Physics - P2: Forces - Measuring Speed
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Page 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is speed?
Speed is distance travelled each second.
Equation for Speed:
Speed = Distance/Time
What are the general units?
Distance is m (meters)
Time is s (seconds)
Speed is m/s (meters/seconds)
How to measure speed simply
Measure a known distance → time how long it takes → use s=d/t
Choosing equipment (short distances)
Use a metre rule (distance) and a timer (time)
Choosing equipments (long distances)
Use a tape measure or trundle wheel for fields/track.
Why choose equipment carefully?
Better matched tools = more accurate distance/time → more accurate speed
What does a light gate do?
Detects when an object blocks a light beam → starts/stops a digital timer.
How do light gates measure an object’s speed?
A light gate can measure how fast something is moving. You put a flat piece called a flag on the object. When the flag passes the light gate, the light is blocked and the timer starts. When it passes the next gate, the timer stops. Speed = distance ÷ time.
If there’s only one gate, speed = length of the flag ÷ time it blocks the light.
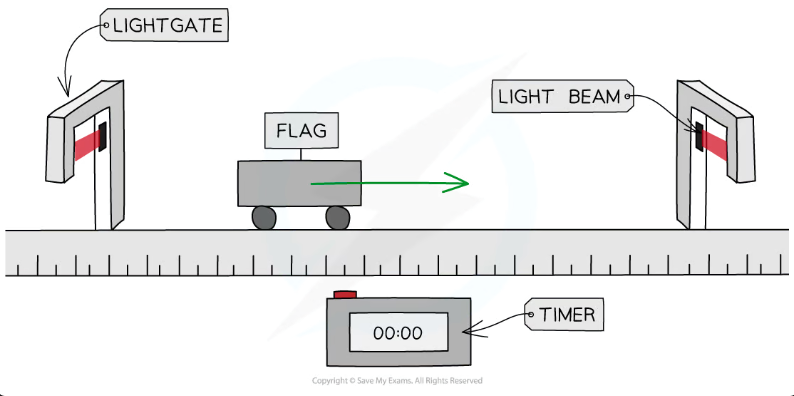
What is the single light gate?
The gate measures the distance and how long the light beam is blocked (speed)
What is the formula for objects moving with constant (uniform) speed?
Speed = Distance/Time
Formula for objects moving with non constant (non uniform) speed?
Average Speed = Total Distance/Time
I ran 100m in 9.53secs. What’s my average Speed?
Average= total Distance/Time. 100 over 9.53= 10.49m/s
Where do all units in physics come from?
The SI Units - Mass, Length, Time, Current, Temperature, Amount of Substance
All quantities can be one of two types:
Scalar and Vector
What does scalar mean?
Scalar - Things with just magnitude, e.g. mass is scalar, you say 70kg not 70kg east.
What does vector mean?
Vector - Both magnitude and direction e.g. velocity of a car can be 60 km/h north (direction)
If it says -60km/h, it is going left
If it says +60km/h it is going right
What is the difference between distance and displacement?
Distance → Total measure of distance → Scalar
Displacement → Total distance from the start point, with direction → Vector
What does a distance time graph show?
It shows how the distance of an object varies over time
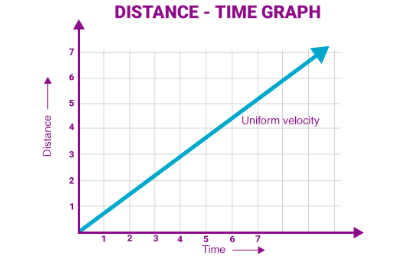
When speed is constant in a D-T graph, the line is straight, When speed is non-constant (non uniform), the line…
is curved. A curve going inwards is increasing in speed. A curve going outwards is decreasing in speed.
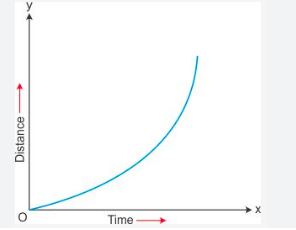
How to find constant speed of a D-T Graph?
Speed = Change in y over Change in x