M6S2: Nitrogen Compounds and Polymers
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
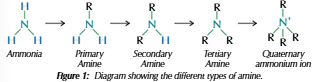
Amines
Suffix: -amine/-amine ion
Nitrogen lone pair can form dative covalent bond with H+ = NH4+
Donates lone pair and accepts lone proton = base
Amines and acids
Amine neutralised = ammonium salts
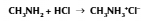
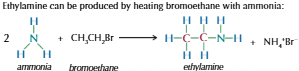
Producing aliphatic amines from haloalkanes
Heat haloalkanes with excess of ethanolic ammonia (ammonia dissolved in ethanol)
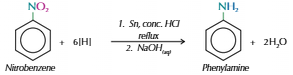
Producing aromatic amines by reducing nitro compounds
Heat mixture of nitro compound with tin metal & conc HCl under reflux = aromatic ammonium salt
Add alkali e.g. sodium hydroxide solution = aromatic amine
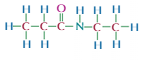
Amides
Carboxylic acid derivative
-CONH2
Acts differently to amines, carboxyl group pulls electrons from rest

Naming amides
If primary, name of stem group, followed by -amide
Secondary have a prefix to describe alkyl chain directly attached to nitrogen group
Suffix in the general form of N-alkyl-
Eg: N-ethylpropanamide
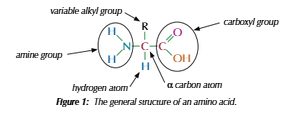
Amino acids
Two functional groups:
Amine(NH2)
Carboxyl(COOH)
General formula: RCH(NH2)COOH
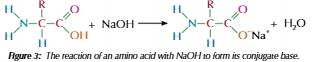
Amino acid and alkali
Carboxylic group in amino acid reach = conjugate base
Can combine with positive ion = salt
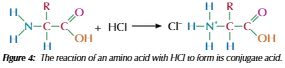
Amino acid and acid
Amine group can reach with acid to form salt of the conjugate acid
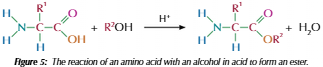
Formation of esters from amino acids
Carboxylic acid in amino acid can react with alcohol in presence of strong acid catalyst to form ester
Chiral carbon
Has four different groups attached to it
Enantiomers/Optical isomers
Mirror images that cannot superimpose
Addition polymer
Double bonds in alkene break and join to make long chains
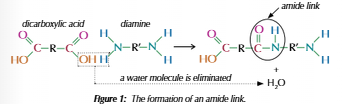
Polyamides
Dicarboxylic acids & Diamines
Carboxyl & amine group form amide link
Water molecule lost every link
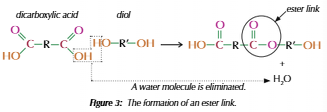
Polyesters
Dicarboxylic acid & Diol
Carboxyl + hydroxyl = ester link
Hydrolysis of polyamides
Hydrolyse easier with acid
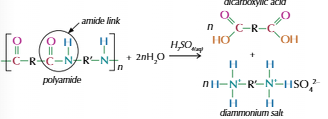
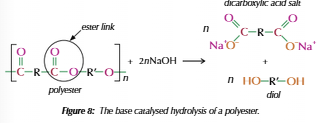
Hydrolysis of polyesters
Hydrolyse easier with base
Metal salt of dicarboxylic acid formed