MAN3025 Module 8: Human Resources Management
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
human resource management (HRM)
The process of planning for, attracting, developing, and retaining an effective workforce
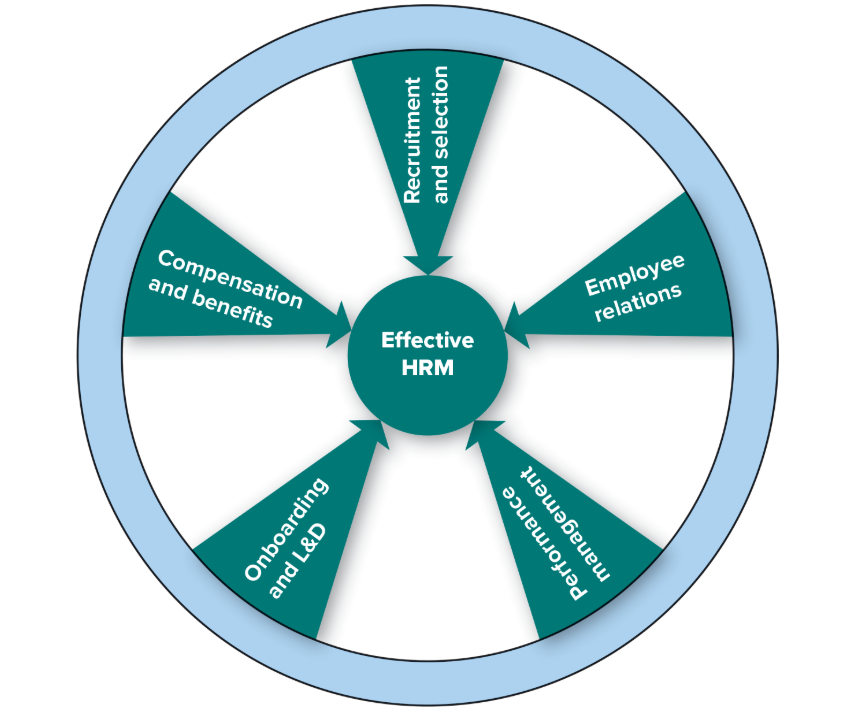
5 Human Resource Practices
Recruitment and selection
Compensation and benefits
Onboarding and L&D
Performance management
Employee relations
strategic human resource management
The process of designing and implementing systems of policies and practices that align an organization’s human capital with its strategic objectives
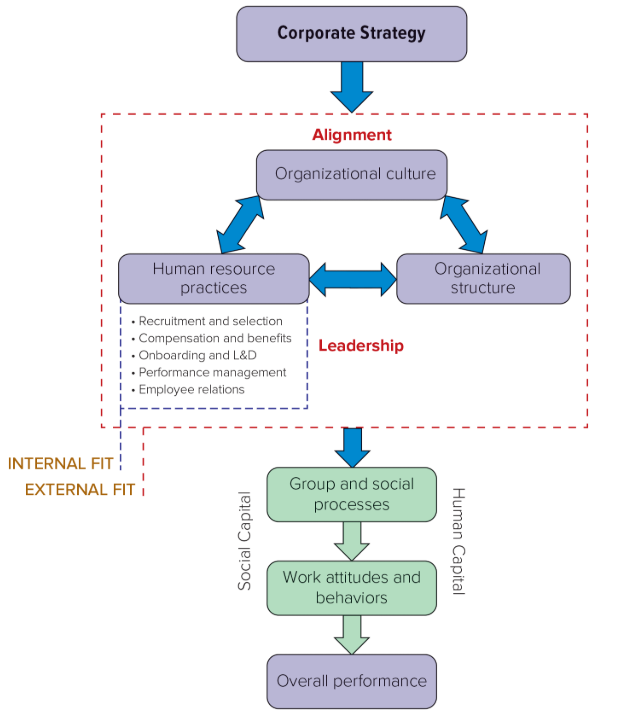
HRM vs. Strategic HRM
HRM is about managing people
Strategic HRM is about generating competitive advantages through people
internal fit
When all of the organization’s HR policies and practices reinforce one another
external fit
When the organization’s HR system as a whole aligns with its culture and structure in a way that supports firm-level strategy
human capital
The economic or productive potential of employee knowledge, experience, and actions
social capital
The economic of productive potential of strong, trusting, and cooperative relationships
Strategic HRM approaches
Talent management
High-performance work systems
talent management
strategic HRM approach that matches high-potential employees with an organization’s most strategically valuable positions
high-performance work system (HPWS)
strategic HRM approach that deploys bundles of internally consistent HR practices in order to improve employee ability, motivation, and opportunities across the organization
recruiting
The process of locating and attracting qualified applicants for job openingsin
internal recruiting
Hiring from the inside, or making people already employed by the organization aware of job openings
external recruiting
Attracting job applicants from outside the organization
talent marketplaces
Digital platforms that use AI to match existing employees with job openings, training opportunities, and mentoring relationships
employee referrals
Tap into existing employees’ social networks to fill open positions with outside applicants
boomerangs
Former employees who return to the organization
person-job fit
Extent to which a worker’s competencies and needs match a specific job
selection
The process of screening job applicants and choosing the best candidate for a position
legal defensibility
The extent to which the selection device measures job-related criteria in a bias free way
reliability
Represents the degree to which a test produces consistent scores
validity
Reflects the degree to which a test measures what it’s supposed to measure
unstructured interviews
Gather information about job candidates without the use of a fixed set of questions or a systematic scoring procedure
structured interview
Asking each applicant the same questions and comparing their responses to a standardized set of answers
situational interviews
Type of structured interview where applicants are asked how they would behave in hypothetical job situations
behavioral-description interviews
Type of structured interview where applicants are asked about how they have behaved in the past
employment tests
Standardized devices organizations use to measure specific skills, abilities, traits, and other tendencies
The 6 Employment Tests
Ability tests
Performance or job skills tests
Personality tests
Integrity tests
Drug and alcohol tests
Criminal and financial background checks
compensation
Payment comprised of three components: wages or salaries, incentives, and benefits
base pay
The basic wage of salary paid to employees in exchange for doing their jobs
incentives
Commissions, bonuses, profit-sharing plans, and stock options
benefits
Additional nonmonetary forms of compensation, like health insurance, retirement, and family leave
onboarding
Programs designed to integrate and transition employees into new jobs and organizations by familiarizing them with corporate policies, procedures, and politics, and clarification of work-role expectations and responsibilities
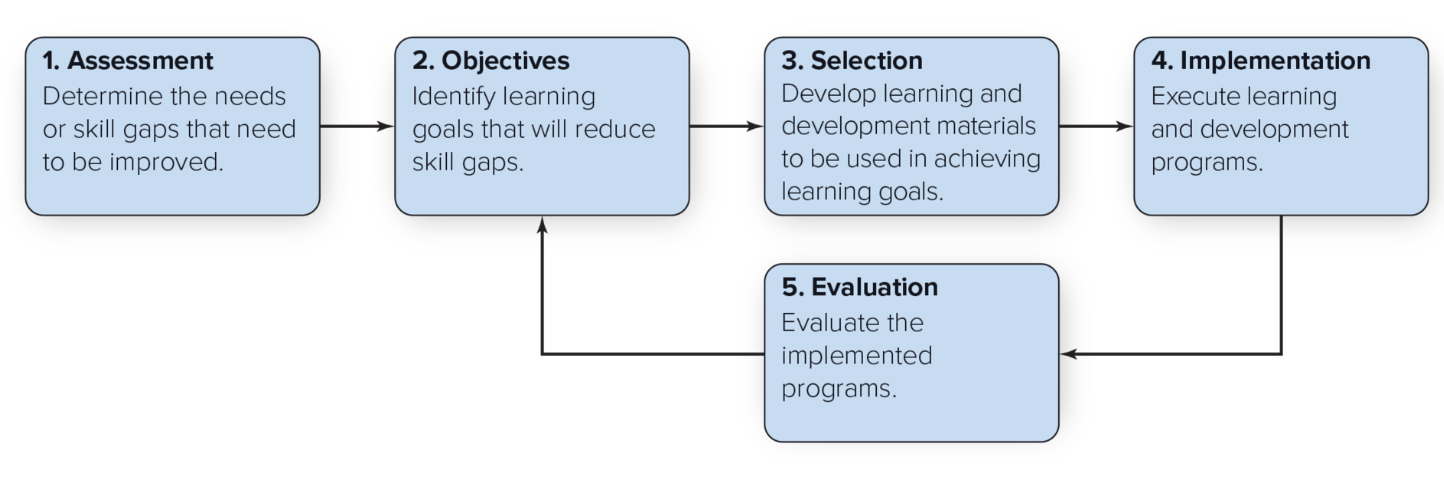
learning and development (L&D)
Fills gaps between what employees know and what they need to know
5 Steps in the L&D Process
Assessment
Objectives
Selection
Implementation
Evaluation
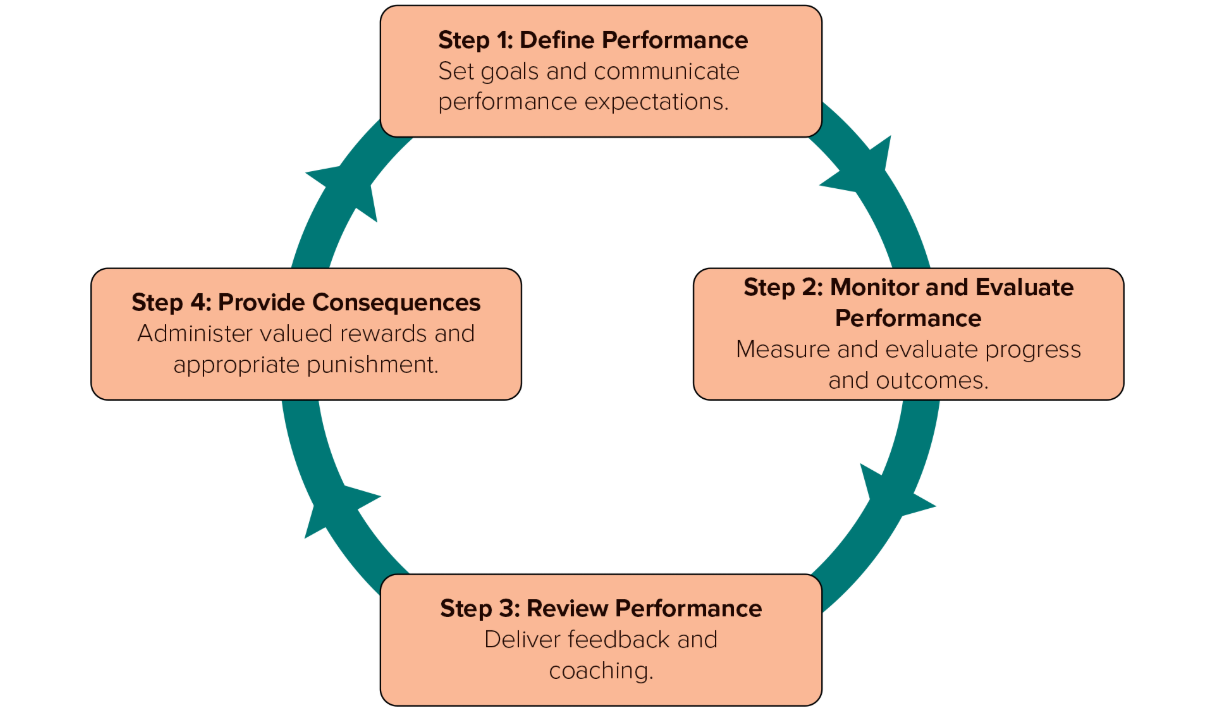
performance management
A set of processes and managerial behaviors that involve defining, monitoring, measuring, evaluating, and providing consequences for performance expectations
4 Steps of Performance Management
Define performance
Monitor and evaluate performance
Review performance
Provide consequences
performance appraisal (review)
Management process that consists of assessing employees’ performance and providing them feedback
objective appraisal
Also called results appraisals; based on facts and are often numerical
subjective appraisal
Based on a manager’s perceptions of an employee’s traits or behaviors
behaviorally anchored rating scale (BARS)
Rates employee gradations in performance according to scales of specific behaviors
360-degree assessment/feedback appraisal
Employees are appraised by not only their managerial superiors but also by peers, subordinates, and clients
forced ranking performance review systems
All employees in a business unit are ranked against one another and grades are distributed along a bell curve
performance improvement plans (PIPs)
Formal policies of progressive discipline that outline employee performance problems, routes to and timelines for improvement, and consequences for not meeting plan objectives
layoff
An employee has been dismissed temporarily
downsizing
An employee has been dismissed permanently
exit interview
A formal conversation between a manager and a departing employee to find out why they are leaving and to learn about potential problems in the organization
nondisparagement agreement
Contract between two parties that prohibits one party from criticizing another
employment at will
Governing principle of employment in the majority of states, that anyone can be dismissed at any time for any reason at all
4 Areas of Employment Law
Labor relations
Compensation and benefits
Health and safety
Equal employment opportunity
collective bargaining
Negotiations between management and employees about disputes over compensation, benefits, working conditions, and job security
National Labor Relations Board (NLRB)
U.S. commission legislated in 1935 that enforces procedures whereby employees may vote to have a union and for collective bargaining
Social Security Act of 1935
Established the U.S. retirement system
Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938
Established minimum living standards for workers engaged in interstate commerce, including a federal minimum wage, overtime, and ban on child labor
Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC)
U.S. panel that enforces antidiscrimination and other employment-related lawsw
workplace discrimination
Occurs when decisions about people are made for reasons not relevant to the job
adverse impact
Occurs when an organization uses an employment practice or procedure that results in unfavorable outcomes for a protected class over another group
disparate treatment
Occurs when employees from protected groups are intentionally treated differently
affirmative action
Focuses on achieving equality of opportunity within an organization
labor unions
Organizations of employees formed to protect and advance their members’ interests by bargaining with management over job-related issues
union security clause
Part of a labor-management agreement that states that employees who receive union benefits must join the union, or least pay dues
right-to-work laws
Statutes that prohibit employees from being required to join a union as a condition of employment
closed shop
Employer may only hire workers who are already in the union
union shop
Workers aren’t required to be union members when hired but must join within a specified time
agency shop
Workers must pay equivalent of union dues but aren’t required to join the union
open shop
Workers may choose whether to join a union
two-tier wage contracts
New employees are paid less or receive fewer benefits than veteran employees
cost-of-living adjustment (COLA) clause
Clause in a union contract that ties future wage increases to increases in the cost of living
grievance
Complaint by an employee that management has violated the terms of the labor-management agreement
mediation
Process where a neutral third party listens to both sides in a dispute, makes suggestions, and encourages them to agree on a solution
arbitration
Process where a neutral third party listens to both parties in a dispute and makes a decision that parties have agreed to abide by