A-Level Biology Paper 1: General Exam Flashcards
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms

B. This is because it cannot be:
A, as macromolecules formed via condensation reactions
C, as lipids don’t form polymers
D, as lipids are macromolecules but aren’t composed of repeating units.

A. This is because extrinsic proteins are embedded within the bilayer. it cannot be:
B, as glycolipids are not proteins
C, as the bilayer is fluid, not rigid.
D, as the bilayer is semi-permeable.

B. This is because invertebrates undergo mechanical ventilation, as muscular contractions of the abdomen allow for air to be forced in and out of the tracheal system, maintains a steep concentration gradient. it cannot be:
A, which decreases volume of tracheal fluid
C, as spiracles lead to tracheae then tracheoles
D, as spiracles are capable of opening and closing, not tracheoles
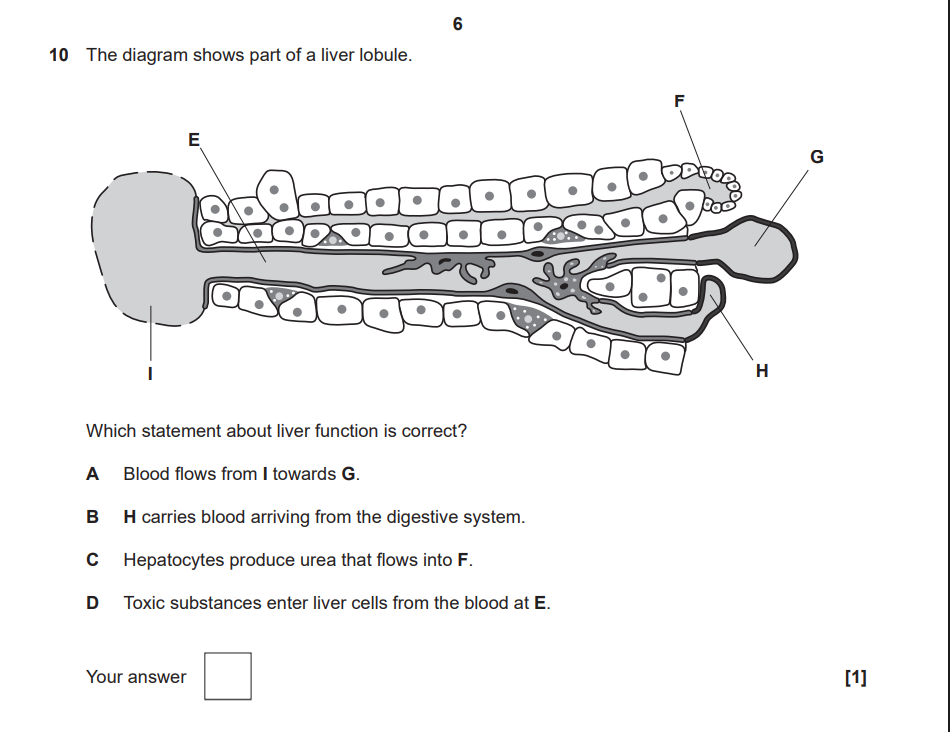
D. This is because E represents the sinusoid, in which blood containing substances absorbed from the digestive system flow through it, and the hepatocytes lining the cell absorb these toxic substances. It cannot be:
A, as blood flows through the periphery to the central vein, the statement implies otherwise
B, as the hepatic portal vein carries blood arriving from the digestive system. H is the branch of the hepatic artery
C, as F represents the bile duct, and hepatocytes produce bile, which is released into the blood to be carried to the kidney.
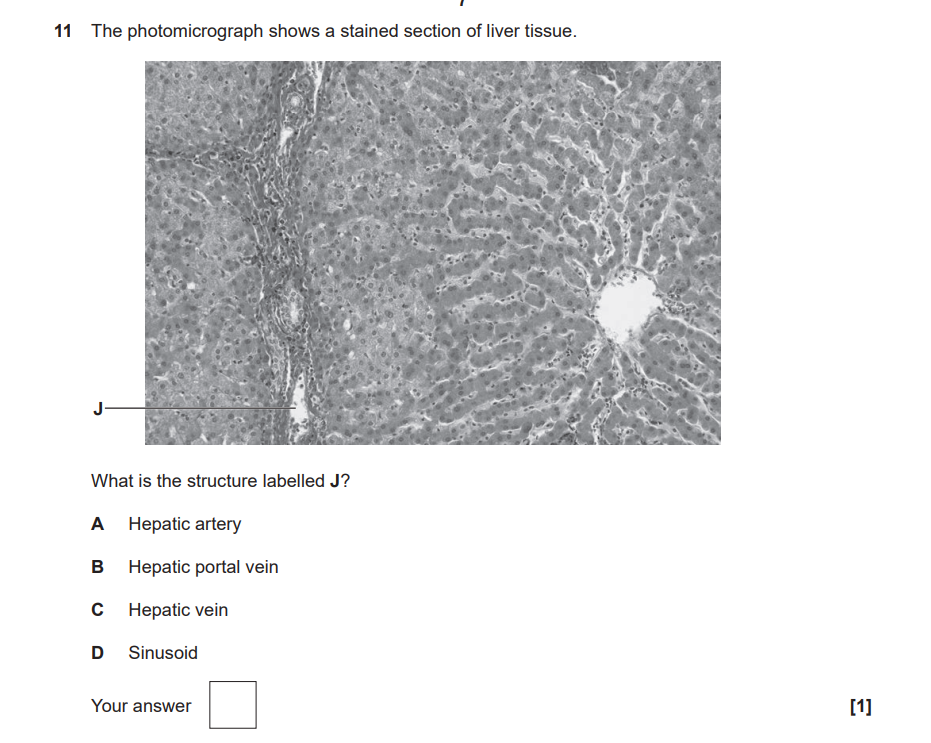
B. The large circular white space on the right side of the image is a Central Vein (center of a lobule).
The structure labelled J is located in the connective tissue between lobules (the portal tract/triad).
The vessel at J has a large, irregular lumen and a thin wall, which distinguishes it as a vein rather than an artery (which would be smaller with a thick muscular wall).
Therefore, J is a branch of the Hepatic portal vein.

A. This is accounted for by: Statement 1 → Low light intensity leads to the LDR slowing down, so less ATP, less NAPDH
Statement 2 → High light intensity, LDR produces more ATP + NAPDH, regeneration of RuBP from TP requiring ATP.
Statement 3 → High light intensity, light not the limiting factor; changes to CO₂ or temperature, if CO₂, slows rate of RuBP conversion to GP, and RuBP regenerated faster than it is accumulated.

C. This is because lipids have significantly higher energy values than proteins. it cannot be:
A, as it has less C-H due to the presence of the OH’s
B, as due to the lipid content, chocolate has a higher energy value
D, as carbohydrates have higher energy value.
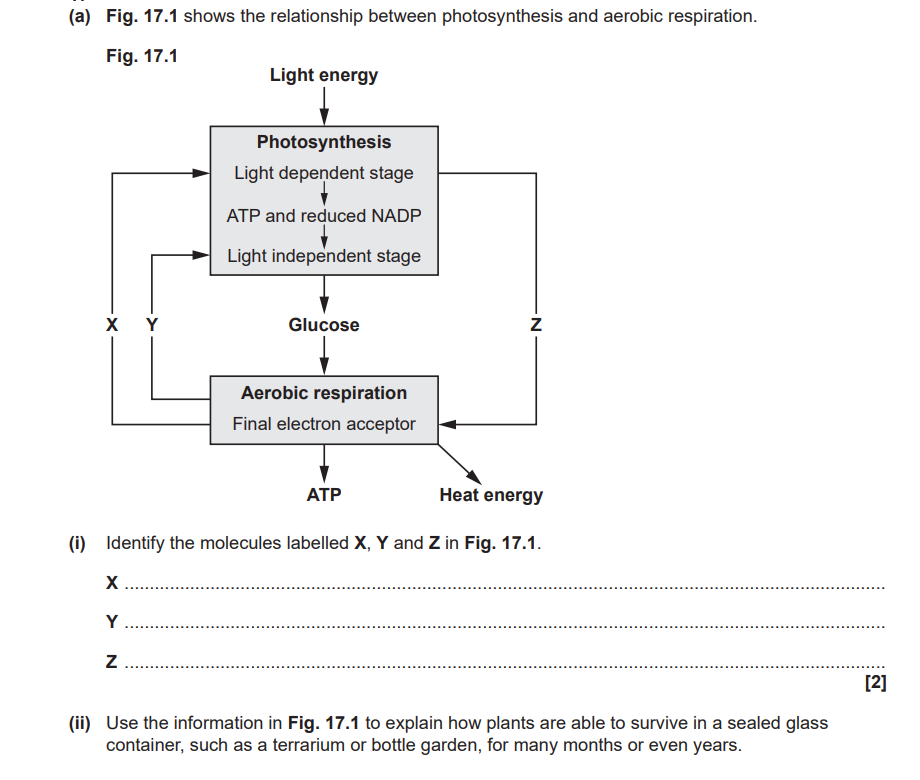
a) Water
Carbon Dioxide
Oxygen
b) Respiration provides water and carbon dioxide, which is used as reactants for photosynthesis
Photosynthesis provides glucose and oxygen which is needed for respiration
Water used for photolysis
CO₂ used for the Calvin Cycle
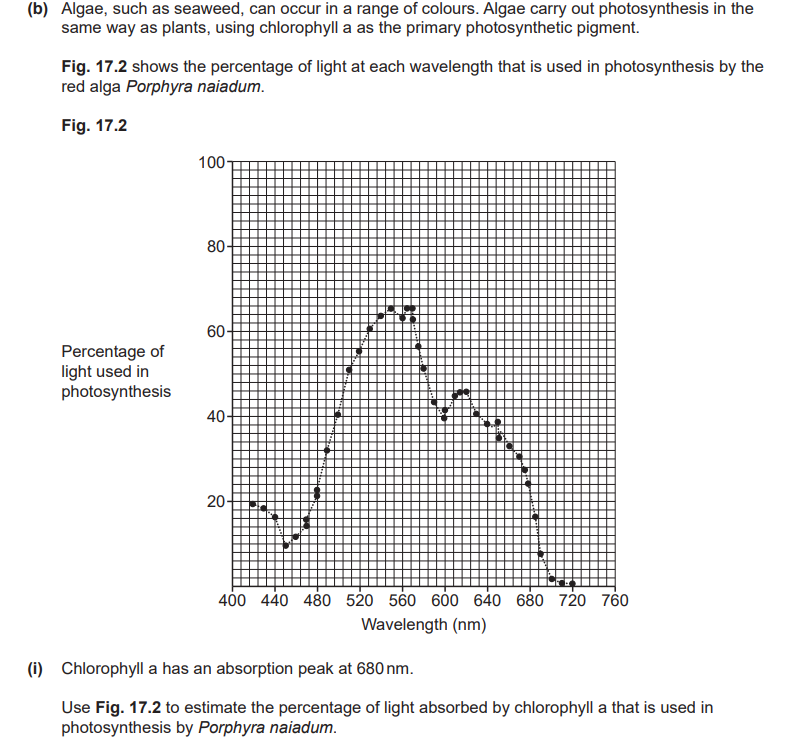
ii) Explain why the percentage of light used in photosynthesis is higher than your answer to part (i) at wavelengths other than 680 nm.
iii) Porphyra naiadum grows in deep water. Use the data in Fig. 17.2 to suggest how it is able to survive in conditions where other types of algae or plant cannot.
i) 24%
ii) Due to the presence of accessory pigments, which absorb different wavelengths of light for use in the LDR.
iii) Algae have pigments that can absorb shorter wavelengths of light, and these wavelengths can penetrate water at greater depths.

iii) Furosemide is a banned substance because it can be used as a masking agent, to hide the use of performance enhancing drugs. Suggest how furosemide could act as a masking agent.
i) Cannabis
ii) Causes rapid water loss, causing a larger volume of urine to be produced.
iii) By increasing urine volume, it dilutes the concentration of other banned substances in the urine.
What is the formula for net pressure?
Formula: Net Pressure = (Net Hydrostatic Pressure) + (Net Oncotic Pressure)
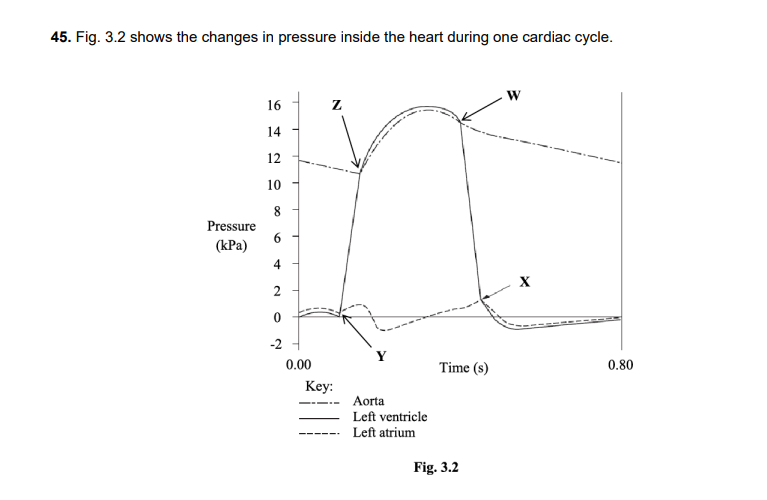
Describe the events taking place at the points marked W, X, Y and Z and explain how these events are related to the changes in pressure shown in the diagram.
Which part of the adrenal gland produces steroid hormones?
The Adrenal Cortex (the outer region).
Which part of the adrenal gland produces adrenaline?
The Adrenal Medulla (the inner region).
What is the primary function of Mineralocorticoids (e.g., Aldosterone)?
They help regulate the balance of salt (K+ and Na+) and water concentrations in the blood.
What is the primary function of Glucocorticoids (e.g., Cortisol)?
They regulate the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats (often raising blood glucose during stress).
Why can hormones from the adrenal cortex pass directly through the cell membrane?
Because they are steroid hormones (lipid-based/derived from cholesterol), allowing them to diffuse through the phospholipid bilayer.
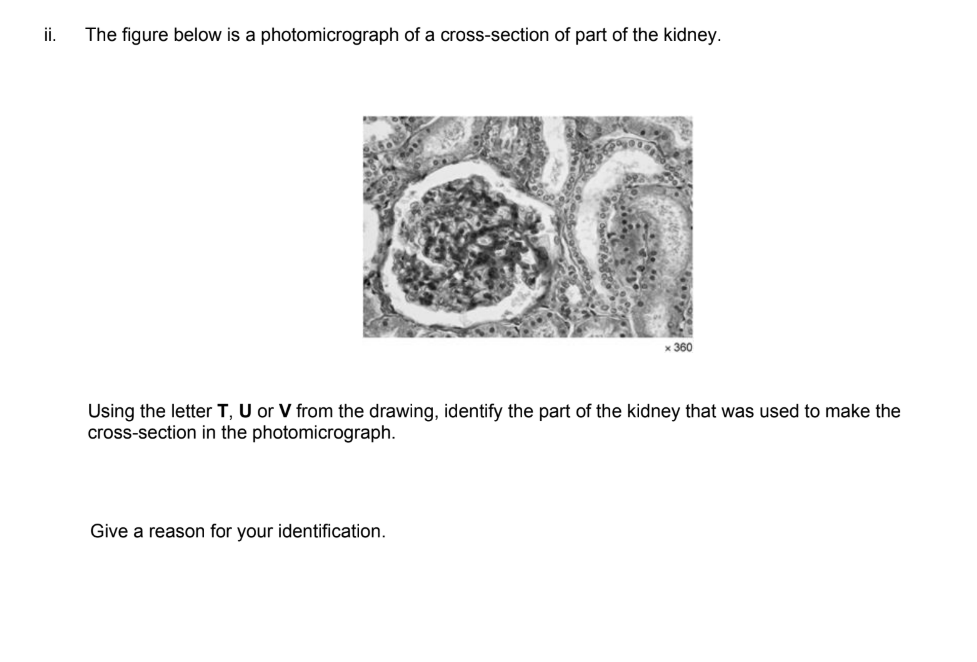
U(Cortex).
Contains the glomerulus and Bowman’s Capsule
Describe the cAMP Second Messenger model for Adrenaline. (4 marks)
Adrenaline (1st messenger) binds to a specific receptor on the cell surface.
This activates the enzyme adenylyl cyclase.
Adenylyl cyclase converts ATP into cyclic AMP (cAMP).
cAMP (2nd messenger) activates enzymes (kinases) in the cytoplasm to trigger a response (e.g., glycogenolysis).
Aldosterone is a mineralocorticoid produced by the cortex. Explain specifically how it acts on the cells of the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) and collecting duct to raise blood pressure. (4 marks)
It makes cells in the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct more permeable to Na+.
More Na+ is reabsorbed into the blood.
Water follows by osmosis down the water potential gradient.
Blood volume increases → Blood pressure increases.
Compare the receptor location and action of Steroid vs. Protein hormones. (2 marks)
Steroid Hormones: Lipid-soluble. Diffuse through the membrane. Bind to receptors in the cytoplasm or nucleus. Act as transcription factors to control protein synthesis.
Protein Hormones: Lipid-insoluble. Bind to receptors on the cell surface membrane. Trigger a second messenger cascade inside the cell.
Which region of the kidney contains the Glomerulus and Bowman's Capsule?
The Cortex (the outer region).
Which region of the kidney contains the Loop of Henle and Collecting Duct?
The Medulla (the inner region).
In a kidney photomicrograph, what does a Glomerulus look like?
A dense, knot-like cluster of capillaries (cells) surrounded by a clear white space (Bowman's space).
The inner layer of the Bowman's capsule is made of specialized cells. Name these cells and explain how their "feet" (pedicels) assist in filtration.
Cell Name: Podocytes.
Function: They have finger-like projections called pedicels (or major and minor processes) that wrap around the capillaries.
These pedicels form gaps called filtration slits. These slits ensure that large proteins and blood cells cannot pass through, while allowing the glomerular filtrate to pass freely.
List the three layers the filtrate must pass through to get from the blood plasma into the Bowman's capsule. (3 marks)
The Capillary Endothelium: This has pores (fenestrations) to allow plasma through.
The Basement Membrane: A mesh of collagen and glycoproteins that acts as the main filter (molecular sieve), stopping large proteins (molecular mass > 69,000).
The Podocyte Epithelium: The filtration slits formed by the pedicels.
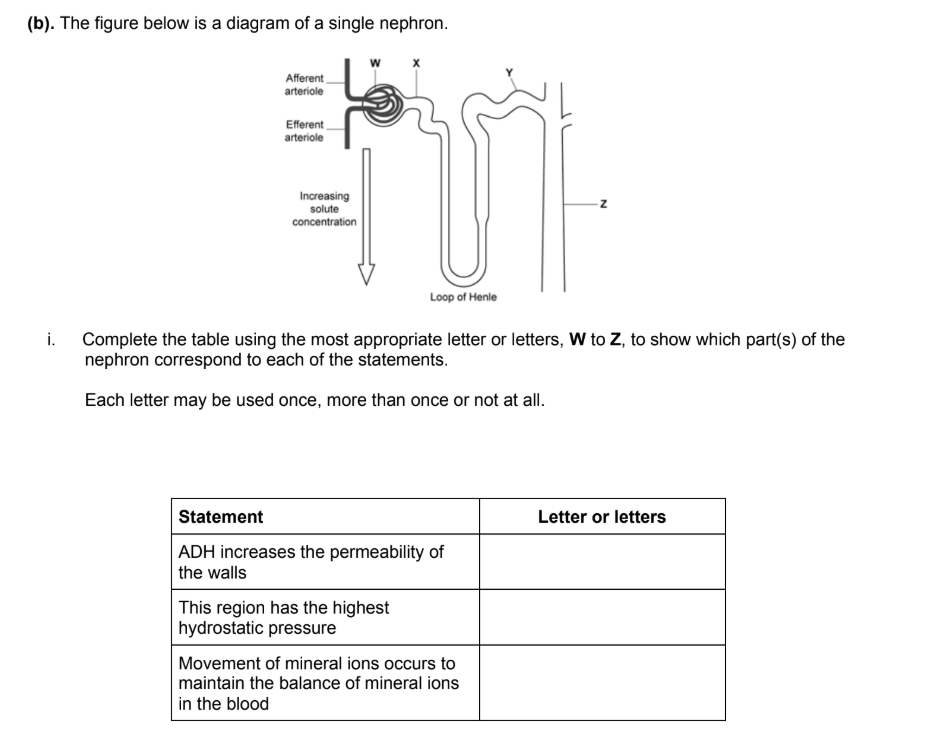
"ADH increases the permeability of the walls"
Correct Letter(s): Y and Z (or just Z)
"This region has the highest hydrostatic pressure"
Correct Letter: W
"Movement of mineral ions occurs to maintain the balance of mineral ions in the blood"
Correct Letter: Y (Distal Convoluted Tubule)
Don’t mix with X as fine-tuning and balancing happens in Y
Outline the processes in the loop of Henle that cause the solute concentration to increase (as shown by the arrow going down into the medulla). (3 marks)
Sodium (Na+) and Chloride (Cl-) ions are actively transported out of the ascending limb.
The ascending limb is impermeable to water, so water stays inside. This raises the solute concentration (lowers water potential) in the surrounding interstitial fluid (medulla tissue fluid).
The descending limb is permeable to water but impermeable to ions.
Water moves out of the descending limb by osmosis into the concentrated interstitial fluid.
As water is lost, the filtrate inside the descending limb becomes increasingly concentrated as it moves down the loop.
(any 3 points)
When ADH binds to receptors on the collecting duct cells (Z), what specific intracellular change occurs to increase permeability? (3 marks)
Binding: ADH acts as a cell-signaling molecule (first messenger) and binds to specific receptors on the cell surface membrane of the collecting duct cells.
Second Messenger: This binding activates an enzyme cascade (involving G-proteins) that leads to the production of cyclic AMP (cAMP) inside the cell.
Vesicle Movement: cAMP triggers a signaling pathway that causes vesicles containing aquaporins (water channel proteins) to move toward and fuse with the luminal membrane (the membrane facing the filtrate).
Increased Permeability: The insertion of these aquaporins increases the permeability of the membrane to water, allowing water to leave the collecting duct by osmosis down a water potential gradient.
Scenario: A drug is discovered that inhibits the enzyme adenylyl cyclase within the cells of the collecting duct.
Task: Predict and explain the effect this drug would have on the volume and concentration of a person’s urine, even if their ADH levels were high. (4 marks)
The Disconnection: ADH (the first messenger) will still bind to the receptors on the cell surface. However, because adenylyl cyclase is inhibited, it cannot convert ATP to cyclic AMP (cAMP).
The Broken Pathway: Without cAMP (the second messenger), the enzyme cascade that normally moves vesicles is never triggered.
The Result: Vesicles containing aquaporins remain in the cytoplasm and do not fuse with the luminal membrane. The collecting duct remains impermeable to water.
Urine Outcome: Water cannot leave the filtrate by osmosis. The patient produces a large volume of dilute urine.
Why is tumor formation a major risk in ANY stem cell therapy?
Because stem cells are defined by their ability to divide indefinitely. If this division is not controlled after transplant, it leads to a mass of cells (cancer/teratoma).
What is the difference between Totipotent and Pluripotent?
Totipotent cells can differentiate into ANY cell type including the placenta/umbilical cord. Pluripotent cells can differentiate into all body cell types except extra-embryonic tissues.
In a graph, what does it mean if the error bars (Standard Deviation) of two groups overlap?
It indicates that there is no significant difference between the means of the two groups.
What is an endocrine gland?
(a group of cells that) secretes / releases /
produces, hormones ✓
(directly) into the blood (stream) ✓
The pancreas contains endocrine glands such as the Islets of Langerhans. It also contains cells that produce digestive enzymes.
Suggest why the cells that produce digestive enzymes are described as exocrine rather than endocrine.
(because digestive enzymes) are released
into ducts ✓
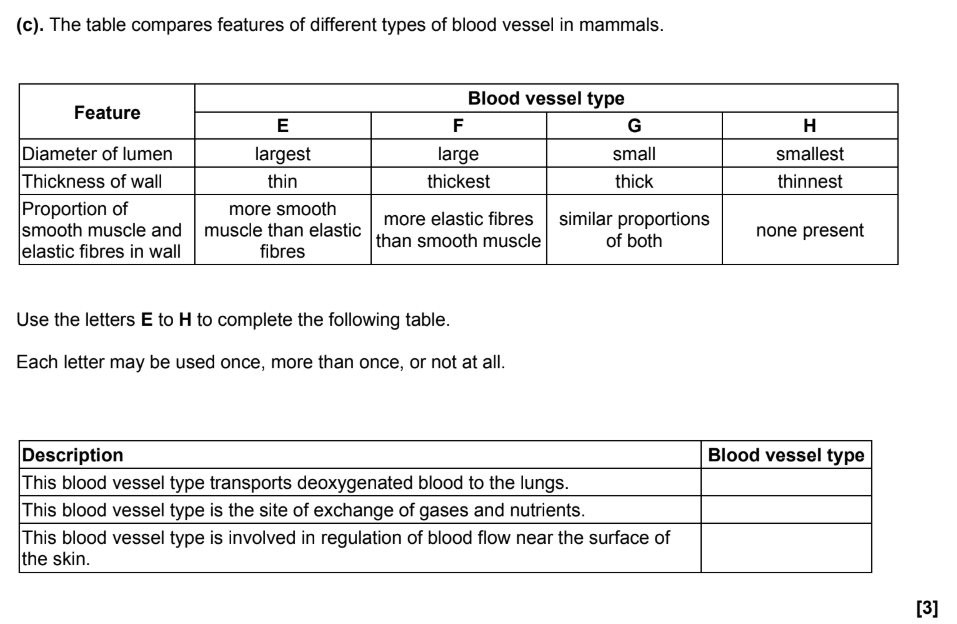
F
H
G
Vessel H (Capillary) is where tissue fluid is formed. Explain how the Hydrostatic Pressure at the arterial end of vessel H causes fluid to leave the blood, and why large proteins remain inside.
Hydrostatic Pressure: At the arterial end of the capillary, the blood is under high hydrostatic pressure (due to contraction of the heart/narrowing of vessels).
The Gradient: This hydrostatic pressure is higher than the oncotic pressure (osmotic pressure) pulling water back in.
Net Flow: This creates a net pressure gradient that forces fluid (water and small dissolved solutes like glucose/ions) out of the capillary and into the spaces between cells.
The Barrier: Large plasma proteins (like albumin) and blood cells are too large to pass through the gaps (fenestrations) in the capillary wall (endothelium), so they remain in the blood.
When the body gets too hot, vessel G (Arteriole) near the skin surface dilates. Name this process and explain how it cools the body. (4 marks)
Name of Process: Vasodilation.
The Mechanism:
The smooth muscle in the walls of the arterioles relaxes.
This causes the arteriole lumen to widen (dilate).
More blood flows through the capillaries closer to the skin surface.
Cooling Effect: Heat is lost from the blood to the surroundings by radiation (and convection/conduction).
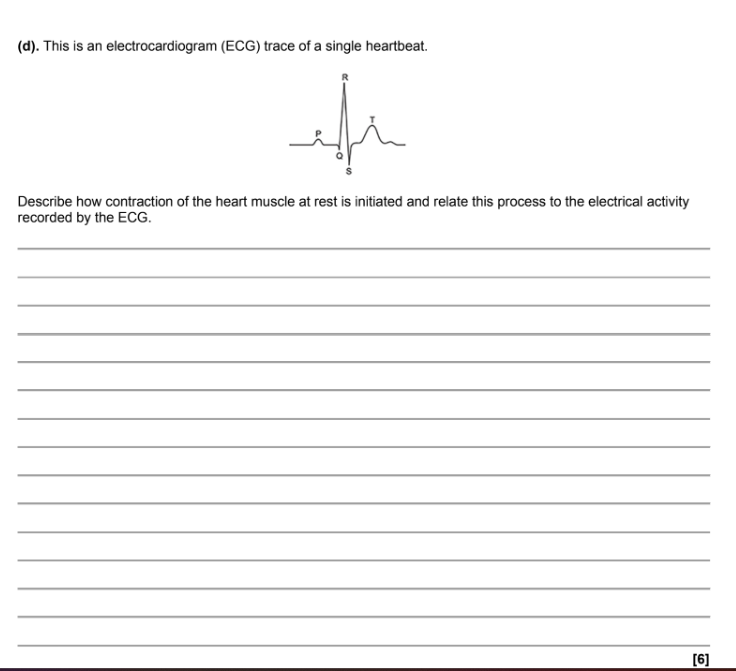
Myogenic Initiation: The heart muscle is myogenic (initiates its own contraction), with the Sino-atrial Node (SAN) acting as the pacemaker.
Atrial Excitation: The SAN releases a wave of excitation (depolarisation) that spreads rapidly across the atrial walls.
P-Wave Link: This depolarisation causes atrial systole (contraction), which generates the P wave on the ECG.
The AVN Delay: The signal reaches the Atrio-ventricular Node (AVN) where there is a short delay. (This ensures the atria fully empty their blood into the ventricles before the ventricles contract).
Transmission: The wave of excitation travels down the Bundle of His (in the septum) and spreads into the Purkyne fibres.
Ventricular Contraction: The Purkyne fibres conduct the impulse to the apex (bottom) of the heart, causing the ventricles to contract from the bottom upwards.
QRS Link: This ventricular depolarisation (contraction) generates the QRS complex on the ECG.
Recovery/T-Wave Link: The ventricles then relax (repolarisation or diastole), which generates the T wave on the ECG.
What specific electrical event does the P wave represent?
Atrial Depolarisation (which leads to Atrial Systole).
Why is the delay at the AVN physiologically important?
It prevents the ventricles from contracting at the same time as the atria, allowing them to fill completely with blood first.
What electrical event does the QRS complex represent?
Ventricular Depolarisation (leading to Ventricular Systole).
If you were to start running, the sympathetic nervous system would activate. Explain how the accelerator nerve increases heart rate at the molecular level (refer to the SAN). (6 marks)
Neurotransmitter Release: The accelerator nerve (sympathetic nerve) releases the neurotransmitter Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine) at the synapse with the Sino-atrial Node (SAN).
Receptor Binding: Noradrenaline binds to specific receptors on the cell surface membrane of the SAN cells.
The Molecular Cascade: This triggers the Second Messenger system (similar to adrenaline's action elsewhere):
It activates the enzyme adenylyl cyclase.
This converts ATP into cyclic AMP (cAMP).
The Effect on the SAN:
cAMP leads to the opening of more Sodium (Na⁺) or Calcium (Ca2+) ion channels.
The membrane depolarises to the threshold potential more quickly (the resting potential drifts up faster).
The Result: The SAN generates waves of excitation (action potentials) at an increased frequency.
22(a). Describe the role of plant hormones in the control of seed germination. (4 marks)
Water is absorbed by the seed.
This stimulates the embryo to produce Gibberellins.
Gibberellins stimulates the synthesis for Amylase.
Amylase breaks down the starch deposits in the endosperm into maltose/glucose.
Which is used in respiration for ATP.
(any four points)
How do you calculate degrees of freedom for an unpaired t-test?
(n1 + n2) - 2 (where n is the sample size of each group).
If the calculated t-value is GREATER than the critical value, what do you conclude?
The difference is significant. Reject the null hypothesis. (p < 0.05).
If the calculated t-value is LOWER than the critical value, what do you conclude?
The difference is not significant. Accept the null hypothesis. The difference is likely due to chance.
What specifically does Gibberellin cause to happen in the stem?
Stem elongation (specifically elongation of the internodes).
What is ALWAYS the Null Hypothesis for a t-test?
"There is no significant difference between the means of [Group A] and [Group B]."
How does inhibiting gibberellin affect plant structure?
It prevents stem elongation (specifically internode elongation), resulting in dwarf (short) plants.
What is the metabolic benefit of keeping crop plants short (dwarf varieties)?
Energy and assimilates are diverted away from vertical growth and towards reproductive growth (seeds/fruits), increasing yield.