Finance 302 Chapter 6 & 7; Exam 3
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What are the characteristics of a stock? What do you own/entitled to?
Major financing vehicle for corporations.
- Provides holders with an opportunity to share in the future cash flows of the issuer.
- Holders have "ownership" in the company (residual claim on profit)
- NO maturity date and variable periodic income (dividends)
This can entitle you to dividends, voting rights, and preemptive rights
What is the difference between Primary (IPO) and secondary markets?
- The primary market (Ex. Initial Public Offering) is where new securities are first sold.
- The secondary market is where previously issued securities are traded between investors. This is where most investors trade.
What is primary IPO (initial public offering)?
The process where a private company sells its stock to the public for the first time, transitioning from private to public ownership.
What are dividends?
Payments made by a company to its shareholders from a portion of its earnings.
What are voting rights?
The right of a shareholder to vote on certain corporate actions
What are preemptive rights?
They give existing shareholders the first opportunity to purchase newly issued shares to prevent their ownership percentage from being diluted.
What is the difference between bid and ask price?
- Bid price: prices investors are willing to pay
- Ask price: the price at which current shareholders are willing to sell their shares
Bid and ask price have to be equal in order for a trade to happen!
What is the difference between market and limit orders?
- Market order: an order to buy or sell a security immediately at the best available current price.
- Limit order: an order to buy or sell a security at a specific price or better.
How are market and limit orders filled?
- Market orders are filled instantly at the best available price, executing immediately when a buy or sell order is placed.
- Limit orders are filled only at the specific price set by the investor or at a better price.
Book vs. Market vs. Liquidation Value
- Book value: the value of a company's assets minus its liabilities, as shown on the balance sheet.
- Market value: the current price at which a stock traded in the market, determined by supply and demand
- Liquidation value: the net amount that could be realized by selling the compay's assets and paying off all debts
What drives a wedge between market and book value?
- Growth opportunities
- Intangible assets
- Market expectations
What is the No Growth Model? (discounted dividend models)
- The firm re-invests no profit
- The firm pays out all profit as a dividend
Formula: P0 = Div/r
What is the constant dividend growth (Gordon Model)?
Hepls in determining a stock's intrinsic value based on expected future dividends growing at a constant rate
What is the non-constant dividend growth model?
When dividends have uneven growth, the future dividends and price must be forecasted to determine today's value
What is sustainable growth rate? How is it calculated?
- It is achieved by a firm re-investing its earnings while keeping long-term debt ratios
- Plowback Ratio x ROE
- Also assumes that ROE and the plowback ratio are constant
What is the present value of growth oppurtunity?
The net present value of a firm's future investments.
Formula: = Market Price - Market Value of Assets in Already in Place

What are assumptions about ROE and r?
- ROE is the key component in calculating the sustainable growth rate
- The most critical assumption in the constant growth dividend discount model (Gordon Model) is the relationship between the required return (r) and the growth rate (g), whisch is driven by ROE
- r must be strictly greager than g
What do DDM models tell us about market valuations (why do these models matter)?
A stock's fair value equals the present value of all its future dividends
What is a periodic return?
- Return over a specified period
- Can be averaged to understand over time
What is a holding period return?
- Return over an entire range of periods
- Simple percentage change from start to end of investment
What is the geometric average return?
- Return implied by compounding over an entire range of periods
- Found using TVM equations
What is average return?
- A simple mathematical average of a series of returns generated over a specified period of time
- It measures investment performance by helping to determine historical performance
Return in the Market
Market indices provide a measure of investment performance (return) for the overall market
Dow Jones Industrial Average (the Dow)
- One share of 30 large, "well-known" firms
- Microsoft, Apple, IBM, Walmart, AMEX, Home Depot, etc.
Standard & Poor's Composite (the S&P 500)
- Capitalization weighted index, 500 firms make up 80% of total market value
- Best indicator of average performance
What is Risk?
It is a measure of the uncertainty in a set of potential outcomes for an event i.e, how those outcomes differ from what is expected
Expected Value (be able to calculate and interpret)
The probability-weighted average of an outcome (X)
See example

Standard Deviation and Variance (Example Attached)
- Standard Deviation A statistical measure of risk. A higher standard deviation means returns are more spread out, indicating higher risk
- Variance: the probability-weighted average of squared deviations from the expected value (mean) an outcome (X)

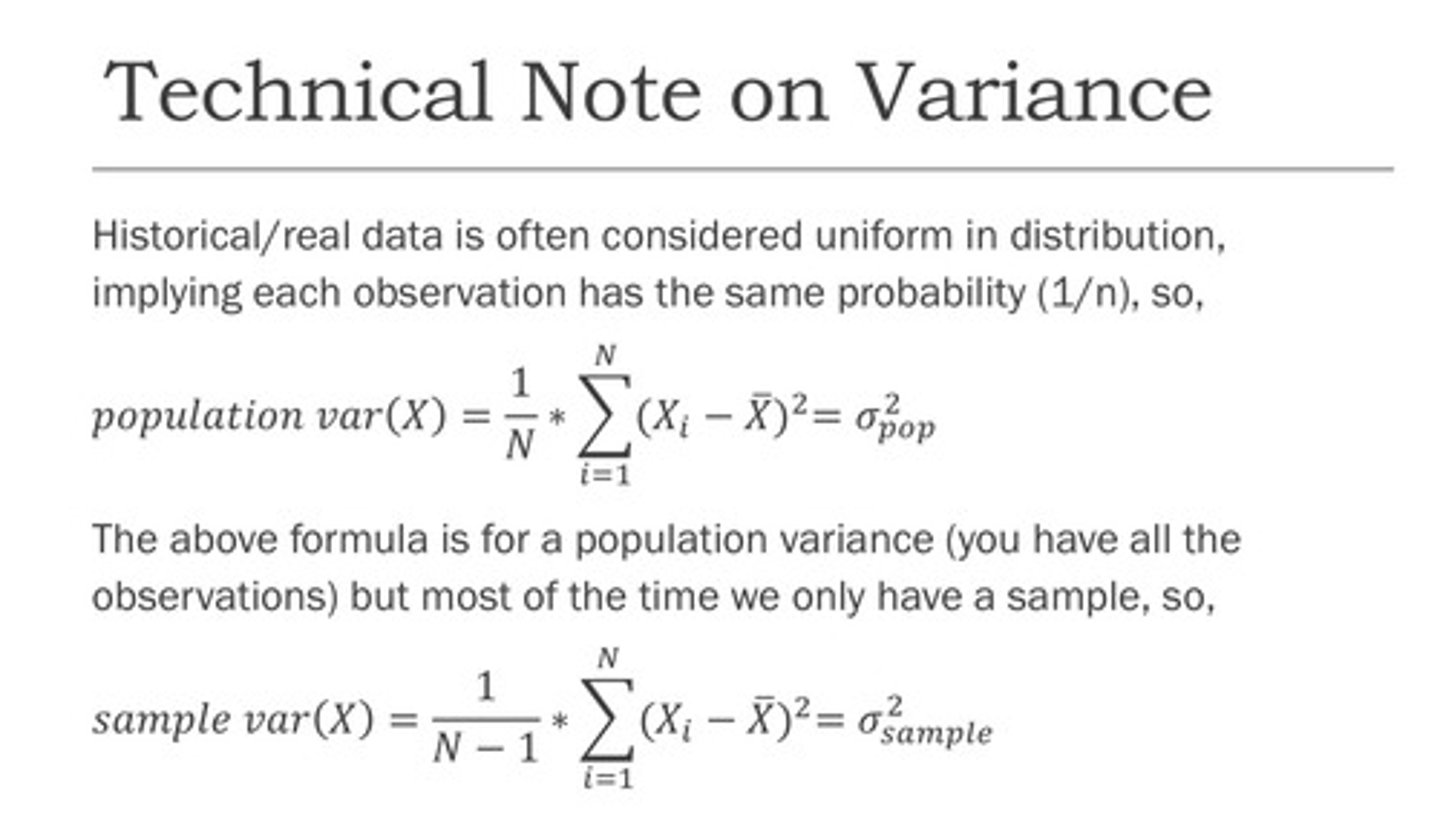
Historical return and risk (Sample vs. Population)
Historical/real data is often considered uniform in distribution, implying each observation has the same probability
What is Diversification?
A strategy designed to reduce risk by spreading the portfolio across many investments
What is needed to achieve diversification?
- Create a mix of assets across different classes, sectors, and regions and regulary rebalance portfolios.
- By dividing up investments across many relatetively low-correlated assets, it is possible to considerably reduce one's exposure to risk
What is Idiosyncratic/Diversable risk?
- Related to asset (company) specific/uncertainty
- Also called firm-specific risk
What is Systematic /Non-Diversifiable risk?
- Economy-wide sources of risk that affect the overall stock market
- also called market risk
What is a Well-diversified portfolio?
One whose specific risk has been eliminated
What is Beta?
- It measures the sensitivity of a stock's return to the return on the market portfolio
- A measure of risk for a "well-diversed portfolio"
How to interpret Beta?
- A beta greater than 1.0 suggests that the stock is riskier than the broader market, and a beta less than 1.0 indicates a stock with lower risk
- Calculated by a linear regression of stock returns on the overall market return
What is Portfolio Beta?
- We can measure the risk of a well-diversified portfolio by measuring the beta of the overall portfolio
- Aids in determining performance (return) relative to risk of a portfolio
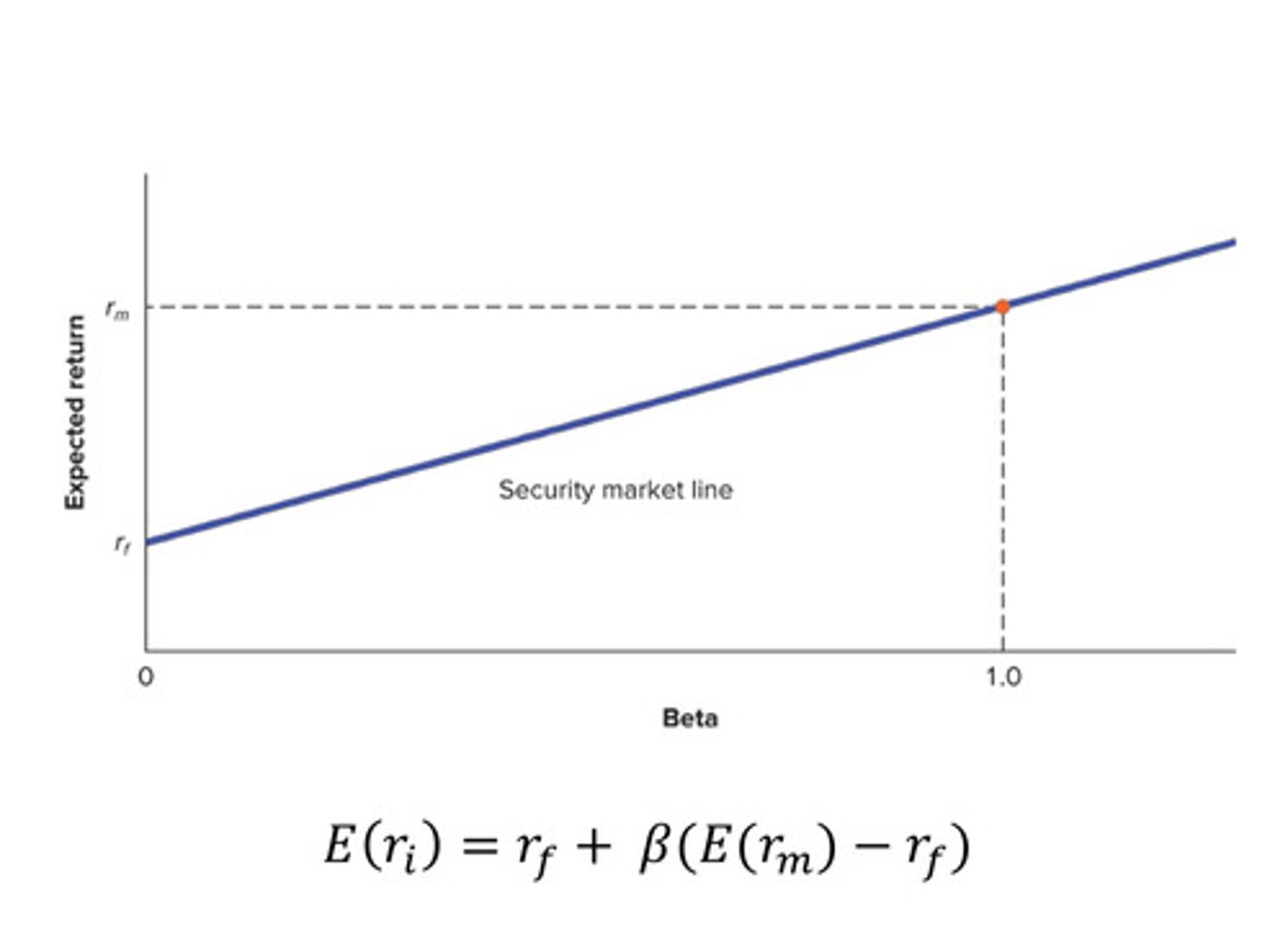
What is the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)?
A financial model that calculates the expected return on an asset based on its risk.
Assumptions of CAPM
- All investors are risk-averse by nature.
- Investors have the same time period to evaluate information.
- There is unlimited capital to borrow at the risk-free rate of return.
- Investments can be divided into unlimited pieces and sizes.
- There are no taxes, inflation, or transaction costs.
- Risk and return are linearly related.
What is the security market line?
- A graphical representation of the CAPM with a given risk-free rate and expected maret return
- Used to evaluate the relative risk to return tradeoff of an equity.