Eduquas A level Biology Core concepts Enzymes
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
structure and function of enzymes
globular proteins (Quaternary structure)
catalyse biological reactions by lowering activation energy
enzyme structure
specific 3D shape with active site complementary to specific substrate
if shape of allosteric site changes, active site shape also changes
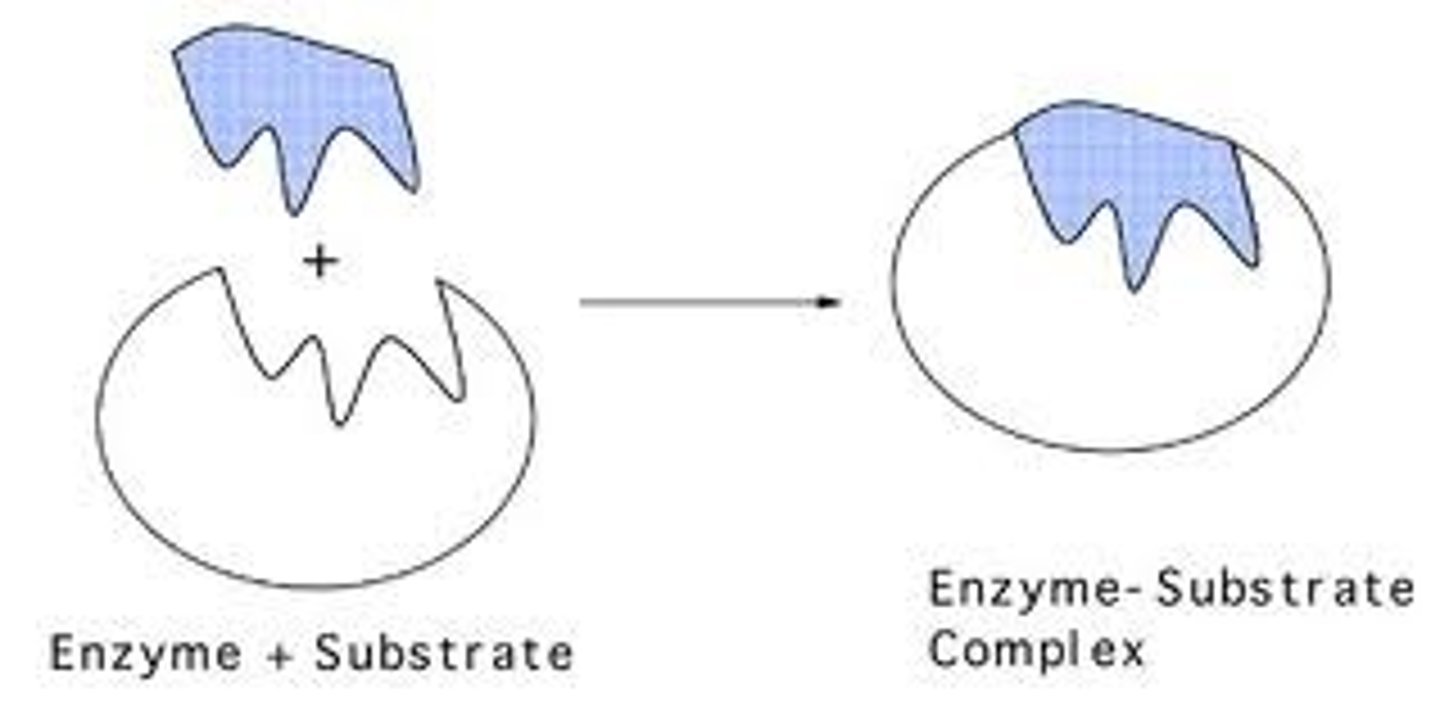
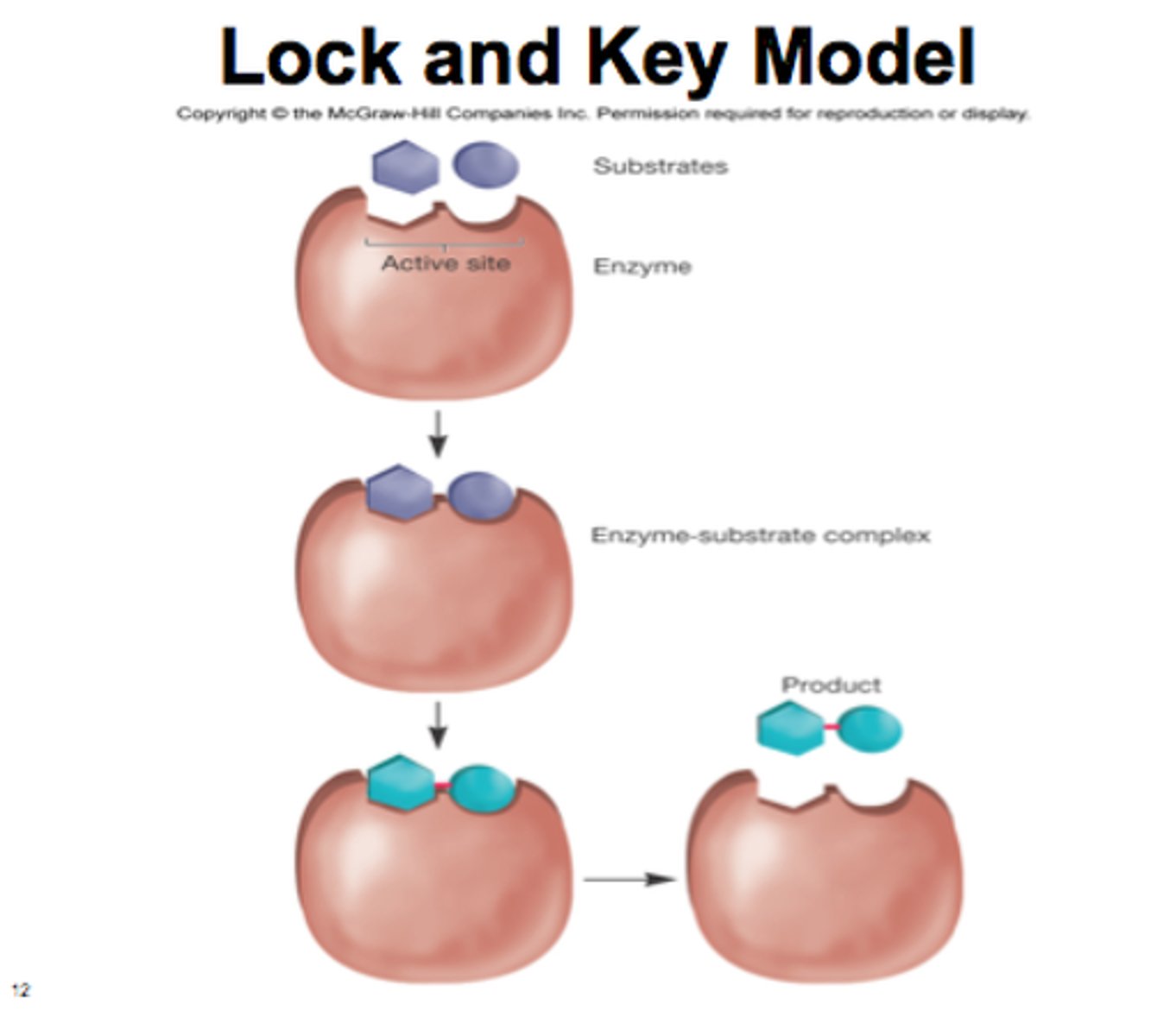
Lock and Key
Active site does not change
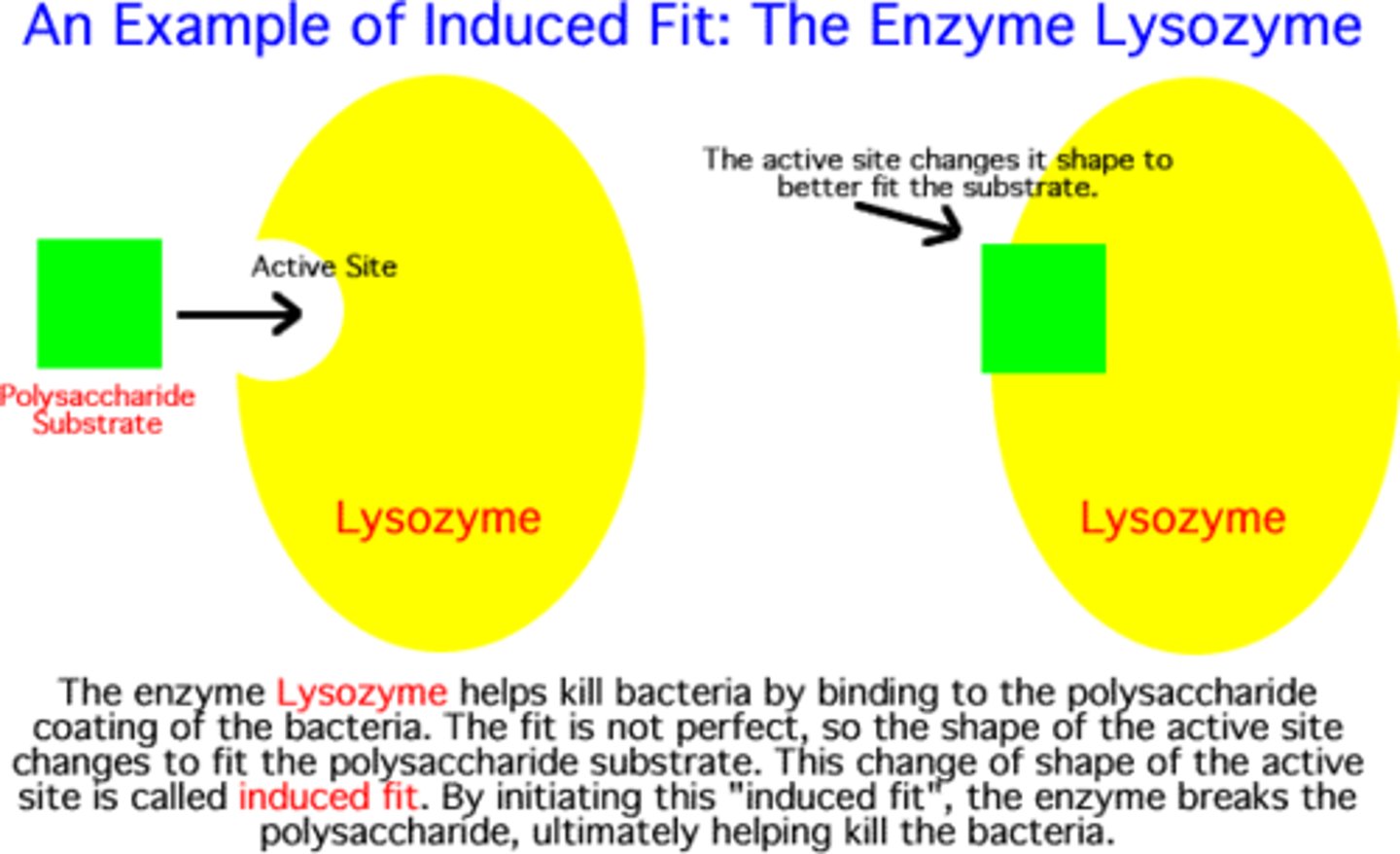
Induced fit
specific but not rigid active site
anabolic reaction
build up
synthesis, polymerisation
catabolic
break down
digestion, hydrolysis
Factors affecting enzyme action
Temperature
pH
Substrate concentration
Enzyme concentration
Enzyme inhibition
how temperature affects enzymes
as temperature increases, rate of reaction increases, until maximum rate of reaction is reached, from then on increasing temperature decreases rate of reaction
- at low temp, less Ek, so molecules move less, less collisions = decreased rate of reaction
- increasing temp, increases Ek, move movements, more successful collisions = more enzyme substrate complexes per unit time = increased rate of reaction
-at OPTIMUM TEMP, molecules move at max velocity = max rate of reaction
- if temperature continues to increase, molecules vibrate, breaking weaker hydrogen bonds in tertiary structure, enzyme shape changes so active site shape changes and is no longer complementary to specific substrate
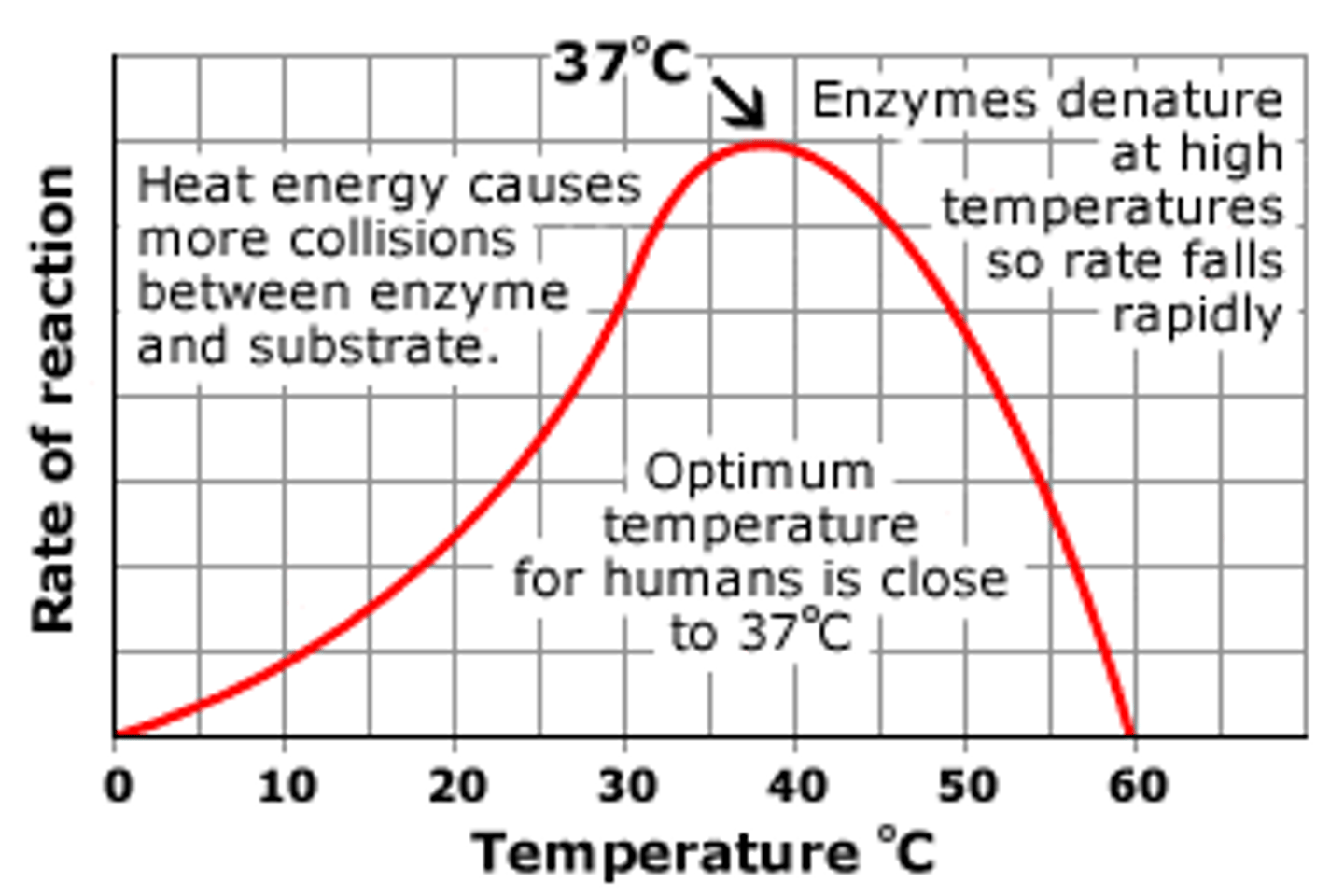
Optimum temperature defintion
temperature at which rate of reaction is at its maximum
denature defintion
molecules in enzyme vibrate, breaking weaker hydrogen bonds in tertiary structure, enzyme shape changes so active site shape changes and is no longer complementary to specific substrate
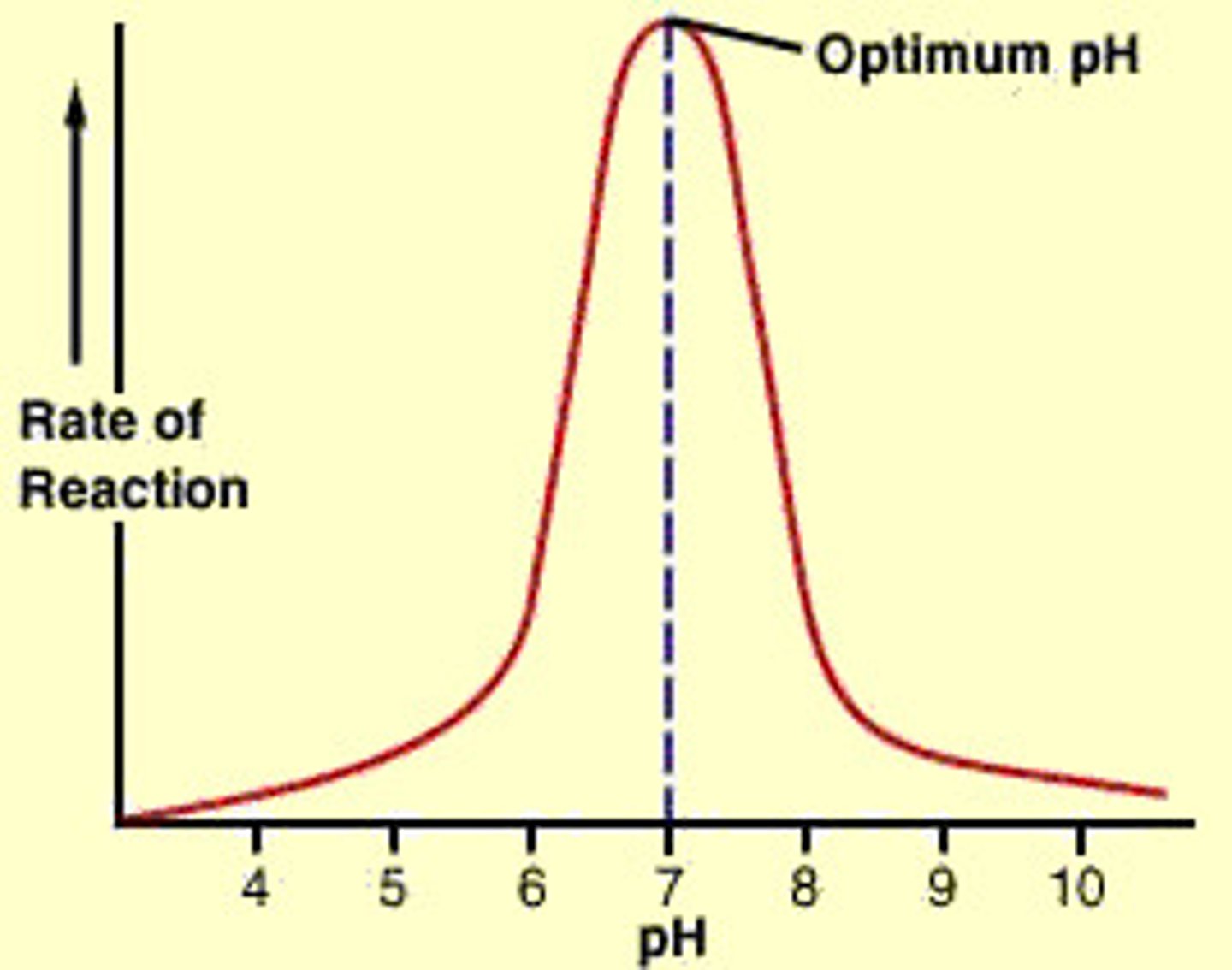
how pH affects enzyme action
change from optimum pH cause decrease in rate of reaction
- small change inactivates enzymes
- big change - enzymes denaturing
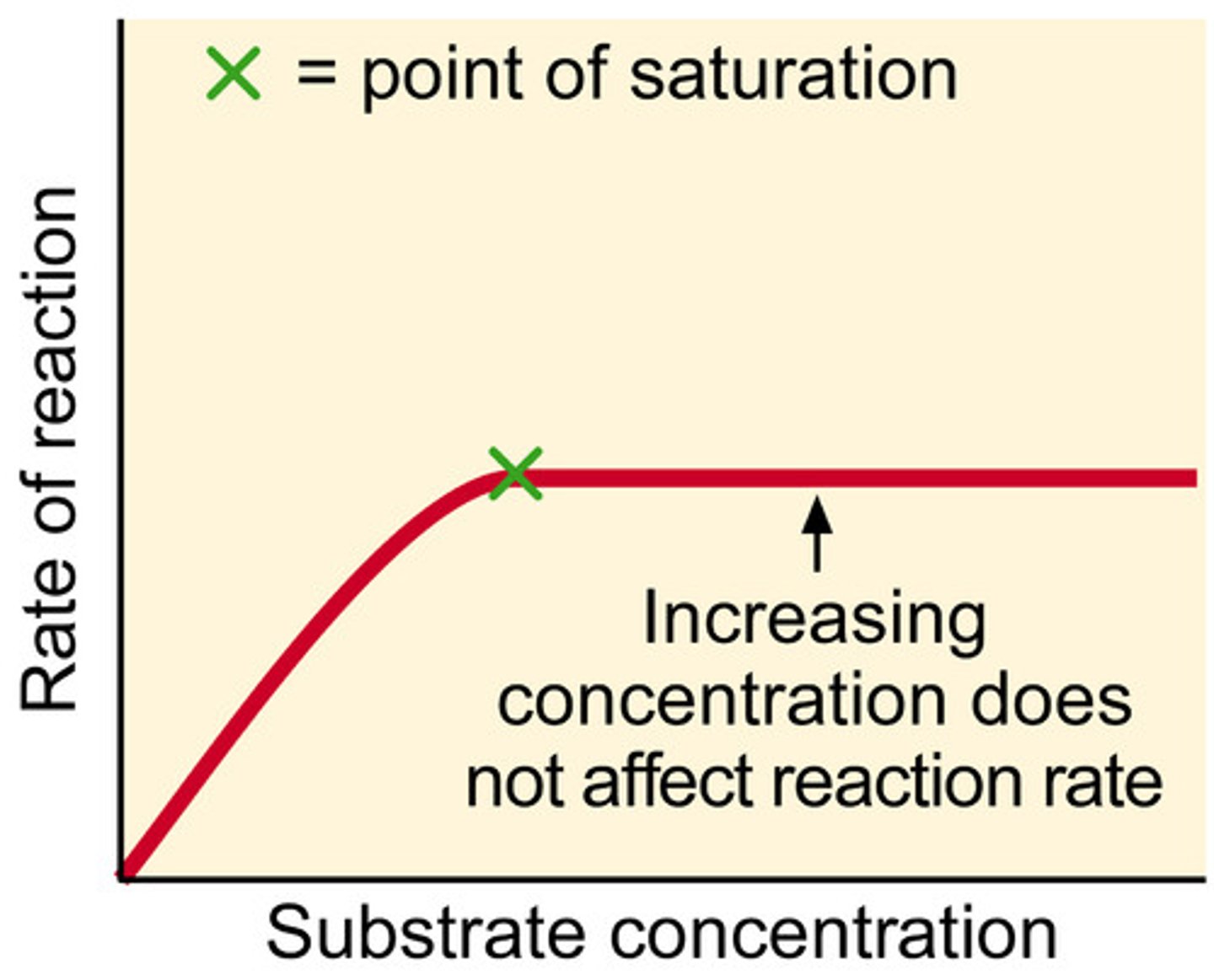
how substrate concentration affects enzyme action
as concentration increases, rate if reaction increases, until x, when increasing concentration does not affect rate of reaction
substrate concentration is limiting factor
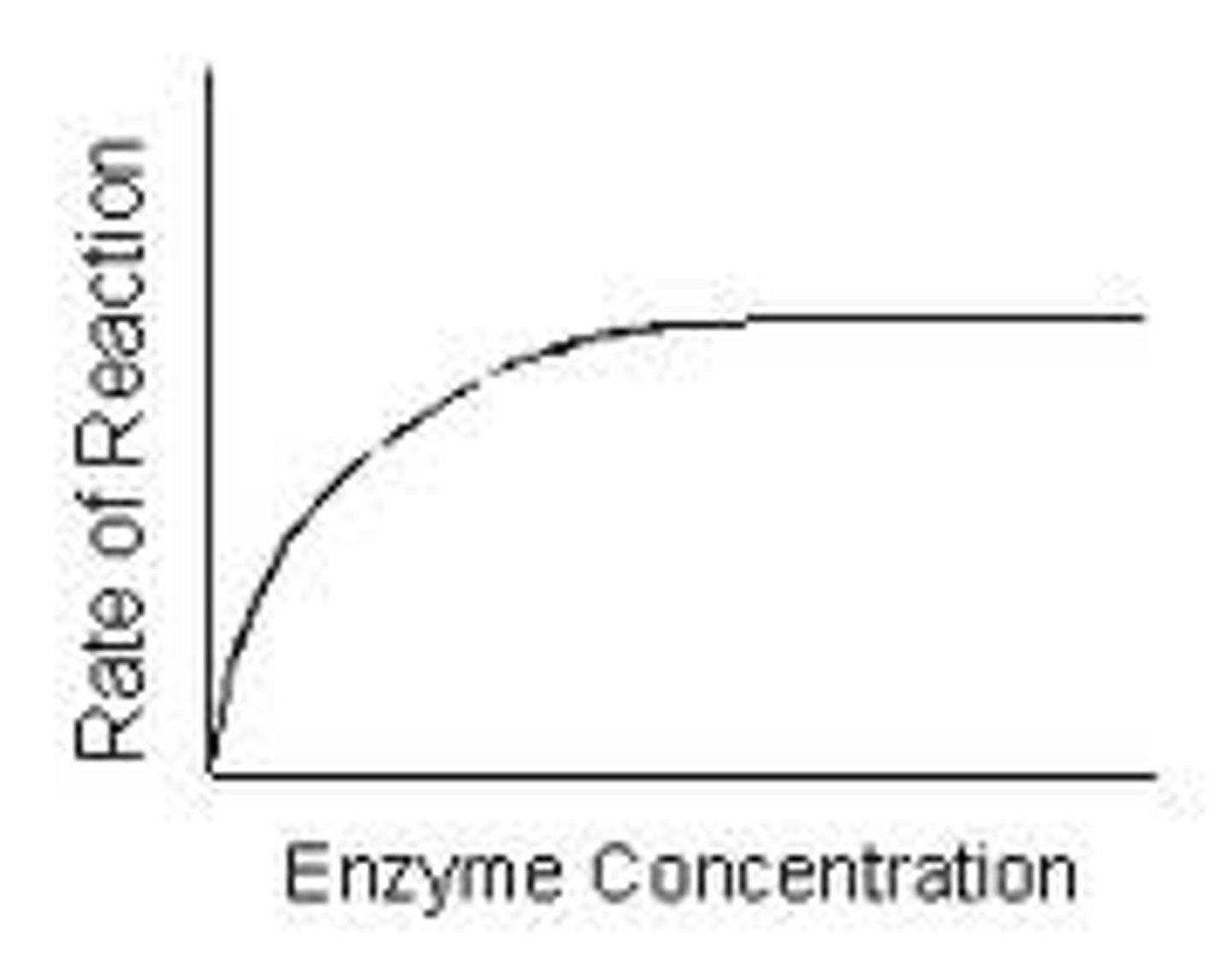
how enzyme concentration affects enzyme action
as concentration increases, rate if reaction increases, until x, when increasing concentration does not affect rate of reaction
enzyme concentration becomes limiting factor
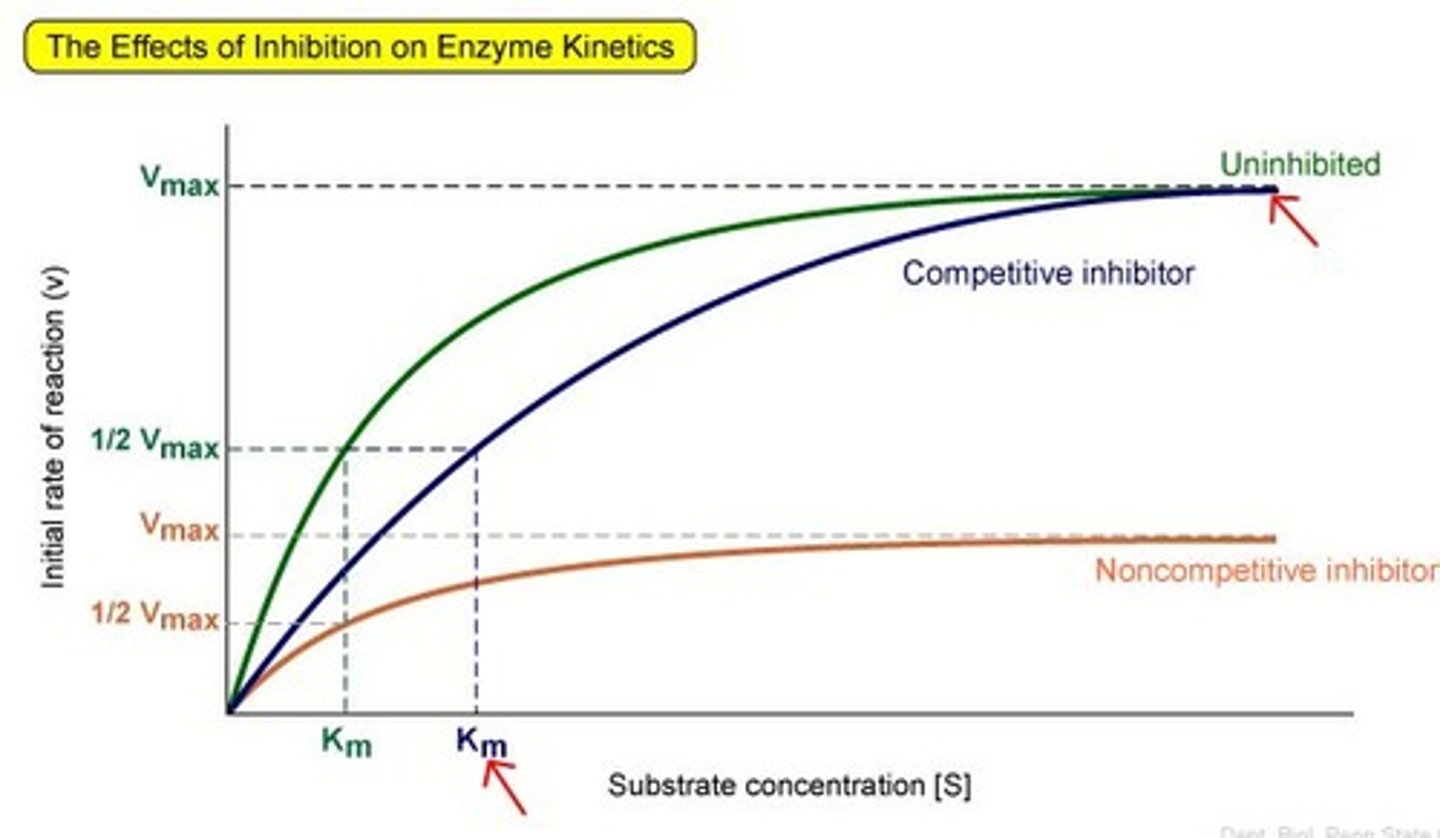
how enzyme inhibition affects enzyme action
Competitive - eg malonate
-compete with substrate for active site
- forms enzyme-inhibitor complex - so substrate cannot bind --> decreasing rate of reaction
- counteract by increasing substrate concentration
Non competitive - eg Potassium cyanide
- binds with allosteric site, causing change in shape of allosteric site and change in shape of active site
- active site in no longer complementary to specific substrate = rate of reaction decreases
- cannot be overcome by increasing substrate concentration
Biosensors function
rapid detection of metabolites
contain enzymes
Simple biosensors
qualitative - on/off
dye
diagnostic tool
Digital biosensors
quantitative - data
very accurate - even at low temp
monitoring tool
convert chemical energy into electric impulse
Immobilised enzymes structure
fitted into inert solid matrix
Entrapment
enzymes in gel membrane
eg silica gel, collagen fibres
Micro encapsulation
enzymes trapped in semi=permeable membrane
eg alginate beads (large surface area)
Advantages of immobilised enzymes
1. inert solid matrix creates physical barrier
- enzymes are more stable at higher temperatures
- work at larger range of pHs
- therefore, several enzymes with different optimums can be used at the same time
2. product not contaminated by enzyme
3. enzyme can be recovered/reused
4. continuous process
disadvantages of immobilised enzymes
1. reduces movement
- decreased activity
2. expensive