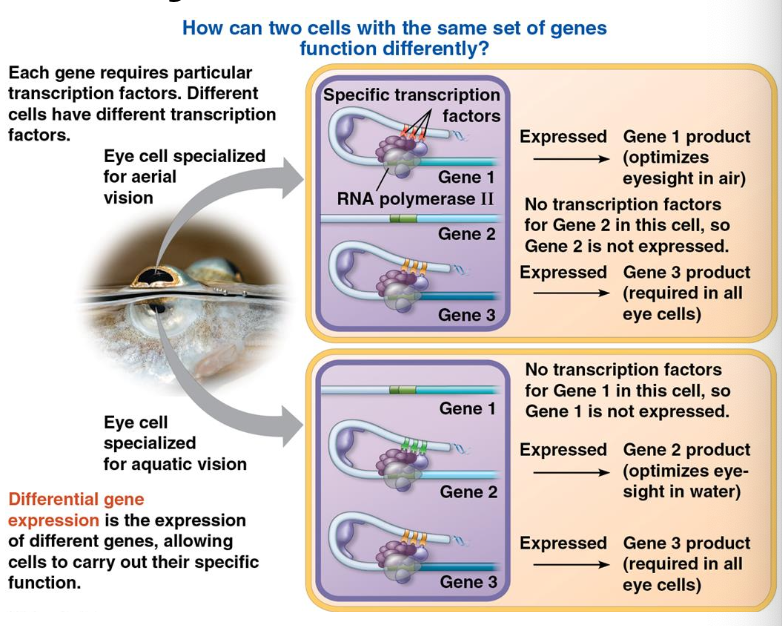
to be expressed, each gene requires a particular set of transcription factors
different cells have different sets of specific transcription factors
ex. an anabelps has eye cells specialized for aerial vision and eye cells specialized for aquatic vision
How can two cells with the same set of genes function differently?
gene regulation
encompasses the ways in which cells control gene expression
where (in which cells) are turned on?
when (during development or in response to changes in the environment) are genes turned on?
how much gene product is made?
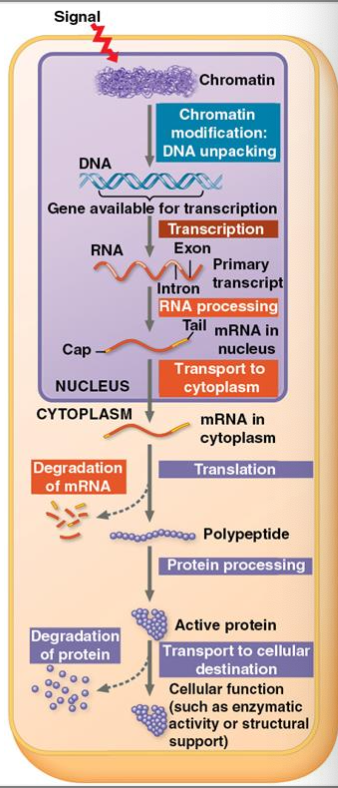
chromatin modification
histone tail modification
DNA methylation
epigenetic inheritance
What are some things that happen pre-transcription?
the proteins that carry out transcription cannot access the DNA
What happens when chromatin is coiled?
chromatin
a complex of DNA, RNA, and proteins that gives chromosomes their structure; the way that eukaryotic DNA is packaged
to allow space for transcriptional enzymes and proteins to work
Why must chromatin unravel?
chromatin remodeling
the nucleosomes are repositioned to expose different stretches of DNA
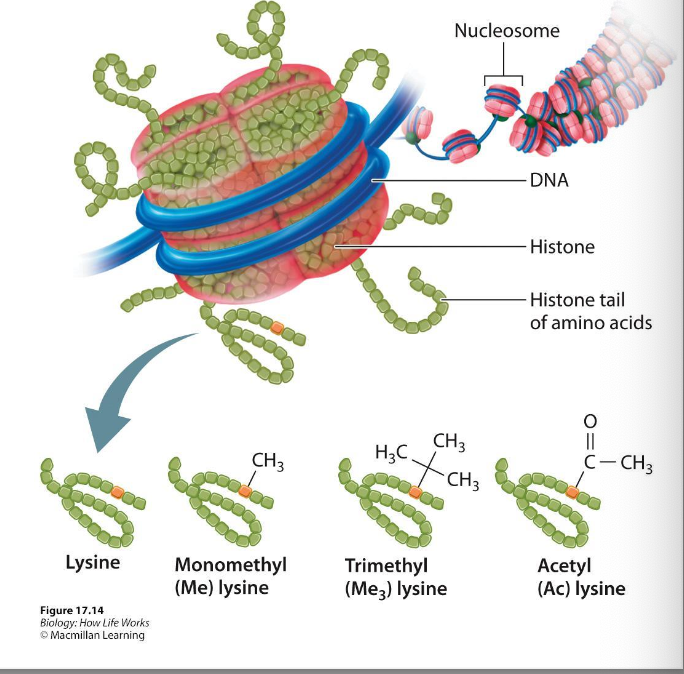
acetyl groups are attached to an amino acid in a histone tail
reduces affinity of DNA to histone
acetyl groups negatively charged
reduces positive charge of histone → makes promoter region available
appears to open up the chromatin structure, thereby promoting the initiation of transcription
What is histone acetylation?
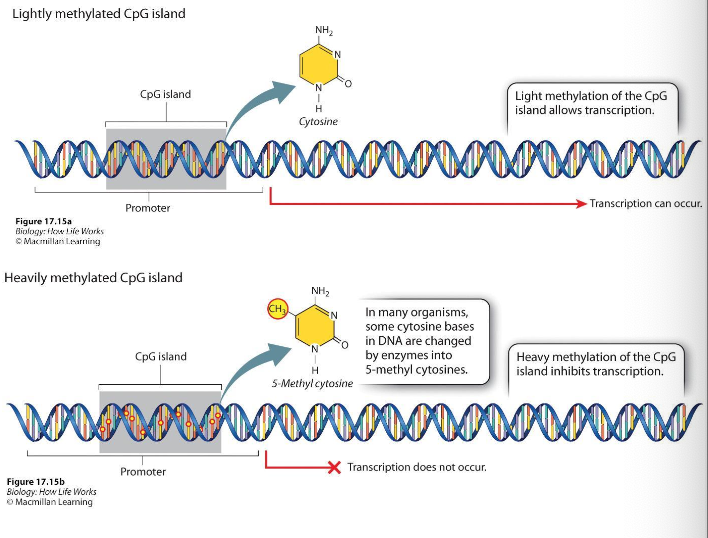
the addition of methyl groups to certain bases in DNA is associated with reduced transcription
the most common chemical modification to DNA is the addition of a methyl group to the base cytosine
can cause long-term inactivation of genes in cellular differentiation
What is DNA methylation?
the inheritance of traits transmitted by mechanisms not directly involving the nucleotide sequence
might explain cases where one identical twin develops a genetically based disease, while the other does not
What is epigenetic inheritance?
modification of cytosine bases
changes to histones
altering chromatin structure
What are some epigenetic effects?
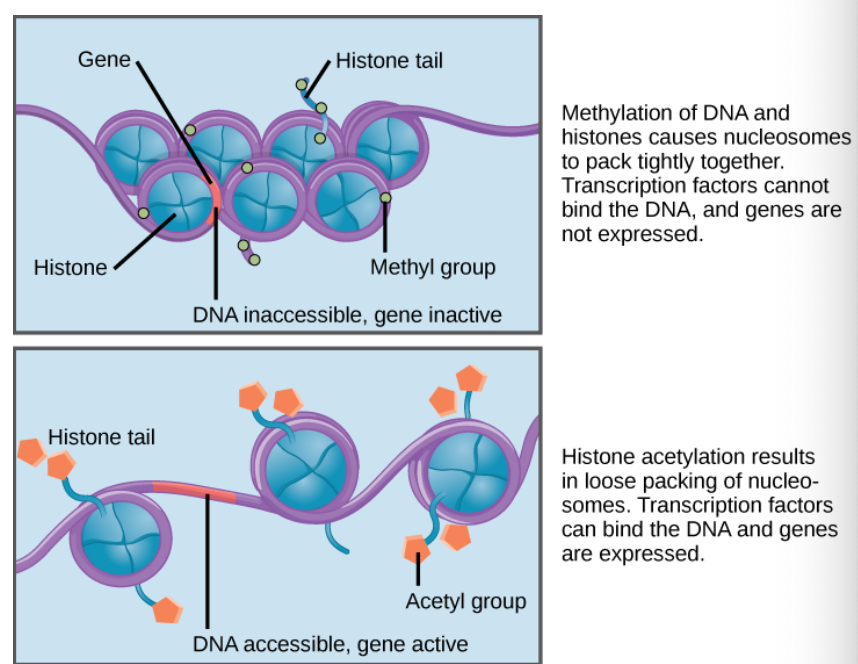
nucelosomes can slide along DNA
when nucleosomes are spaved closely together, transcription factors can’t bind
when nucleosomes are spaced apart DNA is exposed → transcription factors can bind
What are some main points of methylation?
regulation of initiation
transcription factors
proximal regulation
distal regulation
cell-specific transcription
What are some qualities of transcription?
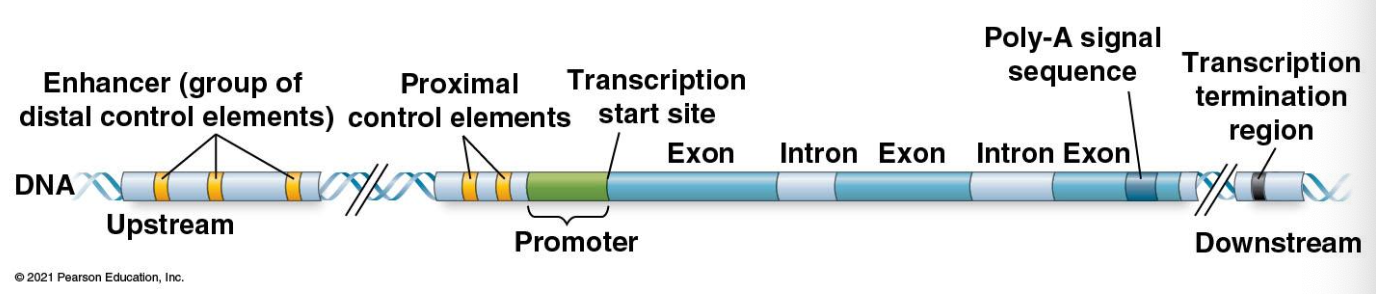
associated with most eukaryotic genes are multiple control elements, segments of noncoding DNA that serve as binding sites for transcription factors that help regulate transcription
control elements and the transcription factors they bind are critical to the precise regulation of gene expression in different cell types
How is transcription initiation regulated?
transcription factors
proteins tha help turn specific genes “on” or “off” by binding to nearby DNA
activators →
repressors → decrease transcription
What are the different types of transcription factors? What do they do?
enhancers
silencers
they can turn a gene on/off in specific parts of the body
What are different transcription factor binding sites? What do they do?
allow cells to perform logic operations and combine different sources of information to “decide” whether to express a gene
What do transcription factors allow cells to do?
general transcription factors
essential for the transcription of all protein-coding genes
brought there by mediator proteins that bind to the TATA box
recruit components of RNA polymerase complex
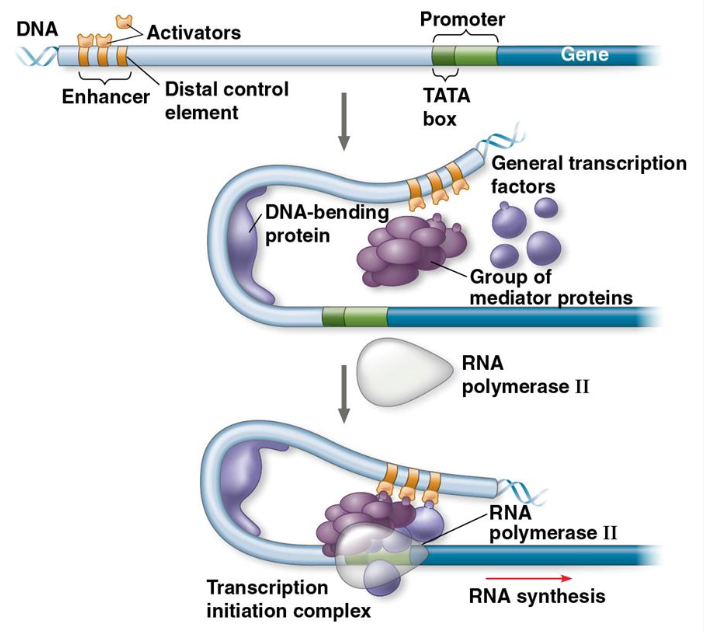
specific transcription factors that bind to control elements that may be close to or farther away (distal) from the promoter
What do some genes require to bind to control elements?
enhancers
groupings of distal control elements
stimulates the transcription of a gene
What happens when activator proteins bind to enhancers?
a sequence of protein → protein interactions that result in enhanced transcription of a given gene
protein mediated bending of DNA brings bound activators into contact with mediator proteins
What do bound activators facilitate?
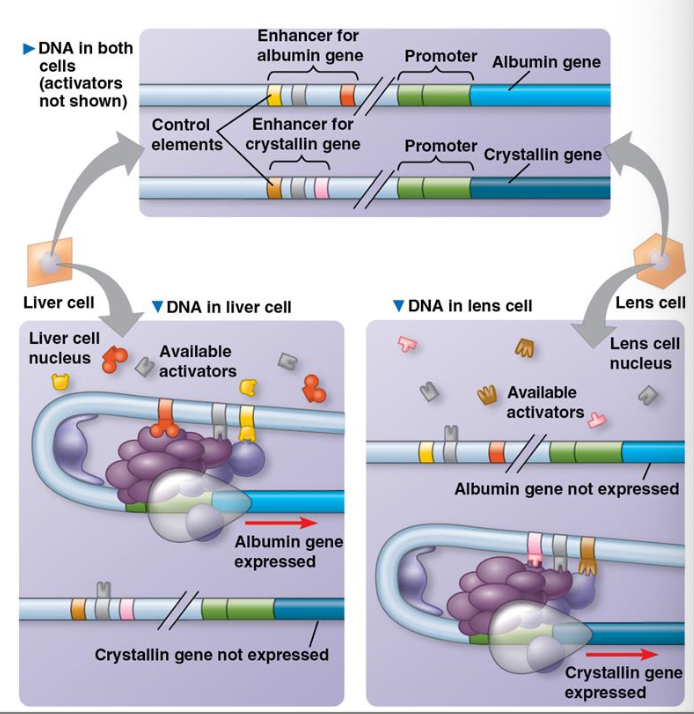
a particular combination of control elements can activate transcription only when the appropriate activator proteins are present
with only a dozen or so control elements, a large number of combinations is possible
e.g. activation of albumin gene in liver vs. Crystallin gene in lens cell
What happens during cell specific transcription?
RNA processing
alternative RNA processing
translation regulation
protein processing (posttranslational modification)
How can gene expression be affected post-transcription?
RNA processing
the modification of pre-mRNA by enzymes in the eukaryotic nucleus before the genetic messages are dispatched to the cytoplasm
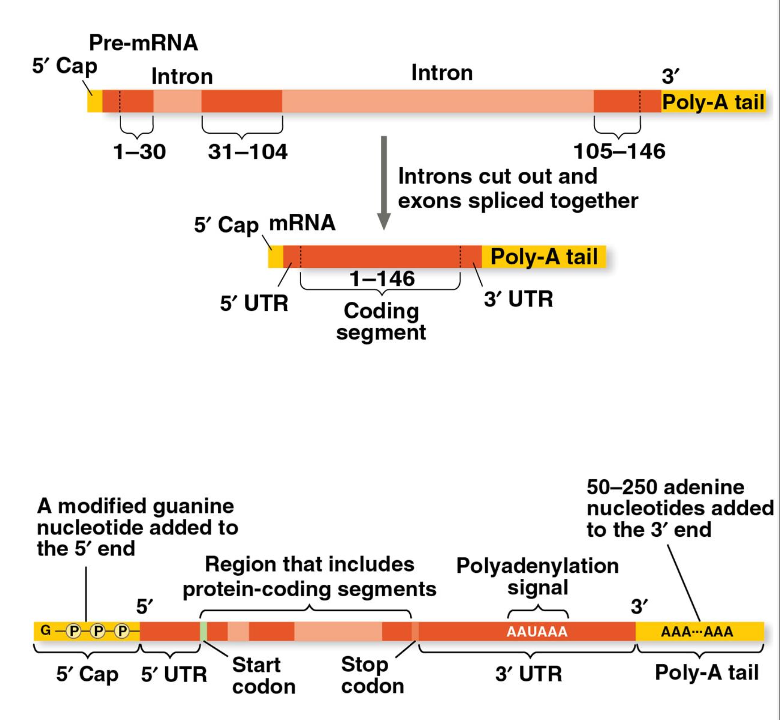
both ends of the primary transcript are altered
the 5’ end receives a modified nucleotide 5’ cap
the 3’ end gets a poly-A-tail
certain interior sections of the molecule (introns) are cut out and the remaining parts (exons) spliced together
What happens during RNA processing?
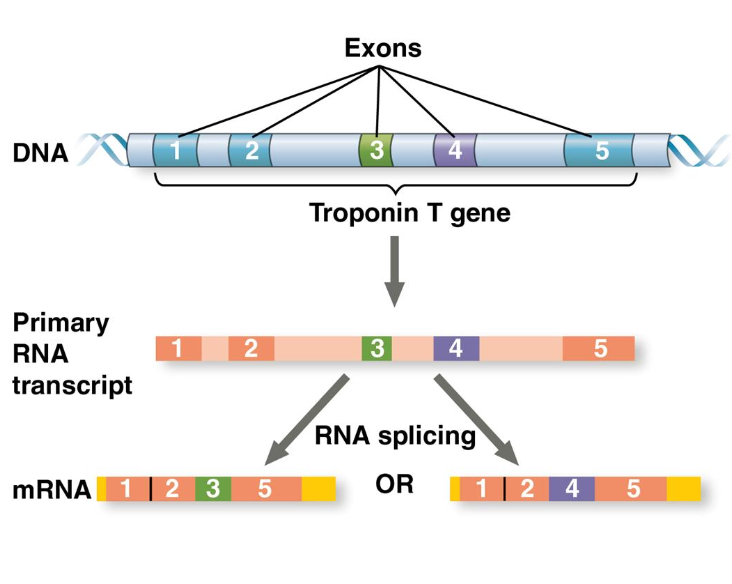
different mRNA molecules are produced from the same primary transcript, depending on which RNA segments are treated as exons and which as introns
can significantly expand the repertoire of a eukaryotic genome
more than 90% of the human protein-coding genes undergo alternative splicing
What is alternative RNA splicing?
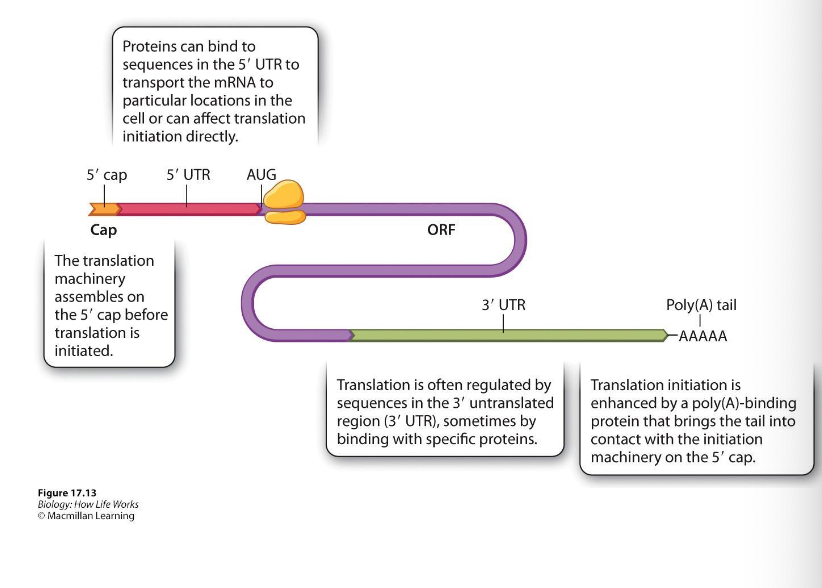
initiation → selected mRNAs can be blocked by regulatory proteins that bind to sequences or structures of the mRNA
alternatively, the translation of all mRNAs in a cell may be regulated simultaneously
translation initiation factors are simultaneously activated in an egg following fertilization
What are some ways that translation is regulated?
processing, including cleavage, and chemical modifications (posttranslational modifications)
the addition of a phosphate group (phosphorylation)
What do polypeptides undergo after translation?