ESS test Unit 3
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Births and immigration are…
Births and immigration are inputs to a human population.
Deaths and emigration are…
Deaths and emigration are outputs from a human population
An urban area are…
An urban area works as a system.
Urban
The natural place where an organism lives.
Population dynamics can be…
Population dynamics can be quantified and analyzed by calculating total fertility rate, life expectancy, doubling time and natural increase.
To what extent are urban systems similar to natural ecosystems?
Both have flows of energy and materials
Both rely on balance and regulation
Both can experience collapse if overstressed
How can reimagining urban systems create a more sustainable future?
Reduce carbon emissions
Improve resilience to climate change
Support human well-being
What role do social equity and inclusivity play in the success of sustainable urban planning?
Social equity and inclusivity are essential because sustainability must benefit everyone, not just a few groups.
For ex: Streets are redesigned to reduce traffic and create public spaces.
How do different urban planning models address climate change and environmental degradation?
Different planning models use different strategies to reduce environmental impact.
Urban system
A city made up of people, buildings, transport, energy, and services that work together.
The global human population has followed…
The global human population has followed a rapid growth curve. Models are used to predict the growth of the future global human population.
Population and migration policies can be…
Population and migration policies can be employed to directly manage growth rates of human populations.
Human population growth can also be managed…
Human population growth can also be managed indirectly through economic, social, health, development and other policies that have an impact on births, deaths or migration.
How can the dynamics of human populations be measured and compared?
Human population dynamics are measured and compared using demographic indicators and population models.
To what extent can the future growth of the human population be accurately predicted?
Population growth can be reasonably predicted in the short term, but long-term predictions are uncertain due to human and environmental factors.
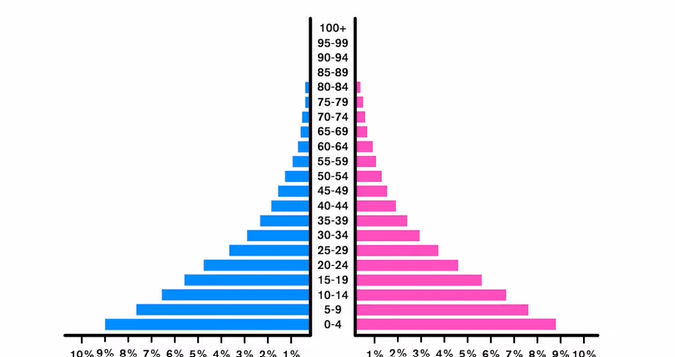
Age seg pyramids
graphs showing population structure
Demographic Transition Model (DTM)
shows how populations change as countries develop
The composition of human populations can be modelled and compared using?
The composition of human populations can be modelled and compared using age–sex pyramids.
What factors have historically influenced the growth of the human population?
Human population growth increased when people had more food, better medicine, and clean water, which helped more people survive.
Ex: In United Kingdom, population grew during the Industrial Revolution because death rates fell.
Define human population dynamics.
Human population dynamics describe how a population changes over time, including its size and age groups.
Ex: Japan has a shrinking population because few babies are born.
Why is understanding population trends important for predicting future growth?
Population trends help predict future needs, such as schools, hospitals, and jobs.
Ex: Nigeria needs more schools because many children are being born
What are the key factors that influence human population growth?
Population growth depends on how many people are born, die, and move.
Ex: India grows fast because many babies are born each year.
How can the future growth of human populations be predicted?
Future growth is predicted by studying past population data and current trends.
Ex: Germany is expected to lose population because it has few births and many elderly people.
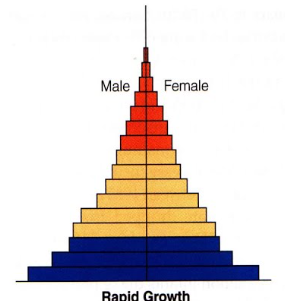
Rapid growth age seg pyramid
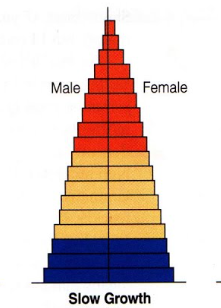
Slow Growth
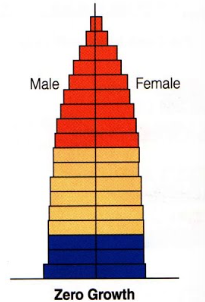
Zero growth
Outline the purpose of a Demographic Transition Model (DTM)
The Demographic Transition Model (DTM) is used to show how a country’s population changes over time as it develops.
Ex: Using the DTM, India is placed in Stage 3 because its death rate is low and its birth rate is falling.
Stage 1
Both birth rates and death rates are high, resulting in slow or stable population growth.
Stage 2
Stage 3
triangle
Expansive population
Ex:
Larger young population
Population is growing
Higher birth rate
Shorter life expectancies
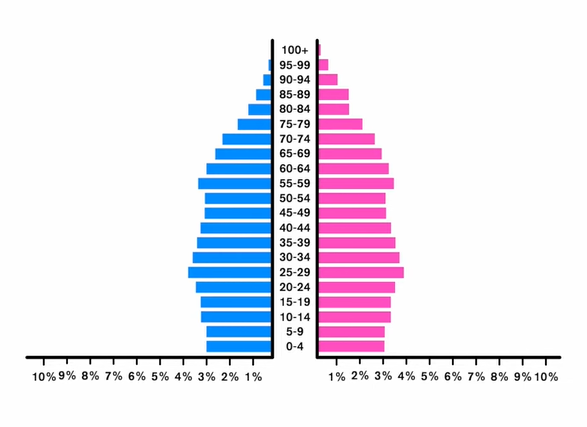
looks like a not fit low body
Stationary population
Ex:
The population is stable, a good one
Similar population across age groups
Lower birth rates
Longer life expectancies.
a fit women with nipple and belly poking out
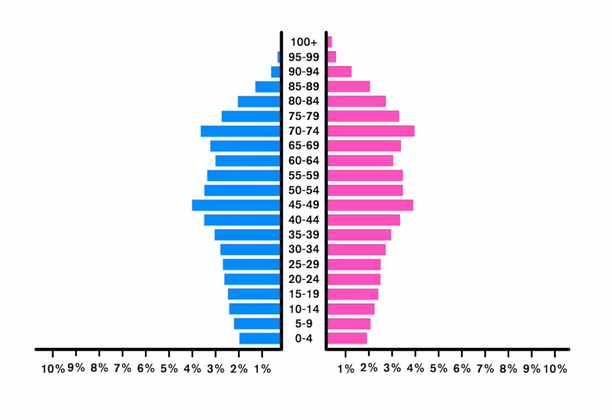
Constrictive population
Ex:
Lower birth rates
Larger older population
Longer life expectancies
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
The number of live births per 1,000 people per year.
(Number of births ÷ Total population) × 1,000 = CBR
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
The number of deaths per 1,000 people per year.
(Number of deaths ÷ Total population) × 1,000 = CDR
Natural Increase Rate (NIR)
Crude Birth Rate - Crude Death Rate = NIR
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
The average number of children a woman is expected to have in her lifetime.
Doubling Time (DT)
The number of years it takes for a population to double in size.
DT= 70 : Growth rate (%)
An urban area is…
An urban area is a built-up area with a high population density, buildings and infrastructure.
Urbanization
Urbanization is the population shift from rural to urban areas.
Rural–urban migration
More people are moving from rural areas to cities to find jobs, education, and better services.
As a result, most people now live in urban areas, and this number is still increasing.
Suburbanization
Suburbanization happens when people move from crowded city centers to less crowded areas outside the city.
Urban and suburban expansion
As cities and suburbs grow, they change the environment.
Urban planning
Urban planning helps decide on the best way to use land and buildings.
Modern urban planning…
Modern urban planning may involve considering the sustainability of the urban system.
Ecological urban planning
Ecological urban planning sees the city as an ecosystem.
It considers living things (biotic) and non-living things (abiotic) and how they interact to create a healthy and balanced city.
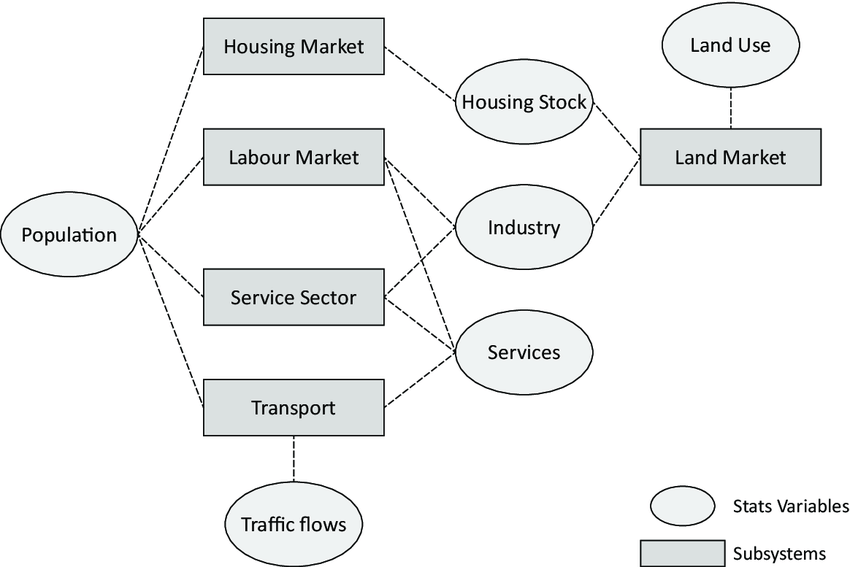
a systems flow diagram representing an urban system.
9 of good quality life
quality affordable housing
integrated public transport
green spaces
security, education, employment
renewable energy
waste management
energy efficiency.
green buildings
involvement of the community:
Define urbanization
Urbanization is the process where more people move from rural areas to urban areas, increasing the size of cities.
Define deurbanization
Deurbanization is when people move away from cities to rural areas.
Define suburbanization and its challenges
Suburbanization is when people move from city centers to outer areas.
Ex:
Increased car use
Loss of green space
Traffic congestion
Social segregation
Define urban sprawl and its effects
Urban sprawl is the uncontrolled spread of cities into rural land.
Effects:
Habitat destruction
Increased pollution
Longer travel times
Higher energy use
Define urban planning and its purposes
Urban planning is deciding how land and buildings are used in cities.
Purposes:
Organize housing and transport
Reduce congestion
Improve quality of life
Protect the environment
Key areas addressed in urban planning
Housing
Transport
Industry
Green spaces
Waste and water management
Environmental considerations in urban planning
Reducing pollution
Protecting green spaces
Managing waste and water
Reducing carbon emissions
Define sustainable planning and its importance
Sustainable planning means designing cities to meet current needs without harming the future.
Principles of ecological urban planning
Treat the city as an ecosystem
Use renewable energy
Protect biodiversity
Reduce waste
Balance human and natural systems
Define particulate matter
Particulate matter (PM) is a mixture of tiny solid particles and liquid droplets suspended in the air that can be inhaled.
Distinguish between PM2.5 and PM10
PM10
Larger particles (less than 10 micrometers)
Sources: dust, construction, road dust
Health impacts: irritates eyes, nose, and throat
PM2.5
Very small particles (less than 2.5 micrometers)
Sources: vehicle exhaust, burning fossil fuels
Health impacts: enters lungs and bloodstream, causes heart and lung disease
Explain how nitrogen oxides (NOx) contribute to urban air pollution
Nitrogen oxides react in the air to form smog, acid rain, and tropospheric ozone, which harm human health and ecosystems.
Outline human activities releasing sulfur dioxide (SO₂)
Burning coal and oil in power plants
Industrial processes (e.g. metal smelting)
One environmental impact of SO₂:
SO₂ causes acid rain, which damages forests, soil, and buildings.
Define primary pollutants
Primary pollutants are pollutants released directly into the atmosphere from a source.
Difference between natural and anthropogenic sources
Natural sources occur naturally (e.g. volcanoes)
Anthropogenic sources are caused by human activities
Two natural sources of primary pollutants
Volcanoes → release sulfur dioxide and ash
Wildfires → release carbon monoxide and particulate matter
Fossil fuel burning and primary pollutants
Burning fossil fuels releases pollutants directly into the air.
Carbon monoxide (CO)
Sulfur dioxide (SO₂)
Two primary air pollutants
Carbon monoxide (CO)
Sulfur dioxide (SO₂)
Two secondary air pollutants
Tropospheric ozone (O₃)
Acid rain (formed from SO₂ and NOx)
Outline formation of tropospheric ozone
Vehicles release NOx
Sunlight causes chemical reactions
Ozone forms near the ground. This creates photochemical smog
Sources and health impacts of particulate matter
Sources:
Vehicle exhaust
Construction
Fossil fuel burning
Health impacts:
PM10: breathing irritation
PM2.5: lung disease, heart problems
Two technological interventions
Catalytic converters: convert harmful gases into less harmful ones
Cleaner fuel technology: reduces emissions from vehicles and power plants
Pedestrianized town centers
Reducing cars in city centers:
Lowers NOx and PM emissions
Improves air quality
Green walls and natural screens
Trap particulate matter
Absorb some air pollutants
Improve local air quality
Catalytic converters (purpose)
Catalytic converters reduce harmful gases from vehicles by converting:
CO → CO₂
NOx → nitrogen and oxygen
Acid rain and marble/limestone corrosion
Acid rain reacts with calcium carbonate
Stone dissolves
Buildings and statues weaken
Catalytic converters and NOx
They break NOx into nitrogen and oxygen, reducing smog and acid rain.
Two strategies to change human activity
Use public transport instead of cars
Switch to renewable energy instead of coal and oil