b) To isolate clove oil from an emulsion of clove oil and water by liquid-liquid extraction/solvent extraction
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Theory
The clove oil extracted from cloves is now separated from the clove oil-water emulsion by adding cyclohexane and performing a liquid-liquid extraction/solvent extraction
Procedure: No.1: Liquid-liquid extraction/Solvent extraction
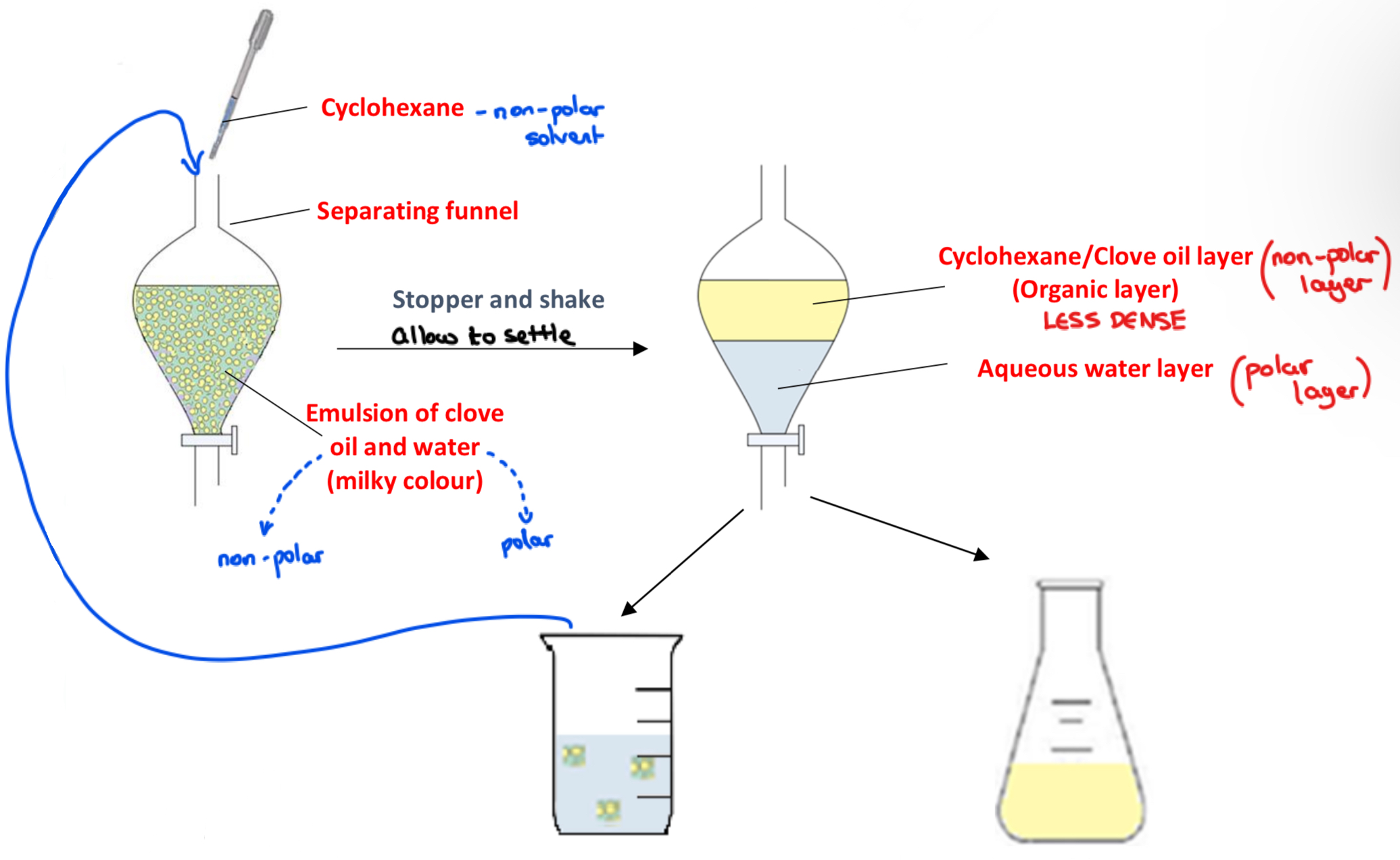
➢ Add the clove oil/water emulsion into a separating funnel and using a dropper add a small amount of cyclohexane
➢ Stopper and shake the separating funnel and allow to settle
Observe: Two separate layers form, an organic layer of cyclohexane/clove oil on top and an aqueous water layer on bottom
➢ Open the tap of the separating funnel and allow the bottom aqueous layer to drain into a beaker, and the organic layer to drain separately into a conical flask
➢ The aqueous layer will still contain droplets of clove oil - it is added back to the separating funnel, more cyclohexane is added, and the procedure is repeated at least two more times to extract the maximum amount of clove oil from the emulsion
What is liquid-liquid extraction/solvent extraction?
• Liquid-liquid extraction is a technique used for separating two immiscible liquids
• A solvent (cyclonexane) is added in which one of the liquids (clove oil) will dissolve but the other liquid (water) will not
Why is cyclohexane added to the clove oil-water emulsion?
• Clove oil is soluble in cyclohexane, but water is not
• Adding cyclohexane dissolves the clove oil from the emulsion but does not dissolve the water
What safety procedure is taken when using the separating funnel to shake the cyclohexane/clove oil-water mixture?*
The separating funnel is inverted when shaking, and the tap is gently opened to release the pressure of vapourised liquid in the separating funnel
Note: Avoid pointing the separating funnel at another person while performing this procedure
Why is this washing and separating procedure carried out at least three times?
At least three washings are required to extract the maximum amount of clove oil from the emulsion
As each new washing is carried out, the emulsion becomes less milky. Explain.
The milky colour is caused by the droplets of clove oil in the water as an emulsion. Each washing extracts more clove oil from the emulsion, and it becomes less milky
Note: The clove/oil cyclohexane mixture will still contain some water - this water needs to be removed before isolating the clove oil
Procedure: No.2: Removing excess water
➢ Using a spatula, add (MGSO4) anhydrous magnesium sulfate (drying agent) to the clove/oil cyclohexane mixture
Observe: The anhydrous magnesium sulfate binds with any water present in the mixture and forms clumps of hydrated magnesium sulfate
➢ Filter the clove/oil cyclohexane mixture using fluted filter paper into a new pre-weighed conical flask to remove the clumps of hydrated magnesium sulfate/excess anhydrous magnesium sulfate
➢ Rinse the original conical flask is with cyclohexane and filter to ensure all clove oil is retrieved
Why is anhydrous magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) added to the cyclohexane/clove oil mixture?
Magnesium sulfate is a drying agent – it absorbs and clumps any water remaining in the cyclohexane/clove oil mixture
How much anhydrous magnesium sulfate should be added to the conical flask?
The magnesium sulfate should be added until it settles at the bottom of the flask and no longer forms clumps – at this stage all of the water has been removed
Why is the mixture filtered?
The mixture was filtered to remove any hydrated magnesium sulfate and excess magnesium sulfate from the mixture
Why is fluted filter paper used?
The surface area of fluted filter paper is greater – the filtration process will be quicker
Procedure: No. 3: Isolating the clove oil/ removing the cyclohexane
➢ Place the clove oil/cyclohexane mixture in a water bath in a fumehood at 81˚C and boil the cyclohexane off to leave the clove oil isolated
➢ Leave the conical flask in the fumehood overnight to ensure all cyclohexane has evaporated
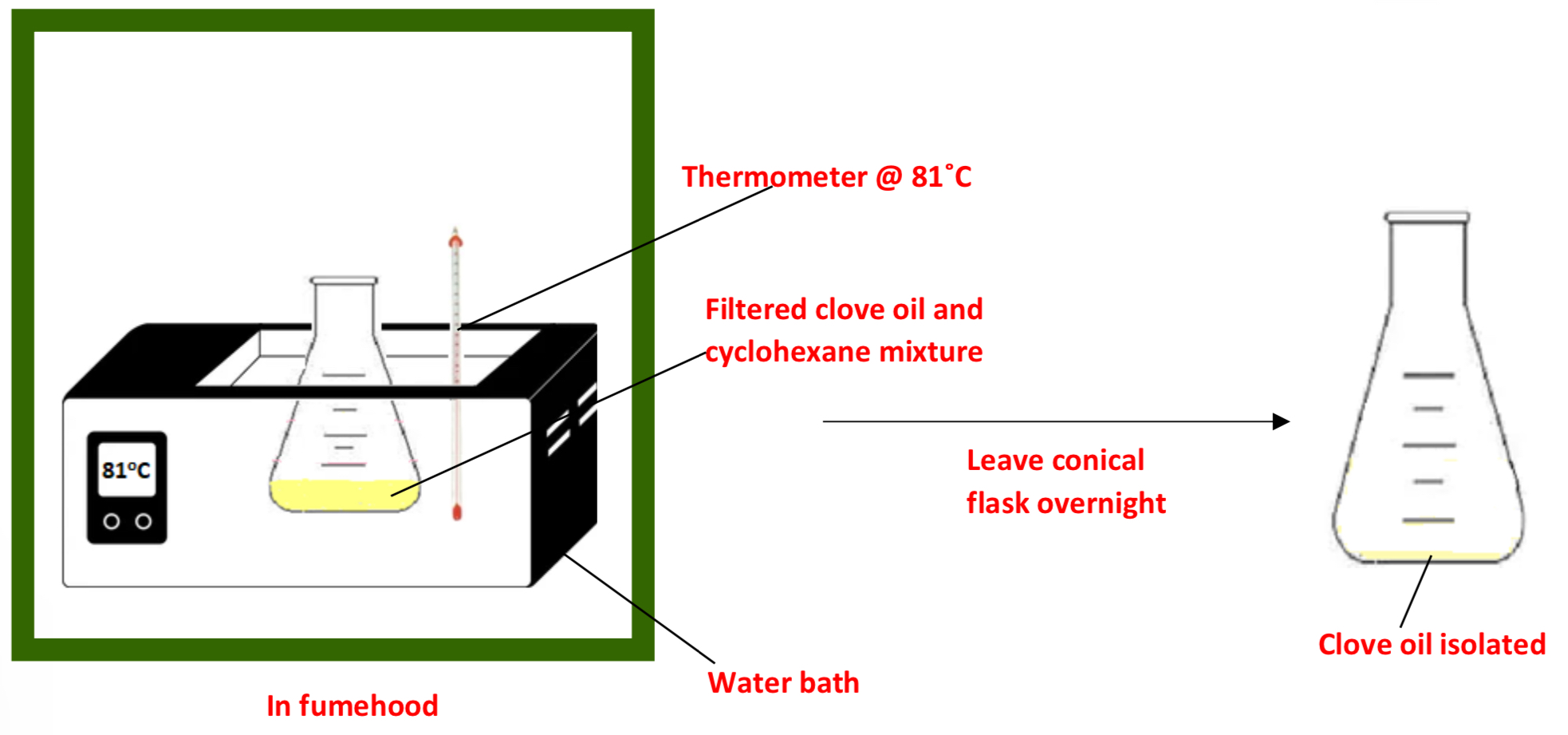
Why is the filtered mixture placed in a water bath?
• Cyclohexane is a volatile organic solvent – it has a boiling point of 81°C
• Placing the filtered mixture in a water bath at 81°C will cause the cyclohexane to boil off leaving the clove oil completely isolated behind
Why is a hot plate not used to evaporate off the cyclohexane?
The clove oil could boil off as well as the cyclohexane
Why is a bunsen burner not used to evaporate off the cyclohexane?
Cyclohexane is a flammable solvent – it must never be heated with a bunsen burner
Give two industrial uses of clove oil
1. Flavouring for meats, sweets, sauces, pickles
2. Perfumes, soaps